What do cardiac and skeletal muscle cells have in common?
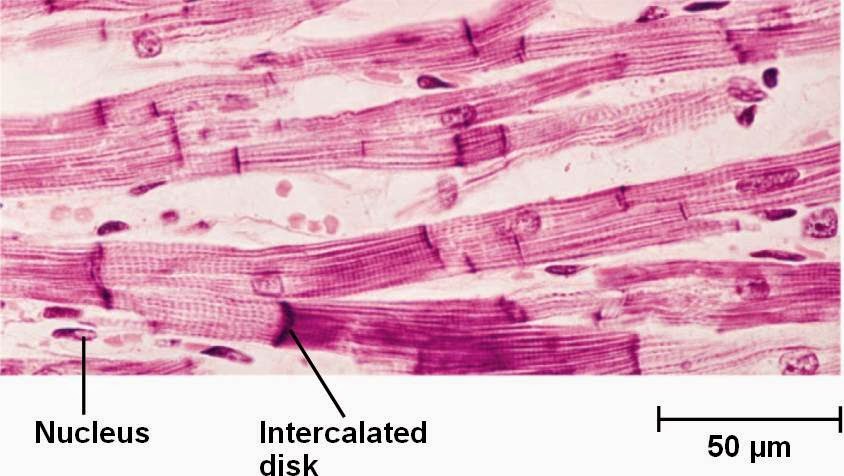
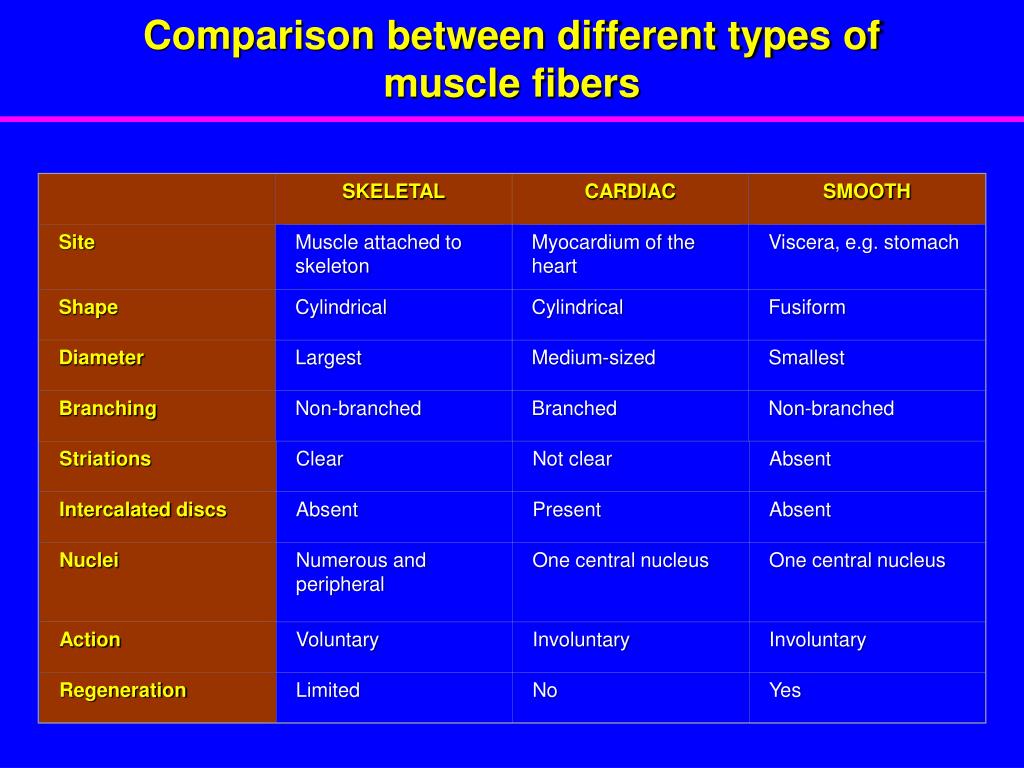
Cardiac and skeletal muscle cells both contain ordered myofibrils and are striated. Cardiac muscle cells are branched and contain intercalated discs, which skeletal muscles do not have.
How do cardiac muscle cells work together?
Anatomy Explorer. When the muscle fibers contract, myosin pulls the actin filaments together like an accordion to shrink the muscle cell and make it contract. While each cell is not very strong by itself, millions of cardiac muscle cells working together are easily able to pump all of the blood in the body through the heart in less than a minute.
Is cardiac muscle branched or intercalated?
Cardiac muscle fibers have a single nucleus, are branched, and joined to one another by intercalated discs that contain gap junctions for depolarization between cells and desmosomes to hold the fibers together when the heart contracts. Click to see full answer. Similarly, it is asked, is cardiac muscle branched or unbranched?
What is the structure and function of cardiac muscle?
Cardiac Muscle Definition 1 Cardiac Muscle Structure. Cardiac muscle exists only within the heart of animals. 2 Function of Cardiac Muscle. As in skeletal muscle, the signal to contract is an action potential. 3 Quiz. Which of the following answers lists components unique to skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle?
Is cardiac muscle branched or striated?
How are cardiac muscle cells similar to and different from skeletal muscle cells? Cardiac and skeletal muscle cells both contain ordered myofibrils and are striated. Cardiac muscle cells are branched and contain intercalated discs, which skeletal muscles do not have.
Why are the cells branched in cardiac muscle?
While each cell is not very strong by itself, millions of cardiac muscle cells working together are easily able to pump all of the blood in the body through the heart in less than a minute. Cardiac muscle cells have a branched shape so that each cell is in contact with three of four other cardiac muscle cells.
What is the shape of cardiac muscle cells?
rectangularThe cardiac muscle cell is rectangular in shape. The contraction of cardiac muscle is involuntary, strong, and rhythmical.
Are cardiac muscle cells elongated branching cells?
Cardiac muscle fibers are long, branched cells, shaped like cylinders joined end-to-end, with one or two nuclei located centrally.
How are cardiac and skeletal muscles different?
Skeletal muscle moves bones and other structures. Cardiac muscle contracts the heart to pump blood. The smooth muscle tissue that forms organs like the stomach and bladder changes shape to facilitate bodily functions.
Are smooth muscles branched?
The smooth muscle fibers group in branching bundles. As opposed to skeletal muscle fibers these bundles do not run strictly parallel and ordered but consist in a complex system. Thus the cells can contract much stronger than striated musculature.
Which muscle fibers are branched?
Cardiac muscle has branching fibers, one nucleus per cell, striations, and intercalated disks.
Are skeletal muscle cells branched?
Four characteristics define skeletal muscle tissue cells: they are voluntary, striated, not branched, and multinucleated.
What structure is unique to cardiac muscle?
intercalated discsOne feature unique to cardiac muscle is the presence of intercalated discs. These were originally believed to be another type of striation or stripe. From studies of these bands with the electron microscope it can be seen that these discs represent the end-to-end junction of adjacent cardiac muscle cells.
Is cardiac muscle elongated?
Cardiac muscle fibers are long cylindrical cells with one or two nuclei.
Are cardiac muscles cylindrical?
The correct option is C Cardiac muscle. Cardiac muscle: It is a contractile tissue present in the heart. The muscle fibres are cylindrical, branched and uninucleate.
How does cardiac muscle differ from skeletal muscle quizlet?
how do cardiac muscles differ from skeletal muscle cells? Cardiac muscle is involuntary and found only in the heart. Cardiac muscle is striated, but the bundles are connected at branching, irregular angles called intercalated discs. Skeletal muscle is striated in regular, parallel bundles of sarcomeres.
What is the muscle called that is found in the heart?
Cardiac muscle , also called myocardium, in vertebrates, one of three major muscle types, found only in the heart. Cardiac muscle is similar to skeletal muscle, another major muscle type, in that it possesses contractile units known as sarcomeres; this feature, however, also distinguishes it from smooth muscle, the third muscle type.
Which node controls cardiac contraction?
The rhythmic contraction of cardiac muscle is regulated by the sinoatrial node of the heart, which serves as the heart’s pacemaker. mammalian heart. Cross section of a four-chambered mammalian heart. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. Read More on This Topic. muscle: Cardiac muscle.
How is cardiac output determined?
The cardiac output is determined by the contractile force developed by the cardiac muscle cells, as well as by the frequency at which they are activated (rhythmicity). The factors affecting the frequency and force of heart muscle contraction are critical in determining the normal pumping performance of the heart and its response to changes in ...
What is the cardiac output?
The amount of blood pumped by the heart per minute (the cardiac output) varies to meet the metabolic needs of peripheral tissues, particularly the skeletal muscles, kidneys, brain, skin, liver, heart, and gastrointestinal tract. The cardiac output is determined by the contractile force developed by the cardiac muscle cells, ...
What is the effect of cardiac contraction on the heart?
The contraction of individual cardiac muscle cells produces force and shortening in these bands of muscle, with a resultant decrease in the heart chamber size and the consequent ejection of the blood into the pulmonary and systemic vessels .
Which muscle is responsible for transporting nutrients and breakdown products?
muscle: Cardiac muscle. The heart is the pump that keeps blood circulating throughout the body and thereby transports nutrients, breakdown products, antibodies,... The heart consists mostly of cardiac muscle cells (or myocardium). The outstanding characteristics of the action of the heart are its contractility, ...
Which protein filaments are arranged into contractile units?
The thick (myosin) and thin ( actin, troponin, and tropomyosin) protein filaments are arranged into contractile units, with the sarcomere extending from Z line to Z line, that have a characteristic cross-striated pattern similar to that seen in skeletal muscle. The rate at which the heart contracts and the synchronization ...
How are cardiac muscle fibers connected?
Cardiac muscle fibers cells also are extensively branched and are connected to one another at their ends by intercalated discs. An intercalated disc allows the cardiac muscle cells to contract in a wave-like pattern so that the heart can work as a pump. Cardiac Muscle Tissue.
Where is cardiac muscle found?
Cardiac muscle tissue is only found in the heart. Highly coordinated contractions of cardiac muscle pump blood into the vessels of the circulatory system. Similar to skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle is striated and organized into sarcomeres, possessing the same banding organization as skeletal muscle ( (Figure) ).
Which muscle cells are branched and contain intercalated discs?
Cardiac and skeletal muscle cells both contain ordered myofibrils and are striated. Cardiac muscle cells are branched and contain intercalated discs, which skeletal muscles do not have.
Which muscle fibers have mitochondria?
However, cardiac muscle fibers are shorter than skeletal muscle fibers and usually contain only one nucleus, which is located in the central region of the cell. Cardiac muscle fibers also possess many mitochondria and myoglobin, as ATP is produced primarily through aerobic metabolism. Cardiac muscle fibers cells also are extensively branched ...
Which cell structure anchors the ends of cardiac muscle fibers to allow contraction to occur?
desmosome. cell structure that anchors the ends of cardiac muscle fibers to allow contraction to occur. intercalated disc. part of the sarcolemma that connects cardiac tissue, and contains gap junctions and desmosomes.
How do pacemakers respond to heart rate?
Although cardiac muscle cannot be consciously controlled, the pacemaker cells respond to signals from the autonomic nervous system (ANS) to speed up or slow down the heart rate . The pacemaker cells can also respond to various hormones that modulate heart rate to control blood pressure.
Why do pacemakers have gap junctions?
Because they are connected with gap junctions to surrounding muscle fibers and the specialized fibers of the heart’s conduction system, the pacemaker cells are able to transfer the depolarization to the other cardiac muscle fibers in a manner that allows the heart to contract in a coordinated manner. Another feature of cardiac muscle is its ...
What are the cells that make up the heart muscle called?
Definition: What are cardiomyocytes? Cardiac muscle cells or cardiomyocytes (also known as cardiac myocytes) are the muscle cells (myocytes) that make up the heart muscle. Cardiomyocytes go through a contraction-relaxation cycle that enables cardiac muscles to pump blood throughout the body.
Which muscle cells are responsible for the pumping force of the heart?
Cardiomyocytes are the true cardiac muscle cells that build up the muscle walls (called myocardium) of both atria (the chambers in which blood enters the heart) and the ventricles (the chambers where blood is collected and pumped out of the heart). These cells can shorten and lengthen their myofibers to create the pumping force of the heart.
Why are cardiac muscles striated?
Like skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle is striated with narrow dark and light bands, due to the parallel arrangement of actin and myosin filaments. Cardiomyocytes do not fuse together. Thus, a majority of cardiomyocytes have a single nucleus (skeletal muscle cells have multiple nuclei).
What is a cardiomyocyte?
Cardiomyocytes are highly specialized cell types in terms of their structures and functions. Each cardiomyocyte contains myofibrils, unique organelles consisting of long chains of sarcomeres, the fundamental contractile units of muscle cells.
Why are mitochondria important?
Mitochondria are the “powerhouse of the cell” because they generate most of the cell’s energy supply of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). It is no doubt that the normal functions of cardiomyocytes require a lot of energy. Effective heart pumping is primarily dependent on oxidative energy production by mitochondria. Cardiomyocytes have a densely packed mitochondrial network, which allows them to produce ATP quickly, making them highly resistant to fatigue.#N#Different types of mitochondria can be distinguished within cardiomyocytes, and their morphological features are usually defined according to their location: intermyofibrillar mitochondria, subsarcolemmal mitochondria, and perinuclear mitochondria.
How big are human cardiomyocytes?
Human cardiomyocytes are about 100 μm long and 10-25 μm in diameter . Cardiac pacemaker cells are modified cardiomyocytes and control the beating of the heart. They generate and send out electrical impulses to cardiomyocytes spontaneously. Pacemaker cells create the rhythmic impulses of cardiac contraction.
Which muscle cells are narrower?
Cardiomyocytes are narrower and much shorter in comparison with skeletal muscle cells. Cardiac muscle cells are branched, allowing for faster signal propagation and contraction in three dimensions. Cardiomyocytes closely connect with each other through intercalated discs.
How do cardiac muscle cells connect to each other?
These cells, unlike skeletal muscle cells, are typically unicellular and connect to one another through special intercalated discs. These specialized cell junction and the arrangement of muscle cells enables cardiac muscle to contract quickly and repeatedly, forcing blood throughout the body.
What is the heart muscle?
Cardiac muscle, also known as heart muscle, is the layer of muscle tissue which lies between the endocardium and epicardium. These inner and outer layers of the heart, respectively, surround the cardiac muscle tissue and separate it from the blood and other organs. Cardiac muscle is made from sheets of cardiac muscle cells.
What is the muscle in between the two sheets?
In between these two sheets lies the cardiac muscle. Cardiac muscle is sometimes referred to as myocardium. This can be seen in the image below. When we look a bit closer at cardiac muscle, we can see that it is arranged in sheets of cells, which are connected to each other in a lattice-work fashion.
What is the function of the AED in the heart?
Intercalated discs and branching are unique to cardiac muscle tissue. 2. An AED (Automated External Defibrillator) is a device used to restart a stopped heart.
What is the heart?
The heart is a relatively simple organ. Through all the twists and turns and various chambers, there are only three layers. The outer layer, known as the epicardium or visceral pericardium, ...
Which layer of the heart protects the heart from blood?
This helps protect it from contact with other organs. The parietal pericardium attaches to this outer layer creates a fluid-filled layer which helps lubricate the heart. The inner layer, or endocardium, separates the muscle from the blood it is pumping within the chambers of the heart. In between these two sheets lies the cardiac muscle.
What is the action potential of a cell?
The action potential, or nerve impulse, on the surface of the cell stimulates a specialized organelle to release calcium ions (Ca 2+ ). This organelle is called the sarcoplasmic reticulum, and is derived from the endoplasmic reticulum found in a general cell.
