Do all cells have chromosomes?
Yes. With a very few exceptions, all your cells have a full set of 46 chromosomes. Exceptions: Red cells - eject their nuclei as they mature. Platelets - bud from cells called megakaryocytes and have no DNA of their own . Skin and hair cells - as they mature and move up they lose their nuclei.
Which organism has most chromosomes?
The organism with the largest number of chromosomes isn't an animal but a fern, Ophioglossum, which has the highest chromosome count of any known living organism, with 1,260 chromosomes. Hermit crabs apparently have 254.
Where are chromosomes located in a cell?
Where Are Chromosomes Located In A Cell? The chromosomes are located in the nucleus of the cell. Both plant cells and animal cells have chromosomes within their nucleus, and every chromosome is comprised of a single molecule of deoxyribonucleic acid and proteins.
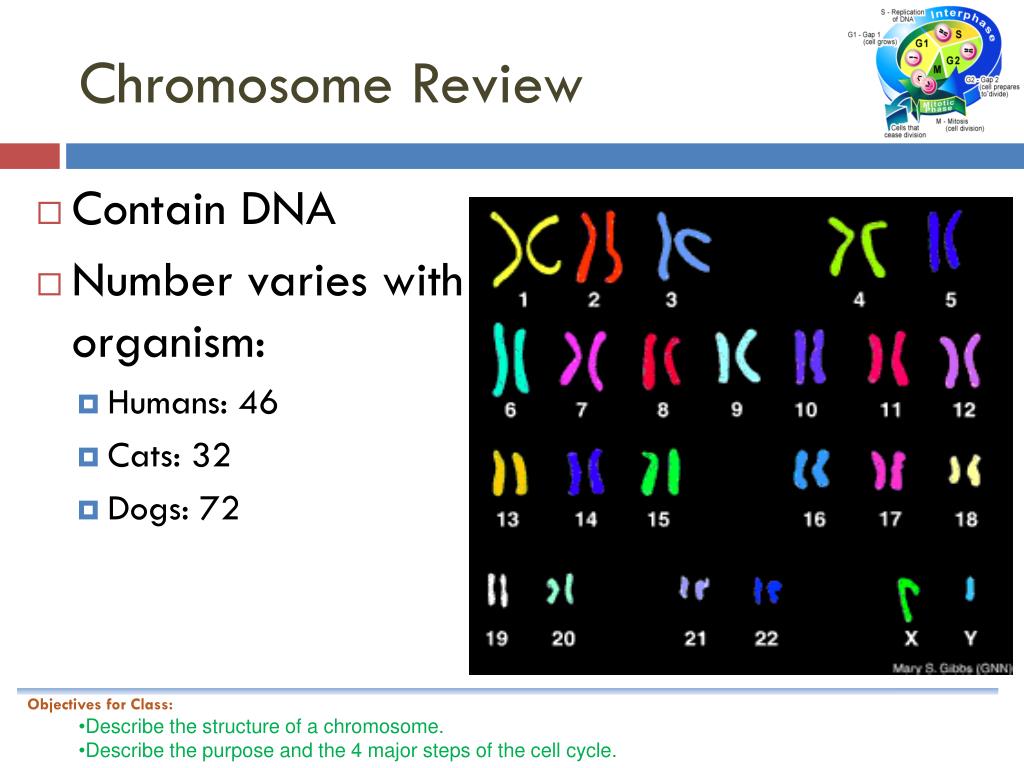
How many chromosomes are in a normal human cell?
In humans, each cell normally contains 23 pairs of chromosomes, for a total of 46. Twenty-two of these pairs, called autosomes, look the same in both males and females. The 23rd pair, the sex chromosomes, differ between males and females.

Where are chromosomes found?
The chromosomes can be found inside the nucleus of the human cell. The chromosomes are made from proteins with one strand of DNA. Your parents will have both passed on their DNA to you, and your chromosomes will contain instructions on how to make you perfectly unique.
How many chromosomes are there in a human?
In total, a human will have 23 pairs of chromosomes. This means that they have 46 chromosomes altogether. Chromosomes come in pairs, so no human or animal will normally have an odd number of chromosomes. For example, you can find four pairs of chromosomes in a fruit fly, and 12 in a rice plant.
Why do old cells need to work together?
The nuclei of the new cell and the old cell need to work together to copy the DNA so that your body still has the strand of your identity. Chromosomes are an essential part of this process.
What is the difference between egg cells and mitochondria?
The only difference with the pattern of inheritance is that the egg cell is the only one to house mitochondria during fertilization. Within the mitochondria is a small chromosome which allows the DNA to be inherited from the mother instead of the father.
Why do different numbers of chromosomes lead to health problems?
Different numbers of chromosomes can lead to health problems such as Down Syndrome. The only cells in our body that don’t have a pair of chromosomes are the reproductive cells, as these have a copy of all of our chromosomes. This is ready to merge with a partner reproductive cell and create a new human being.
How many feet would it take for DNA to squeeze?
If you were to unwind all of your DNA strands inside of your body and placed them together, they would be measurable to six feet. That’s a lot of DNA! As living beings, our cells are always growing and replenishing themselves.
What is DNA in biology?
DNA is genetic information that makes the person who they are. They can determine your traits, such as your eye color and blood type. Humans and animals all have chromosomes within their cells, but the number of chromosomes differs greatly.
What is a chromosome?
A chromosome is a long DNA molecule with part or all of the genetic material of an organism. Most eukaryotic chromosomes include packaging proteins called histones which, aided by chaperone proteins, bind to and condense the DNA molecule to maintain its integrity. These chromosomes display a complex three-dimensional structure, ...
How many chromosomes are in a prokaryote?
The prokaryotes – bacteria and archaea – typically have a single circular chromosome, but many variations exist. The chromosomes of most bacteria, which some authors prefer to call genophores, can range in size from only 130,000 base pairs in the endosymbiotic bacteria Candidatus Hodgkinia cicadicola and Candidatus Tremblaya princeps, to more than 14,000,000 base pairs in the soil-dwelling bacterium Sorangium cellulosum. Spirochaetes of the genus Borrelia are a notable exception to this arrangement, with bacteria such as Borrelia burgdorferi, the cause of Lyme disease, containing a single linear chromosome.
What happens to chromosomes in the S phase?
Before this happens, each chromosome is duplicated ( S phase ), and both copies are joined by a centromere, resulting either in an X-shaped structure (pictured above), if the centromere is located equatorially, or a two-arm structure, if the centromere is located distally.
What is the sister chromatid called?
The joined copies are now called sister chromatids. During metaphase the X-shaped structure is called a metaphase chromosome, which is highly condensed and thus easiest to distinguish and study. In animal cells, chromosomes reach their highest compaction level in anaphase during chromosome segregation.
How many copies of a chromosome are there in a symbiont?
For example, Buchnera, a symbiont of aphids has multiple copies of its chromosome, ranging from 10–400 copies per cell. However, in some large bacteria, such as Epulopiscium fishelsoni up to 100,000 copies of the chromosome can be present.
How many folds does DNA condense?
The DNA is thus condensed about 10,000 fold. The chromosome scaffold, which is made of proteins such as condensin, TOP2A and KIF4, plays an important role in holding the chromatin into compact chromosomes. Loops of 30 nm structure further condense with scaffold into higher order structures.
What is DNA molecule?
DNA molecule containing genetic material of a cell. This article is about the DNA molecule. For the genetic algorithm, see Chromosome (genetic algorithm). This article may be too technical for most readers to understand.
How many chromosomes are in a human somatic cell?
Each set contains 23 chromosomes, for a total of 46 chromosomes. Each chromosome differs in size, from over 250 million nucleotide pairs to less than 50 million nucleotide pairs. Each chromosome contains a specific set of genes, making each chromosome essential to survival.
What is the process of separating two chromosomes and forming two identical daughter cells called?
The formation of two daughter cells is called cytokinesis .
Why is the cell cycle so complex?
The Cell Cycle. Cell division in eukaryotic cells is much more complex than in prokaryotic cells because of the many chromosomes within the nucleus. Both the cytoplasm and the genetic material must be divided, ensuring that each resulting daughter cell receives 46 separate chromosomes.
What is the cell cycle?
The cell cycle is a repeating series of events, during which the eukaryotic cell carries out its necessary functions, including metabolism, cellular growth, and division, resulting in two genetically identical daughter cells. To produce two genetically identical daughter cells, the chromosomes need to replicate and the nucleus ...
Why is cell division important in eukaryotic cells?
Cell division in eukaryotic organisms is necessary for development, growth, and repair.
What is the process of prokaryotic cell division?
In prokaryotic cell division, after the single chromosome is copied, the cell grows larger. Eventually the two chromosomes separate and move to opposite ends of the cell.
How do prokaryotes reproduce?
Prokaryotic organisms reproduce asexually by binary fission, a process that produces identical offspring (Figure 1). In asexual reproduction, a single parent produces genetically identical offspring. As prokaryotes do not have a nucleus, and have only one circular chromosome, they do not need to reproduce by the same mechanism as eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic cell division is a much simpler process. In prokaryotic cell division, after the single chromosome is copied, the cell grows larger. Eventually the two chromosomes separate and move to opposite ends of the cell. Newly formed cell membrane then grows into the center of the cell, separating the two chromosomes, and forming two genetically identical daughter cells. The formation of two daughter cells is called cytokinesis. Under ideal conditions, reproduction in bacteria is extremely efficient, with some bacteria reproducing every 20 minutes. This makes bacteria an extremely effective tool for the molecular biologist. However, bacteria do not usually live in ideal conditions; otherwise, bacteria would grow and divide extremely rapidly, eventually covering the surface of Earth. Bacterial growth is limited by nutrients and water, predation, and by their own wastes.
How many chromosomes are in a cell?
Every cell (except reproductive cells) has at least one set of chromosomes in it. There are 46 chromosomes in a set.
How many chromosomes are there in the human body?
Almost every cell in the human body has its own 23 pairs of chromosomes. Exceptions include: 1 ova (egg cells) in female humans and spermatozoa (sperm cells) in male humans each have 23 chromosomes, one randomly selected from each pair. 2 erythrocytes (red blood cells) lose their chromosomes entirely when they mature. In fact, they lose their entire nucleus, which makes them look a bit like inner tubes. 3 there are probably a few other cell types that lose their genetic material as they mature, but I can’t recall which ones offhand.
What happens when a cell divides and the copying process goes awry?
Every once in a while, the copying process goes awry when a cell divides, and one or both of the daughter cells ends up with an incorrectly copied chromosome, or else with too many or too few chromosomes. Usually, one of two things happens. Either the mistake doesn’t seriously affect the cell’s functioning, or it affects it so badly that the cell dies as a result. However, occasionally the cell continues to live on but with its function seriously disturbed. Sometimes, this leads to cancer.
How many rainbows are there on earth?
Rainbows form frequently enough that at any given moment there are probably several millions rainbows on earth.
Can you be missing a chromosome?
Keep in mind, this is just for the average human. People can be missing a chromosome, or even t
How many chromosomes are there in the human body?
In humans, there are 23 pairs of chromosomes, which are structures found within the nucleus of every cell containing the tightly packed molecules known as deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), the material that carries the genetic code. One pair of the 23 chromosomes, known as sex chromosomes, determines at conception whether a fertilized egg will develop ...
How long ago did humans have chromosomes?
According to Page, about 300 million years ago, humanity’s reptile ancestors had only ordinary chromosomes that, as in today’s turtles, did not determine a newly conceived organism’s sex.
What happened to the X and Y chromosomes during meiosis?
The X chromosome continued to trade genetic information with other X chromosomes through female meiosis. But during male meiosis, the Y became isolated. And damaging mutations that would have ordinarily been purged through the natural sharing process began to accumulate, leaving the Y chromosome smaller and with fewer surviving genes from that earlier ancestor.
How many genes survive on the Y chromosome?
In at least one of eight mammalian species that Page’s team studied, 36 of the 639 genes survive today.
Why are genes read differently?
Most genes are exactly the same in males and females — they are just read differently because of sex chromosomes. Using computer simulations, Page’s team has identified 639 genes that existed on the autosomal ancestor of the X and Y chromosomes humans shared with birds 300 million years ago.
Why are XX and XY pairs functionally equivalent?
For the last 50 years, students have been taught that outside the gonads — reproductive organs where sperm and eggs are produced — cells with XX and XY pairs are functionally equivalent because there is nothing on the Y chromosome that acts outside the testes.
Why are autosomes read differently in males and females?
It’s just that the autosomes are read differently in males and females because of the sex chromosomes, just as the entirety of the genome is read different ly in males and females.”.
How many chromosomes does a bacteria have?
a. A certain bacterial species has 23 chromosomes.
Which type of reproduction requires that parents be diploid?
e. Sexual reproduction requires that parents be diploid.
Which type of cell elongates to form a head and a tail end?
b. The sperm cells elongate to form a head and a tail end.
Is a. homologous or homologous?
a. are almost entirely homologous, despite their different names.
Is the statement true for meiosis I only?
a. The statement is true for meiosis I only.