Are there different types of a molar pregnancy?
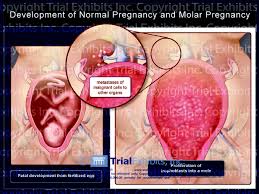
There are two types of molar pregnancy, complete molar pregnancy and partial molar pregnancy. In a complete molar pregnancy, the placental tissue is abnormal and swollen and appears to form fluid-filled cysts. There's also no formation of fetal tissue.
What are the symptoms of a molar pregnancy?
What are the symptoms of a molar pregnancy?
- Bleeding. You may have bright red to dark brown bleeding in the first trimester (up to 13 weeks). ...
- High hCG with severe nausea and vomiting. The hormone hCG is made by the placenta. ...
- Pelvic pain and pressure. Tissues in a molar pregnancy grow faster than they should, especially in the second trimester. ...
Can a baby survive a molar pregnancy?
The fetal tissue may also be formed, but the fetus usually does not survive and there is an early-pregnancy miscarriage. It is difficult for the baby to survive in either cases of molar pregnancy. In case of a complete molar pregnancy, the placental tissue is completely abnormal, swollen and also shows the formation of cysts that are fluid filled.
What exactly is a molar pregnancy?
Molar pregnancy – what you need to know . When you’re trying for a baby, it’s devastating when things go wrong. One rare complication that can cause particular heartbreak is molar pregnancy. Strange name, so what exactly is it? A molar pregnancy, sometimes called hydatidiform mole, occurs when the placenta and foetus don’t form properly.
Do molar pregnancies run in families?
Recurrent molar pregnancy may even be familial, but this is an exceedingly rare condition (2). It is proposed that patients with recurrent hydatidiform moles fall into two groups.
What increases your risk of molar pregnancy?
The cause of molar pregnancy is unknown, but risk factors include: maternal age of less than 20 or more than 40 years. race – Asian women are at increased risk. dietary deficiencies including lack of folate, beta-carotene or protein.
What is the main cause of molar pregnancy?
A molar pregnancy is caused by an abnormally fertilized egg. Human cells normally contain 23 pairs of chromosomes. One chromosome in each pair comes from the father, the other from the mother.
Can you prevent a molar pregnancy?
Can molar pregnancy be prevented? There is no way to prevent a molar pregnancy. If you have had a previous molar pregnancy, you can reduce your likelihood of complications by avoiding another pregnancy for one year after your initial molar pregnancy.
How early can a molar pregnancy be detected?
An ultrasound of a complete molar pregnancy — which can be detected as early as eight or nine weeks of pregnancy — may show: No embryo or fetus. No amniotic fluid. A thick cystic placenta nearly filling the uterus.
What percent of molar pregnancies are cancerous?
Hye Sook Chon, a gynecological oncologist at Moffitt Cancer Center, says 15% to20% of women who experience a complete molar pregnancy, or mole, develop GTN.
Can Covid cause molar pregnancy?
Conclusion: There was a significant increase in the incidence of molar pregnancy during the COVID-19 pandemic, possibly because of the delay in receiving medical care. We recommend providing gynecological primary care services during a crisis, such as a pandemic.
Will a pregnancy test be positive with a molar pregnancy?
Women with a molar pregnancy will have a positive pregnancy test and the same early symptoms of a normal pregnancy. In the absence of medical intervention or diagnosis, the pregnancy might seem normal for the first three to four months.
What are the hCG levels for a molar pregnancy?
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is commonly used as a marker for gestational trophoblastic disease. Total hCG levels greater than 100,000 are highly suggestive of a complete hydatidiform mole (Berkowitz & Goldstein, 2009).
Can you detect a molar pregnancy at 5 weeks?
An ultrasound can detect a complete molar pregnancy as early as eight or nine weeks of pregnancy.
Can Covid cause molar pregnancy?
Conclusion: There was a significant increase in the incidence of molar pregnancy during the COVID-19 pandemic, possibly because of the delay in receiving medical care. We recommend providing gynecological primary care services during a crisis, such as a pandemic.
What was your hCG with molar pregnancy?
The measurement of high hCG levels in excess of 100,000 mIU/mL suggests the diagnosis of a complete molar pregnancy, particularly when associated with vaginal bleeding, uterine enlargement and abnormal ultrasound findings.
What is the symptoms of molar pregnancy?
High hCG with severe nausea and vomiting. The hormone hCG is made by the placenta. It's responsible for giving many pregnant women a certain amount of nausea and vomiting. In a molar pregnancy, there may be more placenta tissue than normal. The higher levels of hCG might lead to severe nausea and vomiting.
Will a pregnancy test be positive with a molar pregnancy?
Women with a molar pregnancy will have a positive pregnancy test and the same early symptoms of a normal pregnancy. In the absence of medical intervention or diagnosis, the pregnancy might seem normal for the first three to four months.
What is a molar pregnancy?
There is two type of molar pregnancy, the complete molar pregnancy in which the sperm fertilizes with an egg which does not have any DNA . The other is partial molar pregnancy which is developed when two sperms fertilize with one egg. Both the cases result in the unviable fetus and an increase in the level of hCG hormone. When the molar pregnancy occurs at least two times, the condition is termed as a recurrent hydatidiform mole (RHM). According to the research, a genetic angle is associated with the occurrence of recurrent hydatidiform mole. The condition is due to the mutation in various genes, however, two important genes, the mutation of which causes a maximum number of the recurrent hydatidiform mole are NLRP7 and KHDC3L.
What are the characteristics of a molar pregnancy?
Ultrasound Characteristics. Molar pregnancy shows distinct characteristics in the uterus. The chronic villi are enlarged and there is an increasing proliferation of trophoblast cells. Further, the mom is formed like a bunch of grapes and presents a pattern of a snowstorm. Trophoblast also has impaired angiogenesis.
What is a recurrent hydatidiform mole?
Recurrent hydatidiform mole is affected by the genetic mutation. The genes involved are NLRP7 and KHDC3L, which are responsible for the development of oocyte. Mutation in these, results in abnormal development. The condition is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern.
What is the genetic disorder that causes a hydatidiform mole?
NLRP7 and KHDC3L are the genes responsible for the development of oocyte and any mutation in these genes results in abnormal development of egg cells. Pregnancy resulting from the fertilization of such oocyte is not viable and hence results in the formation of hydatidiform mole. As the genetic disorder is associated with the development of oocyte, this condition leads to the recurrent hydatidiform mole.
How many pregnancies are there with hydatidiform moles?
The rate of occurrence of hydatidiform mole is 1 in 600 to 1 in 1000 pregnancies. The rate of recurrent hydatidiform mole is 1 to six percent of the women with previous hydatidiform mole. The unviable pregnancy is to be removed with surgery and there are chances that the remaining tissue may lead to a malignant condition such as gestational choriocarcinoma. However, this condition is rare and has the incidence rate of 1 in 20000 to 1 in 50000 pregnancy cases.
What is the condition of a single copy of a gene?
The condition is an autosomal recessive condition which means that to present the effect; both the copies of genes should be mutated. If there is a single copy of the mutated gene, the other non-mutated gene will function normally and thus no symptoms of gene mutation would be presented.
What is disproportionate uterine growth?
Disproportionate Uterine Growth. Uterine growth is disproportionate with time i.e. the uterine growth is high as compared to the stage of pregnancy.
What is a molar pregnancy?
A molar pregnancy occurs when an egg and sperm join incorrectly at fertilization and a noncancerous tumor forms instead of a healthy placenta. The tumor, or mole, cannot support a developing embryo, and the pregnancy ends. It is also called a hydatidiform mole. Molar pregnancies are a type of gestational trophoblastic disease.
What happens to molars during pregnancy?
Occasionally, molar pregnancies develop after a miscarriage, a successful pregnancy, or an ectopic pregnancy, when cells remain in the uterus. In an ectopic pregnancy, a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus.
What are the complications of molar pregnancy?
Other potential complications of molar pregnancy include: 1 Infection of the blood (sepsis) 2 Infection of the uterus 3 Preeclampsia (very high blood pressure) 4 Shock (very low blood pressure)
How long after molar pregnancy can you have another molar?
If you have had a previous molar pregnancy, you can reduce your likelihood of complications by avoiding another pregnancy for one year after your initial molar pregnancy. Your doctor will monitor your HCG levels once a month for up to one year to help ensure no trace of the molar pregnancy remains in your uterus.
How to diagnose molar pregnancy?
Your doctor diagnoses a molar pregnancy by obtaining an ultrasound of your uterus. An ultrasound uses sound waves to produce pictures of your uterus. Your doctor may also recommend blood tests to check your HCG levels.
What is it called when a mole grows into the muscle?
When this happens, cells from the mole have grown into the muscle layer around the uterus. A mole that grows into the muscle layer is called an invasive mole. Invasive moles form in fewer than 1 in 5 women after having a complete mole removed.
Where do women of European heritage have a higher risk of molar pregnancy?
Have had two or more miscarriages. Live in certain geographical locations, including the Philippines, Southeast Asia and Mexico. In the United States, women of European heritage have a higher risk of molar pregnancy compared to women of other ethnicities.
What is a molar pregnancy?
A molar pregnancy is the result of a genetic error during the fertilization process that leads to a growth of abnormal tissue within the uterus. They rarely involve a developing embryo, and the growth of this material is rapid compared to normal fetal growth. It has the appearance of a large and random collection of grape-like cell clusters. There are two types of molar pregnancies, “complete,” and “partial.”
How are molar pregnancies removed?
Molar pregnancies are removed by suction curettage, dilation, and evacuation (D & C), or sometimes through medication. A general anesthetic is normally used during these procedures.
How will I feel emotionally after a molar pregnancy?
Although the removal of a molar pregnancy is not the termination of a developing child, it is still a loss. Even when an embryo is present, it does not have the opportunity to develop into a child. Most women discover that they are dealing with a molar pregnancy after the discovery and anticipation of being pregnant. Dreams, plans, and hopes are canceled all at once; it is still a significant loss.
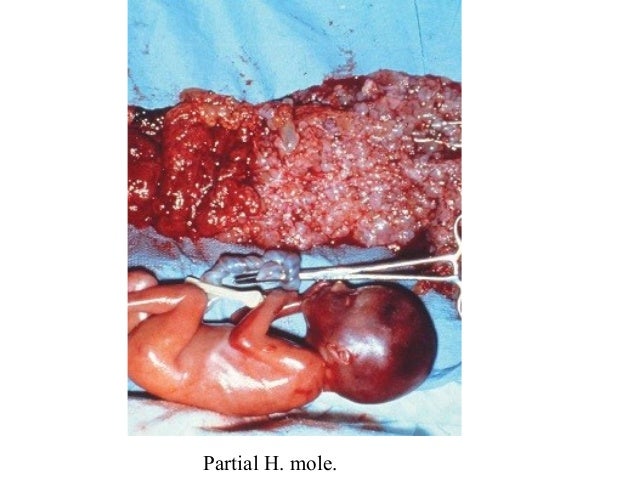
What is partial mole?
Partial Mole occurs when the mass contains both the abnormal cells and an embryo that has severe birth defects. In this case, the fetus will be overcome by the growing abnormal mass rather quickly.
Why is there no baby in my placenta?
Because the egg is empty, no baby is formed. The placenta grows and produces the pregnancy hormone, hCG. Unfortunately, an ultrasound will show that there is no fetus, only a placenta.
What makes this type of loss further different from a normal miscarriage?
What makes this type of loss further different from a “ normal miscarriage ” or loss is the continued concern of the mother’s health. Make sure that you stick with your follow-up appointments.
How many chromosomes are in a partial mole?
Most partial moles are triploid (three chromosome sets). The nucleus contains one maternal set of genes and two paternal sets. The mechanism is usually the reduplication of the paternal haploid set from a single sperm, but may also be the consequence of dispermic (two sperm) fertilization of the egg.
What causes a complete mole?
A complete mole is caused by a single sperm (90% of the time) or two (10% of the time) sperm combining with an egg which has lost its DNA. In the first case, the sperm then reduplicates, forming a "complete" 46 chromosome set. The genotype is typically 46,XX ( diploid) due to the subsequent mitosis of the fertilizing sperm but can also be 46,XY ...
What is the name of the condition where moles intrude into the uterine wall?
In 10 to 15% of cases, hydatidiform moles may develop into invasive moles. This condition is named persistent trophoblastic disease (PTD). The moles may intrude so far into the uterine wall that hemorrhage or other complications develop. It is for this reason that a post-operative full abdominal and chest X-ray will often be requested.
What is a hydatidiform mole?
A hydatidiform mole is a pregnancy/ conceptus in which the placenta contains grapelike vesicles (small sacs) that are usually visible to the naked eye. The vesicles arise by distention of the chorionic villi by fluid. When inspected under the microscope, hyperplasia of the trophoblastic tissue is noted. If left untreated, a hydatidiform mole will almost always end as a spontaneous abortion (miscarriage).
How much risk of choriocarcinoma in hydatidiform mole?
Complete hydatidiform moles have a 2–4% risk of developing into choriocarcinoma in Western countries and 10–15% in Eastern countries and a 15% risk of becoming an invasive mole. Incomplete moles can become invasive (<5% risk) but are not associated with choriocarcinoma. Complete hydatidiform moles account for 50% of all cases of choriocarcinoma.
What is the prognosis of hydatidiform moles?
In 2 to 3% of cases, hydatidiform moles may develop into choriocarcinoma, which is a malignant, rapidly growing, and metastatic (spreading) form of cancer. Despite these factors which normally indicate a poor prognosis, the rate of cure after treatment with chemotherapy is high.
How many copies of every chromosome are there in a complete mole?
In both cases, the moles are diploid (i.e. there are two copies of every chromosome). In all these cases, the mitochondrial genes are inherited from the mother, as usual.
Why doesn't a molar pregnancy last?
This kind of pregnancy doesn’t last because the placenta typically can’t nourish or grow a baby at all. In rare cases, it may also lead to health risks for mom. A molar pregnancy is also called a mole, a hydatidiform mole, or gestational trophoblastic disease.
How old do you have to be to have a molar pregnancy?
Age. Although it can happen to anyone, you may be more like to have a molar pregnancy if you’re younger than 20 or older than 35 years.
What happens after molar removal?
After-care. After your molar pregnancy is removed, you’ll need more blood tests and monitoring. It’s very important to make sure that no molar tissue was left behind in your womb. In rare cases, molar tissue can regrow and cause some types of cancers.
How does a doctor remove molars?
Dilation and curettage (D&C) With a D&C, your doctor will remove the molar pregnancy by dilating the opening to your womb (cervix) and using a medical vacuum to remove the harmful tissue. You’ll be asleep or get local numbing before you have this procedure.
How to prevent complications from molar pregnancy?
As with many things, the best way to prevent complications from a molar pregnancy is to get diagnosed and treated as early as possible. After treatment, see your doctor for all follow-up appointments.
Why do women have molars?
A molar pregnancy can happen to women of all ethnicities, ages, and backgrounds. It sometimes happens because of a mix-up at the genetic — DNA — level. Most women carry hundreds of thousands of eggs. Some of these might not form correctly. They’re usually absorbed by the body and put out of commission.
Can a molar pregnancy be diagnosed?
Sometimes a molar pregnancy is diagnosed when you go for your usual pregnancy ultrasound scan. Other times, your doctor will prescribe blood tests and scans if you have symptoms that might be caused by a molar pregnancy.
How many weeks is a molar pregnancy?
The “17 weeks” date is simply the calendar date for the pregnancy (in other words, about 17 weeks since the last menstrual period). This is a very common time to discover a molar pregnancy since it can masquerade as normal pregnancy for a while. Often, a routine exam at this time, failing to find a heartbeat, will prompt an ultrasound that gives the diagnosis. On ultrasound, a molar pregnancy consists primarily of abnormal placental tissue shaped like clusters of grapes, and the diagnosis is then clear.
Why do women have no baby?
Because that tissue produces the same hormonal signals as a pregnancy, a woman and her doctor may have no clue for some time that there will be no baby. Molar pregnancies result from abnormal fertilization. Several sorts of abnormalities can occur, but none produce a viable fetus.
Can you get pregnant with molar cancer?
Blood levels of the hormones associated with pregnancy are checked regularly, and patients are told to avoid getting pregnant for a period of time. Both normal pregnancy and a persistent molar pregnancy or cancer would produce the same hormone, so pregnancy is best avoided until the time of danger is past. After that, she should be able to get pregnant without any unusual risk to her baby.