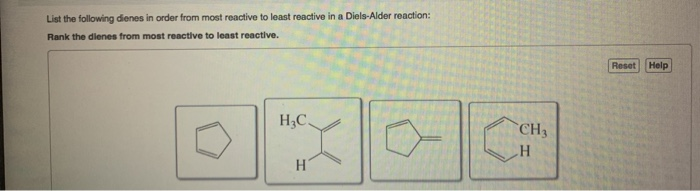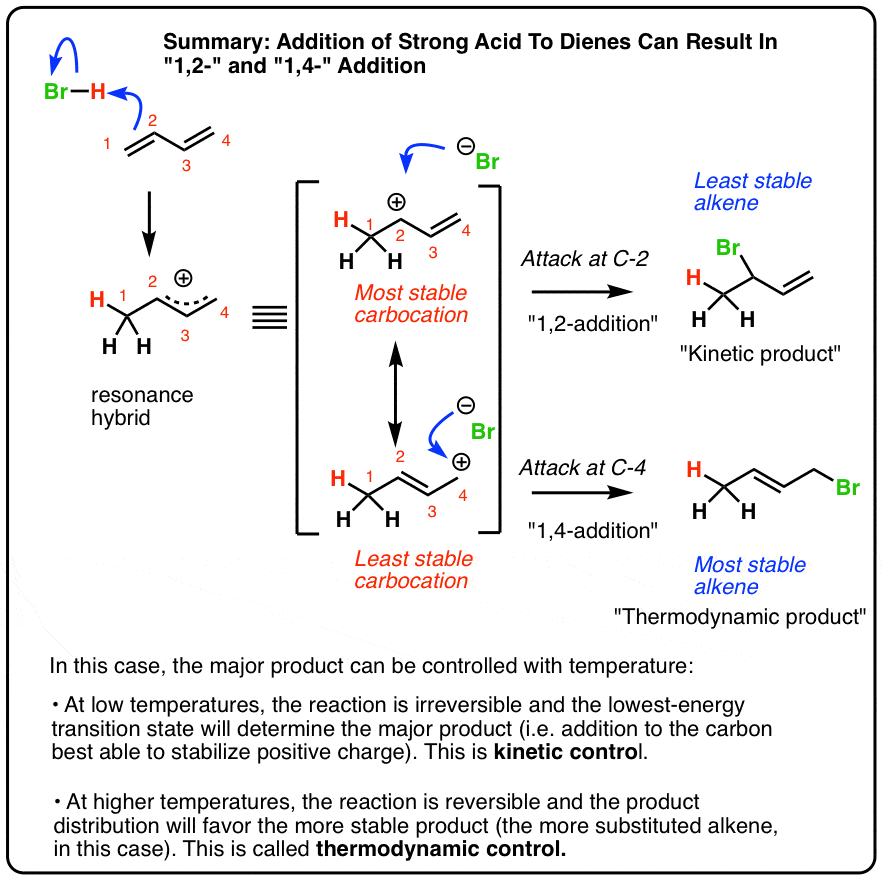
Why is diene more reactive than alkene?
Why is diene more reactive than alkene? Bookmark this question. Show activity on this post. The chemical reduction of 1,3-butadiene with sodium in alcohol gives mainly the 1,4-addition product that is but-2-ene. Under these condition the isolated double bond are not reduced. This suggest that dienes are much more reactive than simple alkenes.
What is the reactivity of the diene and the dienophile?
In this post, we will discuss the reactivity and specifics of the diene and the dienophile in the Diels-Alder reaction. First, a reminder that the Diels-Alder reaction is a type of a pericyclic reaction between a conjugated diene (two double bonds) and a dienophile (an alkene with an electron-withdrawing group).
What is the reaction for conjugated dienes?
An important reaction for conjugated dienes is the Diels–Alder reaction. Many specialized dienes have been developed to exploit this reactivity for the synthesis of natural products (e.g., Danishefsky's diene).
What are the three types of dienes?
Dienes can be divided into three classes, depending on the relative location of the double bonds: Cumulated dienes have the double bonds sharing a common atom. Conjugated dienes have conjugated double bonds separated by one single bond. Unconjugated dienes have the double bonds separated by two or more single bonds.

Are dienes more reactive?
Under these condition the isolated double bond are not reduced. This suggest that dienes are much more reactive than simple alkenes.
What makes a diene reactive?
Dienophile reactivity is increased by: (A) electron-withdrawing substituents, (B) a weak π-bond, and (C) release of ring strain.
Which dienes are most reactive?
The most reactive dienophile is the aldehyde — propenal.
Is a diene more reactive than an alkene?
The conjugated dienes are more reactive than alkenes which in turn are more reactive than alkynes towards electrophilic addition reactions- explain.
Which diene will react faster?
An example of a conjugated diene ring is 1,3-‐cyclohexadiene. Consequently, cyclic conjugated dienes react faster than their linear counterparts.
What makes dienes react faster?
The Diene. In general, Diels-Alder reactions proceed fastest with electron-donating groups on the diene (eg. alkyl groups). The Diels-Alder reaction is a single step process, so the diene component must adopt an s-cis conformation in order for the end carbon atoms (#1 & #4) to bond simultaneously to the dienophile.
Which dienes are most stable?
The result is that conjugated diene reactivity differs to that of simple alkenes. This extra bonding interaction between the adjacent π systems makes the conjugated dienes the most stable type of diene. Conjugated dienes are about 15kJ/mol or 3.6 kcal/mol more stable than simple alkenes.
Why is cyclopentadiene reactive?
Cyclopentadiene is highly reactive in Diels–Alder reactions because only minimal out-of-plane distortion is required to achieve the transition state geometry compared with that of other cyclic and acyclic dienes. Asynchronous transition states have significant out-of-plane distortion about only one double bond.
Which dienophile reacts the fastest?
The diene that would react the fastest with a dienophile is 1, while the diene that would react the slowest is 5. b. Rank by arenium ion stability. The arenium ion that is the lowest in energy (most stable) is 1, while the arenium ion that is highest in energy is 5.
Which alkene is more reactive?
A : Alkynes is more reactive than alkene towards electrophilic addition reaction.
R : Alkynes form stable carbocation than alkene. The conjugated dienes are more reactive than alkenes which in turn are more reactive than alkynes towards electrophilic addition reactions- explain.
Why are double bonds reactive?
Double bonds involving carbon are stronger and shorter than single bonds. The bond order is two. Double bonds are also electron-rich, which makes them potentially more reactive in the presence of a strong electron acceptor (as in addition reactions of the halogens).
Why conjugated dienes are more stable than alkenes?
Conjugated dienes are more stable than non conjugated dienes (both isolated and cumulated) due to factors such as delocalization of charge through resonance and hybridization energy. This stability can be seen in the differences in the energies of hydrogenation between isolated and conjugated alkenes.
Why is cyclopentadiene reactive?
Cyclopentadiene is highly reactive in Diels–Alder reactions because only minimal out-of-plane distortion is required to achieve the transition state geometry compared with that of other cyclic and acyclic dienes. Asynchronous transition states have significant out-of-plane distortion about only one double bond.
What makes a good dienophile?
Good dienophiles often bear one or two of the following substituents: CHO, COR, COOR, CN, C=C, Ph, or halogen. The diene component should be as electron-rich as possible. There are “inverse demand” Diels Alder Reactions that involve the overlap of the HOMO of the dienophile with the unoccupied MO of the diene.
What makes something a dienophile?
The dienophile has two nitriles attached to it both of which are electron withdrawing. Since the two nitriles in the dieneophile are cis to each other the the two nitriles will be cis to each other in the product.
Why is maleic anhydride a reactive dienophile?
In terms of activation, notice that maleic anhydride is a highly reactive dienophile, due to the presence of two electron- withdrawing carbonyl substituents.
What are the different types of dienes?
Dienes can be divided into three classes, depending on the relative location of the double bonds: 1 Cumulated dienes have the double bonds sharing a common atom. The result is more specifically called an allene. 2 Conjugated dienes have conjugated double bonds separated by one single bond. Conjugated dienes are more stable than other dienes because of resonance. 3 Unconjugated dienes have the double bonds separated by two or more single bonds. They are usually less stable than isomeric conjugated dienes. This can also be known as an isolated diene.
What is the result of a cumulative diene?
Cumulated dienes have the double bonds sharing a common atom. The result is more specifically called an allene.
What is an unconjugated diene?
Unconjugated dienes have the double bonds separated by two or more single bonds. They are usually less stable than isomeric conjugated dienes. This can also be known as an isolated diene.
How is butadiene prepared?
On an industrial scale, butadiene is prepared by thermal cracking of butanes. In a similarly non-selective process, dicyclopentadiene is obtained from coal tars . In the laboratory, more directed and more delicate processes are employed such as dehydrohalogenations and condensations.
How many double bonds does diene have?
In organic chemistry a diene ( / ˈdaɪ.iːn / DY-een) ( diolefin ( / daɪˈoʊləfɪn / dy-OH-lə-fin) or alkadiene) is a covalent compound that contains two double bonds, usually among carbon atoms. They thus contain two alk ene units, with the standard prefix di of systematic nomenclature. As a subunit of more complex molecules, ...
What is the name of the strained bicyclic and unconjugated diene?
E: Norbornadiene, a strained bicyclic and unconjugated diene. F: Dicyclopentadiene. According to the Gold Book definition, a "diene" could include one or more heteroatoms which replace unsaturated carbon atoms, giving structures that could more specifically be called heterodienes.
What is the reaction of alkenes?
The most heavily practiced reaction of alkenes, dienes included, is polymerization. 1,3-Butadiene is a precursor to rubber used in tires, and isoprene is the precursor to natural rubber. Chloroprene is related but it is a synthetic monomer.
What happens when a cyclic diene reacts with a mono-substituted die?
If the cyclic diene is reacted with a mono-substituted dienophile then the product contains one stereogenic center and the endo and exo products are formed as two enantiomers:
Which type of diene is locked whether it is cis or trans?
Acyclic dienes usually prefer the s- trans conformation. Cyclic dienes, on the other hand, are locked whether they are cis or trans since there is no free rotation about the sigma bond:
Why does cyclopentadiene dimerize?
For example, cyclopentadiene dimerizes because one molecule acts as the diene and the other as the dienophile. Cyclic dienes produce bridged bicyclic compounds:
Can dienes react in cis?
Let’ start with the diene. The first thing to remember here is that it can only react in the cis conformation. We are not talking about the traditional cis and trans isomerism of the alkenes. Conjugated dienes can also be in cis and trans geometry.
Is diels alder stereospecific?
First, remember that if there are two groups on the dienophile, the product will have them cis or trans exactly as they initially appear in the dienophile. This indicates that Diels-Alder is a stereospecific reaction:
Is the Diels-Alder reaction pericyclic?
First, a reminder that the Diels-Alder reaction is a type of a pericyclic reaction between a conjugated diene (two double bonds) and a dienophile (an alkene with an electron-withdrawing group).
Do electron-withdrawing groups increase reactivity?
As we just mentioned above, electron- withdrawing groups increase the reactivity of the dienophile.
What is the name of the reaction that occurs when a diene is oxidized?
Dienes exhibit unique chemistry such as the Diels-Alder reaction (specifically, a cycloaddition) between a conjugated diene and a substituted alkene, commonly termed the dienophile, to form a substituted cyclohexene system. The reaction can proceed even if some of the atoms in the newly formed ring are not carbon. Butadiene can be oxidized to form explosive peroxides. Many dienes can be induced into polymerization reactions by initiation by acids, bases, metal ions, various metal/organometallic species with the release of large amounts of energy as heat.
What are reactive groups?
Reactive groups are categories of chemicals that typically react in similar ways because they are similar in their chemical structure. Each substance with a chemical datasheet has been assigned to one or more reactive groups, and CAMEO Chemicals uses the reactive group assignments to make its reactivity predictions. More info about reactivity predictions...