
What are essential nutrients in lipids?
Lipids in the diet transport the four fat-soluble vitamins (vitamins A, D, E, and K) and assist in their absorption in the small intestine. Furthermore, what is an example of an essential nutrient? An essential nutrient is a nutrient required for normal body functioning that can not be synthesized by the body.
What is the recommended percent of macronutrients?
Your macronutrient ratio doesn’t directly influence weight loss. The acceptable macronutrient distribution ranges (AMDR) are 45–65% of your daily calories from carbs, 20–35% from fats and 10 ...
What are the major dietary source for lipids?
What is Lipid?
- Triglycerides make up more than 95 percent of lipids in the diet and are commonly found in fried foods, butter, milk, cheese, and some meats. ...
- Phospholipids make up only about 2 percent of dietary lipids. They are water-soluble and are found in both plants and animals. ...
- Sterols are the least common type of lipid. ...
What are micronutrients and do I need them?
What are the essential micronutrients?
- Protein. Share on Pinterest. Protein is having its moment, and not just in the workout community. …
- Carbohydrates. Share on Pinterest. …
- Fats. Share on Pinterest. …
- Vitamins. Share on Pinterest. …
- Minerals. Share on Pinterest. …
- Water. Share on Pinterest.
What are micronutrients?
What is the difference between macronutrients and micronutrients?
What are the nutrients in food?
Why do we count macros?
What are the two primary classifications of nutrients found in food and beverages?
Why are certain nutrients considered essential?
How many calories are in a macronutrient?
See 2 more
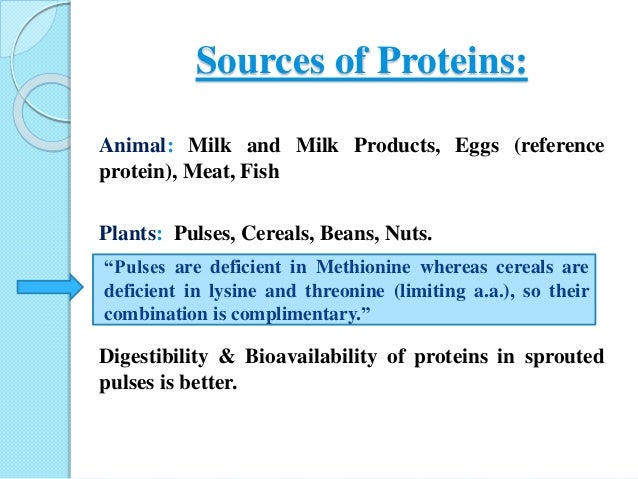
Are lipids a macronutrient?
Lipids, or more technically triglycerides, are an essential macronutrient for the human body and of high importance for the structural integrity of many areas throughout the human body, especially within the brain and nervous system.
Are fats and lipids micronutrients?
We can divide nutrients into two broad categories: macronutrients (those that we need in larger quantities) and micronutrients (those that we need in small quantities). The three basic macronutrients are protein, carbohydrates, and lipids (fats and oils).
Which are micronutrients and macronutrients?
Macronutrients are big picture nutrition categories, such as carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. Micronutrients are smaller nutritional categories, such as individual vitamins and minerals like calcium, zinc, and vitamin B-6.
Are lipids considered a nutrient?
The lipids of nutritional importance are triglycerides (fats and oils), phospholipids (e.g., lecithin), and sterols (e.g., cholesterol). Lipids in the diet transport the four fat-soluble vitamins (vitamins A, D, E, and K) and assist in their absorption in the small intestine.
How are lipids classified?
There are two major types of lipids- simple lipids and complex lipids. Simple lipids are esters of fatty acids with various alcohols. For eg., fats and waxes. On the contrary, complex lipids are esters of fatty acids with groups other than alcohol and fatty acids.
What are the 7 types of macronutrients?
These are carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals, fibre and water. It is important that everyone consumes these seven nutrients on a daily basis to help them build their bodies and maintain their health.
What are the 7 micronutrients?
There are 7 essential plant nutrient elements defined as micronutrients [boron (B), zinc (Zn), manganese (Mn), iron (Fe), copper (Cu), molybdenum (Mo), chlorine (Cl)]. They constitute in total less than 1% of the dry weight of most plants.
What are the 11 macronutrients?
doi: 10.17226/10490. Suggested Citation:"11 Macronutrients and Healthful Diets." Institute of Medicine. 2005. Dietary Reference Intakes for Energy, Carbohydrate, Fiber, Fat, Fatty Acids, Cholesterol, Protein, and Amino Acids.
Are fats micronutrients?
What Are Micronutrients? The term micronutrients is used to describe vitamins and minerals in general. Macronutrients, on the other hand, include proteins, fats and carbohydrates.
What is a lipid in nutrition?
Lipids are a family of organic compounds that are mostly insoluble in water. Composed of fats and oils, lipids are molecules that yield high energy and have a chemical composition mainly of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen.
Which nutrient is classified as a micronutrient?
Vitamins, mineralsSummaryClassificationNutrientMacronutrientCarbohydrate, protein, lipids, waterMicronutrientVitamins, mineralsEnergy-YieldingCarbohydrate, protein, fatOrganicCarbohydrate, protein, lipids, vitamins2 more rows
What are macro nutrients?
Carbohydrates, fat and protein are called macronutrients. They are the nutrients you use in the largest amounts. “Macronutrients are the nutritive components of food that the body needs for energy and to maintain the body's structure and systems,” says MD Anderson Wellness Dietitian Lindsey Wohlford.
What are micronutrients?
The term micronutrients refers to vitamins and minerals, which can be divided into macrominerals, trace minerals and water- and fat-soluble vitamins.
Are protein macronutrients or micronutrients?
Macronutrients are the nutrients your body needs in larger amounts, namely carbohydrates, protein, and fat. These provide your body with energy, or calories. Micronutrients are the nutrients your body needs in smaller amounts, which are commonly referred to as vitamins and minerals.
Are lipids fats?
Lipids are fatty, waxy, or oily compounds that are soluble in organic solvents and insoluble in polar solvents such as water. Lipids include: Fats and oils (triglycerides) Phospholipids.
Which of the following is not a macronutrient?
Calcium, iron, vitamins, iron, minerals, and vitamin C are all micronutrients. Macronutrients are nutrients that are required in large amounts. Humans require three macronutrients: carbohydrates (sugar), lipids (fats), and proteins. Chlorine isn't a macronutrient, so it's not one of these options.
What are macronutrients and micronutrients?
Macronutrients and micronutrients are nutrients required by the human body and are found in food. Macronutrients include carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, while micronutrients include vitamins and minerals. Although all nutrients are essential, gram per gram, the human body requires macronutrients in larger amounts than micronutrients. Generally speaking, consuming a well-balanced diet of whole foods is the best way to ensure you are consuming the required macronutrients and micronutrients for optimal health, with the support of supplementations as needed.
What are the nutrients that are essential to the body?
( 1) In total, there are 6 essential nutrients required by the body: carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, minerals, and water . While all of these nutrients are essential, they are classified into two categories: macronutrients and micronutrients.
What are the building blocks of the human diet?
Macronutrients are the primary building blocks of the human diet, they make up the caloric content of food, and include carbohydrates, proteins, and fats.
What are the minerals that are inorganic?
( 7) Minerals can also be classified by macro and micro terms and include calcium, phosphorus, potassium, sodium, chloride, magnesium, iron, zinc, iodine, chromium, copper, fluoride, molybdenum, manganese, and selenium.
Which macronutrients are required in larger amounts?
Macronutrients include carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, and are required relatively in larger amounts, while micronutrients include vitamins and are required in relatively smaller amounts by the human body. ( 9)
What are proteins made of?
Proteins are made up of amino acids and are found in animal and plant forms. Protein contributes to structural and mechanical function, regulating processes in the cells and body, and provides energy if necessary. ( 3) Protein provides 4 calories of energy per gram and is found in meat, poultry, seafood, eggs, dairy, beans, lentils, nuts, and seeds.
Is a phytochemical a micronutrient?
Phytochemicals, also known as phytonutrients, are antioxidants, flavonoids, and other chemicals that contribute to overall health; however, they are not technically vitamins or minerals and are, therefore, sometimes but not always considered micronutrients. ( 8)
Why are lipids important?
Your cell membrane is a phospholipid bilayer, so lipids are a key component. Lipids are important for the body's temperature regulation and organ protection.
What are the different types of lipids in nursing?
There are several types of dietary lipids that are important to know about for nutrition in nursing; saturated fats, trans fats, and unsaturated fats.
How many amino acids are in proteins?
Proteins are made up of amino acids, and there are 9 essential amino acids and 11 non-essential amino acids.
What are some examples of complex carbohydrates?
Examples of complex carbohydrates include apples, brown rice, and lentils.
What is the role of nutrition in nursing?
Nutrition plays a key role in patient wellness, and patient teaching regarding nutrition is a key part of EVERY nurse’s job. These flashcards will help you understand the basics of nutrition, along with key nutritional and lifestyle considerations for common health disorders.
Why does the body break down glycogen?
For example, if you are working as a nurse, and you have a 12-hour shift and skip lunch, when your blood glucose levels get low enough, your body will start breaking down your stored glycogen to help provide glucose for your muscles and brain. Glycogen stores also get depleted, for example, when running a marathon.
What is the difference between soluble and insoluble fiber?
The difference between soluble and insoluble fiber is that soluble fiber dissolves in fluid and is derived from the inner flesh of plants, while insoluble fiber does not dissolve in fluid and is derived from the outer skin of plants. So, if you had a parent that told you "the skin has all the nutrients," in an effort to get you to eat the whole fruit or vegetable growing up, while this isn't exactly the same thing, the outer skin of plants does contain insoluble fiber that the inside of plants doesn't!
Why is macronutrient important?
Each macronutrient is incredibly important for your body to function optimally. It’s crucial that you get enough carbs, protein, and fat by eating a balanced diet comprising a variety of foods.
How to get enough macronutrients?
To ensure you get enough macronutrients from food, eat a balanced diet with sources of carbs, protein, and fat at every meal.
What are the nutrients that your body needs in large amounts to function optimally?
Macronutrients are nutrients that your body needs in large amounts to function optimally.
What are macronutrients?
Macronutrients include carbohydrates, protein, and fat. They’re needed in relatively larger amounts than other nutrients, hence the term “macro.” Although there are recommended ranges for macronutrient intake, your needs vary based on your personal circumstances.
What are the starchy vegetables?
Vegetables: peas, potatoes, corn, and other starchy veggies
What are the nutrients that make up the body?
Macronutrients include carbs, protein, and fat. They provide energy in the form of calories and are needed to maintain your body’s functions and structure.
How many amino acids are there in the human body?
Proteins are digested into amino acids. Twenty amino acids have important functions in your body, 9 of which are essential and must be obtained from foods ( 5, 6 ).
How many calories are in a gram of carbs?
As you read above, carbohydrates provide 4 calories for every gram we consume; proteins provide 4 calories for every gram we consume; and fats provide 9 calories for every gram we consume. Another source of calories is alcohol. Alcohol is not considered to be a nutrient (because it's not required by the body to perform its basic functions), but it does provide 7 calories of energy for every gram we consume. Vitamins, minerals and water do not provide any calories, but they are still essential nutrients.
How many micronutrients are there?
Micronutrients include all the essential vitamins and minerals. There are 13 essential vitamins and 16 essential minerals (see Tables 1.2. 2 and 1.2. 3 for a complete list and their major functions). In contrast to carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins, micronutrients do not contain calories.
How to measure energy in food?
To measure the number of kilocalories in a particular food substance, a certain amount of food is burned in a device called a calorimeter. As the food burns, heat is created. The heat dissipates to the surrounding water while a thermometer detects the change in temperature of the water. A kilocalorie of energy performs 1,000 times more work than a calorie. In science, a kilocalorie is often written as "kcal" or "Calorie" (with a capital "C"). So, 1 kilocalorie = 1 kcal = 1 Calorie = 1,000 calories. Although kilocalories, kcals, or Calories (with a capital "C") are technically the appropriate terms, most people refer to the amount of energy in food as a calorie (with a lower case "c"), so this text will use calories (with a lower case "c") for the sake of simplicity. On food labels, “calorie” is used when referring to kilocalories. For more on calories, watch the video below.
How many calories are in a protein?
Proteins provide 4 calories of energy per gram; however providing energy is not protein’s most important function. Proteins provide structure to bones, muscles, and skin; support tissue growth, repair, and maintenance; and play a role in conducting most of the chemical reactions that take place in the body.
What are the main sources of carbohydrates?
Carbohydrates. The major food sources of carbohydrates are grains, dairy products, fruits, and starchy vegetables like potatoes. Non-starchy vegetables also contain carbohydrates, but in lesser quantities. When you eat a food that contains carbohydrates, like bread for example, you receive approximately 4 calories of energy for every gram ...
What are the six classes of essential nutrients?
These six classes of essential nutrients are: carbohydrates, lipids (fats), proteins, water, vitamins, and minerals. These nutrients can also be categorized as organic or inorganic.
What is the definition of diet?
What is in Food? Your "diet" is defined as the foods you choose to eat. The diet of most people contains a variety of foods: grains, nuts, fruits, vegetables and more! The foods we eat contain nutrients. Nutrients are substances required by the body to perform its basic functions.
Carbohydrates as macronutrients
The major dietary source of energy for heterotrophs is complex carbohydrates. Most carbohydrates originally come from plant sources. Various polysaccharides, disaccharides, or any of a variety of simple sugars (monosaccharides) can meet this dietary need.
Lipids
Neutral lipids (fats) or triglycerols are contained in fats and oils, meat and dairy products, nuts, and avocados.
Minerals
Our body needs minerals for development and proper functioning. Some minerals are needed in relatively large amounts and are called essential minerals, or macrominerals. For example, sodium and potassium are vital to the functioning of every nerve and muscle in an animal's body.
Vitamins
Normal metabolic activity depends on very small amounts of more than a dozen organic substances called vitamins. Vitamin is the general term for a number of chemically unrelated, organic substances that occur in many foods in small amounts and are necessary for normal metabolic functioning. Vitamins may be water soluble or fat soluble.
What is the combination of cholesterol, phospholipids, reformed triglycerides, and protein?
Lipoprotein; Combination of cholesterol, phospholipids, reformed triglycerides, and protein
Which protein has the highest portion of protein?
Lipoprotein with the highest portion of protein
What are micronutrients?
Micronutrients, in comparison, are consumed in relatively small amounts and include vitamins and minerals and phytochemicals, commonly called phytonutrients. ( 3 ) ( 15) Your body uses vitamins and minerals to support its various metabolic processes, such as cell function, development, and proper growth. ( 4 ) ( 14)
What is the difference between macronutrients and micronutrients?
Getting adequate nutrients from a balanced diet is important to support general health and to prevent the risk of diseases that have been associated with a poor diet. Imbalanced or inadequate intake of certain macronutrients or micronutrients may increase your risk of certain health conditions, such as heart disease, cancer, and osteoporosis. ( 14)
What are the nutrients in food?
Taking a closer look at the macronutrients (carbohydrates, fats/lipids, proteins), and micronutrients (vitamins, minerals) that are found in your food will help you to understand their crucial role role in health and how you can ensure you are consuming the correct amounts for your individual needs.
Why do we count macros?
Many individuals may choose to count their macros to help them reach a healthy body weight, build muscle mass, maintain healthy blood glucose levels, or manage their daily caloric intake. Manually tracking your consumption of micronutrients and macronutrients can become complicated and time-consuming. Fortunately, there are several diet-tracking apps that allow you to easily record and understand your daily macronutrient and micronutrient intake to ensure you are meeting your individual goals.
What are the two primary classifications of nutrients found in food and beverages?
In this article, you’ll learn about macronutrients and micronutrients, the two primary classifications of nutrients found in food and beverages.
Why are certain nutrients considered essential?
Certain nutrients are considered essential because they are required by the body but they can not be synthesized and must be obtained from dietary sources. ( 4 ) ( 12) There are 13 vitamins and 15 minerals that have been identified as essential for health.
How many calories are in a macronutrient?
Each macronutrient provides energy measured in calories: Carbohydrates: 4 kcal per 1 gram of carbohydrate. Lipids: 9 kcal per 1 gram of lipid. Proteins: 4 kcal per 1 gram of protein ( 4) Most foods are made up of a combination of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. Put simply, foods and beverages that are consumed are broken down into smaller ...
