Explore
Surgery would only be considered if:
- your doctor suspects that the adnexal mass is malignant
- a complication occurs
- the mass is so big that it’s likely to cause a problem with the pregnancy
What is the treatment for an adnexal mass?
Treatment depends on the specific case. If the adnexal mass is benign and isn’t causing any pain, then your healthcare provider will likely monitor the situation with periodic imaging tests. However, if the tumor grows, if you have increased pain, internal bleeding, or if it is cancerous, surgery will be recommended.
Is surgery needed for an adnexal mass?
When symptoms are present, they often present as:
- Pelvic pain
- Irregular menstrual cycle
- Difficulty urinating or the frequent urge to do so
- Constipation
- Gastrointestinal problems
What are the symptoms of adnexal mass?
Adnexal tenderness is a technical term for pain in the area of a woman’s uterus. Adnexa is a Latin word meaning attachment or appendages. It refers to the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and ligaments...
What does adnexal tenderness mean?
Why do you get adnexal cysts?
What Causes Adnexal Cysts? Fluid-filled cysts on the ovaries are usually caused by hormonal stimulation or bleeding at the time of ovulation (hemorrhagic ovarian cysts).
How do you treat adnexal cysts?
If the adnexal mass is small and you have no symptoms, then it may not require treatment at all. However, your doctor will likely want to monitor you with regular pelvic exams and ultrasounds. Surgery will be needed if: the mass begins to grow.
How do I know if my adnexal cyst is cancerous?
Oftentimes imaging tests like ultrasound or MRI can determine if an ovarian cyst or tumor is benign or malignant. They may also want to test your blood for CA-125, a tumor marker, or preform a biopsy if there is any question. High levels of CA-125 may indicate the presence of ovarian cancer.
Is an adnexal cyst An ovarian cyst?
Ovarian cysts, also known as ovarian masses or adnexal masses, are frequently found incidentally in asymptomatic women. Ovarian cysts can be physiologic (having to do with ovulation) or neoplastic and can be benign, borderline (low malignant potential), or malignant.
When should an adnexal cyst be removed?
Surgery. Large or persistent ovarian cysts, or cysts that are causing symptoms, usually need to be surgically removed. Surgery is also normally recommended if there are concerns that the cyst could be cancerous or could become cancerous.
What is the normal size of adnexal cyst?
In postmenopausal women, simple cysts greater than 1 cm in size should be described but do not need follow-up imaging unless they are greater than 3–5 cm, using the higher threshold for exceptionally well-visualized simple cysts. These thresholds are greater than 3 cm and greater than 5–7 cm in premenopausal women.
What percentage of adnexal masses are malignant?
In postmenopausal women, 30 percent of adnexal masses are malignant. Ovarian cancer is rare in premenopausal women. Other etiologies, such as functional cysts, leiomyomata, and ectopic pregnancy, are more common and can cause significant morbidity.
Can you tell if a cyst is cancerous from an ultrasound?
Ultrasound images are not as detailed as those from CT or MRI scans. Ultrasound cannot tell whether a tumor is cancer. Its use is also limited in some parts of the body because the sound waves can't go through air (such as in the lungs) or through bone.
What does Adnexa mean on an ultrasound?
INTRODUCTION. Adnexa refer to the anatomical area adjacent to the uterus, and contains the fallopian tube, ovary, and associated vessels, ligaments, and connective tissue.
Do adnexal cysts go away on their own?
Ovarian cysts are common. Most of the time, you have little or no discomfort, and the cysts are harmless. Most cysts go away without treatment within a few months.
Do adnexal cysts cause pain?
Symptoms of an ovarian cyst An ovarian cyst usually only causes symptoms if it splits (ruptures), is very large or blocks the blood supply to the ovaries. In these cases, you may have: pelvic pain – this can range from a dull, heavy sensation to a sudden, severe and sharp pain. pain during sex.
What is a simple adnexal cyst?
An adnexal cyst is a fluid-containing lump in the area of the pelvis around the uterus. This includes the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and surrounding tissues. Simple ovarian cysts frequently form during the normal menstrual cycle and are not considered to be a problem.
Do adnexal cysts go away on their own?
An adnexal (ad-nek-suhl) mass is a growth that develops around the uterus, usually in your ovaries, fallopian tubes and neighboring connective tissues. Some adnexal tumors are fluid-filled, while others are solid. They can appear at any age, and most of them go away on their own within a few months.
How is adnexal mass treated?
Treatment options for adnexal masses vary depending on the specific diagnosis. Some masses can be treated conservatively, and others may require surgery. Observation is generally recommended when the appearance of the adnexal mass on ultrasonography suggests a benign growth.
Can ovarian cyst be treated without surgery?
Functional ovarian cysts usually go away without treatment. If your cyst is likely functional, your provider may suggest a wait-and-see approach. You may have a follow-up ultrasound within a few weeks or months after your diagnosis to see if your cyst has resolved on its own.
Do adnexal cysts cause pain?
Symptoms of an ovarian cyst An ovarian cyst usually only causes symptoms if it splits (ruptures), is very large or blocks the blood supply to the ovaries. In these cases, you may have: pelvic pain – this can range from a dull, heavy sensation to a sudden, severe and sharp pain. pain during sex.
What Are Adnexal Cysts?
The adnexa are made up of the fallopian tubes and ovaries. Cysts are fluid-filled structures that can develop in the adnexa.
Do cysts resolve on their own?
Cysts associated with the fallopian tubes (paraovarian or paratubal cysts) are less likely to resolve on their own and more likely to require surgical intervention if they are causing symptoms. Request an appointment. Because when your child needs expert care, everything matters. Request an Appointment ›.
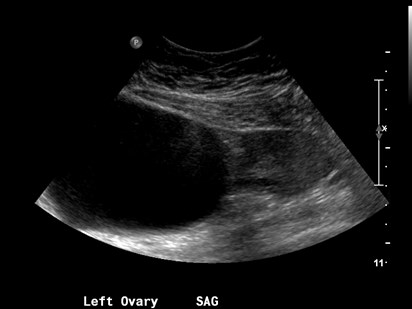
Can a pelvic ultrasound be used to diagnose a cyst?
Adnexal cysts are diagnosed (and monitored) with pelvic ultrasound. If there is uncertainty about the nature of the cyst, rarely pelvic MRI may be needed.
Overview
An adnexal (ad-nek-suhl) mass is a growth that develops around the uterus, usually in your ovaries, fallopian tubes and neighboring connective tissues. Some adnexal tumors are fluid-filled, while others are solid. They can appear at any age, and most of them go away on their own within a few months.
Diagnosis and Tests
Adnexal tumors are most often detected during routine examinations. They may also be discovered during pelvic examinations or ultrasounds. Once you receive a diagnosis, your healthcare provider can run additional lab and imaging tests to determine what caused the adnexal mass.
Management and Treatment
Not always. In many cases, adnexal masses aren’t harmful and will eventually resolve on their own. However, if they cause uncomfortable symptoms, then surgical removal may be recommended. If intense pain or fevers are experienced, you should contact your health care provider immediately to assess for ovarian torsion, which is a surgical emergency.
Prevention
There is currently no way to prevent adnexal tumors. However, with early detection, you can reduce your risk for associated complications. If you’re diagnosed with an adnexal tumor, it’s important to see your healthcare provider for frequent follow-ups. Medications can sometimes be offered to decrease the risk of recurrent ovarian cysts.
Living With
If you’ve been diagnosed with an adnexal tumor, you should see your healthcare provider for frequent follow-ups. During these visits, they will check to see if the tumor has grown. Additionally, you should call your provider any time you develop painful or uncomfortable symptoms.
What is an adnexal cyst?
Adnexal cyst is a condition where tumors form in the adnexa region. The adnexa refer to the area adjoining the uterus, which includes the ovaries, fallopian tubes, blood vessels, ligaments, and connective tissue. Pathological changes in the adnexa may originate in the uterus, bowel or retroperitoneum. In some cases, it can be also due to metastasized cancer from other organs in the body like the breast or stomach. Development of tumor in the adnexa region is known as adnexa cyst.
How to diagnose adnexal cyst?
Diagnosis of Adnexal Cyst In order to diagnose adnexal cyst, a doctor must first inquire about patient’s medical history. Pelvic exam can help the doctor to find adnexal cyst. Type of adnexal cyst also has to be determined so the doctor can choose adequate treatment.
What is the name of the tumor in the adnexa region?
Development of tumor in the adnexa region is known as adnexa cyst. Causes of Adnexal Cyst Normally, as a common part of menstrual cycle, the ovaries produce 6 to 7 follicular cysts each year. Those are benign cysts that do not need to be treated since they disappear on their own.
Why do women have adnexal cysts?
In postmenopausal women, adnexal cyst can be due to fibroids, fibromas, cancer or diverticular abscess.
Can adnexal cysts cause constipation?
In rare instances, there may occur bleeding at adnexal cyst site. The large cysts can cause pressure on the bladder and rectum leading to constipation and urinary problem. Adnexal cyst can be responsible for increase in frequency of urination. Malignant adnexal cysts often cause gastrointestinal disorders.
Is adnexal cyst cancerous?
Malignant or cancerous adnexal cysts are serious medical problem that requires prompt management. Symptoms of Adnexal Cyst Most commonly, adnexal cyst does not cause any symptom.
Can adnexal cysts be removed?
On the other hand, adnexal cysts in postmenopausal women have to be monitored for some time and if needed surgically removed. Surgical treatment is only option if adnexal cysts are found in young girls.
What is the most common type of adnexal mass?
Physiological Ovarian Cysts. These may be either follicular cysts or corpus luteum cysts. They comprise the most common type of adnexal masses in this age group. Follicular cysts – Normally, each month the ovary sheds an egg into fallopian tube. Sometimes, the egg is not shed and remains in the ovary. Later it forms a cyst around itself.
Where does a lump in the adnexa come from?
Any lump or mass found within adnexa of uterus is abnormal and needs to be evaluated. Such a mass usually originates from ovary or fallopian tube. However, it may arise from various other structures such as the bowels, the peritoneal lining covering the viscera, the ligaments holding the uterus in place or the adjoining lymph nodes.
What is the adnexa of the uterus?
Adnexa refers to adjoining anatomical parts of the uterus. It includes the fallopian tubes and ovaries as well as associated vessels, ligaments, and connective tissue. Any lump or mass found within adnexa of uterus is abnormal and needs to be evaluated. Such a mass usually originates from ovary or fallopian tube.
What is the best treatment for cysts in the ovary?
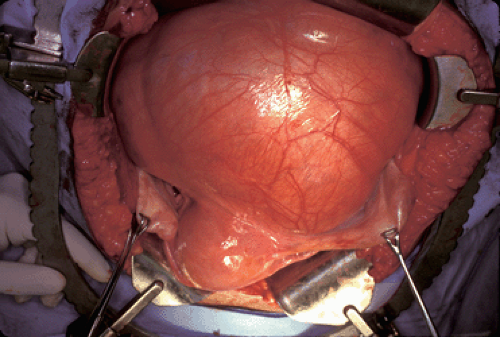
Surgical Treatment. Two types of surgeries are available for ovarian cysts: Exploratory laparotomy. Pelvic laparoscopy to remove the cyst or the ovary. It is important to know the type of tissue in the cystic mass. Ruling out malignancy is also important. The ultimate diagnostic tool is histological examination.
What is the cystic structure that forms during periods?
Endometriomas. Sometimes endometrial tissue (lining of the uterus) enters the ovary by retrograde flow. There, it forms a cystic structure called chocolate cyst. This structure secretes during periods just like normal endometrium, slowly forming a swelling in adnexal region. They typically increase during periods.
Why do babies have cysts?
Causes in a Newborn Baby Girl. In newborns, a small functional cysts (less than 1 to 2 cm) may get formed due to the influence of maternal hormones. They may regress during the first few months of life on their own.
Is a adnexal mass cancerous?
Adnexal masses may be benign or cancerous.
What causes adnexal masses?
Common symptoms associated with adnexal masses include irregular vaginal bleeding, bloating, dyspareunia, urinary symptoms, and pelvic pain. Diagnosis of adnexal masses involves medical history review and physical examination.
What are the most important facts to know about adnexal masses?
The causes of adnexal masses vary and can be either gynecologic or non-gynecologic. Common symptoms associated with adnexal masses include irregular vaginal bleeding, bloating, dyspareunia, urinary symptoms, and pelvic pain. Diagnosis of adnexal masses involves medical history review and physical examination. Blood tests and imaging may be necessary for diagnosis in rare cases. Treatment for adnexal masses largely depends on the underlying cause and can be either conservative or surgical.
What is an adnexal mass?
An adnexal mass refers to a growth that develops in the female pelvic region. Adnexal masses occur near the uterus, usually in the ovaries, fallopian tubes, or connecting tissues. These growths can originate from either the reproductive system or nearby pelvic organs, such as the intestines or the urinary bladder. Adnexal masses usually are not cancerous (i.e., benign), but they can be cancerous (i.e., malignant) in some cases.
How is an adnexal mass diagnosed?
When evaluating adnexal masses, a review of medical history, with a detailed gynecologic and family history, and a careful review of symptoms are often necessary.
How big is a cyst on an ultrasound?
Most of the time, cysts up to 10 cm (approximately 4 inches) in diameter are benign and self-limiting. With appropriate medical follow-up, these masses can be safely monitored using frequent imaging.
What is the procedure for a benign cyst?
For benign masses, minimally invasive techniques are the preferred method of intervention. One such method is laparoscopy, which allows the surgeon to access the inside of the abdomen through small incisions in the skin. In cases of larger or malignant cysts that cannot be extracted laparoscopically, open surgery may be required.
Can adnexal masses cause genital pain?
Lastly, dyspareunia, or genital pain during sexual intercourse, may be experienced by individuals with adnexal masses.
What are adnexal tumors?
Adnexal tumors occur in the: 1 Ovaries 2 Fallopian tubes 3 Connective tissue around the ovaries or fallopian tubes
How to diagnose adnexal tumor?
Diagnosis of adnexal tumors involves a careful physical exam, imaging tests and, sometimes, surgery. Treatment for adnexal tumors depends on the specific location and types of cells involved.
Where do adnexal tumors form?
Adnexal tumors are growths near the uterus. They're also known as adnexal masses. They usually form in the ovaries, which make eggs and hormones, or the fallopian tubes, which connect your uterus and ovaries. The tumors can form in the connective tissue around this part of your body. Many conditions can cause an adnexal tumor and they can happen at any age.
How Are Adnexal Tumors Treated?
The treatment for an adnexal tumor will depend on several factors, including what's causing it and where it's located. Generally, there are three options for treating adnexal masses:
How are benign ovarian tumors different from cysts?
Benign ovarian tumors usually grow slowly and rarely become malignant, or cancerous. A tumor is different from a cyst because it's a solid mass. A cyst is filled with fluid. Tumors are abnormal growths of cells that don't have any purpose. Ovarian tumors are classified based on where they started forming. The most common type starts in the cells that line the surface of the ovary.
How long does it take for a cyst to go away?
Functional cysts are usually harmless and go away without treatment within a few months. Occasionally, cysts can grow large and cause problems such as painful twisting in your ovary. If a cyst ruptures, it can cause severe pain and internal bleeding.
What is the name of the tumor that starts in the middle of the wall of the uterus?
Leiomyoma. Tumors that start in the middle of the wall of your uterus.
Can ovarian cysts be cancerous?
Benign ovarian. These masses are not cancerous and usually don't cause symptoms. They can be functional cysts or tumors. Functional cysts are sacs that form on your ovary and hold an egg. The sac usually goes away after the egg is released. Sometimes the egg isn't released or the sac closes after the egg is released. If this happens the sac can fill with fluid.
Does adnexal mass go away on its own?
Expectant management. If your adnexal mass is not cancerous and your doctor thinks it will go away on its own, you may not need any treatment or follow-up care. This may be the case if you have a small cyst that will probably go away.