Are conifers and angiosperms the same thing?
Unlike conifers, which produce seeds in open cones, angiosperms enclose their seeds in fruit. Each fruit contains one or more carpels, hollow chambers that protect and nourish the seeds. Slice a tomato in half, for instance, and you'll find carpels.
Why are angiosperms dominant over gymnosperms?
The main difference between angiosperms and gymnosperms is their diversity. The diversity of angiosperms is greater than the gymnosperms. The higher diversity indicated the angiosperms adapted to a wide plethora of terrestrial ecosystems. Another characteristic of angiosperms is the flowers and production of fruits.
What plants are gymnosperms?
Key Points on Gymnosperms
- Gymnosperms are non-flowering plants belonging to the sub-kingdom Embophyta.
- The seeds are not enclosed in an ovary or fruit. They are exposed on the surface of the leaf-like structures of the gymnosperms.
- They can be classified as Coniferophyta, Cycadophyta, Ginkgophyta and Gnetophyta.
- Gymnosperms are found in boreal and temperate forests.
What are the names of the four types of gymnosperms?
Key Takeaways
- Diversity of Gymnosperms. Modern gymnosperms are classified into four phyla. ...
- Coniferophytes. Conifers are the dominant phylum of gymnosperms, with the most variety of species. ...
- Cycads. Cycads thrive in mild climates. ...
- Gingkophytes. The single surviving species of the gingkophytes group is the Gingko biloba. ...
- Gnetophytes. ...

Are conifers gymnosperms?
The Gymnosperms (Conifers, cycads and allies) Gymnosperms are seed-bearing vascular plants, such as cycads, ginkgo, yews and conifers, in which the ovules or seeds are not enclosed in an ovary. The word "gymnosperm" comes from the Greek word gymnospermos, meaning "naked seeds".
Are conifers angiosperms or gymnosperms?
Here is the general rule to remember: Conifers are gymnosperms and deciduous trees are angiosperms. There are exceptions to the rule, however. You see, some angiosperms keep their leaves in the winter, such as live oak, sweet bay magnolia, and rhododendron trees.
What gymnosperm is not a conifer?
Non-coniferous Gymnosperms Cycads, which resemble palm trees (palms are angiosperms, unlike cycads), are also gymnosperms. While there are few cycads today, these plants were extremely prevalent during the Jurassic period.
Why are conifers classified as gymnosperms?
Conifers are a magnificent group of gymnosperm plants that produce seeds without fruit or flowers. They include some incredible trees such as the Giant Sequoias of North America that can grow over 110 m tall.
Are all evergreens gymnosperms?
There are many different kinds of evergreen plants, both trees and shrubs. Evergreens include: Most species of conifers (e.g., pine, hemlock, blue spruce, and red cedar), but not all (e.g., larch) Live oak, holly, and "ancient" gymnosperms such as cycads.
Is a fir tree a gymnosperm?
Gymnosperm means as "naked seed". This group is often referred to as softwoods. Gymnosperms usually have needles that stay green throughout the year. Examples are pines, cedars, spruces and firs.
Is the pine tree a gymnosperm?
Conifers. Conifers like the spruce, cedar and pine tree are gymnosperms and have seeds on cones.
Is a cypress tree a gymnosperm?
Interesting Information About Plant: The Bald Cypress is a very interesting and unique tree. The bald cypress is so named due to its uncommon “baldness” (or bare looking branches) as a gymnosperm. The bald cypress is the only member of its family that is native to North America- in fact, according to Yahoo!
What are the 4 groups of gymnosperms?
Comprising 65 genera and 720 species, the gymnosperms are divided into four extant divisions, Coniferophyta (the conifers), Cycadophyta (the cycads), Ginkgophyta (the ginkgoes), Gnetophyta (the gnetophytes) and two extinct divisions, Pteridospermophyta and Cycadeoidophyta.
What is the classification of conifers?
PinophytaConifers / Scientific nameConifers are a group of cone-bearing seed plants, a subset of gymnosperms. Scientifically, they make up the division Pinophyta (/pɪˈnɒfɪtə, ˈpaɪnoʊfaɪtə/), also known as Coniferophyta (/ˌkɒnɪfəˈrɒfɪtə, -oʊfaɪtə/) or Coniferae.
Why are conifers classified as gymnosperms and not angiosperms?
Seed plants that flower are called angiosperms, and their seeds grow inside tissue that is part of the plants' ovaries, more commonly called fruit. Conifers are gymnosperms, and their seeds grow naked, often on the scales of a cone, instead of encased in fruit.
What makes a conifer A conifer?
Conifers are seed plants, and like most other seed plant groups they have wood, megaphyllous leaves, and of course seeds. These seeds are typically produced in woody cones, though the cones of some conifers are reduced to such a degree that they are no longer recognizable as such.
What is a conifer?
Conifer, any member of the division Pinophyta, class Pinopsida, order Pinales, made up of living and fossil gymnospermous plants that usually have needle-shaped evergreen leaves and seeds attached to the scales of a woody bracted cone . Among living gymnosperm divisions, the conifers show little similarity to the Cycadophyta and Gnetophyta but share several vegetative and reproductive traits with the Ginkgophyta. Conifers are most abundant in cool temperate and boreal regions, where they are important timber trees and ornamentals, but they are most diverse in warmer areas, including tropical mountains.
Where do cedar trees grow?
Cedar, any of four species of ornamental and timber evergreen conifers of the genus Cedrus (family Pinaceae), three native to mountainous areas of the Mediterranean region and one to the western Himalayas. Many other coniferous trees known as “cedars” resemble true cedars in being evergreen and in ...
What is a conifer?
Conifers are a group of cone-bearing seed plants, a subset of gymnosperms. Scientifically, they make up the division Pinophyta ( / pɪˈnɒfɪtə, ˈpaɪnoʊfaɪtə / ), also known as Coniferophyta ( / ˌkɒnɪfəˈrɒfɪtə, - oʊfaɪtə /) or Coniferae. The division contains a single extant class, Pinopsida.
Where are conifers found?
Conifer forests, though composed of few species, cover vast areas, as in this forest in the Cascade Range of western North America . Conifers are a group of cone-bearing seed plants, a subset of gymnosperms.
How big are the leaves of Abies grandis?
Leaf size varies from 2 mm in many scale-leaved species, up to 400 mm long in the needles of some pines (e.g. Apache Pine, Pinus engelmannii ).
What is the most common type of growth in conifers?
All living conifers are woody plants, and most are trees, the majority having monopodial growth form (a single, straight trunk with side branches) with strong apical dominance. Many conifers have distinctly scented resin, secreted to protect the tree against insect infestation and fungal infection of wounds.
How old are conifers?
The conifers are an ancient group, with a fossil record extending back about 300 million years to the Paleozoic in the late Carboniferous period; even many of the modern genera are recognizable from fossils 60–120 million years old.
What is a coniferous forest?
Conifer is a Latin word, a compound of conus (cone) and ferre (to bear), meaning "the one that bears (a) cone (s)".
Why are conifer forests important?
While tropical rainforests have more biodiversity and turnover, the immense conifer forests of the world represent the largest terrestrial carbon sink. Conifers are of great economic value for softwood lumber and paper production.
What is a gymnosperm?
Gymnosperms are flowerless plants that produce cones and seeds. The term gymnosperm literally means "naked seed," as gymnosperm seeds are not encased within an ovary. Rather, they sit exposed on the surface of leaf-like structures called bracts. Gymnosperms are vascular plants of the subkingdom Embyophyta and include conifers, cycads, ginkgoes, ...
Where is the gymnosperm found?
This image shows the gymnosperm Welwitschia mirabilis found only in the African desert of Namibia. Artush/iStock/Getty Images Plus
What is the meaning of the term "gymnosperm"?
They belong to the subkingdom Embophyta . The term "gymnosperm" literally means "naked seed.". This is because the seeds produced by gymnosperms are not encased in an ovary. Instead, gymnosperm seeds sit exposed on the surface of leaf-like structures called bracts. The four main divisions of gymnosperms are Coniferophyta, Cycadophyta, Ginkgophyta, ...
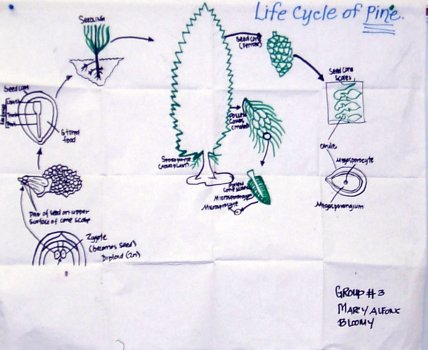
What is the life cycle of a gymnosperm?
In the gymnosperm life cycle, plants alternate between a sexual phase and an asexual phase. This type of life cycle is known as alternation of generations. Gamete production occurs in the sexual phase or gametophyte generation of the cycle. Spores are produced in the asexual phase or sporophyte generation.
What are some examples of conifers?
Examples of conifers include pines, sequoias, firs, hemlock, and spruces. Conifers are an important economic source of lumber and products, such as paper, that are developed from wood. Gymnosperm wood is considered softwood, unlike the hardwood of some angiosperms.
What is the sporophyte of a gymnosperm?
In gymnosperms, the plant sporophyte is recognized as the bulk of the plant itself, including roots, leaves, stems, and cones. The cells of the plant sporophyte are diploid and contain two complete sets of chromosomes. The sporophyte is responsible for the production of haploid spores through the process of meiosis.
What are some examples of vascular plants?
Some of the most recognizable examples of these woody shrubs and trees include pines, spruces, firs, and ginkgoes. Gymnosperms are abundant in temperate forest and boreal forest biomes with species that can tolerate moist ...
What are some examples of gymnosperms?
There are few gymnosperms that were not used by aboriginal peoples; the main exceptions seem to have been in areas where there were few or no people, or in tropical areas where angiosperm diversity far exceeded gymnosperm diversity. Two outstanding examples include: 1 Cycads ( Cycadales ), Bunya pines ( Araucaria bidwillii) and stone pines ( Pinus subsection Cembroides ), all of which produced edible nuts that were a staple food for local cultures. 2 Western redcedar ( Thuja plicata ), which filled virtually all needs of Pacific Northwest Coast peoples except providing food.
What is a gymnosperm?
Gymnosperms are woody plants, either shrubs, trees, or, rarely, vines (some gneto phytes). They differ from flowering plants in that the seeds are not enclosed in an ovary but are exposed within any of a variety of structures, the most familiar being cones.
What is the name of the first macrofossil?
Cretaceous, Aptian (125-112 my): First Gnetales macrofossils, in the form of Drewria potomacensis, an extinct species with leaves resembling those of Gnetum (Crane and Upchurch 1987 in Hill 2005).
Why are gymnosperms in one group?
We might have chosen to put "the gymnosperms" together in one group because they are all relicts, survivors of an ancient flora. They all seem strange to children of the Cenozoic savannas.
How old are gymnosperms?
Many trees have (approximately) annual rings, permitting approximate determination of the age of an individual, but in harsh environments many years may pass before the first ring is made. For example, Ken Lertzman (pers. comm. 1990) found mountain hemlock seedlings up to 18 years old (based on bud scar counts) that had yet to form their first ring. The greatest age known from ring counts is about 5000 years, for Pinus longaeva. Several other species, such as Thuja plicata and Taxus baccata, might achieve comparable ages but we cannot tell because they live in moist climates where the tree's woody heart rots away while the rest of the tree is in the prime of life, so that no record of the rings is left behind. For further detail on the oldest known gymnosperms, see the article How Old Is That Tree?.
Where does gymnosperm lumber come from?
Most of this timber comes from a handful of species, notably Pinus radiata, the most widely planted tree in the world, although it has one of the smallest natural distributions.
Where is gymnosperm diversity best observed?
Observations. Gymnosperm diversity is best observed at botanical gardens and arboreta. Conifers, at least, are also very well represented in ornamental collections throughout the temperate zones of the world.
What are gymnosperms?
Various gymnosperms. The gymnosperms, also known as Acrogymnospermae, are a group of seed-producing plants that includes conifers, cycads, Ginkgo, and gnetophytes. The term gymnosperm comes from the composite word in Greek: γυμνόσπερμος ( γυμνός, gymnos, 'naked' and σπέρμα, sperma, 'seed'), literally meaning 'naked seeds'.
How many species of gymnosperms are there?
Diversity and origin. Over 1000 living species of gymnosperm exist. It is widely accepted that the gymnosperms originated in the late Carboniferous period, replacing the lycopsid rainforests of the tropical region.
What are the two types of spores?
Two spore types, microspores (male) and megaspores (female), are typically produced in pollen cones or ovulate cones, respectively. Gametophytes, as with all heterosporous plants, develop within the spore wall. Pollen grains (microgametophytes) mature from microspores, and ultimately produce sperm cells. Megagametophytes develop from megaspores and ...
What is the name of the tree that has a fern-like morphology?
The fossil record of gymnosperms includes many distinctive taxa that do not belong to the four modern groups, including seed-bearing trees that have a somewhat fern -like vegetative morphology (the so-called "seed ferns" or pteridosperms ).
What is the largest group of gymnosperms?
By far the largest group of living gymnosperms are the conifers (pines, cypresses, and relatives), followed by cycads, gnetophytes ( Gnetum, Ephedra and Welwitschia ), and Ginkgo biloba (a single living species). About 65% of gymnosperms are dioecious,, but conifers are almost all monoecious. Some genera have mycorrhiza, fungal associations ...
What is the non-encased condition of seeds?
The non-encased condition of their seeds contrasts with the seeds and ovules of flowering plants ( angiosperms ), which are enclosed within an ovary. Gymnosperm seeds develop either on the surface of scales or leaves, which are often modified to form cones, or solitary as in yew, Torreya, Ginkgo.
What is the name of the group of seed-producing plants that includes conifers, cycads?
Cycadophyta – Cycads. Gnetophyta – Gnetum, Ephedra, Welwitschia. Encephalartos sclavoi cone, about 30 cm long. The gymnosperms, also known as Acrogymnospermae, are a group of seed-producing plants that includes conifers, cycads, Ginkgo, and gnetophytes. The term gymnosperm comes from the composite word in Greek: γυμνόσπερμος ( γυμνός, gymnos, ...
What is a gymnosperm?
Gymnosperms are a group of plants that produce seeds that are not contained within either the fruit or the ovary of a plant. The seeds of a gymnosperm are open to the air and are directly fertilized by pollination. Another term for gymnosperm, though less frequently used, is acrogymnospermae. It’s a big word for plants you are most likely already ...
Where did the term gymnosperm come from?
The origin of the term gymnosperm is greek. Gymnos, meaning “naked” and sperma being “seed” connects the etymology of the word directly to its specific style of seed production – unenclosed and exposed for pollination. The seed of a gymnosperm develops on the surface of leaves or scales and are often modified into cones.
What is the difference between a female gametophyte and an angiosperm?
The female gametophyte is on exposed bracts of the female cone and is not enclosed in an ovary. Gymnosperms are different from angiosperms in that the latter produces seeds that are enclosed within an ovule. An easy way to remember the difference is that angiosperms are flowering plants like daisies, cactus, roses, tomatoes, orchids, ...
Why are conifers important to the northern hemisphere?
Conifers are economically valued for their soft lumber and the production of paper. Indigenous communities continue to fight for these precious and powerful ecosystems.
Why are conifers important?
While conifers are a smaller group of species than others, they are a hugely important division of plants as they often grow over large landmasses. While the rainforest displays more biodiversity, boreal conifer forests maintain the planet’s largest carbon sink.
How do conifers produce ovules?
A pollen tube will eventually be created to carry the sperm cells to penetrate the egg cell. Female ovulate cones give rise to megaspores (also known as the haploid) in a structure called the megasporangium, then producing ovules. When the pollen fertilizes the ovule, it creates a diploid zygote. This creates an embryo, coated in seed tissue. This process of reproductive structures, fertilization, and seed development can take years.
Why are tropical and subtropical ecosystems under duress?
Tropical and subtropical ecosystems are under duress due to human impact – this includes the ancient species of cycads that have traveled through the ages of our planet’s history. Some species such as Microcycus in Cuba, face extinction today. simultaneously, the large attractive leaves of some species such as the Sage Palm, are increasing in popularity in gardens around the world. Often, different varieties are referred to as palms, but they are not related.
What is a gymnosperm?
Gymnosperms are seed-bearing vascular plants, such as cycads, ginkgo, yews and conifers, in which the ovules or seeds are not enclosed in an ovary. The word "gymnosperm" comes from the Greek word gymnospermos, meaning "naked seeds". Gymnosperm seeds develop either on the surface of scale or leaf-like appendages of cones, or at the end of short stalks.
How many species of gymnosperm are there?
There are around 1000 species of gymnosperm .
What are the sections of the Gymnosperms website?
There are three major sections of the site: Descriptions of all the species and higher-rank taxa of gymnosperms. For each taxon I provide information on classification, description, ecology, ethnobotany, and various other topics of interest. Things that are not strictly tied to a particular species.
What is Gymnosperm Database?
Welcome to the Gymnosperm Database, the web's premier source of information on conifers and their allies. Since we went online on 1997, the Database has attracted worldwide attention as a readily accessible, scientifically accurate source of information on the classification, description, ecology and uses of this culturally and ecologically important group of plants. This home page gives some hints about how to navigate the Database, as well as providing background information for the curious.
When was the Gymnosperm Database created?
The Gymnosperm Database was established as an online entity in the summer of 1997 and has since grown steadily, getting its own URL (Conifers.org) in the summer of 1999. The Database provides information for all species and higher-ranked taxa of the gymnosperms, i.e., conifers, cycads, ginkgo, and the gnetophytes.

Overview
Morphology
- Reproduction within conifers is relatively simple when compared to the mechanism used by angiosperms. Huge amounts of pollen, which is produced in the male cones, is transported by the wind with the hope that some pollen will reach the female cones of another tree and fertilize them. Once fertilized, female cones will begin to grow seeds. It can ta...
Evolutionary history
Taxonomy and naming
Invasive species
All living conifers are woody plants, and most are trees, the majority having monopodial growth form (a single, straight trunk with side branches) with strong apical dominance. Many conifers have distinctly scented resin, secreted to protect the tree against insect infestation and fungal infection of wounds. Fossilized resin hardens into amber. The size of mature conifers varies from le…
Predators
The earliest conifers appear in the fossil record during the Late Carboniferous (Pennsylvanian), over 300 million years ago. Conifers have been suggested to be most closely related to the Cordaitales, a group of Carboniferous-Permian trees and clambering plants whose reproductive structures have some similarities to those of conifers. The most primitive conifers belong to the paraphyletic asse…
Cultivation
Conifer is a Latin word, a compound of conus (cone) and ferre (to bear), meaning "the one that bears (a) cone(s)".
The division name Pinophyta conforms to the rules of the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (ICN), which state (Article 16.1) that the names of higher taxa in plants (above the rank of family) are either formed f…
Conditions for growth
A number of conifers originally introduced for forestry have become invasive species in parts of New Zealand, including radiata pine (Pinus radiata), lodgepole pine (P. contorta), Douglas fir (Pseudotsuga mensiezii) and European larch (Larix decidua).
In parts of South Africa, maritime pine (Pinus pinaster), patula pine (P. patula) …