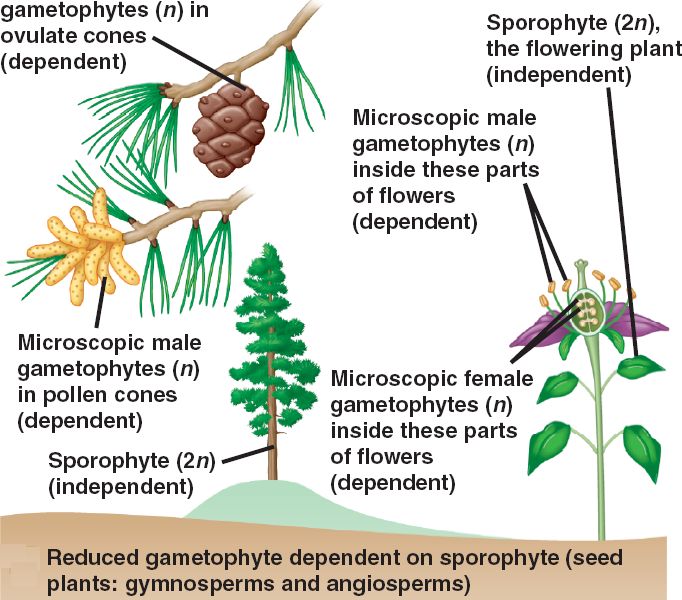
The life cycle of heterosporous plants:
- Heterosporous is seen in all seed plants and few seedless plants. All heterosporous plants have a dominant sporophyte phase.
- For example, in a plant such as lycophytes or angiosperms, sporophyte generation is observed.
- Such plants have alternating haploid and diploid generations with two phases namely sporophyte and gametophyte generation. ...
- The sporangia develop into microsporangia and megasporangia. ...
Is a fern a heterosporous plant?
Whereas lower vascular plants, such as club mosses and ferns, are mostly homosporous (produce only one type of spore), all seed plants, or spermatophytes, are heterosporous. They form two types of spores: megaspores (female) and microspores (male).
What is the difference between homosporous and heterospory?
Heterospory evolved due to natural selection that favoured an increase in propagule size compared with the smaller spores of homosporous plants. Heterosporous plants, similar to anisosporic plants, produce two different sized spores in separate sporangia that develop into separate male and female gametophytes.
What is an example of heterosporous?
Differing sized spores have been observed in many fossilized plant species. For example, the species Lepidophloios, also known as the scale tree, has been shown in fossils to have been heterosporous; The scale tree had separate cones containing either male or female spores on the same plant.
What is the advantage of heterosporous spores in plants?
Heterospory is advantageous in that having two different types of spores increases the likeliness that plants would successfully produce offspring. Heterosporous spores can respond independently to selection by ecological conditions in order to strengthen male and female reproductive function.
Why all seed plants are heterosporous?
Heterospory is thought to be a need for seed production; however, in addition to heterospory, seed plants exhibit the following traits, which have resulted in seed formation. The sporangia of ferns are more specialised than those of sporangia. Micro and large sporangia are two types of sporangia.
Are all angiosperms heterosporous?
Heterospory occurs in all seed bearing plants, i.e., gymnosperms and angiosperms.
Is all Gymnosperm are heterosporous?
Gymnosperms are heterosporous. The microspores and megaspores give rise to male and female gametophytes respectively. The spores produced are of different types and morphologically dissimilar.
Do all plants have heterospory?
A heterosporous life history occurs in some pteridophytes and in all seed plants. It is characterized by morphologically dissimilar spores produced from two types of sporangia: microspores, or male spores, and megaspores (macrospores), or female spores.
Are gymnosperms Homosporous?
Gymnosperms are both homosporous and heterosporous.
How many plants are heterosporous?
Correct answer is (2) 5. Heterospory is production of spores of two different kinds.
Are all bryophytes Homosporous?
A homosporous life history occurs in nearly all bryophytes and in most pteridophytes (lower vascular plants). It is characterized by morphologically identical spores that germinate to produce bisexual (both male and female) gametophytes in pteridophytes but either bisexual or, more usually, unisexual…
Are bryophytes heterosporous?
Bryophytes are not heterosporous. They are homosporous since they produce spores of only one kind.
Are flowering plants Homosporous or heterosporous?
heterosporousMosses and most ferns are homosporous. Conifers and flowering plants are heterosporous.
Are seed plants Homosporous or heterosporous?
Whereas lower vascular plants, such as club mosses and ferns, are mostly homosporous (produce only one type of spore), all seed plants, or spermatophytes, are heterosporous. They form two types of spores: megaspores (female) and microspores (male).
Which one of the following plants is not heterosporous?
Heterospory is the production of two different types of spores by the sporophytes of land plants. Of all the options given in the question Selaginella, Pinus and Cycas all produce micorspores and megaspores for reproduction. However, Pteridium on the other hand is homosporous.
How do you know if a plant is heterosporous?
2:583:59What is the Difference Between Homosporous and Heterosporous ...YouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipGive rise to a male gametophyte and a female gametophyte separately. And that is a major difference.MoreGive rise to a male gametophyte and a female gametophyte separately. And that is a major difference. Hope things are clear your with plant signs for a.com.
Is an angiosperm Homosporous or heterosporous?
Answer and Explanation: Flower plants are heterosporous, meaning that they produce two different types of spores.
Why angiosperms are heterosporous?
Because the two spores produce different types of gameotphytes, They are called heterosporous, a feature found only in a few species of ferns, , and all of the seed plants (i.e., gymnosperms and angiosperms).
Are flowering plants Homosporous or heterosporous?
heterosporousMosses and most ferns are homosporous. Conifers and flowering plants are heterosporous.
Why gymnosperms are called heterosporous?
Gymnosperms are able to produce male and female cones. This means that both gametes required for fertilization are present, making these groups of plants heterosporous.
What is the role of Megaspores in the development of archegonia?
They develop archegonia that produce egg cells that are fertilized by sperm of the male gametophyte originating from the microspore. This results in the formation of a fertilized diploid zygote, that develops into the sporophyte embryo.
What is a microspore?
Microspores are haploid spores that in endosporic species contain the male gametophyte, which is carried to the megaspores by wind, water currents or animal vectors. Microspores are nearly all nonflagellated, and are therefore not capable of active movement. The morphology of the microspore consists of an outer double walled structures surrounding the dense cytoplasm and central nucleus.
How does heterospory affect the evolution of plants?
The retention of megaspores and the dispersal of microspores allow for both dispersal and establishment reproductive strategies . This adaptive ability of heterospory increases reproductive success as any type of environment favors having these two strategies. Heterospory stops self-fertilization from occurring in a gametophyte, but does not stop two gametophytes that originated from the same sporophyte from mating. This specific type of self-fertilization is termed as sporophytic selfing, and in extant plants it occurs most commonly among angiosperms. While heterospory stops extreme inbreeding from occurring, it does not prevent inbreeding altogether as sporophytic selfing can still occur.
What is the name of the plant that produces megaspores?
Heterospory. A female pinecone ( Pinophyta) produces the megaspores of this heterosporic plant. A male pinecone ( Pinophyta) produces the microspores of this heterosporic plant. Heterospory is the production of spores of two different sizes and sexes by the sporophytes of land plants. The smaller of these, the microspore, ...
Why is heterospory beneficial?
Heterospory is advantageous in that having two different types of spores increases the likeliness that plants would successfully produce offspring.
How did heterospory evolve?
Heterospory evolved due to natural selection that favoured an increase in propagule size compared with the smaller spores of homosporous plants . Heterosporous plants, similar to anisosporic plants, produce two different sized spores in separate sporangia that develop into separate male and female gametophytes.
How did heterosporous plants start?
It is proposed that the emergence of heterosporous plants started with the separation of sporangia, which allowed for the development of two different spore types; numerous small spores that are easily dispersed, and fewer, larger spores that contain adequate resources to support the developing seedling.
What are some examples of heterospory?
Explanation: Examples of heterospory are Selaginella, Salvinia and Marsilea, etc. The gymnosperms and angiosperms not only lack some reproductive structures found in the homosporous and heterosporous pteridophytes but also have certa
What is heterospory in plants?
Heterospory is the phenomenon found in the plants. This is the phenomenon of formation of two types of spores, i.e., smaller microspore and larger megaspore. Explanation: Examples of heterospory are Selaginella, Salvinia and Marsilea, etc
What is the production of spores of two different sizes and sexes by the sporophytes?
Heterospory is the production of spores of two different sizes and sexes by the sporophytes of land
What are the different types of spores?
Those who produce different types of spores - small microspore and large megaspore. Like in some pteridophytes like salvinia, all gymnospermic and all angiosperm plant.
Is a club moss a heterosporous plant?
Whereas lower vascular plants, such as club mosses and ferns, are mostly homosporous (produce only one type of spore), all seed plants, or spermatophytes, are heterosporous. They form two types of spores: megaspores (female) and microspores (male).
How much does a 5' tall sage plant cost?
It's important to note that these plants are slow growing and can therefore get very expensive. I saw a 5' tall one at a local nursery going for $150. With my normally brown-thumbed self, that was not a risk I was willing to take.
Why is the Poke Me Boy tree extinct?
The tree, endemic to the British Virgin Islands of Fallen Jerusalem and Anegada, could soon become extinct due to rising sea levels threatening to wash away these low growing shrubs. Cultivars of this plant, however, have been established in the Royal Botanic Gardens of United Kingdom at Kew to keep the species alive if its wild counterparts meet with an unfortunate episode of extinction.

Overview
Origin of heterospory
Heterospory evolved due to natural selection that favoured an increase in propagule size compared with the smaller spores of homosporous plants. Heterosporous plants, similar to anisosporic plants, produce two different sized spores in separate sporangia that develop into separate male and female gametophytes. It is proposed that the emergence of heterosporous plants started with the separation of sporangia, which allowed for the development of two differ…
Microspores and megaspores
Microspores are haploid spores that in endosporic species contain the male gametophyte, which is carried to the megaspores by wind, water currents or animal vectors. Microspores are not flagellated, and are therefore not capable of active movement. The morphology of the microspore consists of an outer double walled structures surrounding the dense cytoplasm and central nucleus.
Reproduction
Heterospory was a key event in the evolution of both fossil and surviving plants. The retention of megaspores and the dispersal of microspores allow for both dispersal and establishment reproductive strategies. This adaptive ability of heterospory increases reproductive success as any type of environment favors having these two strategies. Heterospory stops self-fertilization from occurring in a gametophyte, but does not stop two gametophytes that originated from the …