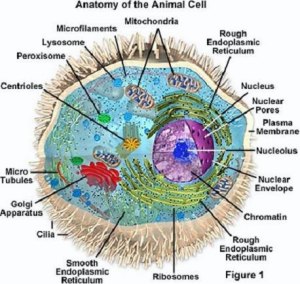
Is the cilia an organelle?
Cilia are the oldest known cellular organelle, first described in 1675 by Anthony van Leeuwenhoek in protozoa [1].
Which organelle makes cilia and flagella?
CentriolesCentrioles/basal bodies (CBBs) are microtubule-based cylindrical organelles that nucleate the formation of centrosomes, cilia, and flagella.
What organelle has flagella?
A flagellum is built on a template organelle called the basal body, which is constructed by modifying a centriole recruited from a centrosome (or from a pre-existing basal body) (Figure 1).
What type of cell is cilia and flagella?
eukaryotic cellsCilia and flagella are found in eukaryotic cells whereas, flagella are also present in prokaryotic cells. Cilia are found in paramecium organism and flagella are present in bacteria and sperm cells. Let us discuss the key differences between these two structures.
Is a flagella an organelle?
Cilia and flagella are important cellular organelles, which are composed of more than 600 kinds of proteins and perform various kind of functions in cells.
What organelles help move cells?
The cytoskeletonThe cytoskeleton provides a structural framework for the cell, serving as a scaffold that determines cell shape and the general organization of the cytoplasm. In addition to playing this structural role, the cytoskeleton is responsible for cell movements.
What is the organelle?
Listen to pronunciation. (OR-guh-NEL) A small structure in a cell that is surrounded by a membrane and has a specific function.
What organelle does cilia work with?
It has emerged that the cilium should not be viewed in isolation but rather as intrinsically linked to other organelles - the basal body, centrosome, actin, and microtubular cytoskeleton; to other cellular processes - cell cycle, division, and cytokinesis; and to other signaling pathways important for development: ...
Is flagella a membrane bound organelles?
Other organelles, that are not membrane bound include ribosomes, peroxisomes, cilia, flagella, centrioles, microtubules, cytoskeleton, centrosomes, and the cell wall.
What are the cell organelles and their function?
Organelles are small structures within the cytoplasm that carry out functions necessary to maintain homeostasis in the cell. They are involved in many processes, for example energy production, building proteins and secretions, destroying toxins, and responding to external signals.
What is a cilia and flagella simple definition?
Cilia and flagella are tube-like appendages which allow for motion in eukaryotic cells. If a cell has a single appendage, which often looks tail-like, it is called a flagellum, but if it has many, they are called cilia.
What organelle makes proteins?
The endoplasmic reticulum can either be smooth or rough, and in general its function is to produce proteins for the rest of the cell to function. The rough endoplasmic reticulum has on it ribosomes, which are small, round organelles whose function it is to make those proteins.
What makes cilia and flagella move?
The dynein motor proteins generate the motive force to bend the flagellum and cause it to move with a whip‐like motion through the surrounding fluid. This motion is referred to as the flagellar or ciliary beat.
Which of the following helps make cilia and flagella?
Microtubules also make up two types of cellular appendages important for motion: cilia and flagella. Cilia are found on many cells of the body, including the epithelial cells that line the airways of the respiratory system.
What is required to form cilia or flagella?
Cilia and flagella are highly conserved eukaryotic microtubule-based organelles that protrude from the surface of most mammalian cells. These structures require large protein complexes and motors for distal addition of tubulin and extension of the ciliary membrane.
Where are cilia and flagella found?
Cilia are present in organisms such as paramecium while flagella can be found in bacteria and sperm cells. Cilia are shorter and numerous than flagella. Cilia and flagella are the most common organelles for locomotion in unicellular organisms.
What are the functions of the flagella and cilia?
The Flagella and Cilia are microscopic, contractile and filamentous processes of the cytoplasm which are capable of producing a current in the fluid medium for locomotion and passage of substances. Also, they act as sensory organs and perform many mechanical functions of the cell.
Where are molecular cilia found?
Motile cilia are found on the cell surface in larger numbers. These are also found in the respiratory epithelium of the human respiratory tract and helps by clearing the mucus or the dust particles out of the lungs.
What is the name of the hair-like structure that moves cells or substances along the outer surface of the cell?
Cilla. Cilia (singular = cilium) are short, hair-like structures that are used to move entire cells or substances along the outer surface of the cell. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic flagella are different in chemical composition and structure.
What are the parts of a prokaryotic flagella?
The bacterial flagella have the following features: The bacterial flagellum is made up of the flagellin protein. Each flagellum has three parts, hook, shaft, and the basal body.
What are the two types of flagella?
Ans: There are two main types of flagella in eukaryotes: 1. Whiplash flagellum is one that does not have hairy flimmers on the surface. 2. The tinsel flagellum is one that has lateral hair-like projections or flimmers, or mastigonemes on the surface.
What is the structure that extends from the plasma membrane?
Flagella (singular = flagellum) are long, hair-like structures that extend from the plasma membrane and are used in the movement of an entire cell.
What are the three parts of the flagellum?
Each flagellum has three parts, hook, shaft, and the basal body. This has a helical structure and very sharp bending outside the outermost membrane. This is called the hook. The hook is made up of different types of proteins. A long shaft runs between the hook and the basal body.
What Are Cilia and Flagella?
Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells contain structures known as cilia and flagella. These extensions from the cell surface aid in cell movement. They also help to move substances around cells and direct the flow of substances along tracts. Cilia and flagella are formed from specialized groupings of microtubules called basal bodies. If the protrusions are short and numerous they are termed cilia. If they are longer and less numerous (usually only one or two) they are termed flagella.
Where Can Cilia and Flagella Be Found?
Both cilia and flagella are found in numerous types of cells. For instance, the sperm of many animals, algae, and even ferns have flagella. Prokaryotic organisms may also possess a single flagellum or more. A bacterium, for example, may have: one flagellum located at one end of the cell (montrichous), one or more flagella located at both ends of the cell (amphitrichous), several flagella at one end of the cell (lophotrichous), or flagella distributed all around the cell (peritrichous). Cilia can be found in areas such as the respiratory tract and female reproductive tract. In the respiratory tract, cilia helps to sweep mucus containing dust, germs, pollen, and other debris away from the lungs. In the female reproductive tract, cilia helps to sweep sperm in the direction of the uterus.
What are the protrusions of cilia and flagella called?
Cilia and flagella are formed from specialized groupings of microtubules called basal bodies. If the protrusions are short and numerous they are termed cilia. If they are longer and less numerous (usually only one or two) they are termed flagella.
What are the two types of internal and external cell structures?
Cilia and flagella are two of the many types of internal and external cell structures. Other cell structures and organelles include: Cell Membrane: This outer membrane of eukaryotic cells protects the integrity of the interior of the cell. Cytoskeleton: The cytoskeleton is a network of fibers that forms the internal infrastructure of the cell.
What are cilia used for?
In higher organisms, cilia is often used to propel substances in a desired direction. Some cilia, however, do not function in movement but in sensing.
What are the sacs of enzymes that digest cellular macromolecules?
Lysosomes: Lysosomes are sacs of enzymes that digest cellular macromolecules.
Where are flagella located?
A bacterium, for example, may have: one flagellum located at one end of the cell (montrichous), one or more flagella located at both ends of the cell (amphitrichous), several flagella at one end of the cell (lophotrichous), or flagella distributed all around the cell (peritrichous). Cilia can be found in areas such as the respiratory tract ...

Define Flagella and Cilia
- Flagella
Flagella (singular = flagellum) are long, hair-like structures that extend from the plasma membrane and are used in the movement of an entire cell. - Cilla
Cilia (singular = cilium) are short, hair-like structures that are used to move entire cells or substances along the outer surface of the cell. Fig: Cilia and Flagella Eukaryotic and prokaryotic flagella are different in chemical composition and structure.
Structure of Flagella and Cilia
- Both Flagella and Cilia are structurally similar and possess similar parts, i.e., basal body, rootlets, basal plate and shaft.
Structure of Prokaryotic Flagella
- The flagella structure and chemical composition are different in eukaryotes and prokaryotes. The bacterial flagella have the following features: 1. The bacterial flagellum is made up of the flagellin protein. 2. Each flagellum has three parts, hook, shaft, and the basal body. 3. This has a helical structure and very sharp bending outside the outermost membrane. This is called the hook. 4. T…
Types of Flagella Arrangement in Bacteria
- Based on the number and arrangement of flagella, there are the following types of bacteria: 1. Monotrichous – Vibrio choleraehas a single flagellum only at one end of the cell. 2. Amphitrichous – Nitrosomonashas a single flagellum at each pole. 3. Lophotrichous – Spirillum volutanshas a cluster of flagella at one or both ends. 4. Peritrichous – Flagella are spread fairly evenly over the …
What Is The Main Function of Flagella?
- Some of the functions of flagella and cilia are as follows: i. These help in locomotion in flagellated and ciliated organisms. ii. The flagella or cilia also help capture food in many protozoans and some animals. iii. They create water currents in certain aquatic animals for obtaining food. iv. The flagella circulate food in the gastrovascular cavity of coelenterates. v. The cilium of the respirato…
Summary
- Through this article, we understood the structure and functions of flagella and cilia and the difference between them. These are the microscopic contractile and filamentous structure of the cytoplasm. It creates food currents, acts as sensory organs and performs many mechanical functions of the cell. Cilia and Flagella are identical structures, but both can be distinguished by …
FAQs
- Q.1. Write one function of cilia. Ans:The cilia also help in capturing food in many protozoans and some animals. They also help in feeding, locomotion, aeration, circulation, etc. Q.2. Do all bacteria have flagella? Ans:Flagella occur on both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, and their presence can be useful in identification. For example, they are found on many species of bacilli …