Does a hemangioma go away on its own?
The hemangioma then enters a rest phase and, eventually, it begins to slowly disappear. About half of all hemangiomas resolve by age 5, and nearly all hemangiomas are resolved by age 10. Although the color of the birthmark also fades, faint — but permanent — discoloration of the skin or residual extra skin may remain.
What is the difference between an angioma and a hemangioma?
Angiomas are benign growths made of blood vessels or lymphatic vessels, whereas hemangiomas are small growths made of blood vessels only. Cherry angiomas are most commonly associated with adults. Hemangiomas can appear in early infancy through childhood. How common are cherry angiomas?
Can a hemangioma grow on a 10 year old?
Hemangioma. A hemangioma grows during the first year of life, and then recedes over time. A child who had a hemangioma during infancy usually has little visible trace of the growth by age 10. A hemangioma can occur anywhere on the body, but most commonly appears on the face, scalp, chest or back.
How common are hemangiomas in the US?
Hemangiomas most often appear in adults between the ages of 30 and 50. They are very common and occur in approximately 10 percent of the world’s population. Most cases show no symptoms. Symptomatic hemangiomas represent less than one percent of all hemangiomas, and are more common in women than in men.
What is a hemangioma?
Where do hemangiomas form?
How do hemangiomas develop?
How to tell if you have hemangioma?
What is the first line of defense for hemangiomas?
What is the best treatment for hemangiomas?
Why do you inject corticosteroids into hemangioma?
See 4 more
About this website

Can hemangiomas last forever?
Congenital hemangiomas either go away over the first few months of life (RICH, or rapidly involuting congenital hemangiomas) or remain unchanged forever (NICH, or noninvoluting congenital hemangiomas).
Should I get my hemangioma removed?
Most infantile hemangiomas do not need to be treated with surgery. Surgery is less common now than in years past because of the medicines available now that are safe and effective. Hemangiomas that have noticeable scar tissue left after shrinking may need surgery.
When should I be worried about a hemangioma?
Contact your child's doctor if the hemangioma bleeds, forms a sore or looks infected. Seek medical care if the condition interferes with your child's vision, breathing, hearing or elimination.
What happens if hemangioma is left untreated?
Hemangiomas look painful, but they don't typically cause any discomfort. After a brief period of rapid growth, they often shrink on their own without treatment. They're noncancerous and complications are very rare.
Why do people get hemangiomas?
What causes hemangiomas? Hemangiomas are caused by blood vessels that don't form properly. The direct cause is unknown. In children, hemangiomas are caused by blood vessels that don't develop correctly during pregnancy.
Can hemangioma become cancerous?
Because hemangiomas very rarely become cancerous, most do not require any medical treatment. However, some hemangiomas can be disfiguring, and many people seek a doctor's care for cosmetic reasons. In most cases of hemangioma, treatment does not involve surgery.
What does a cancerous hemangioma look like?
Symptoms of a hemangioma are: A red to reddish-purple, raised growth on the skin. A massive, raised, bluish tumor with visible blood vessels.
What are the two types of hemangiomas?
The two main types of infantile hemangiomas are:Superficial hemangiomas, or cutaneous ("in-the-skin") hemangiomas, grow on the skin surface. ... Deep hemangiomas grow under the skin, making it bulge, often with a blue or purple tint.
Is a hemangioma a birth defect?
The most common birth defect, affecting about 2 percent of all newborns, hemangiomas are benign, blood vessel tumors that can appear anywhere on a child's body, at or shortly after birth, occurring more often in females than males.
What happens if you pop a hemangioma?
If a hemangioma is cut or injured, it can bleed or develop a crust or scab. The blood vessels that make up hemangiomas are not normal. When hemangiomas bleed, they tend to bleed rapidly, but only for a short time. You should be able to stop the bleeding by applying gentle, direct pressure to the wound for 15 minutes.
Is hemangioma genetic?
Hemangiomas and vascular malformations usually occur by chance. However, they can also be inherited in a family as an autosomal dominant trait. Autosomal dominant means that one gene is necessary to express the condition, and the gene is passed from parent to child with a 50/50 risk for each pregnancy.
What is the most common treatment for hemangiomas?
Since 2008, beta-blocker medications have become the most commonly used treatment for hemangiomas. Oral propranolol is an FDA-approved medication for treating hemangiomas in infants who are 5 weeks of age or older. The medication is usually given twice a day for at least six months.
How much does it cost to remove a hemangioma?
There can be some crusting or darkening of the hemangioma for up to 5-7 days afterwards. Most patients need 1-2 treatments and cost depends on the number of lesions and complexity of the hemangioma but can range from $150 to $550.
Do hemangiomas go away in adults?
Because they're so common with aging, they're also called senile angiomas. Cherry angiomas don't go away. In fact, you'll probably get more of them as you age. If their appearance bothers you, a dermatologist (skin specialist) can remove them.
Will a hemangioma come back?
Segmental hemangiomas can grow for up to 2 years. Any treatment, whether it be steroids, propranolol or surgery, done before the end of this period can result in regrowth but is least likely with surgery.
When do hemangiomas start to fade?
About 80 percent of hemangiomas stop growing by about 5 months, Dr. Antaya says. After hitting this plateau phase, they stay unchanged for several months, and then begin to slowly disappear over time (called involution). By the time children reach 10 years of age, hemangiomas are usually gone.
Hemangioma of the Skin: Causes, Identification, and Diagnosis - Healthline
Hemangiomas of the skin are generally deep red or blue-purple. They appear as raised lesions or tumors on the skin. The deeper the hemangioma, the darker it’s color.
What Is a Liver Hemangioma? - WebMD
A liver hemangioma is a benign tumor in your liver. It’s made up of a tangle of blood vessels and is rarely serious and doesn’t turn into liver cancer.
Liver Hemangioma: What it Is, Causes, Symptoms & Treatment
Overview What is a liver hemangioma? A liver hemangioma (hepatic hemangioma) is a noncancerous tumor in your liver.It’s made up of clumped, malformed blood vessels that are fed by the hepatic artery. Hemangioma tumors can occur in various organs, including the brain, where they can sometimes cause problems.In the liver, though, they rarely do.
Where does hemangioma appear?
A hemangioma can occur anywhere on the body, but most commonly appears on the face, scalp, chest or back. Treatment for a baby's hemangioma (infantile hemangioma) usually isn't needed as it fades over time.
How do you know if you have hemangioma?
It starts as a flat red mark anywhere on the body, most often on the face, scalp, chest or back. Usually a child has only one mark.
What is a birthmark that consists of an abnormally dense group of blood vessels?
Close. Hemangioma. Hemangioma. An infantile hemangioma is a birthmark that consists of an abnormally dense group of blood vessels. The hemangioma appears on the surface of the skin as a spongy mass. A hemangioma (he-man-jee-O-muh) is a bright red birthmark that shows up at birth or in the first or second week of life.
What to do if your child has hemangioma?
Your child's doctor will monitor the hemangioma during routine checkups. Contact your child's doctor if the hemangioma bleeds, forms a sore or looks infected. Seek medical care if the condition interferes with your child's vision, breathing, hearing or elimination.
Can hemangioma cause bleeding?
Occasionally, a hemangioma can break down and develop a sore. This can lead to pain, bleeding, scarring or infection. Depending on where the hemangioma is situated, it may interfere with your child's vision, breathing, hearing or elimination, but this is rare.
How to remove hemangioma?
Laser surgery can remove a large hemangioma of the skin that’s uncomfortable or is causing problems. Laser treatments can also reduce remaining discoloration after a hemangioma has healed. Your healthcare provider may also prescribe topical timolol maleate to treat thin or superficial hemangiomas.
What is hemangioma of the skin?
Complications. Outlook. What is a hemangioma of the skin? A hemangioma of the skin is an abnormal buildup of blood vessels on or under the surface of the skin. A hemangioma of the skin may look like a red-wine or strawberry-colored plaque, and it may protrude from the skin. Infantile hemangiomas are a specific type ...
What are the symptoms of hemangioma?
What are the symptoms of a hemangioma of the skin? Hemangiomas of the skin are generally deep red or blue-purple. They appear as raised lesions or tumors on the skin. The deeper the hemangioma, the darker it’s color. Growths on the skin’s surface (strawberry, capillary, or superficial hemangiomas) are usually deep red.
How to diagnose hemangioma of the skin?
How is a hemangioma of the skin diagnosed? A healthcare provider can diagnose a hemangioma of the skin just by looking at it. No other testing is usually necessary. Your healthcare provider may order blood tests or a skin biopsy if a growth appears to be abnormal or other sores are present.
How long does it take for hemangiomas to grow?
Hemangiomas in infants tend to grow rapidly for the following 4 to 6 months. After this period of growth, hemangiomas enter a resting phase.
Where do infantile hemangiomas appear?
Infantile hemangiomas are a specific type of hemangioma that appear most frequently on the trunk of the body, but they can also appear on the face or neck. They generally develop soon after birth and can affect both boys and girls. Hemangiomas can occur on the top layer of the skin or deeper in the body. Treatment depends on a multitude of factors ...
Where do hemangiomas occur?
Hemangiomas can occur on the top layer of the skin or deeper in the body. Treatment depends on a multitude of factors including: Hemangiomas look painful, but they don’t typically cause any discomfort. After a brief period of rapid growth, they often shrink on their own without treatment.
How long does a hemangioma last?
Hemangiomas can grow for up to 18 months and then begin a long slow regression known as involution. This involution can last from 3- 10 years. While all hemangiomas eventually ‘involute” the result is not always cosmetically acceptable. Early intervention has been shown to reduce the need for corrective surgery after “involution” has occurred; or to, at least, minimize extensive corrective surgeries in the future. Psycho-social scarring which occurs when a child has been forced to live with a facial deformity until “involution” has been completed can be avoided by early, aggressive intervention.
When do hemangiomas grow?
The most rapid and significant growth occurs between 1 and 3 months of age and that growth is completed by 5 months of age in most cases. Because many Infantile Hemangiomas leave behind permanent skin changes, there is a window of opportunity to treat higher-risk infantile hemangiomas and optimize outcomes.
How many babies have hemangioma?
Hemangiomas occur in up to 12 percent of all infants by one year of age. They occur 5 times more often in females than in males and predominantly in Caucasians. Twenty-three percent of babies born with hemangioma are very low birthweight (2.2 pounds or less). Low birthweight infants (less than 2.2 pounds) have a twenty six percent chance ...
What is the chance of developing a hemangioma in a low birthweight child?
Low birthweight infants (less than 2.2 pounds) have a twenty six percent chance of developing a hemangioma. The reason for the high incidence of vascular lesions in low birthweight children is unknown. Hemangioma are the most common benign tumor in infants.
What is a benign tumor?
A hemangioma is a benign, blood-filled tumor. Fourteen in 100 children are born with a vascular birthmark; most are hemangiomas. Ten percent of these children require the opinion of a specialist while the others have insignificant hemangiomas or lesions which are small and located in an area covered by clothing.
How are hemangioma and vascular malformations different?
Hemangioma and vascular malformations are vastly different from each other; they have different outcomes, and they are treated differently. To assure the best outcome in treating any congenital lesion (birthmark) the doctor has to first be sure what it is. Early and accurate diagnosis leads to the correct treatment.
How long does it take for a baby to get hemangioma?
What is a typical treatment protocol? Hemangioma at 10 weeks and at one year, after treatment with propranolol. Early intervention and/or referral (ideally by 1 month of age) is recommended for infants who have potentially problematic Infantile Hemangiomas.
When do hemangiomas grow?
Most infantile hemangiomas show some mark or colored patch on the skin at birth or within a few weeks after birth. During a baby’s first five months, an infantile hemangioma will grow quickly. This time is called the proliferative phase or growth phase.
What is it called when you have a deep hemangioma?
Some are deep under the skin and look either blue or skin-colored; these are called deep infantile hemangiomas. When a deep and a superficial part are present, they are called mixed infantile hemangiomas. An illustration of the vessel grouping that causes infantile hemangioma. © Eleanor Bailey.
What are the types of infantile hemangioma?
Most hemangiomas appear on the skin surface and are bright red. These are called superficial infantile hemangiomas and are sometimes called “strawberry birthmarks.”
How are infantile hemangiomas diagnosed?
Doctors can diagnose most hemangiomas by doing an exam and asking about the pregnancy and the baby’s health. Hemangiomas that are deep under the skin can sometimes be harder to diagnose. As the hemangioma grows during the proliferative phase (from birth to 1 year old), diagnosis will be easier.
What is the best medicine for hemangioma?
Most hemangiomas that need medical treatment are treated with medicines called beta blockers. Propranolol is a beta blocker (part of a class of drugs used to manage problems in the heart) that is approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration to treat infantile hemangioma.
When do infantile hemangiomas appear?
These blood vessels receive signals to grow rapidly early in a baby’s life. Most infantile hemangioma will appear at birth or within the first few weeks after birth. Most infantile hemangiomas show some mark or colored patch on ...
Do you need a special test for hemangioma?
As the hemangioma grows during the proliferative phase (from birth to 1 year old), diagnosis will be easier. Most hemangiomas do not need any special tests. If a doctor thinks your child has an infantile hemangioma, he or she may use ultrasound to see more detail under the skin.
Where do hemangiomas occur?
Spinal Hemangioma. Spinal hemangiomas are the most common primary tumor of the spine. These mostly occur in the mid-back and lower-back.
How to treat hemangioma pain?
Radiation therapy is effective in the treatment of pain caused by hemangiomas. Ethanol injections with fluoroscopic guidance have also proven effective in treating pain. Another treatment option is embolization followed by removal of the small bones that make up a vertebra ( laminectomy) or removal of the vertebra (vertebrectomy).
How does UPMC treat hemangiomas?
At UPMC, we treat hemangiomas with surgical removal (resection) of the tumor or the affected vertebra, and radiation therapy to treat pain. Ethanol injections and laminectomy may also be performed.
How do you know if you have a hemangioma?
Hemangioma symptoms. Most hemangiomas are symptom-free, but symptoms may include: Back pain. Pain that radiates along a nerve due to inflammation or irritation of the nerve root. Spinal cord compression. Treatment. Hemangioma Treatment. Treatment for hemangiomas depends on the size and location of the tumor.
What is a hemangioma in the back?
Spinal hemangiomas are benign tumors that are most commonly seen in the mid-back (thoracic) and lower back (lumbar). Hemangiomas most often appear in adults between the ages of 30 and 50. They are very common and occur in approximately 10 percent of the world’s population. Most cases show no symptoms. Symptomatic hemangiomas represent less than one percent of all hemangiomas, and are more common in women than in men. If left untreated, symptomatic hemangiomas can cause serious neurological effects.
Can hemangiomas cause neurological problems?
Most cases show no symptoms. Symptomatic hemangiomas represent less than one percent of all hemangiomas, and are more common in women than in men. If left untreated, symptomatic hemangiomas can cause serious neurological effects.
How long does it take for hemangiomas to stop growing?
About 80 percent of hemangiomas stop growing by about 5 months, Dr. Antaya says. After hitting this plateau phase, they stay unchanged for several months, and then begin to slowly disappear over time (called involution). By the time children reach 10 years of age, hemangiomas are usually gone.
What is the color of a hemangioma?
Hemangiomas lacking the bright red color and/or with a purplish or bluish hue probably originate deeper below the skin. While most diagnoses can be made in the doctor’s office, some hemangiomas in deeper tissues require further evaluation through ultrasound with Doppler or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
What does an infantile hemangioma look like?
Hemangiomas usually appear as bright red bumps or patches or bluish lumps anywhere on the surface of the skin, says Yale Medicine pediatric dermatologist Richard J. Antaya, MD. These growths tend to grow quickly and go away very slowly.
What causes infant hemangioma?
Unfortunately, many parents blame themselves for their infant’s hemangioma, but the truth is there are no known links between the condition and maternal diet, genetics, environmental factors, or parental behavior. The cause of these birthmarks is unknown.
How is infantile hemangioma diagnosed?
Usually a doctor needs only to see the skin marks to diagnose infantile hemangioma. The condition has a fairly straightforward appearance and pattern of growth and coloration with hemangiomas near the surface of the skin evolving from red little patches to bright red papules or bumps. Hemangiomas lacking the bright red color and/or with a purplish or bluish hue probably originate deeper below the skin.
What are the risks for babies with hemangiomas of the skin?
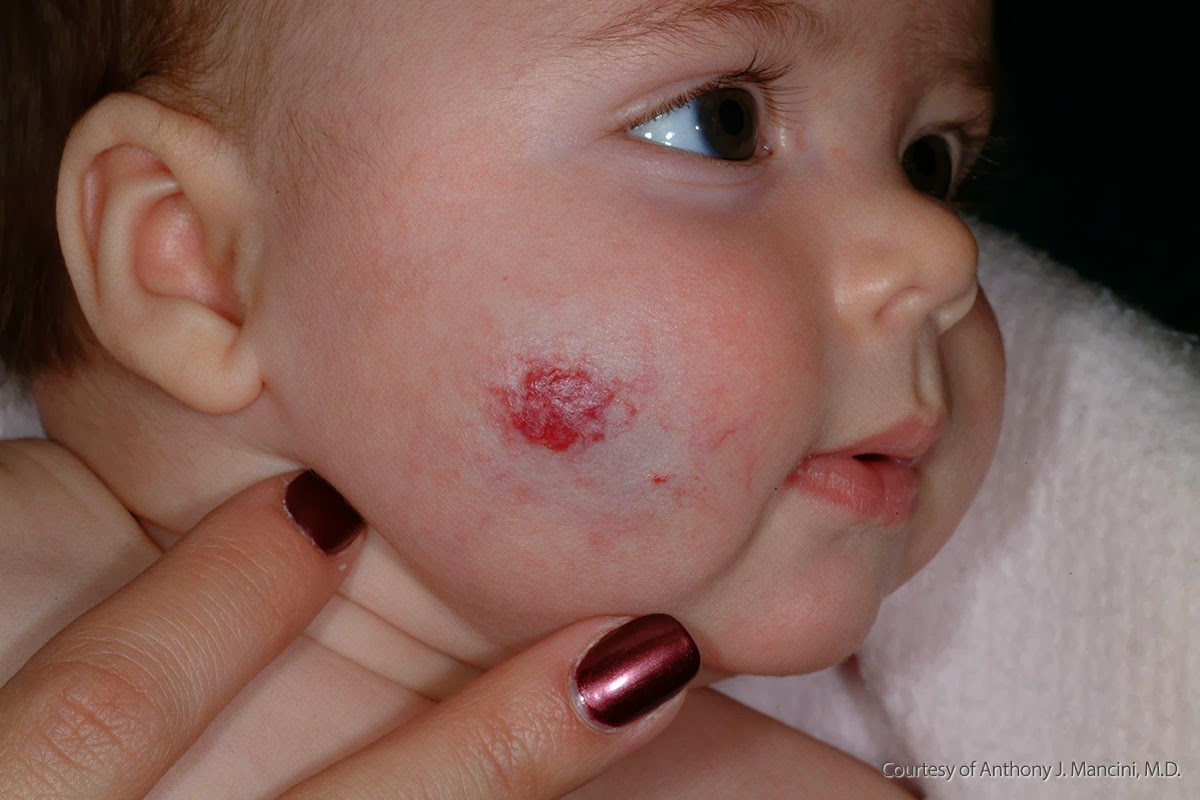
Most of the time, hemangiomas are harmless. But in about some cases, the growths will ulcerate or form sores, which can be extremely painful for babies. Ulcerations can appear anywhere, but high-risk sites include the lips, the neck, the diaper area, the lower back, and folds such as the armpit. Hemangiomas in the diaper area have about a higher of developing an ulcer.
What makes Yale Medicine’s approach to treating infantile hemangiomas unique?
We offer inpatient and outpatient treatment, including laser treatments in the office to surgeries performed under general anesthesia at our pediatric surgical center. The doctors take the time to explain every part of the process to parents.
What is a hemangioma?
Hemangiomas, or infantile hemangiomas, are noncancerous growths of blood vessels. They’re the most common growths or tumors in children. They usually grow for a period of time and then subside without treatment.
Where do hemangiomas form?
Hemangiomas of the liver (hepatic hemangiomas) form in and on the liver’s surface. These can be related to infantile hemangiomas, or they can be unrelated. The non-infantile hemangiomas of the liver are thought to be sensitive to estrogen.
How do hemangiomas develop?
Hemangiomas of the skin develop when there’s an abnormal proliferation of blood vessels in one area of the body.
How to tell if you have hemangioma?
Hemangiomas inside the body present with symptoms specific to the organ that’s affected. For example, a hemangioma affecting the gastrointestinal tract or liver may present with symptoms such as: 1 nausea 2 vomiting 3 abdominal discomfort 4 loss of appetite 5 a feeling of fullness in the abdomen
What is the first line of defense for hemangiomas?
Oral propranolol: Oral propranolol is the first line of defense for hemangiomas needing systemic treatments. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved hemangeol (oral propranolol hydrochloride) in 2014.
What is the best treatment for hemangiomas?
Topical beta-blockers, such as timolol gel: These beta-blockers can be used for small, superficial hemangiomas. They may also have a role in treating smaller ulcerated hemangiomas. This medication is generally considered safe when used properly under the care of a healthcare provider.
Why do you inject corticosteroids into hemangioma?
Corticosteroids may be injected into a hemangioma to reduce its growth and to stop inflammation.
