
Key Points
- Isotopes are atoms of the same element that contain an identical number of protons, but a different number of neutrons.
- Despite having different numbers of neutrons, isotopes of the same element have very similar physical properties.
- Some isotopes are unstable and will undergo radioactive decay to become other elements.
What are isotopes of an element?
Isotopes are atoms of the same element having the same numbers of protons (atomic number), but different numbers of neutrons.
Can isotopes of the same element have different mass numbers?
You can have two isotopes of the same mass, like C-14 and N-14, that aren’t the same element at all, with atomic numbers 6 and 7, respectively. To find out how many neutrons an isotope harbors, subtract its atomic number from its mass number. Do isotopes actually do anything? For the most part, no.
Are all atoms isotopes of carbon?
Carbon has 15 known isotopes ( 8–22) but only carbon 12 and carbon13 are stable, and yes all atoms are isotopes. Yes, all atoms are isotopes. An isotope is a variation of a particular element. C-12, C-13, C-14, etc. are all isotopes of carbon. There is no such thing as C-6 since that wouldn’t have any neutrons at all.
What is the difference between isotopes/nuclides and radioactive isotopes?
as uranium two-thirty-five (American English) or uranium-two-three-five (British) instead of 235-92-uranium. Some isotopes/nuclides are radioactive, and are therefore referred to as radioisotopes or radionuclides, whereas others have never been observed to decay radioactively and are referred to as stable isotopes or stable nuclides.
Are isotopes are atoms?
Isotopes are atoms with different atomic masses which have the same atomic number. The atoms of different isotopes are atoms of the same chemical element; they differ in the number of neutrons in the nucleus.
Which atoms have no isotopes?
Elements that have no isotopesBeryllium-9.Fluorine-19.Sodium-23.Aluminum-27.Phosphorus-31.Scandium-45.Manganese-55.Cobalt-59.More items...
What isn't an isotope?
Look up at the atom on the periodic table of elements and find out what its atomic mass is. Subtract the number of protons from the atomic mass. This is the number of neutrons that the regular version of the atom has. If the number of neutrons in the given atom is different, than it is an isotope.
Why do atoms have isotopes?
Neutrons exist to stabilize the nucleus – without them, the nucleus would consist of nothing but positively-charged protons in close proximity to one another. Because there are different ways of stabilizing the protons, there are different isotopes.
Is there any element without isotopes?
In 2 additional cases (bismuth and protactinium), mononuclidic elements occur primordially which are not monoisotopic because the naturally occurring nuclide is radioactive, and thus the element has no stable isotopes at all. For an element to be monoisotopic, it must have one stable nuclide.
Is there any element with no isotopes?
Solution : Neon is an inert gas, so does not form isotopes.
How do you know if two atoms are isotopes?
If two atoms have different numbers of protons, they are different elements. However, if two atoms have the same number of protons, but different numbers of neutrons we refer to them as isotopes . Two terms we use to identify nuclides (isotopes) are atomic number and mass number .
How do you identify an isotope?
0:3512:42What are Isotopes? - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThe atomic number of an element identifies the element. So carbon will always have an atomic numberMoreThe atomic number of an element identifies the element. So carbon will always have an atomic number of six. So z represents the atomic. Number.
Can an atom be both an ion and an isotope?
An ion is an atom that has had electrons added or removed to give an overall electric charge. It is therefore obvious that any isotope of an element can be ionised, as the number of neutrons has no effect on the electronic structure of the atom.
What is the difference between atom and isotope?
Isotopes are atoms with different atomic masses which have the same atomic number. The atoms of different isotopes are atoms of the same chemical element; they differ in the number of neutrons in the nucleus.
Can two atoms with the same mass Be isotopes?
Atoms of an element with the same mass number make up an isotope of the element. Different isotopes of the same element cannot have the same mass number, but isotopes of different elements often do have the same mass number, e.g., carbon-14 (6 protons and 8 neutrons) and nitrogen-14 (7 protons and 7 neutrons).
What element has the most isotopes?
The elements with the most isotopes are cesium and xenon with 36 known isotopes. Some isotopes are stable and some are unstable. When an isotope is unstable it will decay over time and eventually it will turn into another isotope or element. Unstable isotopes are considered radioactive.
What are 2 examples of isotopes?
Examples of radioactive isotopes include carbon-14, tritium (hydrogen-3), chlorine-36, uranium-235, and uranium-238. Some isotopes are known to have extremely long half-lives (in the order of hundreds of millions of years). Such isotopes are commonly referred to as stable nuclides or stable isotopes.
Does fluorine have isotopes?
Fluorine is the most chemically reactive element on the periodic table. Only one isotope of fluorine occurs naturally, the stable isotope 19F.
What two atoms are isotopes?
If two atoms have different numbers of protons, they are different elements. However, if two atoms have the same number of protons, but different numbers of neutrons we refer to them as isotopes . Two terms we use to identify nuclides (isotopes) are atomic number and mass number .
Is lithium an isotope?
Lithium has two stable isotopes Li-6 and Li-7, the latter being 92.5% in nature (hence relative atomic mass of natural lithium of 6.94).
What is an isotope?
An isotope is one of two or more species of atoms of a chemical element with the same atomic number and position in the periodic table and nearly i...
Why do isotopes have different properties?
Differences in the properties of isotopes can be attributed to either of two causes: differences in mass or differences in nuclear structure. Scien...
When are isotopes stable?
Isotopes are said to be stable if, when left alone, they show no perceptible tendency to change spontaneously. A uniform scale of nuclear stability...
How were isotopes discovered?
The existence of isotopes emerged from two independent lines of research, the first being the study of radioactivity. The unambiguous confirmation...
How many stable isotopes are there in the universe?
As discussed above, only 80 elements have any stable isotopes, and 26 of these have only one stable isotope. Thus, about two-thirds of stable elements occur naturally on Earth in multiple stable isotopes, with the largest number of stable isotopes for an element being ten, for tin (. 50Sn. ).
What is the difference between isotopes and nuclides?
A nuclide is a species of an atom with a specific number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus, for example carbon-13 with 6 protons and 7 neutrons. The nuclide concept (referring to individual nuclear species) emphasizes nuclear properties over chemical properties, whereas the isotope concept (grouping all atoms of each element) emphasizes chemical over nuclear. The neutron number has large effects on nuclear properties, but its effect on chemical properties is negligible for most elements. Even for the lightest elements, whose ratio of neutron number to atomic number varies the most between isotopes, it usually has only a small effect although it matters in some circumstances (for hydrogen, the lightest element, the isotope effect is large enough to affect biology strongly). The term isotopes (originally also isotopic elements, now sometimes isotopic nuclides) is intended to imply comparison (like synonyms or isomers ). For example, the nuclides 12#N#6C#N#, 13#N#6C#N#, 14#N#6C#N#are isotopes (nuclides with the same atomic number but different mass numbers ), but 40#N#18Ar#N#, 40#N#19K#N#, 40#N#20Ca#N#are isobars (nuclides with the same mass number ). However, isotope is the older term and so is better known than nuclide and is still sometimes used in contexts in which nuclide might be more appropriate, such as nuclear technology and nuclear medicine .
How are isotopes used to determine the concentration of a substance?
Isotopes are commonly used to determine the concentration of various elements or substances using the isotope dilution method , whereby known amounts of isotopically-substituted compounds are mixed with the samples and the isotopic signatures of the resulting mixtures are determined with mass spectrometry.
What is the name of the element that indicates the atomic number?
An isotope and/or nuclide is specified by the name of the particular element (this indicates the atomic number) followed by a hyphen and the mass number (e.g. helium-3, helium-4, carbon-12, carbon-14, uranium-235 and uranium-239 ).
How are isotopes separated?
Lighter elements such as lithium, carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen are commonly separated by gas diffusion of their compounds such as CO and NO. The separation of hydrogen and deuterium is unusual because it is based on chemical rather than physical properties, for example in the Girdler sulfide process. Uranium isotopes have been separated in bulk by gas diffusion, gas centrifugation, laser ionization separation, and (in the Manhattan Project) by a type of production mass spectrometry .
What is the atomic number of carbon?
The atomic number of carbon is 6, which means ...
Which isotope has zero neutrons?
From left to right, the isotopes are protium ( 1 H) with zero neutrons, deuterium ( 2 H) with one neutron, and tritium ( 3 H) with two neutrons. Isotopes are two or more types of atoms that have the same atomic number (number of protons in their nuclei) and position in the periodic table (and hence belong to the same chemical element ), ...
What is an isotope?
An isotope is just a variation on a basic element. Just like “all purpose flour” is different than “baking flour”. They’ll both cook up the same, but the end results may be different.
How many isotopes are there in carbon?
Carbon has 15 known isotopes ( 8–22) but only carbon 12 and carbon13 are stable, and yes all atoms are isotopes.
How many neutrons are in C12?
So yes, C12 and C14 are isotopes of carbon, their nucleus contain respectively 6 neutrons and 8 neutrons. Carbon 6, doesn’t exist, six is its atomic number, which corresponds to the number of protons in its nucleus. There is three isotopes of carbon in nature, C12, C13 and C14. C11 can be created artificially.
How do you know if an element is an isotope?
All atoms are isotopes. The number of protons (+1 charge) determines what element that atom is. If the number of protons changes, then you have a different element. Each element has fairly predictable chemistry and the isotopes of each element are all fairly consistent in their chemical interactions. As an example, carbon-12 and carbon-14 each have the same tendency to combine with 2 oxygen atoms to form CO2 or sometimes just CO. But carbon-12 is stable (non-radioactive) and carbon-14 is unstable (radioactive with a half-life of over 5000 years). Each element can have a number of different iso
What is a nuclide?
A nuclide is a more generic term. That is simply a combination of protons and neutrons.
Is carbon 6 an isotope?
Carbon 6 is an isotope of carbon.
Is there an oprobium attached to the word "isotope"?
There is no oprobium attached to the word “isotope”. It is just one of the thousands of possibilities of atomic configuration.
Atomic Number and Mass
Atoms of each element contain a characteristic number of protons and electrons. The number of protons determines an element’s atomic number and is used to distinguish one element from another. The number of neutrons is variable, resulting in isotopes, which are different forms of the same atom that vary only in the number of neutrons they possess.
The Periodic Table
The different elements are organized and displayed in the periodic table. Devised by Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev (1834–1907) in 1869, the table groups elements that, although unique, share certain chemical properties with other elements.
Electron Shells and the Bohr Model
It should be stressed that there is a connection between the number of protons in an element, the atomic number that distinguishes one element from another, and the number of electrons it has. In all electrically neutral atoms, the number of electrons is the same as the number of protons.
Chemical Reactions and Molecules
All elements are most stable when their outermost shell is filled with electrons according to the octet rule. This is because it is energetically favorable for atoms to be in that configuration and it makes them stable.
Ions and Ionic Bonds
Some atoms are more stable when they gain or lose an electron (or possibly two) and form ions. This fills their outermost electron shell and makes them energetically more stable. Because the number of electrons does not equal the number of protons, each ion has a net charge. Cations are positive ions that are formed by losing electrons.
Covalent Bonds and Other Bonds and Interactions
Another way the octet rule can be satisfied is by the sharing of electrons between atoms to form covalent bonds. These bonds are stronger and much more common than ionic bonds in the molecules of living organisms. Covalent bonds are commonly found in carbon-based organic molecules, such as our DNA and proteins.
Hydrogen Bonds and van der Waals Interactions
Ionic and covalent bonds between elements require energy to break. Ionic bonds are not as strong as covalent, which determines their behavior in biological systems. However, not all bonds are ionic or covalent bonds. Weaker bonds can also form between molecules. Two weak bonds that occur frequently are hydrogen bonds and van der Waals interactions.
What are the different isotopes of an element?
When an element has atoms that differ in the number of neutrons in the nuclei, these atoms are called different isotopes of the element. All isotopes of one element have identical chemical properties. This means it is difficult to separate isotopes from each other by chemical processes. However, the physical properties of the isotopes, such as their masses, bpoints, and freezing points, are different. Isotopes can be most easily separated from each other using physical processes.
What are the particles in an atom?
Atoms are made of small particles called protons, neutrons, and electrons. Each of these particles is described in terms of measurable properties, including mass and charge. Mass is the amount of matter that an object contains. The proton and neutron have roughly the same mass and have approximately one thousand times the mass of the electron. The proton and electron have equal, but opposite, electrical charges. A neutron does not have an electrical charge.
How do you know if an atom has an electron?
The electrons of the atom move rapidly around the nucleus. If we attempt to detect an electron in an atom, we might find evidence of it located almost anywhere around the nucleus. However, if we repeat this experiment many times, it will be found that the electron is much more likely to be located in certain regions of space surrounding the nucleus than in other regions of space. We might think that the electron is rapidly moving around the nucleus and our experiment "catches" the electron as an instantaneous "snapshot" of it in motion. The probability of finding the electron in any region of space can then be described by a cloud that rapidly thins out as one goes farther from the nucleus. The density of the cloud at any point is the probability of finding the electron at that point.
How is the mass of an atom expressed?
The mass of an atom or particle is expressed in atomic mass units or amus. One atomic mass unit is a very small amount of mass. An amu is 1/12 the mass of one atom of 12C, or about 1.66 x 10-27 kg.
How to tell the difference between elements?
To distinguish between elements, we often refer to their atomic numbers . The atomic number is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom of that element (which is equal to the number of electrons around that atom's nucleus). Hydrogen's atomic number is 1, while helium's atomic number is 2. Gold has an atomic number of 79, which means it has 79 protons in its nucleus. The modern periodic table of the elements shows the different elements arranged in increasing order of atomic number.
How do atoms interact with other atoms?
Atoms interact with other atoms by sharing or transferring electrons that are farthest from the nucleus. These electrons are sometimes called valence electrons. These outer electrons determine the chemical properties of the element, such as how readily it interacts with other elements and the allowable ratios for its combinations with other substances.
What is the basic structure from which all matter is composed?
An atom is the basic structure from which all matter is composed, in the same manner as a brick is the basic structure from which a wall is built. Although atoms are too small to be seen with our eyes, scientists have long had indirect evidence for the existence of atoms. We can now use the world's most powerful scanning tunneling microscopes to "see" the magnified images of atoms and to study surface reaction sites on an atom-by-atom basis.
What are isotopes?
Isotopes are atom families that have the same number of protons, but different numbers of neutrons. The term is drawn from ancient Greek words isos and topos, meaning ‘equal place’, to signify that they belong to the same elements on the periodic table.
How many isotopes are there in the universe?
Which is just peachy for us. Taken together, the 81 stable elements known to us can boast some 275 stable isotopes. There are over 800 more radioactive (unstable) isotopes out there — some natural, and some we’ve created in the lab. Imagine the headache it would cause if they all behaved in a different way. Carbon itself has 3 stable isotopes — would we even exist today if each had its own quirks?
How are isotopes formed?
Isotopes can also be formed from other atoms or isotopes that have undergone changes over time. One example of such a process is radioactive decay: basically, unstable isotopes tend to shift towards a stable configuration over time. This can cause one unstable isotope to change into a stable one of the same element, or into isotopes of other elements with similar nucleic structures. U-238, for example, decays into Th-234.
Why do isotopes look different?
This, agian, is caused by their extra mass — the shape and masses of atoms in a molecule change how it vibrates, which in turn, changes how they interact with photons in the infrared range.
How to find out how many neutrons an isotope harbors?
To find out how many neutrons an isotope harbors, subtract its atomic number from its mass number.
Why are hydrogen isotopes important?
Hydrogen’s isotopes are important enough for industrial and scientific applications that they received their own names. Image credits BruceBlaus / Wikimedia. For example, two of hydrogen’s natural isotopes, H-2 and H-3, have 1 and 2 neutrons respectively.
What are the building blocks of matter?
Atoms are the building blocks of matter. The screen you’re reading this on, the brain you’re reading with, they’re all very organized groups of atoms. They interact in specific ways, obeying specific rules, to maintain the shape and function of objects.
What are Isotopes?
As we have stated above, isotopes are atoms with the same atomic number (Z), but a different mass number (A). This is because they have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons .
Identifying Isotopes
Now, after knowing about isotope and their definitions, a major question arises is to how to identify isotopes?
Radioactive Isotopes
For most nuclei, there is a stable ratio of protons and neutrons. In some isotopes, this ratio is not maintained. As a result, the nucleus is unstable and can decay radioactively. Such isotopes are radioactive and are also called as radioisotopes.
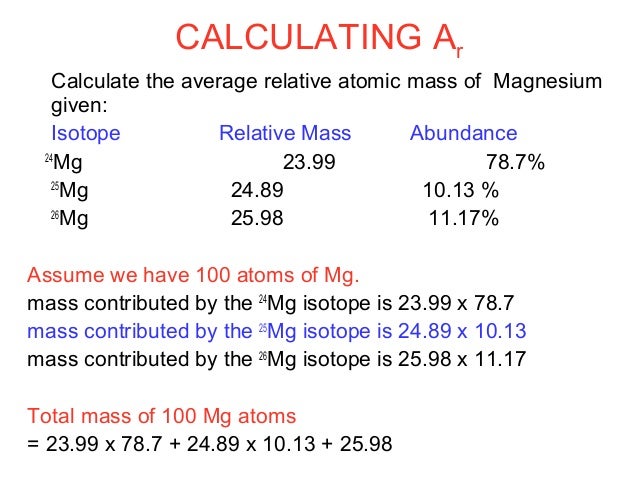
Finding Average Atomic Mass
When an element has multiple isotopes, its average mass is calculated using the masses and abundances of its isotopes.

Overview
Isotopes are two or more types of atoms that have the same atomic number (number of protons in their nuclei) and position in the periodic table (and hence belong to the same chemical element), and that differ in nucleon numbers (mass numbers) due to different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei. While all isotopes of a given element have almost the same chemical properties, they have differ…
Isotope vs. nuclide
A nuclide is a species of an atom with a specific number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus, for example carbon-13 with 6 protons and 7 neutrons. The nuclide concept (referring to individual nuclear species) emphasizes nuclear properties over chemical properties, whereas the isotope concept (grouping all atoms of each element) emphasizes chemical over nuclear. The neutron number has large effects on nuclear properties, but its effect on chemical properties is negligibl…
Notation
An isotope and/or nuclide is specified by the name of the particular element (this indicates the atomic number) followed by a hyphen and the mass number (e.g. helium-3, helium-4, carbon-12, carbon-14, uranium-235 and uranium-239). When a chemical symbol is used, e.g. "C" for carbon, standard notation (now known as "AZE notation" because A is the mass number, Z the atomic number, and E for element) is to indicate the mass number (number of nucleons) with a superscript at …
Radioactive, primordial, and stable isotopes
Some isotopes/nuclides are radioactive, and are therefore referred to as radioisotopes or radionuclides, whereas others have never been observed to decay radioactively and are referred to as stable isotopes or stable nuclides. For example, C is a radioactive form of carbon, whereas C and C are stable isotopes. There are about 339 naturally occurring nuclides on Earth, of which 286 are primordial nuclides, meaning that they have existed since the Solar System's formation.
History
The existence of isotopes was first suggested in 1913 by the radiochemist Frederick Soddy, based on studies of radioactive decay chains that indicated about 40 different species referred to as radioelements (i.e. radioactive elements) between uranium and lead, although the periodic table only allowed for 11 elements between lead and uranium inclusive.
Several attempts to separate these new radioelements chemically had failed. For example, Sod…
Variation in properties between isotopes
A neutral atom has the same number of electrons as protons. Thus different isotopes of a given element all have the same number of electrons and share a similar electronic structure. Because the chemical behavior of an atom is largely determined by its electronic structure, different isotopes exhibit nearly identical chemical behavior.
Occurrence in nature
Elements are composed either of one nuclide (mononuclidic elements), or of more than one naturally occurring isotopes. The unstable (radioactive) isotopes are either primordial or postprimordial. Primordial isotopes were a product of stellar nucleosynthesis or another type of nucleosynthesis such as cosmic ray spallation, and have persisted down to the present because their rate of decay is so slow (e.g. uranium-238 and potassium-40). Post-primordial isotopes wer…
Atomic mass of isotopes
The atomic mass (mr) of an isotope (nuclide) is determined mainly by its mass number (i.e. number of nucleons in its nucleus). Small corrections are due to the binding energy of the nucleus (see mass defect), the slight difference in mass between proton and neutron, and the mass of the electrons associated with the atom, the latter because the electron:nucleon ratio differs among isotopes.
The mass number is a dimensionless quantity. The atomic mass, on the other hand, is measure…