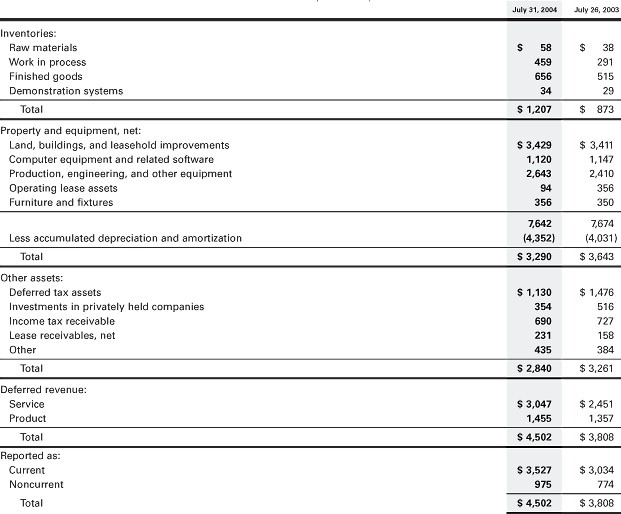
A due from account is an asset account in the general ledger
Ledger
A ledger is the principal book or computer file for recording and totaling economic transactions measured in terms of a monetary unit of account by account type, with debits and credits in separate columns and a beginning monetary balance and ending monetary balance for each a…
Full Answer
Are intercompany accounts assets or liabilities?
What is the correct why to set up Intercompany accounts between separate Companies, are they asset accounts? The inter-co balances may be debit or credits depending on who owes. If you know in advance that one co will always be borrowing and another will be lending, then set them us as liabilities & assets respectively.
How to balance intercompany accounts?
- " Final Rules Govern U.S. Country-by-Country Reporting ," JofA, June 30, 2016
- " Profit Shifting: Effectively Connected Income and Financial Statement Risks ," JofA, Feb. 2016
- " Temporary Regs. Under Sec. ...
- " Don't Let Foreign Currency Fluctuations Impair Performance Measurements ," JofA, Dec. 2015
What are intercompany payables?
Types of Intercompany Payables
- Exchange of raw materials. If you run a bakery and your pastry department runs out of butter, it's much easier to get a few pounds from the line crew than ...
- Exchange of finished products. ...
- Exchange of labor. ...
How to record intercompany loans?
- The parent sends cash to subsidiary in order to cover the operating losses or to finance the operations or whatever.
- The subsidiary sends cash to the parent just because the local lending is cheaper that the lending in parent’s domestic country.
- The companies within the same group are sending cash to each other in order to improve cash management…

Is intercompany receivable an asset?
A due from account is an asset account in the general ledger used to track money owed to a company that is currently being held at another firm. It is typically used in conjunction with a due to account and is sometimes referred to as intercompany receivables.
What are intercompany receivables?
Intercompany receivables occur when one of your company's organizations incurs a payable or receivable on behalf of another organization. This typically happens during a posting process that involves a control account.
Is other receivables a current asset?
Other receivables generally come with the headings “Trade receivables and others” in the financial statement of large listed public companies. Other receivables are disclosed under the headings “Current Assets” in the balance sheet of the company at the end of the period.
What type of accounts is intercompany receivable?
Intercompany Receivables means all account, note or loan payables and all advances (cash or otherwise) or any other extensions of credit that are receivable by Seller or any of its Affiliates (other than the Bank or the Transferred Subsidiaries) from the Bank or the Transferred Subsidiaries.
Can you offset intercompany receivables and payables?
Intercompany netting is the offsetting of accounts receivable and accounts payable between two business entities owned by the same parent. This means that payment is only made for the net difference between their receivables and payables, resulting in significantly lower cash flows between the parties.
How do you account for intercompany transfers?
0:208:00Intercompany Transactions 420 Advanced Financial AccountingYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipTransactions if you have a receivable. For example on the books of the parent that is from theMoreTransactions if you have a receivable. For example on the books of the parent that is from the subsidiary. Then you would also have a payable on the book she would think equal and opposite.
Which is not included in current assets?
Other current assets is a default classification of "current asset" general ledger accounts. It does not include cash, marketable securities, accounts receivable, inventory, and prepaid expenses.
What all comes under other current assets?
Examples of other current assets shall include: Restricted cash or investments. Advances paid to employees or suppliers. The cash surrender value of life insurance policies. Property that is being readied for sale. Marketable securities in negligible balance.
Which one of the following is not a current asset?
Land is regarded as a fixed asset or non-current asset in accounting and not a current asset.
What is intercompany account balances?
Intercompany Balances means, as of any date, all balances as of such date between Seller and the Non-Company Affiliates, on the one hand, and the Company and the Company Subsidiaries, on the other hand, including intercompany accounts receivable and intercompany accounts payable.
How do you classify intercompany transactions?
Intercompany sales can be divided into three main categories:Downstream transaction: This is a transaction from the origin to the subsidiary. ... Upstream transaction: This is a performance from subsidiary to parent.Lateral transaction: This is a transaction between two subsidiaries of the same company.
How are intercompany transactions treated?
Examples of how to handle intercompany transactionsIn consolidated income statements, eliminate intercompany revenue and cost of sales arising from the transaction.In the consolidated balance sheet, eliminate intercompany payable and receivable, purchase, cost of sales, and profit/loss arising from transaction.
What are some examples of intercompany transactions?
Examples of intercompany transactions Intercompany operations may involve trading operations, such as sale or purchase of inventory or fixed assets, providing or receiving of loans, guarantees or other commitments, declaration and payment of dividends. Sale of goods: Parent, Inc.
What is an intercompany journal entry?
Also Know, what is an intercompany journal entry? An Inter Company Journal Entry is done between organizations that belong to the same group. You can create Inter Company Journal Entry if you are making transactions with multiple Companies. You can select the Accounts which you wish to use in the Inter Company transactions.
What is due from account?
A due from account is an asset account in the general ledger used to track money owed to a company that is currently being held at another firm. It is typically used in conjunction with a due to account and is sometimes referred to as intercompany receivables.
Is an intercompany note considered an asset?
Intercompany notes and debt are generally presented as assets or liabilities (i.e., not collapsed into equity) when supported by a written agreement that includes principal amounts, interest rate, maturity date, etc.
Will intercompany transactions be eliminated in the Carve Out?
Intercompany transactions and balances between entities within the carve-out business will continue to be eliminated in preparing the carve-out financial statements.
What is intercompany accounting?
What and How? Intercompany transactions are used for a variety of mundane accounting reasons, most of which are purely innocent in nature. They can involve either transfers of value or assignment of obligations. Generally, the transactions are simply a method for tracking the daily operations of the company.
Why is it so difficult to determine the value of a company?
Due to the complex nature of today's corporate structures, and the relatively high level with which consolidated financial statements are presented , it is often extremely difficult for an investor, lender or other stakeholder to determine the value of an entity receiving an investment, loan or payments for services. Although lenders may have greater access to information through interaction with management and have the ability to gain additional clarity with regards to certain financial data, they must still ask the right questions to understand how a corporate structure affects their relationship to the company. Most often, intercompany transfers of value are not explicitly or sufficiently discussed in the financial statements to allow this assessment.
Why are utilities facing financial ruin?
Similarly, ratepayers and their protectors, the local public utility commissions (PUCs), are finding that even staid utilities are facing potential financial ruin, due in part to an inability to monitor intercompany transfers of value between the utility subsidiary and parental holding companies. A northeastern corporate holding company provides an ideal case study of how poor financial statement disclosure of value transfers from a utility subsidiary to its corporate parent (the corporation) caught the PUC, and the ratepayers it is supposed to protect, off-guard. The PUC engaged an auditing firm in mid-2003 to audit the activities of the corporation with specific areas of focus to include analysis of affiliate transactions. The preliminary audit report revealed a multitude of issues not apparent when reading the corporation's annual report. Essentially, the regulated utility subsidiary had been funding a variety of money-losing ventures entered into by the corporation at the expense of ratepayers and investors alike. Although several lines of business were discontinued, the damage had been done, and losses were realized.
Can parent companies contribute to existing or new entities?
Finally, parent companies may contribute cash or assets to existing or new entities (corporate or partnership) to create or capitalize new lines of business. All of the aforementioned transaction examples represent intercompany transactions or transfers of value one would expect in the normal course of business.
Do lenders have access to information?
Although lenders may have greater access to information through interaction with management and have the ability to gain additional clarity with regards to certain financial data, they must still ask the right questions to understand how a corporate structure affects their relationship to the company.
What is the correct why to set up Intercompany accounts between separate Companies, are they asset accounts?
The inter-co balances may be debit or credits depending on who owes. If you know in advance that one co will always be borrowing and another will be lending, then set them us as liabilities & assets respectively.
What is the correct why to set up Intercompany accounts between separate Companies, are they asset accounts?
The inter-co balances may be debit or credits depending on who owes. If you know in advance that one co will always be borrowing and another will be lending, then set them us as liabilities & assets respectively.
What is the correct why to set up Intercompany accounts between separate Companies, are they asset accounts?
The recording of inter company transactions largely depends on whether the reporting entity is part of the group or not (in terms of group accounts)
What are current assets?
Current assets, on the other hand, are all the assets of a company that are expected to be conveniently sold, consumed, utilized, or exhausted through standard business operations. They can easily be liquidated for cash, usually within one year, and are considered when calculating a firm's ability to pay short-term liabilities. Examples of current assets include cash and cash equivalents (CCE), marketable securities, accounts receivable, inventory, and prepaid expenses.
What are some examples of current assets?
Examples of current assets include cash and cash equivalents (CCE), marketable securities, accounts receivable, inventory, and prepaid expenses.
Why are OCA accounts considered other?
They are referred to as “other” because they are uncommon or insignificant, unlike typical current asset items such as cash, securities, accounts receivable, inventory , and prepaid expenses . The OCA account is listed on the balance sheet and is a component of a firm's total assets.
When are other current assets (OCA) discussed?
When other current assets (OCA) are discussed, information will be provided in the footnotes to the financial statements. Explanations may be necessary, for example, when there is a notable change in other current assets (OCA) from one period to the next. Other current assets (OCA) are expected to be disposed within a year or to mature ...
Is current asset liquid?
They have useful lives that span over a year and are not liquid . Current assets, on the other hand, are all the assets of a company that are expected to be conveniently sold, consumed, utilized, or exhausted through standard business operations.
What is intercompany revenue?
Intercompany Revenues means, in respect of any Subsidiary of FIL for any period, revenues of such Subsidiary that would not, after taking into account offsetting entries in the consolidation process, be recognized in accordance with GAAP as revenues of FIL in the consolidated Financial Statements of FIL and its Subsidiaries for such period.
What is current asset?
Current Assets means, with respect to the Borrower and the Restricted Subsidiaries on a consolidated basis at any date of determination, all assets (other than cash and Cash Equivalents) that would, in accordance with GAAP, be classified on a consolidated balance sheet of the Borrower and its Restricted Subsidiaries as current assets at such date of determina tion, other than amounts related to current or deferred Taxes based on income or profits (but excluding assets held for sale, loans (permitted) to third parties, pension assets, deferred bank fees and derivative financial instruments).
What is consolidated cash interest expense?
Consolidated Cash Interest Expense means, for any period, the excess of (a) the sum of (i) the interest expense (including imputed interest expense in respect of Capital Lease Obligations) of the Borrower and the Subsidiaries for such period, determined on a consolidated basis in accordance with GAAP, (ii) any interest accrued during such period in respect of Indebtedness of the Borrower or any Subsidiary that is required to be capitalized rather than included in consolidated interest expense for such period in accordance with GAAP and (iii) any cash payments made during such period in respect of obligations referred to in clause (b) (ii) below that were amortized or accrued in a previous period, minus (b) the sum of (i) to the extent included in such consolidated interest expense for such period, non-cash amounts attributable to amortization of financing costs paid in a previous period, (ii) to the extent included in such consolidated interest expense for such period, non-cash amounts attributable to amortization of debt discounts or accrued interest payable in kind for such period, and (iii) any break funding payment made pursuant to Section 2.14.
What is net cash payment?
Net Cash Payments means, with respect to any Disposition, the aggregate amount of all cash payments, and the fair market value of any non-cash consideration (but only as and when subsequently converted to cash), received by the Borrowers and their Subsidiaries directly or indirectly in connection with such Disposition; provided that (a) Net Cash Payments shall be net of the amount of any legal, accounting, broker, title and recording tax expenses, commissions, finders’ fees and other fees and expenses paid by the Borrowers and their Subsidiaries in connection with such Disposition and (b) Net Cash Payments shall be net of any repayments by the Borrowers and their Subsidiaries of Indebtedness to the extent that (i) such Indebtedness is secured by a Lien on the Property that is the subject of such Disposition and (ii) the transferee of (or holder of a Lien on) such Property requires that such Indebtedness be repaid as a condition to the purchase of such Property.
What is net cash flow?
Net Cash Flow means the gross cash proceeds of the Company less the portion thereof used to pay or establish reserves for all Company expenses, debt payments, capital improvements, replacements, and contingencies, all as reasonably determined by the Directors. “Net Cash Flow” shall not be reduced by depreciation, amortization, cost recovery deductions, or similar allowances, but shall be increased by any reductions of reserves previously established.
What is consolidated revenue?
Consolidated Revenues means, with respect to any date, the consolidated total revenues of the Group for such date, as reported in the most recently published consolidated financial statements of the Group;
What is operating revenue cash flow?
Operating Revenue Cash Flows means the Company’s cash flow from ownership and/or operation of (i) Properties, (ii) Loans, (iii) Permitted Investments, (iv) short-term investments, and (v) interests in Properties, Loans and Permitted Investments owned by any Joint Venture or any partnership in which the Company or the Partnership is, directly or indirectly, a co-venturer or partner.
Why is separating receivables and payables important?
The process of separating receivables and payables also helps in tax charges as movement in and out of due from accounts or due to accounts marks when funds were distributed and therefore the appropriate tax charge required on the funds.
Why separate outgoing and incoming funds?
Advantages of a Due From Account. The primary reason for separating the incoming and outgoing funds is for ease of accounting. This keeps all incoming payments focused in one account and outgoing in another.
What does it mean when an account has a negative balance?
If a negative balance occurs, the most likely culprit is incorrectly entered data. Meanwhile, if the account ever reflects a zero balance, this means there are no receivables or payables expected at that time.
What is a due from account?
Key Takeaways. A due from account is a debit account that indicates the number of deposits currently held at another company. A due from account tracks assets owed to a company and is not used for the tracking of any liabilities or obligations.
Why is separation of funds important?
The separation of funds is particularly useful when disbursements are scheduled for payments, transfers to other bank locations, or to a company's subsidiaries.
Can due from accounts be negative?
Due from accounts and due to accounts should never be negative, which would signify bad data. Both accounts can, however, be zero.
What are some examples of intercompany receivables?
Examples of Intercompany Receivables in a sentence. Where no balance is listed , the Debtors do not believe, based on information currently available, that theapplicable Debtor has any Intercompany Receivables or Intercompany Payables.
Is intercompany receivable collateral?
Intercompany Receivables constitute Collateral for the Borrower's Obligations to the Bank; however, intercompany Receivables do not qualify as Eligible Receivables for purposes of determining the amount of Available Commitment from time to time.
Why Is It Important to Understand Intercompany Transactions?
- In a perfect world, investors and lenders should be able to look at a company's financial statements and easily makeinformed investing and lending decisions. In reality, that is easier said than done. What if you are a lender orpotential purchaser of corporate bonds secured by specific assets of a company? Examples of such transactionshappen freque...
What and How?
- Intercompany transactions are used for a variety of mundane accounting reasons, most of which are purely innocentin nature. They can involve either transfers of value or assignment of obligations. Generally, the transactions aresimply a method for tracking the daily operations of the company. For example, many larger companies typicallycontain either multiple lines of busines…
Buyers (or Lenders) Beware...
- When analyzing financial statements and their related footnote disclosures, it is important to read between the lines.Consolidated financial statements do not necessarily provide the full picture of a company's operations, particularlyas related to intercompany or related-party transactions. Unless broad changes for disclosing intercompanytransactions are made to financial-reporting r…
Footnotes
- 1 Robert L. Sammon is a manager in Huron Consulting Group's Energy and Valuation practice. He has a broad background in financial and tax reporting, deal structuring and assetvaluation as related to acquisitions and project development. He has provided financial advisory services to a variety of regulated and merchant energy clients over the pasteight years in the energy industry. …