Amino acids
| Amino acid | Single Letter Code | Three Letter Code | Charge (+/-/ neutral) | Polarity |
| alanine | A | Ala | neutral | nonpolar |
| arginine | R | Arg | +ve | polar |
| asparagine | N | Asn | neutral | polar |
| aspartate | D | Asp | -ve | polar |
How many non polar amino acids are there?
There are basically three major classifications for amino acids (1) those with nonpolar R group, (2) those with uncharged polar R groups, and (3) those with charged polar R group. The table below shows us all 20 amino acids with their codes.
What is the best amino supplement?
- AMINO BLEND – a perfectly blended mix of amino acids to aid in muscle recovery*
- ENERGY BLEND – With 100MG of caffeine coming from green tea and/or green coffee extracts to supply you with a boost of energy to help you get through the day ...
- MENTAL FOCUS – don’t allow the day to get the best of you, the unique formula in ESSENTIAL AMIN.O. ...
Do amino acids enter the cell simple or facilitated?
Amino acids enter cells from the blood principally by Na + -dependent cotransporters and, to a lesser extent, by facilitated transporters. The Na + -dependent transport in liver, muscle, and other tissues allows these cells to concentrate amino acids from blood.
What are neutral polar amino acids?
Serine, threonine, glutamine, and asparagine are polar but neutral (uncharged) amino acids. These side chains can form multiple hydrogen bonds, so they prefer to project into the aqueous phase. If they are on the inside of the protein they are hydrogen-bonded to other buried polar groups.
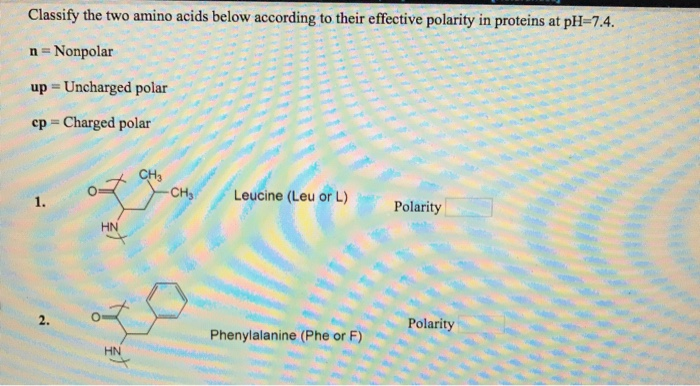
Is amino polar or nonpolar?
Amino acids can also be characterised as polar or non-polar and these dictate the amino acid function. There are 10 non-polar amino acids found in protein core, and there are 10 polar amino acids.
How do you know if amino acid is polar or nonpolar?
Just a recap, if you have on the end a Hydroxyl group, so OH. You have an Amino group, like an NH2, or you have a Sulfhydryl group, like an SH group on the end, then that would tell you that you have a polar R-Group for that particular Amino acid.
Are any amino acids nonpolar?
Nonpolar amino acids include alanine (Ala), leucine (Leu), isoleucine (Ile), proline (Pro), tryptophan (Trp), valine (Val), phenylalanine (Phe), and methionine (Met). The side chains of these amino acids are long carbon chains or carbon rings, making them bulky. They are hydrophobic, meaning they repel water.
What are polar and non-polar amino acids?
Water soluble proteins: Non-polar amino acids tend to be found in the centre of the molecule (stabilise the structure) Polar amino acids tend to be located on the protein surface (capable of interacting with water molecules)
What makes amino acids polar?
All polar amino acids have either an OH or NH2 group (when in aqueous environment), and can therefore make hydrogen bonds with other suitable groups. Polarity of the amino acids affects the overall structure of a protein.
Which amino acid is most polar?
Arginine and Lysine are pretty much tied for most polar. These scales are used to create “hydropathy plots” to predict the parts of protein sequences that are likely to be transmembrane.
Why amino acids are non-polar?
Non-polar amino acids are a class of amino acids in which the variable R-group is comprised of mostly hydrocarbons; the amino acids cysteine and methionine also feature a sulphur atom, but (due to its similar negativity to carbon) this does not confer any polar properties to either of these amino acids.
What makes amino acids nonpolar?
Nonpolar amino acids are amino acids that have no polarity. That is because these amino acids have equal numbers of carboxylic acid groups and amine groups. This makes these nonpolar amino acids to have a neutral charge. They have no charge on the “R” group.
Are proteins polar or non-polar?
Since proteins have nonpolar side chains their reaction in a watery environment is similar to that of oil in water.
Which amino acid is the most nonpolar?
The number of alkyl groups also influences the polarity. The more alkyl groups present, the more non-polar the amino acid will be. This effect makes valine more non-polar than alanine; leucine is more non-polar than valine.
How do you classify amino acids?
Amino acids are classified into three groups: Essential amino acids. Nonessential amino acids. Conditional amino acids....The human body uses amino acids to make proteins to help the body:Break down food.Grow.Repair body tissue.Perform many other body functions.
What makes an amino acid nonpolar?
Non-polar amino acids are a class of amino acids in which the variable R-group is comprised of mostly hydrocarbons; the amino acids cysteine and methionine also feature a sulphur atom, but (due to its similar negativity to carbon) this does not confer any polar properties to either of these amino acids.
How do you know if a functional group is polar or nonpolar?
Instead, it's about the types of bonds between atoms. When 2 equally strong (electronegative) atoms are bound, the sharing of electrons will be equal between them. If a functional group is composed of an atom that has strong-weak bonds, the group will be polar.
Is NH2 polar or nonpolar?
So, does NH2- polar or nonpolar? Yes, NH2- is polar in nature. The Nitrogen atom is more electronegative than Hydrogen atoms due to which unequal distribution of charge exists on the atoms of nitrogen and hydrogen that results in a net dipole moment and bent shape. Therefore, the NH2- (Amide ion) is polar in nature.
How can you tell if an amino acid is hydrophilic or hydrophobic?
The key difference between hydrophobic and hydrophilic amino acids is that the hydrophobic amino acids are nonpolar whereas the hydrophilic amino acids are polar. Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins.
What Are Nonpolar Amino Acids?
Of the 20 common amino acids in the human body that build protein structures, 9 of them are essential (meaning we must eat or otherwise consume them to get them), and half of them are nonpolar. What are nonpolar amino acids? Which are they, and what does "nonpolar" mean? The review of the topic in this article will help explain.
What are the chemical properties of nonpolar amino acids?
The chemical properties of amino acids are largely determined by one group of molecules, what's known as the R group: a side chain that differs on each amino acid. To visualize the amino acid groups, picture a pizza with four toppings, and a little support table in the middle that's there to keep the cheese from sticking ...
What is the best amino acid for muscle recovery?
Leucine is a branched-chain amino acid ( BCAA) along with valine and isoleucine, all of which help to promote post-exercise muscle recovery, leucine being particularly effective, as it converts to glucose the fastest of the three. That is also why leucine is closely linked with the regulation of blood sugar, and why a leucine deficiency causes symptoms like hypoglycemia: headaches, fatigue, dizziness, confusion, depression, and irritability.
What amino acid is responsible for regulating blood sugar?
Valine . Valine is a branched-chain amino acid (BCAA) that works with the other two BCAAs (isoleucine and leucine) to regulate blood sugar, repair tissues, and provide the body with energy. Valine assists in stimulating the central nervous system and is necessary for mental functioning.
What amino acid is used to convert glucose into energy?
Alanine is an amino acid that helps convert glucose into energy and helps eliminate excess toxins from your liver. Alanine keeps muscle protein from being cannibalized by the body during intense aerobic exercise or activity, and it's needed to balance nitrogen and glucose levels in the body, which it does via the alanine cycle.
Why are nonpolar molecules hydrophobic?
The nonpolar molecules we'll be talking about are hydrophobic amino acids, meaning "water fearing" because they don't mix with water molecules. You know how oil and water don't mix? That's because oil is hydrophobic.
What are the three groups of amino acids?
Every amino acid has three groups/toppings in common: the amino group (-NH2), the carboxyl group (COOH), and a hydrogen atom , which in pizza terms would be three standard toppings, say pepperoni, sausage, and cheese (cheese is hydrogen, which is just one atom and not a group of them, and so it gets the plainest topping).
Which amino acid is non-proteinogenic?
Non-proteinogenic amino acids often occur as intermediates in the metabolic pathways for standard amino acids – for example, ornithine and citrulline occur in the urea cycle, part of amino acid catabolism (see below).
What are the elements in amino acids?
The key elements of an amino acid are carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), and nitrogen (N), although other elements are found in the side chains of certain amino acids.
How many amino acids are there in the human body?
Aside from the 22 proteinogenic amino acids, many non-proteinogenic amino acids are known. Those either are not found in proteins (for example carnitine, GABA, levothyroxine) or are not produced directly and in isolation by standard cellular machinery (for example, hydroxyproline and selenomethionine ).
What are the roles of amino acids in proteins?
Beyond their role as residues in proteins, amino acids participate in a number of processes such as neurotransmitter transport and biosynthesis .
Why are amino acids important?
Because of their biological significance, amino acids are important in nutrition and are commonly used in nutritional supplements, fertilizers, feed, and food technology. Industrial uses include the production of drugs, biodegradable plastics, and chiral catalysts .
How is nitrogen assimilated into organic compounds?
In plants, nitrogen is first assimilated into organic compounds in the form of glutamate, formed from alpha-ketoglutarate and ammonia in the mitochondrion. For other amino acids, plants use transaminases to move the amino group from glutamate to another alpha-keto acid. For example, aspartate aminotransferase converts glutamate and oxaloacetate to alpha-ketoglutarate and aspartate. Other organisms use transaminases for amino acid synthesis, too.
What are the main excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters?
For example, in the human brain, glutamate (standard glutamic acid) and gamma-aminobutyric acid ("GABA", nonstandard gamma-amino acid) are, respectively, the main excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters. Hydroxyproline, a major component of the connective tissue collagen, is synthesised from proline. Glycine is a biosynthetic precursor ...
Which acid is more polar than Serine?
Some may be more polar than others; for example, Aspartic acid is more polar than Serine as an acid functional group is more polar than one that is alcoholic.
What are the R groups of amino acids?
Their R-groups will be pure hydrocarbon alkyl groups (alkane branches) or aromatic (benzene rings; the exception to this is the aromatic amino acid Tyrosine, which is polar).
Is valine polar or nonpolar?
Some may be more non-polar than others ; this is based on the number of alkyl groups. For example, this makes valine more non-polar than alanine. Tend to be hydrophobic, and thus face towards the inside of protein structures.