These amino acids can then be used to make proteins in the body. Lipids Lipids are made of fatty acids and glycerol This medication is used as a moisturizer to treat or prevent dry, rough, scaly, itchy skin and minor skin irritations.Glycerin
Is a lipid A amino acid?
The primary role of amino acids is to form and maintain proteins in the body while lipids serve to provide sources of energy.
What is the lipids made of?
Lipids are an essential component of the cell membrane. The structure is typically made of a glycerol backbone, 2 fatty acid tails (hydrophobic), and a phosphate group (hydrophilic). As such, phospholipids are amphipathic.
Is amino acid lipid or protein?
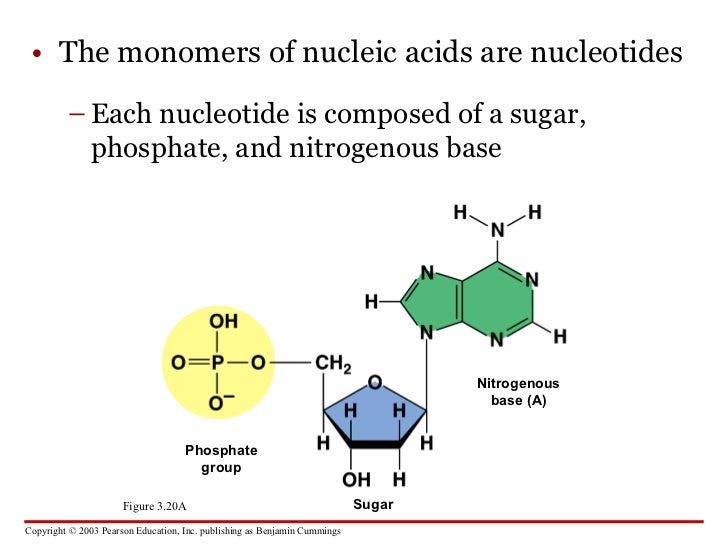
Types of biological macromoleculesBiological macromoleculeBuilding blocksExamplesLipidsFatty acids and glycerolFats, phospholipids, waxes, oils, grease, steroidsProteinsAmino acidsKeratin (found in hair and nails), hormones, enzymes, antibodiesNucleic acidsNucleotidesDNA, RNA1 more row
Are lipids made from glycerol and amino acids?
A lipid is a polymer composed of three fatty acid molecules and one glycerol molecule. Lipids produce a special polymer form which is considered to be a key component of cell membranes and hormones. Lipids help to store energy, provide cushion, protect tissues, separate the body, and form membranes of cells.
What defines a lipid?
What is a lipid? A lipid is any of various organic compounds that are insoluble in water. They include fats, waxes, oils, hormones, and certain components of membranes and function as energy-storage molecules and chemical messengers.
Which is not true about lipids?
The answer is d. All lipids contain fatty acids. The statement that is not true is choice (d) All lipids contain fatty acids. Not all lipids contain fatty acid molecules.
Is protein a lipid?
Lipids are molecules that contain hydrocarbons and make up the building blocks of the structure and function of living cells. Examples of lipids include fats, oils, waxes, certain vitamins (such as A, D, E and K), hormones and most of the cell membrane that is not made up of protein.
What are amino acids made of?
An amino acid is an organic chemical. Organic chemicals contain carbon-hydrogen bonds. All amino acids have the same basic structure. Each molecule has a central carbon atom linked together with a basic amino group, a carboxylic acid group, a hydrogen atom and an R-group, or side-chain group.
Is amino acid a protein?
Amino acids are molecules that combine to form proteins. Amino acids and proteins are the building blocks of life. When proteins are digested or broken down, amino acids are left.
Is lipid a polymer of amino acid?
Explanation: Lipids are not polymers, they are normally esters of fatty acids and alcohol, e.g. triglycerides. Proteins are the polymers of amino acids, nucleic acids are the polymer of nucleotides and polysaccharides are the polymer of monosaccharides.
Are nucleic acids made of amino acids?
Nucleic acid monomers are called nucleotides; protein monomers are called amino acids; lipid monomers are called fatty acids; and carbohydrate monomers are called monosaccharides (MAH-nuh-SA-kuh-riyd). All types of monomers are organic molecules, meaning that they contain carbon-to-carbon bonds.
What are two main parts of a lipid?
Answer and Explanation: The two main parts of a triglyceride lipid are glycerol and fatty acids.
What are the 2 main parts of a lipid?
Answer and Explanation: The two main parts of a triglyceride lipid are glycerol and fatty acids.
Where do lipids come from?
Lipids are utilized directly, or otherwise synthesized, from fats present in the diet. There are numerous biosynthetic pathways to both break down and synthesize lipids in the body. The main biological functions of lipids include storing energy, as lipids may be broken down to yield large amounts of energy.
What are the 4 main types of lipids?
Major types include fats and oils, waxes, phospholipids, and steroids.
What are the 3 types of lipids?
Lipids are important fats that serve different roles in the human body. The three main types of lipids are triacylglycerols (also known as triglycerides), phospholipids, and sterols.
What are lipids?
Lipids are organic compounds that are fatty acids or derivatives of fatty acids, which are insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents. For...
How are lipids important to our body?
Lipids play a very important role in our body. They are the structural component of the cell membrane. They help in providing energy and produce ho...
How are lipids digested?
The enzyme lipase breaks down fats into fatty acids and glycerol, which is facilitated by bile in the liver.
What is lipid emulsion?
It refers to an emulsion of lipid for human intravenous use. These are also referred to as intralipids which is the emulsion of soybean oil, glycer...
How are lipids metabolized?
Lipid metabolism involves the oxidation of fatty acids to generate energy to synthesize new lipids from smaller molecules. The metabolism of lipids...
How are lipids released in the blood?
The medium-chain triglycerides with 8-12 carbons are digested and absorbed in the small intestine. Since lipids are insoluble in water, they are ca...
What are the main types of lipids?
There are two major types of lipids- simple lipids and complex lipids. Simple lipids are esters of fatty acids with various alcohols. For eg., fats...
What are lipids made up of?
Lipids are made up of a glycerol molecule attached to three fatty acid molecules. Such a lipid is called triglyceride.
What are Lipids?
These organic compounds are nonpolar molecules, which are soluble only in nonpolar solvents and insoluble in water because water is a polar molecule. In the human body, these molecules can be synthesized in the liver and are found in oil, butter, whole milk, cheese, fried foods and also in some red meats.
What is the lipid structure?
Lipid Structure. Lipids are the polymers of fatty acids that contain a long, non-polar hydrocarbon chain with a small polar region containing oxygen. The lipid structure is explained in the diagram below: Lipid Structure – Saturated and Unsaturated Fatty Acids.
What is the process of oxidation of fatty acids?
Lipid metabolism involves the oxidation of fatty acids to generate energy to synthesize new lipids from smaller molecules. The metabolism of lipids is associated with carbohydrate metabolism as the products of glucose are converted into lipids.
Why do fatty acids have a straight rod shape?
The saturated fatty acids have higher melting points compared to unsaturated acids of the corresponding size due to their ability to pack their molecules together thu s leading to a straight rod-like shape.
What is saponifiable lipid?
A saponifiable lipid comprises one or more ester groups, enabling it to undergo hydrolysis in the presence of a base, acid, or enzymes, including waxes, triglycerides, sphingolipids and phospholipids. Further, these categories can be divided into non-polar and polar lipids.
What are the properties of lipids?
Lipids are a family of organic compounds, composed of fats and oils. These molecules yield high energy and are responsible for different functions within the human body. Listed below are some important characteristics of Lipids. Lipids are oily or greasy nonpolar molecules, stored in the adipose tissue of the body.
What is the name of the lipid that contains a phosphate group?
The name phospholipid is derived from the fact that phosphoacylglycerols are lipids containing a phosphate group.
How many categories of lipids are there?
Lipids have been classified into eight categories by the Lipid MAPS consortium as follows:
What is the middle structure of a lipid?
The middle structure is a triglyceride composed of oleoyl, stearoyl, and palmitoyl chains attached to a glycerol backbone. At the bottom is the common phospholipid phosphatidylcholine. In biology and biochemistry, a lipid is a micro biomolecule that is soluble in nonpolar solvents.
What are the components of the membranes of eukaryotic cells?
Eukaryotic cells feature the compartmentalized membrane-bound organelles that carry out different biological functions. The glycerophospholipids are the main structural component of biological membranes, as the cellular plasma membrane and the intracellular membranes of organelles; in animal cells, the plasma membrane physically separates the intracellular components from the extracellular environment. The glycerophospholipids are amphipathic molecules (containing both hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions) that contain a glycerol core linked to two fatty acid-derived "tails" by ester linkages and to one "head" group by a phosphate ester linkage. While glycerophospholipids are the major component of biological membranes, other non-glyceride lipid components such as sphingomyelin and sterols (mainly cholesterol in animal cell membranes) are also found in biological membranes. In plants and algae, the galactosyldiacylglycerols, and sulfoquinovosyldiacylglycerol, which lack a phosphate group, are important components of membranes of chloroplasts and related organelles and are the most abundant lipids in photosynthetic tissues, including those of higher plants, algae and certain bacteria.
Why is the word "lipide" anglicized?
The word lipide was later anglicized as lipid because of its pronunciation ('lɪpɪ d). In French, the suffix -ide, from Ancient Greek -ίδης (meaning 'son of' or 'descendant of'), is always pronounced (ɪd). In 1947, T. P. Hilditch divided lipids into "simple lipids", with greases and waxes (true waxes, sterols, alcohols).
What is the name of the phospholipids found in the brain?
Thudichum discovered in human brain some phospholipids ( cephalin ), glycolipids ( cerebroside) and sphingolipids ( sphingomyelin ). The terms lipoid, lipin, lipide and lipid have been used with varied meanings from author to author. In 1912, Rosenbloom and Gies proposed the substitution of "lipoid" by "lipin".
What are the precursors of lipids?
The most familiar saccharolipids are the acylated glucosamine precursors of the Lipid A component of the lipopolysaccharides in Gram-negative bacteria. Typical lipid A molecules are disaccharides of glucosamine, which are derivatized with as many as seven fatty-acyl chains.
What is the self-organization of phospholipids?
Self-organization of phospholipids: a spherical liposome, a micelle, and a lipid bilayer.
What are Lipids?
Lipids are a group of diverse macromolecules consisting of fatty acids and their derivatives that are insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents.
What is biological lipid?
Biological lipids are a chemically diverse group of compounds, and the biological functions of the lipids are as diverse as their chemistry.
Why are lipids important?
The lipids are essential constituents of the diet because of their high energy value. These are also essential for the fat-soluble vitamins and the essential fatty acids found with the fat of the natural foodstuffs. Fats combined with proteins (lipoproteins) are essential constituents of the cell membranes and mitochondria of the cell.
What is the main constituent of body fat?
Triglycerides are a type of lipid which is an ester of three fatty acids with glycerol. Triglycerides are the main constituents of body fat in humans, other vertebrates, and vegetable fats.
How many carbon atoms are in a fatty acid chain?
In naturally occurring triglycerides, the fatty acid chains mostly contain 16, 18, or 20 carbon atoms.
What are the components of the cell membrane?
Fats combined with proteins (lipoproteins) are essential constituents of the cell membranes and mitochondria of the cell. Lipids occur naturally in living beings like plants, animals, and microorganisms that form various components like cell membranes, hormones, and energy storage molecules.
Which type of fat is unbranched linear chains of CH2 groups linked together by carbon-carbon single bonds?
Saturated fatty acids are the simplest form of fats that are unbranched linear chains of CH2 groups linked together by carbon-carbon single bonds with a terminal carboxylic acid.
