The pattern of branching in a phylogenetic tree reflects how species or other groups evolved from a series of common ancestors. In trees, two species are more related if they have a more recent common ancestor and less related if they have a less recent common ancestor. Phylogenetic trees can be drawn in various equivalent styles.
Full Answer
What is the difference between evolutionary tree and phylogenetic tree?
An evolutionary tree is a visual demonstration of the evolution of species from its point of origin. A phylogenetic tree is a diagrammatic representation of the development of biological species. It is a branching representation that portrays a cladistic relationship between all kinds of species.
Is all life on Earth part of a phylogenetic tree?
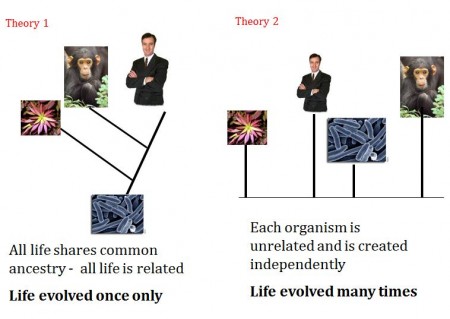
All life on Earth is part of a single phylogenetic tree, indicating common ancestry . In a rooted phylogenetic tree, each node with descendants represents the inferred most recent common ancestor of those descendants, and the edge lengths in some trees may be interpreted as time estimates.
What are the three branches of the phylogenetic tree?
A phylogenetic tree based on rRNA genes, showing the three life domains: bacteria, archaea, and eukaryota. The black branch at the bottom of the phylogenetic tree connects the three branches of living organisms to the last universal common ancestor.
Why do different branches of phylogeny show different rates of evolution?
The primary reason for this observation is that morphological evolution can occur at different rates on different branches of a phylogeny. In the example from Figure 4, the similarities of salamanders and lizards (e.g., sprawling gait and lack of fur) are features that trace back to the common ancestor of lizards, salamanders, and mammals.

How do phylogenetic trees represent evolution of organisms?
The pattern of branching in a phylogenetic tree reflects how species or other groups evolved from a series of common ancestors. In trees, two species are more related if they have a more recent common ancestor and less related if they have a less recent common ancestor.
Does a phylogenetic tree show evolution?
A phylogenetic tree, also known as a phylogeny, is a diagram that depicts the lines of evolutionary descent of different species, organisms, or genes from a common ancestor.
How do you tell which species are more closely related on a phylogenetic tree?
On a phylogenetic tree, more closely related terminal taxa are connected by shallower nodes (i.e., nodes nearer to the tips of the tree) and more distantly related terminal taxa are connected by deeper nodes (i.e., nodes nearer to the base of the tree).
Where in a phylogenetic tree would you expect to find the organism that has evolved most recently?
The trunk at the base of the tree is actually called the root, and the root node represents the most recent common ancestor of all of the taxa represented on the tree.
What are the limitations of phylogenetic trees?
In phylogenetic trees, branches do not usually account for length of time. They depict evolutionary order and evolutionary difference. Phylogenetic trees do not simply grow in only one direction after two lineages diverge; the evolution of one organism does not necessarily signify the evolutionary end of another.
What can a phylogenetic tree tell you?
A phylogenetic tree can help trace a species back through evolutionary history, down the branches of the tree, and locate their common ancestry along the way. Over time, a lineage may retain some of their ancestral features but will also be modified to adapt to the changing environment.
How do you read and interpret phylogenetic trees?
0:354:50How to Interpret Phylogenetic Trees - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnd not individuals phylogenetic tree is read from the root to the taxon. The rue is where commonMoreAnd not individuals phylogenetic tree is read from the root to the taxon. The rue is where common lineage from which all species on the tree are derived. The directions from the root to the taxon.
Which two species are most closely related?
Ever since researchers sequenced the chimp genome in 2005, they have known that humans share about 99% of our DNA with chimpanzees, making them our closest living relatives.
Can organisms that appear closely related may not actually be closely related?
Some organisms that appear very closely related on a phylogenetic tree may not actually be closely related. Why is this? In most cases, organisms that appear closely related actually are; however, there are cases where organisms evolved through convergence and appear closely related but are not.
Do phylogenetic trees show extinct species?
Its important to realize that a true phylogenetic tree would be a tree that branches from the very first life form, all the way to the present time (including all extinct species as well). The phylogenetic tree depicts evolutionary history of the species or groups.
What can be concluded about when these two features evolved along the phylogenetic tree shown in the figure?
What can be concluded about when these two features evolved along the phylogenetic tree shown in the figure? Peptidoglycans evolved sometime after point 2, and membrane-bound nuclei evolved sometime after point 3.
How important is phylogenetic tree?
Phylogenetic trees are so useful because they provide the historical narrative for explaining the similarities and differences among those entities placed on the tree.
What are phylogenetic trees used for?
Phylogenetics is a powerful approach in finding evolution of current day species. By studying phylogenetic trees, scientists gain a better understanding of how species have evolved while explaining the similarities and differences among species.
What does a phylogenetic tree show quizlet?
A phylogenetic tree is a diagram that biologists use to predict the evolutionary relationships of organisms. It starts with the common ancestor from far back, and shows the process of speciation and how through evolution the common ancestor branches out into new organisms.
Which statement below best describes a phylogenetic tree?
Which statement below most accurately describes a phylogenetic tree? A phylogenetic tree is a branching diagram used to illustrate a scientist's hypothesis about how divergence took place among evolutionary lines.
How important is phylogenetic tree?
Phylogenetic trees are so useful because they provide the historical narrative for explaining the similarities and differences among those entities placed on the tree.
What is the root of a phylogenetic tree?
Rooted phylogenetic tree optimized for blind people. The lowest point of the tree is the root, which symbolizes the universal common ancestor to all living beings. The tree branches out into three main groups: Bacteria (left branch, letters a to i), Archea (middle branch, letters j to p) and Eukaryota (right branch, letters q to z). Each letter corresponds to a group of organisms, listed below this description. These letters and the description should be converted to Braille font, and printed using a Braille printer. The figure can be 3D printed by copying the png file and using Cura or other software to generate the Gcode for 3D printing.
Where does the term "phylogenetics" come from?
The term phylogenetic, or phylogeny, derives from the two ancient greek words φῦλον ( phûlon ), meaning "race, lineage", and γένεσις ( génesis ), meaning "origin, source".
How do unrooted trees illustrate the relatedness of the leaf nodes without making assumptions about ancestry?
Unrooted trees can always be generated from rooted ones by simply omitting the root. By contrast, inferring the root of an unrooted tree requires some means of identifying ancestry. This is normally done by including an outgroup in the input data so that the root is necessarily between the outgroup and the rest of the taxa in the tree, or by introducing additional assumptions about the relative rates of evolution on each branch, such as an application of the molecular clock hypothesis.
What is the phylogenetic tree based on rRNA genes?
Not to be confused with Philogyny. A phylogenetic tree based on rRNA genes, showing the three life domains: bacteria, archaea, and eukaryota. The black branch at the bottom of the phylogenetic tree connects the three branches of living organisms to the last universal common ancestor.
When are phylogenetic networks used?
Phylogenetic networks are used when bifurcating trees are not suitable , due to these complications which suggest a more reticulate evolutionary history of the organisms sampled.
What is the tree of life?
The idea of a " tree of life " arose from ancient notions of a ladder-like progression from lower into higher forms of life (such as in the Great Chain of Being ). Early representations of "branching" phylogenetic trees include a "paleontological chart" showing the geological relationships among plants and animals in the book Elementary Geology, by Edward Hitchcock (first edition: 1840).
What is the difference between a labeled tree and an unlabeled tree?
A labeled tree has specific values assigned to its leaves, while an unlabeled tree, sometimes called a tree shape, defines a topology only. Some sequence-based trees built from a small genomic locus, such as Phylotree, feature internal nodes labeled with inferred ancestral haplotypes.
How to Make a Phylogenetic Tree?
You can build a Phylogenetic tree following the below-mentioned steps.
Why is phylogenetic tree misrepresentation?
It is known to be a misrepresentation because it shows that different groupings with the common ranks are equivalent.
What is the best software for a phylogenetic tree diagram?
However, for simulating the Phylogenetic tree diagram virtually, the best user-friendly software is EdrawMax that helps you create 2D diagrams, flow charts, Gantt charts, and all kinds of Phylogenetic trees and models.
What is the tree of life?
Since a phylogenetic tree is known as the " tree of life ," it's an upgraded understanding of an old conception that says that life progresses from lower to higher tiers like a ladder, referring to it be like the Great Chain of Being. Early perceptions, outlines, and sketches represent a branching phylogenetic tree comprising a paleontological chart. This primarily indicated the geological associations and correlations between plants and animals.
What is phylogenetic network?
A phylogenetic network does not look like a tree, and it is rather a generic diagram or graph. It is primarily used for overcoming the drawbacks or limitations fundamental to trees.
What does the root of a tree mean?
The root of the tree means the common ancestor from which all species have been developed. And the tip means the group of species (a part of the common ancestry).
What is the taxa of a tree?
The Taxa is known as the "tips" of the tree branches or the study being conducted. You can find the “Taxa” at any systematic level indicating the species, orders, or population. In addition to this, this "Taxa" is called "OTUs," which is abbreviated as "Operational Taxonomic Units."
How to Make a Phylogenetic Tree?from edrawsoft.com
You can build a Phylogenetic tree following the below-mentioned steps.
What data can be used to construct a phylogenetic tree?from bioprinciples.biosci.gatech.edu
Constructing phylogenetic trees. Many different types of data can be used to construct phylogenetic trees, including morphological data, such as structural features, types of organs, and specific skeletal arrangements; and genetic data, such as mitochondrial DNA sequences, ribosomal RNA genes, and any genes of interest .
What is the best software for a phylogenetic tree diagram?from edrawsoft.com
However, for simulating the Phylogenetic tree diagram virtually, the best user-friendly software is EdrawMax that helps you create 2D diagrams, flow charts, Gantt charts, and all kinds of Phylogenetic trees and models.
What is the tree of life?from edrawsoft.com
Since a phylogenetic tree is known as the " tree of life ," it's an upgraded understanding of an old conception that says that life progresses from lower to higher tiers like a ladder, referring to it be like the Great Chain of Being. Early perceptions, outlines, and sketches represent a branching phylogenetic tree comprising a paleontological chart. This primarily indicated the geological associations and correlations between plants and animals.
Why is phylogenetic tree misrepresentation?from edrawsoft.com
It is known to be a misrepresentation because it shows that different groupings with the common ranks are equivalent.
Which taxon has a more recent common ancestor?from bioprinciples.biosci.gatech.edu
The reason is that taxon A and taxon B share a more recent common ancestor than they do with taxon C. A group of taxa that includes a common ancestor and all of its descendants is called a clade. A clade is also said to be monophyletic. A group that excludes one or more descendants is paraphyletic; a group that excludes ...
What does the root of a tree mean?from edrawsoft.com
The root of the tree means the common ancestor from which all species have been developed. And the tip means the group of species (a part of the common ancestry).
What is the assumption that characteristics of organisms change over time?
The assumption that characteristics of organisms change over time is the most important one in cladistics. It is only when characteristics change that we are able to recognize different lineages or groups. We call the “original” state of the characteristic plesiomorphic and the “changed” state apomorphic.
Why do biologists avoid using primitive words?
However, many biologists avoid using these words because they have inaccurate connotations. We often think of primitive things as being simpler and inferior — but in many cases the original (or plesiomorphic) state of a character is more complex than the changed (or apomorphic state). For example, as they have evolved, many animals have lost complex traits (like vision and limbs). In the case of snakes, the plesiomorphic characteristic is “has legs” and the apomorphic characteristic is “doesn’t have legs.”
Is all life on Earth related?
This assumption is supported by many lines of evidence and essentially means that all life on Earth today is related and shares a common ancestor. Because of this, we can take any collection of organisms and hypothesize a meaningful pattern of relationships, provided we have the right kind of information.

Overview
External links
• Human Y-Chromosome 2002 Phylogenetic Tree
• iTOL: Interactive Tree Of Life
• Phylogenetic Tree of Artificial Organisms Evolved on Computers
• Miyamoto and Goodman's Phylogram of Eutherian Mammals
History
The idea of a "tree of life" arose from ancient notions of a ladder-like progression from lower into higher forms of life (such as in the Great Chain of Being). Early representations of "branching" phylogenetic trees include a "paleontological chart" showing the geological relationships among plants and animals in the book Elementary Geology, by Edward Hitchcock (first edition: 1840).
Charles Darwin (1859) also produced one of the first illustrations and crucially popularized the n…
Properties
A rooted phylogenetic tree (see two graphics at top) is a directed tree with a unique node — the root — corresponding to the (usually imputed) most recent common ancestor of all the entities at the leaves of the tree. The root node does not have a parent node, but serves as the parent of all other nodes in the tree. The root is therefore a node of degree 2, while other internal nodes have a mini…
Special tree types
A dendrogram is a general name for a tree, whether phylogenetic or not, and hence also for the diagrammatic representation of a phylogenetic tree.
A cladogram only represents a branching pattern; i.e., its branch lengths do not represent time or relative amount of character change, and its internal nodes do not represent ancestors.
Construction
Phylogenetic trees composed with a nontrivial number of input sequences are constructed using computational phylogenetics methods. Distance-matrix methods such as neighbor-joining or UPGMA, which calculate genetic distance from multiple sequence alignments, are simplest to implement, but do not invoke an evolutionary model. Many sequence alignment methods such as ClustalW also create trees by using the simpler algorithms (i.e. those based on distance) of tree …
Limitations of phylogenetic analysis
Although phylogenetic trees produced on the basis of sequenced genes or genomic data in different species can provide evolutionary insight, these analyses have important limitations. Most importantly, the trees that they generate are not necessarily correct – they do not necessarily accurately represent the evolutionary history of the included taxa. As with any scientific result, they are subject to falsification by further study (e.g., gathering of additional data, analyzing the e…
See also
• Clade
• Cladistics
• Computational phylogenetics
• Evolutionary biology
• Evolutionary taxonomy