ATP and NADPH are two types of ?protein? carriers. How does ATP synthase produce ATP? Atp synthase allows H+ ions to pass thru the thylakoid membrane,and the Atp synthase rotates, creating the energy to bind Adp and a phosphate group to produce Atp.
Is it true that ATP and NADPH are two types of carriers?
It is not true that ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) and NADPH (Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate) are two types of protein carriers but rather ATP and NADPH are two types of energy carriers.
What is the difference between ATP and NADPH coenzyme?
August 27, 2018 Posted by Samanthi. The key difference between ATP and NADPH is that the ATP is the energy currency of many of the living organisms while the NADPH is the typical coenzyme used for the reduction reactions of anabolic processes seen in plants.
What are the main components of ATP?
ATP is mainly consists ADP and a phosphate group. There are three major components in an ATP molecule namely a ribose sugar, an adenine base and a triphosphate group. NADPH serves as an electron carrier in a number of reactions.
Why does the activity of ATP mainly depend on the triphosphate group?
The activity of ATP mainly depends on the triphosphate group because the energy of ATP comes from the two high-energy phosphate bonds (phosphoanhydride bonds) formed between phosphate groups. The Gamma phosphate group is the first phosphate group hydrolyzed upon an energy requirement, and it locates farthest from the ribose sugar.
See more

Is NADPH a proton carrier?
NADPH – The reduced version of NADP+, which serves as a proton donor and electron carrier. NADH – NADPH without an extra phosphate group, used mostly in catabolic reactions. Electron Carrier – A molecule used to transfer electrons to various reactions and enzymes.
What type of energy is ATP and NADPH?
The overall purpose of the light-dependent reactions is to convert solar energy into chemical energy in the form of NADPH and ATP. This chemical energy will be used by the Calvin cycle to fuel the assembly of sugar molecules.
Is NADPH an electron carrier in photosynthesis?
The light-dependent reactions use light energy to make two molecules needed for the next stage of photosynthesis: the energy storage molecule ATP and the reduced electron carrier NADPH. In plants, the light reactions take place in the thylakoid membranes of organelles called chloroplasts.
Is NADPH a high electron carrier?
NADPH carries high-energy electrons to the electron transport chain in photosynthesis.
What do NADPH and ATP have in common?
Similarities Between ATP and NADPH ATP and NADPH are two types of adenine nucleotides that link biochemical reactions. The ribose sugar makes the core of the both. Also, both molecules contain an adenine group. Additionally, both are phosphorylated.
What are the roles of ATP and NADPH in the Calvin cycle?
ATP is the energy source, while NADPH is the reducing agent that adds high-energy electrons to form sugar. The Calvin cycle actually produces a three-carbon sugar glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P). For the Calvin cycle to synthesize one molecule of sugar (G3P), three molecules of CO2 Must enter the cycle.
What are the electron carriers in photosynthesis?
Electron flow between the photosynthetic complexes is mediated by two mobile carriers, plastoquinone and plastocyanin in the lipid bilayer and lumenal space, respectively.
What is ATP and NADPH role in photosynthesis?
ATP and NADPH are energy storage and electron carrier/donor molecule. Both ATP and NADPH are used in the next stage of photosynthesis. The chlorophyll molecule regains the lost electron from a water molecule through a process called photolysis, which releases dioxygen (O2) molecule.
What is the carrier molecule involved in photosynthesis?
In the light-dependent reactions, energy absorbed by sunlight is stored by two types of energy-carrier molecules: ATP and NADPH. The energy that these molecules carry is stored in a bond that holds a single atom to the molecule.
Is NADH an energy carrier?
NADH: High energy electron carrier used to transport electrons generated in Glycolysis and Krebs Cycle to the Electron Transport Chain.
Is NADPH an electron acceptor?
The final electron acceptor is NADP+, which is reduced to NADPH. NADPH generated from light reactions is used in sugar synthesis in dark reactions. Light reactions also generate a proton motive force across the thylakoid membrane, and the proton gradient is used to synthesize ATP.
What is the difference between NADH and NADPH?
NADPH and NADH are coenzymes, which take part in various metabolic processes. NADPH contains an extra phosphate group. NADH is involved in cellular respiration, whereas NADPH is involved in photosynthesis. NADPH and NADH are the reduced forms of NADP+ and NAD+, respectively.
What is ATP and NADPH role in photosynthesis?
ATP and NADPH are energy storage and electron carrier/donor molecule. Both ATP and NADPH are used in the next stage of photosynthesis. The chlorophyll molecule regains the lost electron from a water molecule through a process called photolysis, which releases dioxygen (O2) molecule.
What is ATP energy?
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the source of energy for use and storage at the cellular level. The structure of ATP is a nucleoside triphosphate, consisting of a nitrogenous base (adenine), a ribose sugar, and three serially bonded phosphate groups.
What are ATP and NADPH used for in the light-independent reactions?
ATP and NADPH are used to convert the six molecules of 3-PGA into six molecules of a chemical called glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P). That is a reduction reaction because it involves the gain of electrons by 3-PGA.
How are ATP and NADPH made in the light-dependent reactions?
The light-dependent reactions convert light energy into chemical energy. The goal of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis is to collect energy from the sun and break down water molecules to produce ATP and NADPH. These two energy-storing molecules are then used in the light-independent reactions.
What is the Difference Between ATP and NADPH?
ATP is a versatile energy currency for cells while NADPH is a source of electrons that can pass along to an electron acceptor. The function of ATP is that it acts as a major energy storing and transferring molecule. On the other hand, NADPH works as a coenzyme and reducing the power of biochemical reactions.
What are the components of ATP?
ATP is mainly consists ADP and a phosphate group. There are three major components in an ATP molecule namely a ribose sugar, an adenine base and a triphosphate group. NADPH serves as an electron carrier in a number of reactions. It can be oxidized (NADP +) and reduced (NADPH).
What is the energy of ATP?
It is known as the energy currency of life, and its value is only second to DNA of the cell. It is a high energy molecule that has the chemical formula of C 10 H 16 N 5 O 13 P 3. ATP is mainly consists ADP and a phosphate group. There are three major components in an ATP molecule namely a ribose sugar, an adenine base and a triphosphate group. NADPH serves as an electron carrier in a number of reactions. It can be oxidized (NADP +) and reduced (NADPH). It also works as a coenzyme of various dehydrogenase enzymes. This is the difference between ATP and NADPH.
What happens when the terminal phosphate group removes from the ATP molecule?
When the terminal phosphate group removes from the ATP molecule, and it converts into Adenosindiphoshate ( ADP ). This conversion releases 30.6 kJ/mol of energy to cells. ADP converts back into ATP immediately inside the mitochondria by the enzyme called ATP synthase during the cellular respiration.
How does ATP work in cells?
Cells produce ATP via several processes such as substrate-level phosphorylation, oxidative phosphorylation, and photophosphorylation. Other than working as an energy currency, ATP fulfils several other functions as well. It acts as a coenzyme in glycolysis.
What are the three phosphate groups in ATP?
Three phosphate groups of the ATP molecule are alpha (α), beta (β), and gamma (γ) phosphates. The activity of ATP mainly depends on the triphosphate group because the energy of ATP comes from the two high-energy phosphate bonds (phosphoanhydride bonds) formed between phosphate groups. The Gamma phosphate group is the first phosphate group ...
Which phosphate group is the first to hydrolyze ATP?
The Gamma phosphate group is the first phosphate group hydrolyzed upon an energy requirement, and it locates farthest from the ribose sugar. ATP is an unstable molecule. Hence, the hydrolysis of ATP is always feasible via an exergonic reaction. When the terminal phosphate group removes from the ATP molecule, and it converts into Adenosindiphoshate ...
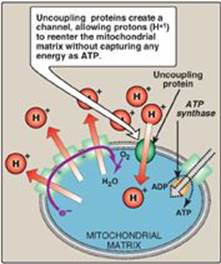
What is the function of the Atp synthase?
Atp synthase allows H+ ions to pass thru the thylakoid membrane,and the Atp synthase rotates, creating the energy to bind Adp and a phosphate group to produce Atp.
What energy sources do reactions use?
The reactions use ATP and NADPH as energy sources, they don't directly require light
What molecule is used in ATP?
METABOLISM. ATP, NAD AND FAD. ATP. Cells use a molecule called Adenosine Triphosphate(or ATP) as an energy source (See figure 2). The phosphates in this molecule can supply energy to substrates in our cells. Enzymes exist in our cells that can remove a phosphate from ATP and attach it to a different molecule-usually a protein (See Figure 3).
What is the function of ATP?
ATP is used to phosphorylate a protein. An enzyme, called a kinase (not shown) removes a phosphate from ATP and facilitates a bond between the phosphate and some other protein. The bonding of a phosphate to a protein in this manner is called phosphorylation. The phosphate bone with the protein has higher energy.
Why are nad and fad considered electron carriers?
It is often stated that these compounds are electron carriers because they accept electrons (become reduced) during catabolic steps in the breakdown of organic molecules such as carbohydrates and lipids. Then, these reduced coenzymes can donate these electrons to some other biochemical reaction normally involved in a process that is anabolic (like the synthesis of ATP).
What is the reaction called when adenine dinucleotide is oxidized?
Flavin adenine dinucleotide in its oxidized state is called FAD. After being reduced, it is called FADH 2. See figure 5 for a molecular illustration. The vitamin, riboflavin (or B2) is used to derive this compound. Riboflavin provides the ring structures that will directly participate in the transfer of two hydrogen atoms (each with one electron this time). Similar to NAD, FAD works in association with a " dehydrogenase " enzyme. The reaction removes two hydrogen atoms; each a proton with one electron. Both hydrogen atoms bond with FAD. This reaction does not release an H+ into solution like the reduction of NAD does.
Why is NADH important in biochemistry?
NADH will be important as it will deliver the hydrogens and electrons that it picks up to biochemical processes that can use the electrons and hydrogens to make ATP.
What is the name of the oxidized state of adenine dinucleotidein?
NAD+ / NADH. Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotidein its oxidized state is called NAD+, after being reduced (or accepting electrons), it is referred to as NADH. See figure 4 for a molecular illustration. The vitamin Niacin (also called B3) is used to derive this compound.
How many electrons are removed from a substrate in NAD?
In metabolic reactions that involve NAD, two hydrogen atoms and two electrons are removed from a substrate and transferred to NAD+. NAD+accepts a hydride ion (a hydrogen with 2 electrons) and becomes Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide in the reduced form (NADH).
How are proteins involved in photosynthesis?
The proteinsinvolved in the light reactionsof photosynthesisin plants are organized into five complexes in the thylakoid membrane(Figure 10.22). Two of these complexes are photosystems (photosystems Iand II), in which light is absorbed and transferred to reaction center chlorophylls. High-energy electrons are then transferred through a series of carriers in both photosystems and in a third protein complex, the cytochromebfcomplex. As in mitochondria, these electron transfers are coupled to the transfer of protons into the thylakoid lumen, thereby establishing a proton gradient across the thylakoid membrane. The energy stored in this proton gradient is then harvested by a fourth protein complex in the thylakoid membrane, ATP synthase, which (like the mitochondrial enzyme) couples proton flow back across the membrane to the synthesis of ATP.
How many protons are transported across the thylakoid membrane?
For each pair of electrons transported, two protons are transferred across the thylakoid membraneat photosystem II and two to four protons at the cytochrome bfcomplex. Since four protons are needed to drive the synthesis of one molecule of ATP, passage of each pair of electrons through photosystems I and II by noncyclic electron flow yields between 1 and 1.5 ATP molecules. Cyclic electron flow has a lower yield, corresponding to between 0.5 and 1 ATP molecules per pair of electrons.
What is the energy used in photosynthesis?
During photosynthesis, energy from sunlight is harvested and used to drive the synthesis of glucose from CO2 and H2O. By converting the energy of sunlight to a usable form of potential chemical energy, photosynthesis is the ultimate source of metabolic energy for all biological systems. Photosynthesis takes place in two distinct stages.
Which photosystems carry electrons?
From photosystem II , electrons are carried by plastocyanin (a peripheral membrane protein) to photosystem I, where the absorption of additional photons again generates high-energy electrons. Photosystem I, however, does not act as a proton pump; instead, it uses these high-energy electrons to reduce NADP+to NADPH.
Which bacteria has the best photosynthetic reaction center?
The best characterized photosynthetic reaction center is that of the bacterium Rhodopseudomonas viridis, the structure of which was determined by Johann Deisenhofer, Hartmut Michel, Robert Huber, and their colleagues in 1985 (Figure 10.21).
Is ATP stored in the thylakoid membrane?
The ATP synthaseof the thylakoid membraneis similar to the mitochondrial enzyme. However, the energy stored in the proton gradient across the thylakoid membrane, in contrast to the inner mitochondrial membrane, is almost entirely chemical in nature. This is because the thylakoid membrane, although impermeable to protons, differs from the inner mitochondrial membrane in being permeable to other ions, particularly Mg2+and Cl-. The free passage of these ions neutralizes the voltage component of the proton gradient, so the energy derived from photosynthesisis conserved mainly as the difference in proton concentration (pH) across the thylakoid membrane. However, because the thylakoid lumen is a closed compartment, this difference in proton concentration can be quite large, corresponding to a differential of more than three pH units between the stroma and the thylakoid lumen. Because of the magnitude of this pH differential, the total free energy stored across the thylakoid membrane is similar to that stored across the inner mitochondrial membrane.