
Is Gram negative or Gram positive?
‘Gram-positive’ and ‘gram-negative’ are terms used to broadly categorize two different types of bacteria. This distinction is made based on the structure of their cell walls, and their reaction to Gram staining. Gram-positive bacteria have cell walls made of a thick layer of peptidoglycan.
Are Gram positive rods a contaminant?
approximately 40% of all positive blood cultures adjudicated by infectious diseases physicians, and just over 80% of blood cultures with gram-positive rods, are contaminants. ( 10,11) the most commonly isolated gram-positive rods—corynebacterium, propionobacterium, and bacillus species—are almost always contaminants. ( 10,11) other factors, …
What does Gram positive mean?
What does it mean if you are gram-positive? Charlotte Fuller If they are positive, it indicates that bacteria were present. Gram-positive bacteria show purple under a microscope due to the staining process employed, whereas gram-negative bacteria look pink. The shape, size, and number of germs present will also reveal details about your infection.
What is Gram negative and Gram positive?
The gram-positive bacteria retain the crystal violet colour and stains purple whereas the gram-negative bacteria lose crystal violet and stain red. Thus, the two types of bacteria are distinguished by gram staining. Gram-negative bacteria are more resistant against antibodies because their cell wall is impenetrable.
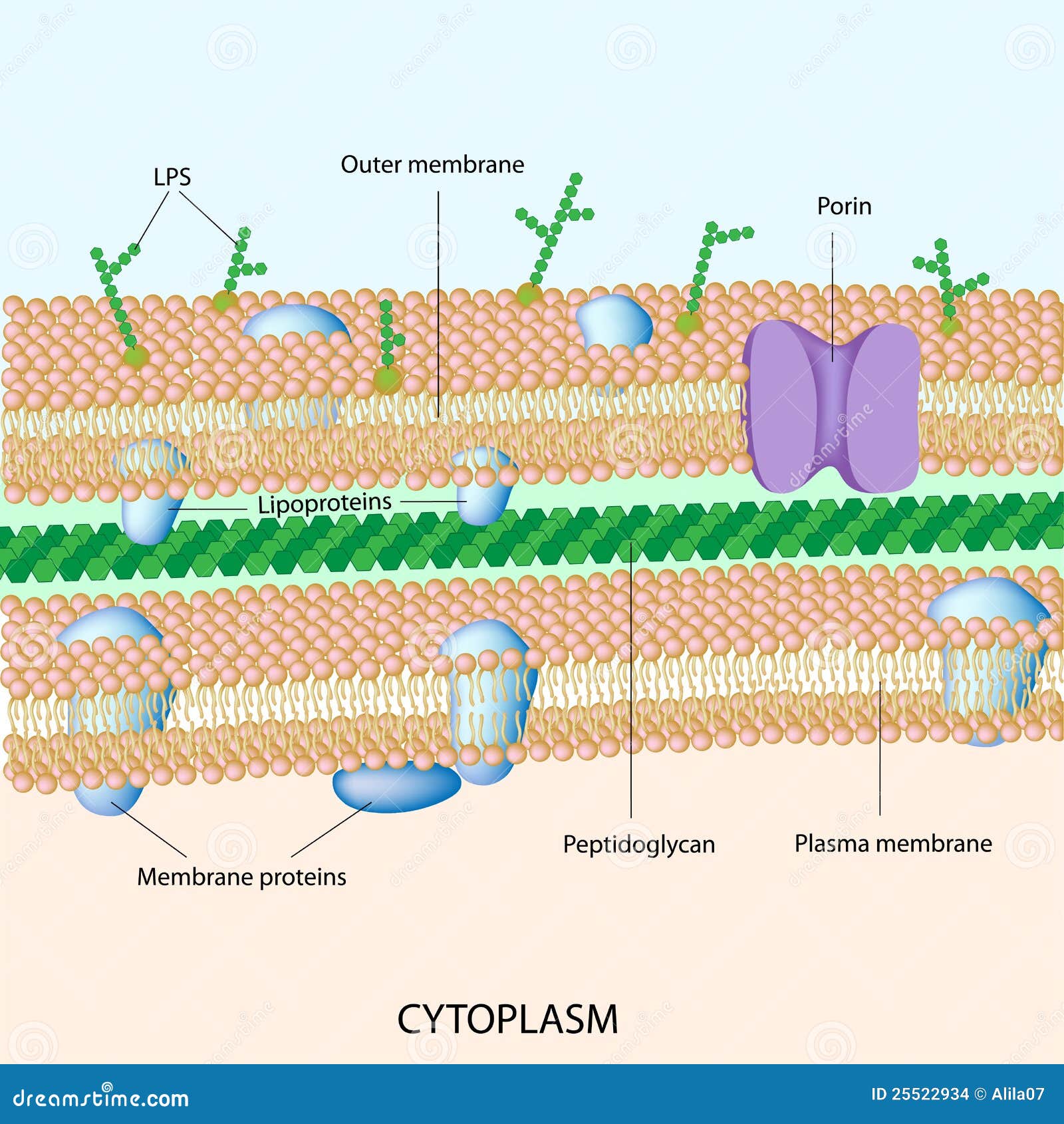
Are gram-positive bacteria harmful to humans?
Gram-positive cocci: Staphylococcus aureus is a gram-positive, catalase-positive, coagulase-positive cocci in clusters. S. aureus can cause inflammatory diseases, including skin infections, pneumonia, endocarditis, septic arthritis, osteomyelitis, and abscesses.
How serious is gram-positive bacteria?
Though gram-negative bacteria are harder to destroy, gram-positive bacteria can still cause problems. Many species result in disease and require specific antibiotics.
Which is more harmful gram-positive or Gram-negative bacteria?
The majority of the WHO list is Gram-negative bacterial pathogens. Due to their distinctive structure, Gram-negative bacteria are more resistant than Gram-positive bacteria, and cause significant morbidity and mortality worldwide.
What infections are caused by gram-positive bacteria?
They also cause different types of infections, and different types of antibiotics are effective against them. Some Gram-positive bacteria cause disease....Gram-positive bacilli cause certain infections, including the following:Anthrax. ... Diphtheria.Enterococcal infections. ... Erysipelothricosis. ... Listeriosis.
How do you get rid of gram-positive bacteria?
Abstract. Most infections due to Gram-positive organisms can be treated with quite a small number of antibiotics. Penicillin, cloxacillin, and erythromycin should be enough to cover 90 per cent of Gram-positive infections.
What are the most common gram-positive bacteria?
Among all BSI isolates, the most common Gram-positive bacterial species was Staphylococcui (65.5%), followed by Enterococcus spp. (17.5%), Streptococcus spp. (7.1%) and other bacterial pathogens (9.9%).
Which is harder to treat Gram-positive or negative?
Gram-negative bacteria are harder to kill because of their harder cell wall. When their cell wall is disturbed, gram-negative bacteria release endotoxins that can make your symptoms worse. Gram-negative bacteria can cause many serious infections, including: Cholera, a serious intestinal infection.
Is Gram-positive cocci serious?
Gram-positive infections are causing more serious infections than ever before in surgical patients, who are increasingly aged, ill, and debilitated. Invasive procedures disrupt natural barriers to bacterial invasion, and indwelling catheters may act as conduits for infection.
What is the main difference between Gram-positive and Gram-negative?
Gram positive bacteria have a thick peptidoglycan layer and no outer lipid membrane whilst Gram negative bacteria have a thin peptidoglycan layer and have an outer lipid membrane.
How do you get a gram-positive infection?
Most gram-positive infections are caused by normal resident microflora of the skin, mucous membranes, and gastrointestinal tract. Critically ill hospitalized patients are at increased risk for infections with opportunistic gram-positive bacteria.
What is meant by gram-positive bacteria?
In bacteriology, gram-positive bacteria are bacteria that give a positive result in the Gram stain test, which is traditionally used to quickly classify bacteria into two broad categories according to their type of cell wall.
Do gram-positive bacteria cause UTI?
Gram-positive bacteria are a common cause of urinary tract infection (UTI), particularly among individuals who are elderly, pregnant, or who have other risk factors for UTI.
What does mixed Gram-positive flora in urine mean?
Because “mixed flora”* implies that at least 2 organisms are present in addition to the identified organism, the urine culture does not meet the criteria for a positive urine culture with 2 organisms or less. Such a urine culture cannot be used to meet the NHSN UTI criteria.
What does a Gram stain test for?
A Gram stain is a test used to help identify bacteria. The tested sample can be taken from body fluids that do not normally contain bacteria, such as blood, urine, or cerebrospinal fluid. A sample can also be taken from the site of a suspected infection, such as the throat, lungs, genitals, or skin.
What is a normal Gram stain?
A Gram stain is a laboratory test that checks for bacteria at the site of a suspected infection or in certain bodily fluids. A medical laboratory scientist processes the Gram stain, which gives relatively quick results, so healthcare providers can know if bacteria are present, and, if so, the general type(s).
What is Gram positive?
Gram-positive bacteria are bacteria classified by the color they turn in the staining method. Hans Christian Gram developed the staining method in 1884. The staining method uses crystal violet dye, which is retained by the thick peptidoglycan cell wall found in gram-positive organisms. This reaction gives gram-positive organisms a blue color ...
How to differentiate Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria?
Health professionals need to understand the important difference between gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Gram-positive bacteria are bacteria classified by the color they turn in the staining method. Hans Christian Gram developed the staining method in 1884. The staining method uses crystal violet dye, which is retained by the thick peptidoglycan cell wall found in gram-positive organisms. This reaction gives gram-positive organisms a blue color when viewed under a microscope. Although gram-negative organisms classically have an outer membrane, they have a thinner peptidoglycan layer, which does not hold the blue dye used in the initial dying process. Other information used to differentiate bacteria is the shape. Gram-positive bacteria comprise cocci, bacilli, or branching filaments.
When was the Gram staining method invented?
Hans Christian Gram developed the staining method in 1884. The staining method uses crystal violet dye, which is retained by the thick peptidoglycan cell wall found in gram-positive organisms. This reaction gives gram-positive organisms a blue color when viewed under a microscope.
What are the different groups of streptococcus bacteria?
Streptococcus bacteria subdivide into Strep. pyogenes (Group A), Strep. agalactiae (Group B), enterococci (Group D), Strep viridans, and Strep pneumonia. Gram-positive bacilli (rods) subdivide according to their ability to produce spores.
What is a gram positive spore-forming rod?
Clostridia is a gram-positive spore-forming rod consisting of C. tetani, C. botulinum, C. perfringens, and C. difficile. C. difficileis often secondary to antibiotic use (clindamycin/ampicillin), PPI use, and recent hospitalization. Treatment involves primarily with oral vancomycin.
Which cell wall is thicker, Gram positive or Gram negative?
Gram-positive organisms have a thicker peptidoglycan cell wall compared with gram-negative bacteria. It is a 20 to 80 nm thick polymer while the peptidoglycan layer of the gram-negative cell wall is 2 to 3 nm thick and covered with an outer lipid bilayer membrane.
Do Gram positive bacteria have blue dye?
Although gram-negative organisms classically have an outer membrane, they have a thinner peptidoglycan layer, which does not hold the blue dye used in the initial dying process. Other information used to differentiate bacteria is the shape. Gram-positive bacteria comprise cocci, bacilli, or branching filaments. NCBI.
What are the characteristics of Gram positive bacteria?
In general, the following characteristics are present in gram-positive bacteria: 1 Cytoplasmic lipid membrane 2 Thick peptidoglycan layer 3 Teichoic acids and lipoids are present, forming lipoteichoic acids, which serve as chelating agents, and also for certain types of adherence. 4 Peptidoglycan chains are cross-linked to form rigid cell walls by a bacterial enzyme DD-transpeptidase. 5 A much smaller volume of periplasm than that in gram-negative bacteria.
Why are Gram positive bacteria more receptive to antibiotics than Gram negative bacteria?
Despite their thicker peptidoglycan layer, gram-positive bacteria are more receptive to certain cell wall targeting antibiotics than gram-negative bacteria, due to the absence of the outer membrane.
Why are mycoplasmas gram negative?
A number of other bacteria—that are bounded by a single membrane, but stain gram-negative due to either lack of the peptidoglycan layer, as in the Mycoplasmas , or their inability to retain the Gram stain because of their cell wall composition —also show close relationship to the Gram-positive bacteria. For the bacterial cells bounded by ...
Why do Gram positive bacteria have purple stains?
This is because the thick peptidoglycan layer in the bacterial cell wall retains the stain after it is washed away from the rest of the sample, in the decolorization stage of the test.
What is Gram staining?
Along with cell shape, Gram staining is a rapid method used to differentiate bacterial species. Such staining, together with growth requirement and antibiotic susceptibility testing, and other macroscopic and physiologic tests, forms the full basis for classification and subdivision of the bacteria (e.g., see figure and pre-1990 versions of Bergey's Manual ).
How many basal body rings does a Gram positive have?
Also, only some species are flagellates, and when they do have flagella, have only two basal body rings to support them, whereas gram-negative have four. Both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria commonly have a surface layer called an S-layer. In gram-positive bacteria, the S-layer is attached to the peptidoglycan layer.
What is a gram positive cocci?
Violet-stained gram-positive cocci and pink-stained gram-negative bacilli. In bacteriology, gram-positive bacteria are bacteria that give a positive result in the Gram stain test, which is traditionally used to quickly classify bacteria into two broad categories according to their type of cell wall . Gram-positive bacteria take up the crystal ...
What is the color of gram positive bacteria?
Overview of Gram-Positive Bacteria. Gram-positive bacteria are classified by the color they turn after a chemical called Gram stain is applied to them. Gram-positive bacteria stain blue when this stain is applied to them. Other bacteria stain red. They are called gram-negative.
What are some examples of Gram positive cocci?
For example, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) bacteria are resistant to most antibiotics that are related to penicillin. Methicillin is a type of penicillin.
What is the cause of enterococcal infection?
Enterococcal Infections Enterococcal infections are caused by a group of gram-positive bacteria called enterococci, which normally reside in the intestine of healthy people but sometimes cause infection. (See also... read more
What is the name of the gram positive bacteria that causes erysipelothrix rhus?
Erysipelothricosis Erysipelothricosis is a skin infection caused by the gram-positive bacteria Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae. People are infected when they have a puncture wound or scrape while they are handling... read more
What are the three basic shapes of bacteria?
All bacteria may be classified as one of three basic shapes: spheres (cocci), rods (bacilli), and spirals or helixes ( spirochetes ). Gram-positive bacteria may be cocci or bacilli. (See figure How Bacteria Shape Up .) Some Gram-positive bacteria cause disease. Others normally occupy a particular site in the body, such as the skin.
What is the bodywide response to bacteremia?
Sepsis is a serious bodywide response to bacteremia or other type of infection plus malfunction or failure of an essential system in the body. Which of the following is always one of the body’s responses to sepsis ?
Why do bacteria stain red?
Other bacteria stain red. They are called gram-negative. Gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria stain differently because their cell walls are different. They also cause different types of infections, and different types of antibiotics are effective against them. All bacteria may be classified as one of three basic shapes: spheres (cocci), ...
Why is it important to know if a bacteria is Gram positive or negative?
This is because Gram positive bacteria react differently to the environment than Gram negative ones, and it all comes down to that peptidoglycan outer layer.
Why is Gram positive important?
As a classification, Gram positive is useful because it’s one of the two categories that all known bacteria fit into. It should come as no surprise that the other category is known as Gram negative. So it’s clear that if your bacteria isn’t one, it’s the other, but what exactly does it mean to have a Gram positive bacteria?
What is Gram negative?
Gram developed a dye that reacted with peptidoglycan, staining it purple whenever it was present and making it stand out when viewed under a microscope. Bacteria without the layer tested negative by not absorbing the stain, thus prompting the terms “Gram positive” and “Gram negative”.
Which is more susceptible to being killed by antibiotics and sanitizing agents?
While Gram positive bacteria have that thick outer layer, this ironically makes them more susceptible to being killed by antibiotics and sanitizing agents. Peptidoglycan is highly absorbent, making it easier for antimicrobial agents to take care of it. Gram negative bacteria, meanwhile, might have a thinner cell wall, but these bacteria are much less absorbent.
What is the difference between a Gram positive and a Gram negative?
The differences between Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria are primarily related to their cell wall composition. Gram positive bacteria have cell walls composed mostly of a substance unique to bacteria known as peptidoglycan, or murein. These bacteria stain purple after Gram staining.
Why do Gram positive bacteria have thick layers?
The thick layers also enable Gram positive bacteria to retain most of the crystal violet dye during Gram staining causing them to appear purple.
What are some examples of Gram positive cocci that colonize the skin?
Examples of Gram positive cocci that colonize the skin include Staphylococcus epidermidis, Staphylococcus aureus, and Streptococcus pyogenes . Staphylococcus aureus is a Gram-positive coccus (round) bacteria that is found on the skin and mucous membranes of humans and many animals.
What is the role of teichoic acid in bacteria?
Teichoic acid helps some Gram positive bacteria to infect cells and cause disease. Some Gram positive bacteria have an additional component, mycolic acid, in their cell walls.
Why are mycolic acid and gram positive bacteria called acid fast bacteria?
Gram positive bacteria with mycolic acid are also called acid-fast bacteria because they require a special staining method, known as acid-fast staining, for microscope observation. Pathogenic Gram positive bacteria cause disease by the secretion of toxic proteins known as exotoxins.
What is the acid in a Gram positive cell?
Some Gram positive bacteria have an additional component, mycolic acid, in their cell walls. Mycolic acids produce a waxy outer layer that provides additional protection for mycobacteria, such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Gram positive bacteria with mycolic acid are also called acid-fast bacteria because they require a special staining method, known as acid-fast staining, for microscope observation.
What are the cell walls of Gram positive bacteria?
The cell walls of Gram positive bacteria differ structurally from the cell walls of Gram negative bacteria. The primary component of bacterial cell walls is peptidoglycan. Peptidoglycan is a macromolecule composed of sugars and amino acids that are assembled structurally like woven material. The amino sugar component consists of alternating molecules of N-acetylglucosamine (NAG) and N-acetylmuramic acid (NAM). These molecules are crosslinked together by short peptides which help give peptidoglycan strength and structure. Peptidoglycan provides protection for bacteria and defines their shape.
What is Gram positive bacteria?
Gram-positive bacteria are bacteria classified by the color they turn in the staining method.
What is Gram positive and Gram negative?
Health professionals need to understand the important difference between gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Gram-positive bacteria are bacteria classified by the color they turn in the staining method. Hans Christian Gram developed the staining method in 1884.
What is the difference between gram positive and gram negative bacteria?
Although gram-negative organisms classically have an outer membrane, they have a thinner peptidoglycan layer, which does not hold the blue dye used in the initial dying process. Other information used to differentiate bacteria is the shape. Gram-positive bacteria comprise cocci, bacilli, or branching filaments.
What is Gram positive?
Gram-positive bacteria are bacteria classified by the color they turn in the staining method. Hans Christian Gram developed the staining method in 1884. The staining method uses crystal violet dye, which is retained by the thick peptidoglycan cell wall found in gram-positive organisms. This reaction gives gram-positive organisms a blue color ...
Which bacteria colonizes the mucosal lining of the human stomach?
Presence: H. pylori colonize s the mucosal lining of the human stomach.
Who said bacteria are the first half of geological time?
Most creatures still are bacteria, and each one of our trillions of cells is a colony of bacteria. – Richard Dawkins.
What is the role of B. longum in the intestine?
This inhibits the growth of pathogenic bacteria by controlling pH levels in the intestines. B. longum helps in the breakdown of non-digestible plant polymers. B. longum and B. infantis help prevent diarrhea, candidiasis, and other yeast infections in infants and children.
What is the benefit of B. longum?
This inhibits the growth of pathogenic bacteria by controlling pH levels in the intestines. B. longum helps in the breakdown of non-digestible plant polymers . B. longum and B. infantis help prevent diarrhea, candidiasis, and other yeast infections in infants and children. Owing to these benefits, this particular species are also included in commercially available probiotics.
Where are bifidobacteria found?
Presence: Bifidobacteria are present in the gastrointestinal tract of humans. Benefit: Similar to lactobacilli these are also known for lactic acid production. In addition, it also produces acetic acid. This inhibits the growth of pathogenic bacteria by controlling pH levels in the intestines.
Which pathogens have long doubling times?
Disease: The bacteria under the genus Mycobacterium are pathogens with long doubling times. M. tuberculosis and M. leprae, the most notorious species, are the causative agents for tuberculosis and leprosy, respectively. M. ulcerans causes ulcerated and non-ulcerated nodules in the skin. M. bovis causes tuberculosis in cattle.
Is a bacteria free living?
They are either free-living or form a symbiotic relationship with animals or plants. The list of helpful and harmful bacteria contain some of the most commonly known beneficial and deadly bacteria.
Overview
Pathogenicity
In the classical sense, six gram-positive genera are typically pathogenic in humans. Two of these, Streptococcus and Staphylococcus, are cocci (sphere-shaped). The remaining organisms are bacilli (rod-shaped) and can be subdivided based on their ability to form spores. The non-spore formers are Corynebacterium and Listeria (a coccobacillus), whereas Bacillus and Clostridium produce …
Characteristics
In general, the following characteristics are present in gram-positive bacteria:
1. Cytoplasmic lipid membrane
2. Thick peptidoglycan layer
3. Teichoic acids and lipoids are present, forming lipoteichoic acids, which serve as chelating agents, and also for certain types of adherence.
Classification
Along with cell shape, Gram staining is a rapid method used to differentiate bacterial species. Such staining, together with growth requirement and antibiotic susceptibility testing, and other macroscopic and physiologic tests, forms the full basis for classification and subdivision of the bacteria (e.g., see figure and pre-1990 versions of Bergey's Manual).
Importance of the outer cell membrane in bacterial classification
Although bacteria are traditionally divided into two main groups, gram-positive and gram-negative, based on their Gram stain retention property, this classification system is ambiguous as it refers to three distinct aspects (staining result, envelope organization, taxonomic group), which do not necessarily coalesce for some bacterial species. The gram-positive and gram-…
Bacterial transformation
Transformation is one of three processes for horizontal gene transfer, in which exogenous genetic material passes from a donor bacterium to a recipient bacterium, the other two processes being conjugation (transfer of genetic material between two bacterial cells in direct contact) and transduction (injection of donor bacterial DNA by a bacteriophage virus into a recipient host bacterium). In transformation, the genetic material passes through the intervening medium, and …
Orthographic note
The adjectives Gram-positive and Gram-negative derive from the surname of Hans Christian Gram; as eponymous adjectives, their initial letter can be either capital G or lower-case g, depending on which style guide (e.g., that of the CDC), if any, governs the document being written. This is further explained at Gram staining § Orthographic note.
External links
• This article incorporates public domain material from the NCBI document: "Science Primer".
• 3D structures of proteins associated with plasma membrane of gram-positive bacteria
• 3D structures of proteins associated with outer membrane of gram-positive bacteria