Precautions

Is vitamin B12 IM or SQ?
Vitamin B12 is rapidly absorbed from intramuscular (IM) and subcutaneous (SC) sites of injection; peak plasma concentrations are reached within 1 hour after IM injection.
What happens if B12 is given subcutaneously?
Subcutaneous Vitamin B12 Injections Basically, this is an injection under the skin into the fatty tissue. It may sound unpleasant, but when done right, administering such an injection can be virtually painless, and will allow the absorption of vitamin B12 over a 24-hour period.
Should B12 be given IM or SUBQ?
Which method is best for you depends on your need, comfort and who is administering the injection. Both B12 and B complex shots are given using either intramuscular or subcutaneous injections. Both injection methods have few associated side effects and deliver effective treatment.
Does B12 have to be injected intramuscular?
Vitamin B12 shots are the most common way to prevent or treat a deficiency. The injections are prescribed by a doctor and given intramuscularly, or into muscle. Injections are usually given as hydroxocobalamin or cyanocobalamin.
Where is the best place to give a B12 injection?
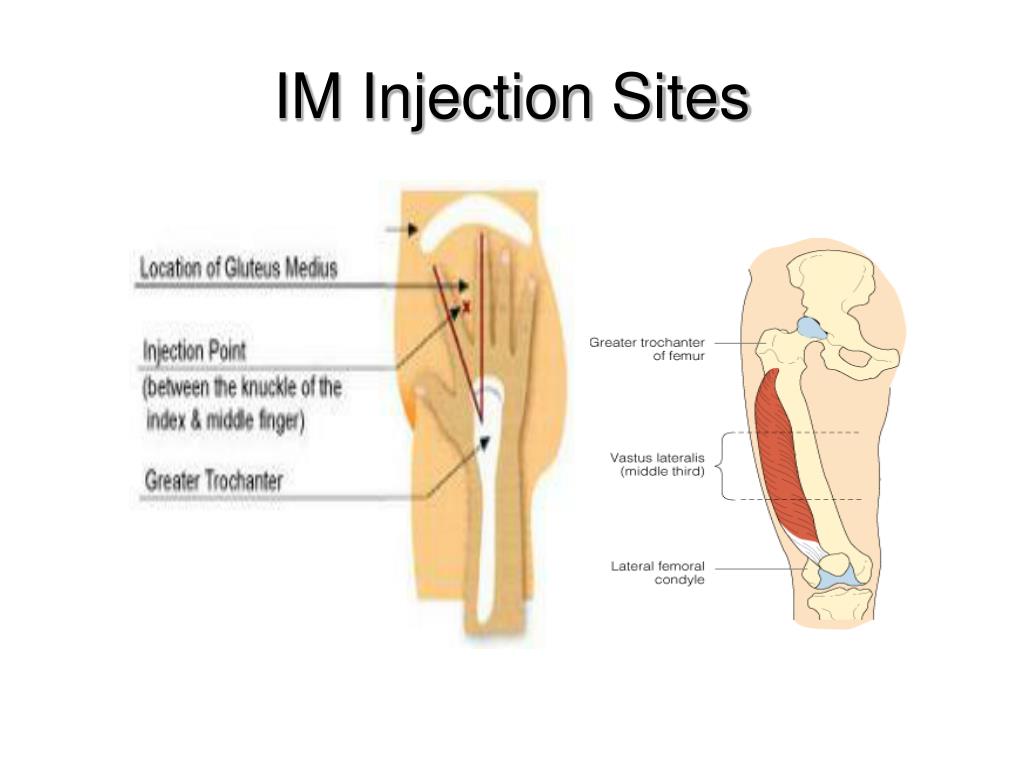
The easiest site when self-administering an IM injection is the middle third of the vastus lateralis muscle of the thigh. Other options include the deltoid muscle of the upper arm and the dorsogluteal site on the bottom. This maybe useful if you have a carer or a family member willing to administer your injection.
Where should B12 injections be given?
Vitamin B-12 shots are usually administered as intramuscular injections, meaning the best B-12 injection sites are predominantly anywhere that muscle is abundant. Therefore, vitamin B-12 injection sites include the upper arms, buttocks and thigh area.
What happens if you give a subcutaneous injection intramuscularly?
Subcutaneous injections can lead to localised cellulitis, granuloma formation and abscess. The COVID-19 vaccine has shown to have high efficacy if given correctly intramuscularly. Subcutaneous injection can happen inadvertently (figure 1), affecting efficacy of vaccination and potentiate local adverse events.
Why is B12 administered intramuscularly?
Traditionally, vitamin B12 replacement has been administered intramuscularly because absorption through the gastrointestinal tract is deficient. However, this route is less convenient for patients than oral medication and may not be covered by health insurance.
How soon do you feel less tired after a B12 injection?
Key facts. Hydroxocabalamin starts to work straight away. However, it may take a few days or weeks before your symptoms start to improve and you feel better. At first, you may need to have the injection a few times a week to boost your levels of vitamin B12.
How are vitamin B12 injections administered?
This medication is injected into a muscle or deeply under the skin. It is usually given in a clinic or care team's office. However, your care team may teach you how to inject yourself.
How quickly do B12 injections work?
Since B12 shots are injected intramuscularly bypassing the digestive process, they start to work immediately. Typically, our patients experience positive effects between 24-72 hours after the treatment.
Can you give B-12 shots in the abdomen?
The Abdomen is an easy place for most people to access when self-injecting vitamin B-12, which is why it is a very common area for B-12 injections. The name for the method of injecting into the belly (abdomen) area is subcutaneous injection.
How do you administer B-12 injections?
The needle will be inserted at a 45 degree angle, just below your skin, as opposed to deep in your muscle. The outer skin may be pulled away from the muscle tissue to ensure the needle does not pierce the muscle. The best site for this type of injection is your upper arm.
Can you give hydroxocobalamin subcutaneous?
Cyanocobalamin and hydroxocobalamin are generally given by the intramuscular route, although cyanocobalamin may be given orally or subcutaneously, or intranasally.
How much B-12 do you inject?
For B12 deficiency, a typical injection dose is 1,000 mcg once a week for 4 to 8 weeks and then 1,000 mcg once a month. But dosages can vary depending on if you're treating severe, mild, or asymptomatic B12 deficiency.