What are the most common side effects of ACE inhibitors?
The most serious, but rare, side effects of ACE inhibitors are:
- Kidney failure
- Allergic reactions
- Pancreatitis
- Liver dysfunction
- A decrease in white blood cells
- Swelling of tissues ( angioedema ).
Are ACE inhibitors the best drug for hypertension?
You may be given one or more of these medications:
- Diuretics, also called water pills. A diuretic removes excess water and sodium from your body, so there's less fluid flowing through your veins and arteries. ...
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors. ...
- Angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs). ...
- Calcium channel blockers. ...
- Beta blockers. ...
- Renin inhibitors. ...
What do ACE inhibitors have less side effect?
The most common side effect is a persistent dry cough. If you have this side effect, your doctor may prescribe a different type of medicine called an angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB) instead of ACE inhibitors. They work in a similar way but don’t tend to cause a cough. Other possible side effects of ACE inhibitors include:
What are the most common ACE inhibitors?
The following is a list of the ACE inhibitors that are available in the United States:
- benazepril ( Lotensin, Lotensin Hct),
- captopril ( Capoten ),
- enalapril (Vasotec),
- fosinopril ( Monopril ),
- lisinopril ( Prinivil, Zestril ),
- moexipril (Univasc)
- perindopril (Aceon),
- quinapril ( Accupril ),
What is the effect of ACE inhibitors on the kidney?
Can ACE inhibitors be withheld?
Can ACE inhibition cause renal failure?
Does filtration pressure affect renoprotection?
Does ACE help with hypertension?
See more
About this website

Are ACE inhibitors nephrotoxic drugs?
Angiotensin-I converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can be nephrotoxic and may synergistically compromise renal function.
Do ACE inhibitors damage kidneys?
Long-Term Use of ACE Inhibitors May Cause Kidney Damage, Study Results Suggest. New research raises concerns about the commonly prescribed medications used to treat heart failure and high blood pressure, though investigators say patients should continue to take them.
How do ACE inhibitors cause nephrotoxicity?
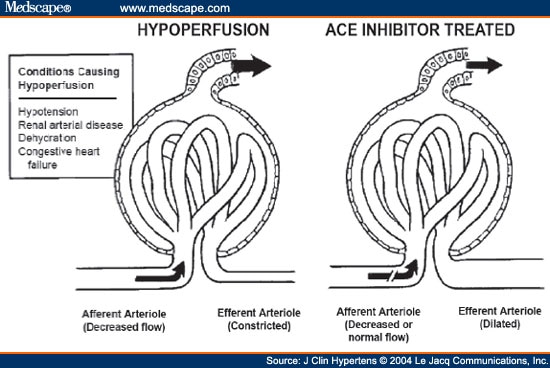
During ACEI initiation, renal dysfunction can occur due to a drop in renal perfusion pressure and subsequent decrease in glomerular filtration. This is attributed to the drug's preferential vasodilation of the renal efferent arteriole, which impairs the kidney's ability to compensate for low perfusion states.
Are ACE and ARBs nephrotoxic?
This triple therapy can increase the risk of acute renal failure. This triple therapy can increase the risk of acute renal failure.
Which medications are nephrotoxic?
Certain drugs are inherently nephrotoxic and include aminoglycosides, amphotericin B, cisplatin, contrast dye, and cyclosporine. For others, such as those associated with chronic interstitial nephritis and crystal deposition, nephrotoxicity is dose dependant or related to prolonged duration of treatment.
Why are ACE inhibitors not used in renal failure?
In conditions in which glomerular filtration is critically dependent on angiotensin II-mediated efferent vascular tone (such as a post-stenotic kidney, or patients with heart failure and severe depletion of circulating volume), ACE inhibition can induce acute renal failure, which is reversible after withdrawal of the ...
Why are ACEI contraindicated in AKI?
Clinicians managing patients with AKI therefore frequently stop drugs that lower blood pressure (particularly ACEI and ARBs, which selectively reduce glomerular pressure) and diuretics. ACEIs, ARBs and potassium-sparing diuretics may also be stopped because of hyperkalaemia.
Are ACE inhibitors contraindicated in AKI?
no use of ACEI/ARB, (no prescription in the 6 months before or 6 months after the AKI admission) new use (≥1 prescription within 6 months after discharge from the index hospitalization, with no prescriptions in the 6 months before admission) prior use (≥1 prescription in the 6 months before admission)
Can ACEI cause AKI?
ACE inhibitors or ARBs, with or without diuretics, are associated with an increased risk of AKI; the addition of NSAIDs significantly increases this risk.
Are ACE inhibitors renal protective?
Because of their favorable intrarenal hemodynamic effects (particularly reduction of glomerular capillary pressure), ACE inhibitors may provide a renal protective effect in addition to their systemic antihypertensive effects.
Can ACE inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers be detrimental in CKD patients?
We reviewed the literature along these lines and submit that ACEIs and ARBs often cause unrecognized significant worsening renal failure in CKD patients, sometimes irreversible, and that more caution is required regarding their use, especially in the older hypertensive patients, with likely ischemic hypertensive ...
What blood pressure meds can cause kidney damage?
Popular diuretics include hydrochlorothiazide, furosemide, and spironolactone. They are associated with a risk for acute kidney injury.
What blood pressure medicine is easiest on the kidneys?
ACE inhibitors and ARBs are two types of blood pressure medicine that may slow the loss of kidney function and delay kidney failure. You can tell if you're taking one of these medicines by its generic name.
Can lisinopril damage your kidneys?
This can damage the blood vessels of the brain, heart, and kidneys resulting in a stroke, heart failure, or kidney failure. Lowering blood pressure can reduce the risk of strokes and heart attacks.
What is the most common side effect of ACE inhibitors?
Dry cough. Increased potassium levels in the blood (hyperkalemia) Fatigue. Dizziness from blood pressure going too low.
The 10 Worst Medications for Your Kidneys - GoodRx
1) NSAIDS. NSAIDS, or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs like ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) and naproxen (Aleve), lead the list for drugs that cause kidney damage because of their widespread use. NSAIDS are used to treat a host of conditions such as fever, rheumatoid arthritis, menstrual pain, and inflammation, but they can also reduce the amount of blood flow to the kidneys, resulting in a ...
Do ACE-Inhibitors Protect The Kidneys? - Walrus
In our latest question and answer, we discuss how the ACE-Inhibitor class of medications may protect the kidneys.
Are ACE inhibitors and ARBs recommended for renal disease?
ACE inhibitors and ARBs have been shown effective in preventing or at least slowing the process of renal disease in patients with diabetes by interfering with the renin-angiotensin system.
Long-Term Use of ACE Inhibitors May Cause Kidney Damage, Study Results ...
New research from the University of Virginia (UVA) School of Medicine raises concerns about the long-term use of commonly prescribed medications used to treat heart failure and high blood pressure (BP) and how they may contribute to kidney damage. 1 However, investigators say patients should continue to take the potentially life-saving medications, which include well-known and widely ...
ACE Inhibitors and Protection Against Kidney Disease Progression
Abstract and Introduction. Although angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors are frequently used as antihypertensive agents to lower blood pressure and slow progression of nephropathy in patients ...
Is Lisinopril harmful to the kidneys? | National Kidney Foundation
Lisinopril is an angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor. ACE-inhibitors are used in chronic kidney disease (CKD) to protect kidneys, slow progression of CKD and to treat protein in the urine. Hence, Lisinopril is generally a safe and effective treatment of CKD. It must be monitored carefully by your doctor.
Can ACE inhibitors be nephrotoxic?
Angiotensin-I converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can be nephrotoxic and may synergistically compromise renal function. A computer-assisted study was done to asses the prevalence of compromised renal function and the clinical importance of this drug interaction.
Can NSAIDs cause nephrotoxicity?
Nephrotoxicity associated with concomitant ACE inhibitor and NSAID therapy. Angiotensin-I converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can be nephrotoxic and may synergistically compromise renal function.
How do diuretics affect the kidney?
Diuretics can reduce plasma volume leading to reduced renal blood flow. This may lead to increased serum creatinine concentrations. The kidney can compensate via the renin-angiotensin system by constricting the efferent renal arteriole to increase glomerular filtration pressure and favor water and sodium retention.
What happens when you triple a NSAID?
When triple therapy with an NSAID plus diuretic and an ACEI or ARB is administered, the kidney is unable to use its normal compensatory mechanisms and may suffer an acute reduction in glomerular filtration that is marked by a rising serum creatinine.
Does double therapy increase kidney injury?
The risk of kidney disease in the patients was compared with matched control patients not exposed to the double or triple therapy. The use of double therapy was not associated with an increased risk of kidney injury. Triple therapy was associated with a 31% increase in risk of injury.
Can NSAIDs cause elevated creatinine?
Patients receiving NSAIDs chronically in combination with diuretics, ACEIs, or ARB, are at risk for diminished hypotensive response, elevated serum creatinine, and acute kidney injury. They should be monitored for altered blood pressure and serum creatinine, particularly during the first few months of combination therapy.
How long after ACE inhibitor surgery can you use a contrast?
There is a low level of evidence that discontinuation of ACE-inhibitors (on day of procedure up to 24 hours after procedure) does not reduce the risk of post contrast acute kidney injury compared to continuing ACE-inhibitor use around angiography in patients with chronic kidney disease.
Can iodine blockers cause kidney injury?
The use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, diuretics, ACE-inhibitors or angiotensin II receptor blockers has been associated with an increased risk of acute kidney injury following intravascular iodine-containing contrast administration. This has led to the perception that withholding these agents is a useful strategy to prevent acute kidney injury. However, there is insufficient scientific evidence to support this hypothesis.
Does intravascular contrast increase risk of PC-AKI?
In most of the studies, the combination of diuretics and controlled hydration was superior in preventing the risk of PC-AKI indirectly supporting the concept that the use of diuretics before using intravascular contrast does not increase the risk of PC-AKI if adequate hydration is performed.
Can ACE blockers reduce glomerular filtration?
Thus, if glomerular filtration depends on post-glomerular filtration, which may be the case in patients with renal artery stenosis, hypovolemia or very poor cardiac output, the use ACE-inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers can reduce glomerular filtration, a fully reversible process.
Is ACE inhibitor nephrotoxic?
Patients with congestive heart failure, for instance, are at increased risk of developing PC-AKI and are likely to use ACE-inhibitors. Finally, and most importantly, ACE-inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers are not nephrotoxic, although they are referred to as nephrotoxic drugs by guidelines and in literature.
Does discontinuing PC-AKI reduce PC-AKI?
Other nephrotoxic drugs. No RCT’s have been published on the effect of discontinuation of PC-AKI on the reduction of PC-AKI. Thus, there is no evidence whether discontinuation of nephrotoxic drugs will reduce the incidence of PC-AKI. Their combined use with iodine-containing CM could however increase the risk of harm to the kidney.
What is the effect of ACE inhibitors on the kidney?
A risk-benefit assessment. ACE inhibitors effectively reduce systemic vascular resistance in patients with hypertension, heart failure or chronic renal disease. This antihypertensive efficacy probably accounts for an important part of their long term renoprotective effects in patients with diabetic ...
Can ACE inhibitors be withheld?
Therefore, ACE inhibitors should not be withheld in these patients, but dosages should be carefully titrated, with monitoring of renal function and serum potassium levels.
Can ACE inhibition cause renal failure?
In conditions in which glomerular filtration is critically dependent on angiotensin II-mediated efferent vascular tone (such as a post-stenotic kidney, or patients with heart failure and severe depletion of circulating volume), ACE inhibition can induce acute renal failure , which is reversible after withdrawal of the drug.
Does filtration pressure affect renoprotection?
The fall in filtration pressure presumably contributes to the antiproteinuric effect as well as to long term renoprotection. The former is suggested by the positive correlation between the fall in filtration fraction and the reduction in proteinuria found during ACE inhibition.
Does ACE help with hypertension?
ACE inhibitors effectively reduce systemic vascular resistance in patients with hypertension, heart failure or chronic renal disease. This antihypertensive efficacy probably accounts for an important part of their long term renoprotective effects in patients with diabetic and non-diabetic renal disease. The renal mechanisms underlying the renal ...