
What is the comparison between prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
Well, to summarise, prokaryotic cells are unicellular micro-organisms, whereas eukaryotic cells are multi-cellular organisms. The nucleus is present in eukaryotic cells, while there is no nuclei present in prokaryotic cells.
What is a prokaryote vs eukaryote?
The main difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes is that eukaryotes contain membrane-bound organelles, and prokaryotes do not. This means that prokaryotes do not have a nucleus; instead, they keep their DNA in a cell region called the nucleoid.
Which description distinguishes eukaryotes from prokaryotes?
Eukaryotes: What Are the Differences?
- Understanding Cells and Cell Membranes. The cell is a fundamental component of our modern definition of life and living things. ...
- Prokaryotes. Prokaryotes are organisms made up of cells that lack a cell nucleus or any membrane-encased organelles.
- Eukaryotes. ...
Are humans made of prokaryotes or eukaryotes?
The human body is a combination of both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. The human body contains a large number of prokaryotes. In the real sense of it, the number of prokaryotes in the human body exceeds the number of human cells present in the body. Prokaryotes do not only live in the human body. They are everywhere around us and in our environment.

Are prokaryotes microscopic or macroscopic?
Prokaryotes are microscopic organisms belonging to the domains Bacteria and Archaea, which are two out of the three major domains of life. (Eukarya, the third, contains all eukaryotes, including animals, plants, and fungi.)
Can you see prokaryotes without a microscope?
Bacteria are too small to see without the aid of a microscope. While some eucaryotes, such as protozoa, algae and yeast, can be seen at magnifications of 200X-400X, most bacteria can only be seen with 1000X magnification. This requires a 100X oil immersion objective and 10X eyepieces..
Are both prokaryotes and eukaryotes microscopic?
As with eukaryotic cells, the plasma membrane may not be obvious under the microscope, but the cell wall should be visible. Most prokaryotic cells are 10-100 times smaller than eukaryotic cells, X Research source although there are exceptions to this.
Can eukaryotes be microscopic?
Characteristics of Protists. The word protist is a historical term that is now used informally to refer to a diverse group of microscopic eukaryotic organisms.
Which bacteria can be seen without a microscope?
Most bacteria are too small to be seen without a microscope, but in 1999 scientists working off the coast of Namibia discovered a bacterium called Thiomargarita namibiensis (sulfur pearl of Namibia) whose individual cells can grow up to 0.75mm wide.
Why do you need a microscope to see prokaryotic cells?
Most cells are so small that they cannot be viewed with the naked eye. Therefore, scientists must use microscopes to study cells. Electron microscopes provide higher magnification, higher resolution, and more detail than light microscopes.
Can eukaryotes be seen without a microscope?
The human eye cannot see most cells without the aid of a microscope. However, some large amoebas and bacteria, and some cells within complex multicellular organisms like humans and squid, can be viewed without aids.
Are eukaryotes microscopic or macroscopic?
Almost every organism you can see without a microscope -- and some microscopic organisms as well -- are examples of eukaryotes. Eukaryotes have many cellular characteristics that distinguish them from prokaryotes like bacteria.
Which is not true about prokaryotes?
Evolutionary origin is about 1.2 million years ago is the right answer which is option d. this fact is not true about prokaryotes. Looking at Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells. Prokaryotes are single-celled life forms of the areas Bacteria and Archaea.
What is the main difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
Prokaryotes are always unicellular, while eukaryotes are often multi-celled organisms. Additionally, eukaryotic cells are more than 100 to 10,000 times larger than prokaryotic cells and are much more complex. The DNA in eukaryotes is stored within the nucleus, while DNA is stored in the cytoplasm of prokaryotes.
What are 4 differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
Prokaryotes are creatures without a nucleus or other organelles in their cells....Prokaryotic CellsEukaryotic CellsDNA is circular in prokaryotes.DNA is linear in eukaryotes.Prokaryotes lack a nucleus.The nucleus is present in eukaryotes.Membrane-bound organelles are absent.Membrane-bound organelles are present.1 more row
How can you tell prokaryotes from eukaryotes?
Comparing prokaryotes and eukaryotes The primary distinction between these two types of organisms is that eukaryotic cells have a membrane-bound nucleus and prokaryotic cells do not. The nucleus is where eukaryotes store their genetic information.
Why can't you see a prokaryotic cell with a light microscope?
The cells are all prokaryotic . This means they do not have a nucleus or any other structures which are surrounded by membranes . Larger bacterial cells may be visible using a light microscope, however an electron microscope would be needed to see the details of the cell organelles.
What are 2 ways you could distinguish a eukaryote from a prokaryote under a microscope?
The difference between the two groups is the presence or absence of a nucleus surrounded by a nuclear membrane. Prokaryotic cells do not contain a membrane-bound nucleus. They are generally smaller and less complicated than eukaryotic cells. Bacteria are prokaryotic.
What microscope is used to see prokaryotic cells?
electron microscopeThe electron microscope The scanning electron microscope (SEM) has a large depth of field so can be used to examine the surface structure of specimens.
What do prokaryotes look like under a microscope?
Microbiology. The study of prokaryotic cells involves the study of bacteria – single cells that can be as tiny as two microns and look like dots under a compound microscope.
What makes up the majority of prokaryotes?
Bacteria makes up most Prokaryote’s species. They are found everywhere on Earth and have many symbiotic (helpful) and parasitic (not helpful) relationships with other organisms. Bacteria has essentially helped all other life on Earth succeed, as they help animals process vitamins and other nutrients.
How big are prokaryotes?
Prokaryotes range in size from 0.3 micrometer to 10 micrometers long and reproduce asexually through binary fission. Typical examples of prokaryotes include Spirochaete bacteria, Cyanobacteria, and Proteobacteria. All cells are one or the other type.
Why are archaea so hard to classify?
However, Archaea are rather hard to classify because they are difficult to isolate in a laboratory setting, so Archaea remain an active area of research. Archaea are generally regular in shape, being flat, squares, or cylindrically shaped. Bacteria makes up most Prokaryote’s species.
Do prokaryotes have unicellular organisms?
This means that prokaryotes can reproduce asexually, without another prokaryote to split genetic information. But just because they are unicellular, doesn’t mean that they do not form communities with other prokaryotes of the same species. Many kinds of bacteria and archaea form communities called “biofilms”, where they can potentially create complex structures and colonies.
Which structure in a prokaryotic cell is the only one that has a barrier between the inside and outside?
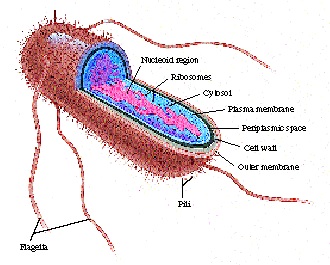
Cell Wall – Prokaryotes still have a definitive barrier separating the inside from the outside of the cell. Nucleoid – The general region within the cell where genetic material is stored. Note that this is not a defined structure like the nucleus, but rather an area where genetic information is kept.
Who first identified prokaryotes?
However in the early 60’s microbiologists C.B van Niel and Roger Stainer are credited with defining a prokaryote by the feature of having nuclear material not surrounded by a membrane. Since then, the difference between Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes were mainstream in microbiology with C.B van Niel and Roger Stainer ’s definition remaining the standard.
Where can bacteria be found?
Bacteria can be found in our body (like our stomach to aid in digestion), fermented foods (like cheese, pickles, yogurt), or in chemical processes and materials. Archaea, on the other hand, are much more rare.
History
- Prokaryotes and eukaryotes were first defined by microbiologist Edouard Chatton who first made a distinction between prokaryote and eukaryote in 1925. However in the early 60’s microbiologists C.B van Niel and Roger Stainer are credited with defining a prokaryote by the feature of having nuclear material not surrounded by a membrane. Since then, th...
Organelles in Prokaryotes
- Prokaryotes lack a many organelles and structures that are present in Eukaryotes. The organelles prokaryotes do have are not bounded by membrane and are more “free-floating” throughout the interior of the cell. They are often much more simple and smaller than eukaryotes. Sowhat DOprokaryotes have? 1. Cell Wall– Prokaryotes still have a definitive barrier separating the insid…
Prokaryote Functions, Reproduction, and Life
- Prokaryotes are unicellular organisms – they only actas one unit. This means that prokaryotes can reproduce asexually, withoutanother prokaryote to split genetic information. But just because they areunicellular, doesn’t mean that they do not form communities with otherprokaryotes of the same species. Many kinds of bacteria and archaea formcommunities called “biofilms”, where th…
Evolution of Prokaryotes
- As mentioned earlier, Prokaryotes can survive in extreme environments. That is why the current consensus believes that prokaryotes where among one of the first living organisms on Earth. Early earth was a violent, chemically-dangerous place due to volcanic activity and lack of a safe atmosphere. This type of environment was too rough for eukaryotes because photosynthesis an…
Key Features of Prokaryotes
- DNA and Nucleus
As mentioned before, prokaryotes do not have a defined nucleus. They have a plasmid, which houses the DNA which is necessary for prokaryote reproduction. The DNA of prokaryotes are actually significantly different from eukaryote DNA, despite both having the same function. Prok… - Size
Because Prokaryotes are much simpler in structure, they are often very small. Prokaryotes are usually 0.3 – 10 micrometers in size – the size of human hair is usually 100 micrometers so nearly 33 prokaryotes can fit on the diameter of your hair!
Takeaways
- All living organisms are built upon one or two different kind of cells: prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Prokaryotes are cells that lack any kind of organized, membrane-encased structures within the cell.They are much smaller and simpler in structure than eukaryotes, as they lack a lot of the complicated organelles that eukaryotes have. Prokaryotes are divided into two main classificati…
References