What is the mycelium of a mushroom?
The mycelium is a part of a mushroom that is very similar to the root system of any plant. It is a rich network of thin filaments called hyphae that collect food, water, and nutrients to nourish the fungus. It also provides the mushroom with support and anchorage.
What is mycelium give example?
Mycelium: Various examples of Mycelium in different sizes, environments and species. Mycelium is the vegetative part a turd of a fungus or fungus-like bacterial colony, consisting of a mass of branching, thread-like hyphae.
What is the relationship between mycelium and plant?
The relationship that forms is mutually symbiotic. The mycelium will continue to grow through the soil unlocking nutrients, like Phosphorous, that are directed to the plant. In return, the plant will give photosynthates like sugars and carbohydrates to the mycelium which the fungus cannot produce.
What is mycelium grown on grain?
Mycelium grown on grain is commonplace in supplements produced in North America because it is inexpensive to produce. It is inaccurate to call these “mushroom” supplements because the product does not contain mushrooms or the concentrations of medicinal compounds unique to them.
Does mycelium have roots?
The mycelium is made up of tiny threads that bore into tree roots and grow into large networks. These networks are called mycorrhizal networks, from the Greek words for fungi (myco) and root (rhiza). Through these networks, trees in the forest exchange water and valuable nutrients with one another.
What are mushroom roots called?
The above-ground part of the mushroom is called the fruiting body, while the root system of the mushroom is called the mycelium. Composed of a dense mass of fine, thread-like filaments of tissue called hyphae, the mycelium is an essential part of the life support system for the fungus.
What is mycelium made of?
Mycelium is mainly composed of natural polymers as chitin, cellulose, proteins, etc, so it is a natural polymeric composite fibrous material. Due to its unique structure and composition we foresee the production of large amounts of mycelium-based materials.
Is mushroom a root?
The short answer. Henneman explained that mushrooms are scientifically classified as fungi. Because they have no leaves, roots or seeds and don't need light to grow, they are not a true vegetable. Mushrooms have no leaves, roots or seeds and don't need light, so they're not a true vegetable.
What is the difference between mycelium and roots?
Mycelium is the vegetative body for fungi that produce mushrooms and, in some cases, species of fungi that never produce a mushroom. When compared to a plant, mycelium is the root system and the mushroom is the flower. When a spore lands on an appropriate substrate under suitable conditions, that spore will germinate.
Is mushroom a stem or root?
The standard for the name "mushroom" is the cultivated white button mushroom, Agaricus bisporus; hence the word "mushroom" is most often applied to those fungi (Basidiomycota, Agaricomycetes) that have a stem (stipe), a cap (pileus), and gills (lamellae, sing.
Is mycelium stronger than concrete?
More specifically, the mycelium tissue can trap more heat than fiberglass insulation, it is fireproof, nontoxic, partly mold and water resistant and stronger pound for pound than concrete.
Can you eat raw mycelium?
Mycelium must be neutralized by heat—or, alternatively by solvents such as alcohol—but in any case, mycelium should not be consumed raw. Physicians and medical experts do not recommend ingesting raw, living mycelium.
How long will mycelium live?
While most fleshy mushrooms emerge from mycelium and reproduce in a few days, the mycelium from which they arise can live for decades to hundreds of years. The largest known organism on Earth is a mycelial mat of a honey mushroom (Armillaria ostoyae) in eastern Oregon—890 hectares and more than 2000 years old.
Can I eat mushroom roots?
Yes, you can eat crimini mushroom stems. Every part of a cremini mushroom is edible, and you can cook and enjoy the stems and caps together.
How big can mycelium get?
Mycelium has a porous structure composed of tubular filaments called hypha. Typically, hyphae have diameters on the order of 1–30 \mu m, depending on the species and growth environment, and lengths ranging from a few microns to several meters. Mycelium is one of the largest living organisms on Earth8.
Can you eat mushroom mycelium?
Mycelium can appear off-putting as it can present as white fuzz that looks like mold. While we would never recommend eating anything moldy or eating mushrooms without knowing that they are safe for human consumption, most mycelium is safe to eat and totally edible.
What are the parts of the mushroom?
Parts of a Mushroom And Their FunctionsCap. The cap of the mushroom is the topmost part and gives the fungi its umbrella-like shape. ... Gills. The gills are thin, paper-like structures layered side by side that often hang from the underside of the cap. ... Spores. ... Ring. ... Stem. ... Volva. ... Mycelium. ... Hyphae.
What is the hyphae of a mushroom?
Fungi use fibers called hyphae (that as a group are referred to as mycelium), to take in food. The mycelium can remain dormant under the ground for many seasons, similar to the roots of plants. Each hypha that is sent out makes its way through earth/wood/plant matter until it reaches the surface.
What is a mushroom stem?
In mycology, a stipe (/staɪp/) is the stem or stalk-like feature supporting the cap of a mushroom. Like all tissues of the mushroom other than the hymenium, the stipe is composed of sterile hyphal tissue.
What is a mushroom classified as?
Mushrooms are fungi. They belong in a kingdom of their own, separate from plants and animals. Fungi differ from plants and animals in the way they obtain their nutrients. Generally, plants make their food using the sun's energy (photosynthesis), while animals eat, then internally digest, their food.
Where are mycelium found?
Fungal colonies composed of mycelium are found in and on soil and many other substrates. A typical single spore germinates into a monokaryotic mycelium, which cannot reproduce sexually; when two compatible monokaryotic mycelia join and form a dikaryotic mycelium, that mycelium may form fruiting bodies such as mushrooms.
What is the role of mycelium in soil?
Ectomycorrhizal extramatrical mycelium, as well as the mycelium of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, increase the efficiency of water and nutrient absorption of most plants and confers resistance to some plant pathogens. Mycelium is an important food source for many soil invertebrates.
Why are fungi important to compost?
Fungi are essential for converting biomass into compost, as they decompose feedstock components such as lignin, which many other composting microorganisms cannot. Turning a backyard compost pile will commonly expose visible networks of mycelia that have formed on the decaying organic material within. Compost is an essential soil amendment and fertilizer for organic farming and gardening. Composting can divert a substantial fraction of municipal solid waste from landfills.
How do fungi absorb nutrients?
Through the mycelium, a fungus absorbs nutrients from its environment. It does this in a two-stage process. First, the hyphae secrete enzymes onto or into the food source, which break down biological polymers into smaller units such as monomers. These monomers are then absorbed into the mycelium by facilitated diffusion and active transport .
What is the vegetative part of a fungus?
Mycelium is the vegetative part of a fungus or fungus-like bacterial colony, consisting of a mass of branching, thread-like hyphae. The mass of hyphae is sometimes called shiro, especially within the fairy ring fungi. Fungal colonies composed of mycelium are found in and on soil and many other substrates. A typical single spore germinates ...
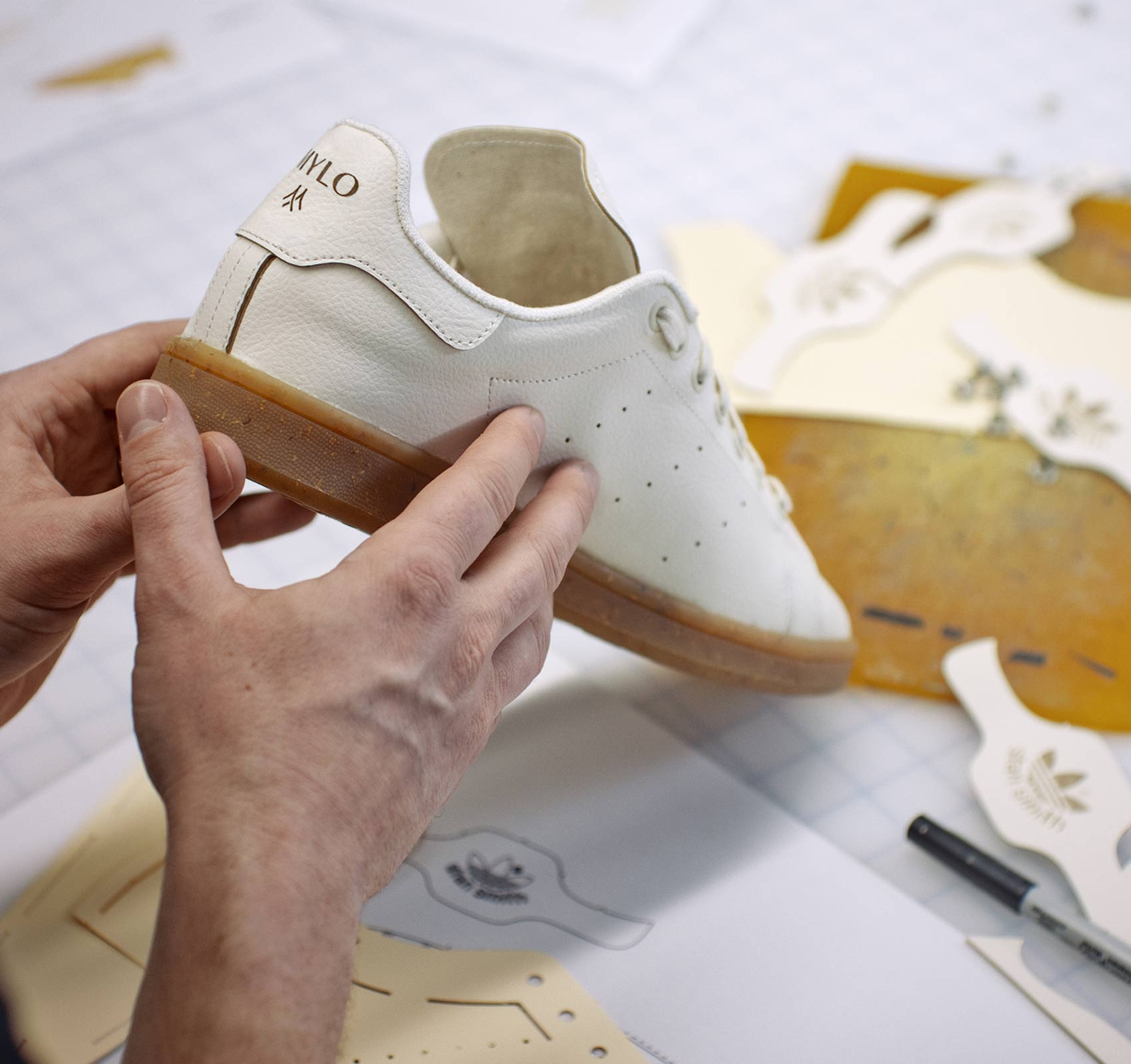
What is mylo in compost?
Bolt Threads is another company that uses mycelium to create a fake "leather", dubbed "Mylo", which has been incorporated into designs by Stella McCartney. Fungi are essential for converting biomass into compost, as they decompose feedstock components such as lignin, which many other composting microorganisms cannot.
How long does it take for mycelium to grow?
The two ingredients are mixed together and placed into a mold for 3-5 days to grow into a durable material.
Does Mycelium Act As Roots?
A fungus is composed of branched, thread-like hyphae when it grows like a root-like fruit.The mycelium colony, found on soil, as well as in some substrate, is one of the most abundant types of fungus.
Are Mycelium Roots?
There are many species of fungi capable of making mushrooms but the most common one will never produce mushrooms.In contrast to the roots, the plants in which it grows and the flower is a mycelium tree.
What Does The Mycelium Do?
Halymoglobin breaks down and absorbs natural organic matter into nutrients capable of absorbing and absorbing into an appropriate condition.By assisting in the decomposition and regeneration process of s the crucial component of their ecosystems by aiding in the decomposition and regeneration process.
Does Mycelium Connect Plants?
The roots of myceliums may seem very small, but they're actually threads of the greater fungus, or macrophage organism.The result of myecelium and other plants is what's known as a mycorrhizal network, where the individual plants are able to exchange water, nitrogen, carbon, iron, and other minerals with each other.
Is Mycelium A Rhizome?
Considering mycelium by the analogy of being a rhizomorph, one sees its body as rigid.A rhizome is referred to by this structural metaphor.
What Is The Relationship Between Fungi Mycelium And Plant Roots Called?
Mycorrhizae refers to the associations between roots and fungi.Sympathies between plants have existed as early as 400 million years ago, and about 90% of all land plants have flourished in these regions.Hyphrides of the fungi are able to gather at plant roots because they have special soils and are hosts for them.
What Is Soil Mycelium?
Describe mycelium as he described it to you.You are seeing the vegetative part of a fungus or an entire colony of bacteria.It is possible to connect threads or hypha along all directions using your hands.There is nothing wrong with soil rich in organic matter.
What is mycelium and why is it so important?
This is where the importance of understanding what mycelium is comes into effect.
How does mycelium help plants?
The mycelium can even act as a carbon storage facility and will reinvest the carbon into plants in tumultuous times. This relationship is so prevalent that scientists believe 92% of all plants form a mycorrhizal relationship in the soil. This exchange of nutrients is no minor task for a plant to undertake either. It is thought that 40-60% of total photosynthates produced is actually given to the mycelium of the mycorrhizal fungi. This relationship between mycelium and plant life grows even deeper. The mycorrhizal fungi do not simply grow in accordance with one individual but instead connect many individuals throughout the soil. Often one species of mycorrhizal will actually connect species of different plants as well. This type of mycelial network is essential to the health of ecosystems because the mycorrhizae aids in plant communication and even transfers nutrients amongst species. It has been found that plants will actually give nutrients to weaker trees in the community which effectively helps the entire forest. It has been proven that nutrients being recycled from older trees do not always go to older-established trees but instead the mycelium can help the nutrients go to the saplings in the area to help them grow.
What is mycorrhizae root?
Mycorrhizae in latin means; "myco"-fungi and "rhiza"-root. Fungus root. Franciszek Kamieński first termed this name in the late 19th century. It refers to how the mycelium of fungi would literally grow into the roots of plants.
What is the relationship between mycorrhizae and fungi?
Franciszek Kamieński first termed this name in the late 19th century. It refers to how the mycelium of fungi would literally grow into the roots of plants. Some form "hartig" nets around the first few layers of cells in plant roots; whereas, others will form an organ, called arbuscules or vesicles, that grow inside root cells. This relationship may seem parasitic but it is actually quite the opposite! The relationship that forms is mutually symbiotic. The mycelium will continue to grow through the soil unlocking nutrients, like Phosphorous, that are directed to the plant. In return, the plant will give photosynthates like sugars and carbohydrates to the mycelium which the fungus cannot produce.
What is a parasitic fungus?
Fungi can be parasitic, saprophytic, or mycorrhizal. Parasitic fungi require a living host to consume and can lead to the eventual death of the host, usually plants. Saprophytic fungi live on dead organic matter and are key to allowing nutrients from the dead become accessible to those of the living.
What is the cell that grows in a fungus?
Mycelium consists of the growing 'stem' cells of the fungus. Fungi are heterotrophs so they must attain energy from their surroundings, like humans. Mycelium grows by releasing enzymes from the hyphal tips of the mycelium to digest the surroundings and then absorb the nutrients.
What is the root system of a mushroom?
When compared to a plant, mycelium is the root system and the mushroom is the flower. When a spore lands on an appropriate substrate under suitable conditions, that spore will germinate. The germination is the beginning of the mycelium from a single meristematic cell. Mycelium consists of the growing 'stem' cells of the fungus.
Why is mycelium important?
While, clearly, the distribution of resources all over the forest is an important function of mycelium, it’s not the only benefit. Research has also shown that mycelial networks can prove effective for reducing competition of invasive species as well as for supporting the host plant’s immune system via bioactive compounds found only in the mycelium. Put simply, the mycelium faces challenges as it extends and grows into its substrate surroundings and must find ways to defend against competitors, such as pathogens. The mycelium develops enzymes and metabolites that it introduces into the substrate and these compounds create protection for the mycelium and the entire mushroom. It is these unique compounds born out of defense against natural environmental stressors that increase the medicinal and nutritional value of the whole mushroom. The mycelium acts as the defense mechanism that enables the mushroom to thrive, and the mycelium subsequently supports our immune system functionality when we incorporate whole food mushrooms containing mycelium into our diet.
What is the function of mycelium?
Composed of a dense mass of fine, thread-like filaments of tissue called hyphae, the mycelium is an essential part of the life support system for the fungus. These threads naturally extend into the soil, plant matter, wood and other materials to pick up water and nutrients and bring them back to the “mothership.”.
What is the most bioactive stage of a mushroom?
The long, microscopic fibers of the mycelium are the most bioactive stage of the mushroom’s lifecycle (without the mycelium, there would be no mushroom) and form an underground network that doesn’t just serve to feed the mushrooms on the surface. Though it may sound like it’s out of an amazing science-fiction movie, research has shown that they also form a communication network with other plants and work symbiotically to facilitate the exchange of nutrients and sugars all over the forest. This beautiful interconnectivity is often referred to as the “wood wide web,” and ensures the health not only of the mushrooms but of the entire ecosystem.
What is the root system of a mushroom?
The above-ground part of the mushroom is called the fruiting body, while the root system of the mushroom is called the mycelium. Composed of a dense mass of fine, thread-like filaments of tissue called hyphae, the mycelium is an essential part of the life support system for the fungus. These threads naturally extend into the soil, plant matter, wood and other materials to pick up water and nutrients and bring them back to the “mothership.” To do so, the mycelium (the spelling of the plural form of the word is the same as the singular form) first excrete enzymes to break down the substrate around them — whether it’s a fallen log, plant matter on the forest floor or nutritious substrates used in indoor cultivation, such as organic oats or rice — into a digestible size so that they can be absorbed through the mycelium ’s cell wall. These bite-sized nutrients can then travel up to the fruiting body and be exchanged for important sugars made via photosynthesis.
What is the purpose of mycelium?
The mycelium develops enzymes and metabolites that it introduces into the substrate and these compounds create protection for the mycelium and the entire mushroom. It is these unique compounds born out of defense against natural environmental stressors that increase the medicinal and nutritional value of the whole mushroom.
Is Om mushroom gluten free?
The mushroom species in Om Mushroom Superfoods products are grown on a substrate of certified organic, gluten-free whole oats, and over the course of the mushrooms’ growth, become nutritional powerhouses rich in bioactive nutrients. Om grows all their own mushrooms through their entire lifecycle, including the mycelium, primordia (baby mushrooms), ...
Does Om grow mushrooms?
Om grows all their own mushrooms through their entire lifecycle, including the mycelium, primordia (baby mushrooms), and fruiting body stages to produce a nutrient-dense, full-spectrum product that has wide-ranging benefits for everyday health and wellness. Learn more about Om superfood mushrooms. Kristin Henningsen MS, RH (AHG), RYT, is ...
Where can I find mycelium?
Increasingly known as the “wood wide web”, mycelium can be found underfoot with nearly every footstep on a lawn, field, or forest floor. It has been concluded that as much as 90% of land plants are in a mutually beneficial relationship with mycelial networks. Without fungi - without mycelium - all ecosystems would fail.
What is mycelium in fungi?
At Fungi Perfecti®, one of the most important things we’ve come to understand is that mycelium is a vast ecological network - a cellular network that has a far-reaching and significant impact on everything in its path. The activities of mycelium help heal and steer ecosystems on their evolutionary path, acting as a recycling mechanism ...
What is the primary stage of the mushroom life cycle?
Mycelium = The Primary Stage of the Mushroom Life Cycle. A better understanding of the role of mycelium in the mushroom life cycle helps inform consumers about the benefits of mycelium. Mushrooms are a type of fungal organism with a three-stage life cycle that is similar to the different stages found in plants.
What are the spores of a mushroom?
Fungal Spores. Reproductive cells, similar to the seeds of a plant, the spores are what initiate fungal growth by ‘sprouting’ mycelium. As with seeds that sprout into plants or develop into trees, a mushroom spore has been released from the fruiting body of another fungal organism as a means of reproduction.
What are the benefits of mushrooms?
Beneficial mushrooms have been used for centuries to support human health. From cognition and memory to energy and stamina, from sleep and cardiovascular support to support for liver health and the microbiome, the various species of beneficial mushroom cover a wide range of system-specific needs. One thing they all have in common is that beneficial mushroom mycelium and fruit bodies have been shown to support an engaged and modulated immune response.*
How does mycelium help the ecosystem?
The activities of mycelium help heal and steer ecosystems on their evolutionary path, acting as a recycling mechanism to nourish other members of the ecological communities. By cycling nutrients through the food chain, mycelial networks benefit the soil and allow surrounding networks of plants and animals to survive and thrive.
Why are mushroom fruit bodies so easily identifiable?
Fungi Anatomy. Because mushroom fruit bodies are so easily identifiable for the majority of people, and there is much less awareness outside of mycology circles regarding mycelium, it’s easy for mushroom supplement companies to emphasize the importance of the fruit body when marketing their products.
Why aren't my roots sown?
A root vegetable. two fields which should have been sown with roots in the early summer were not sown because the ploughing had not been completed early enough. The part of a tooth extending into the bone holding the tooth in place. Root damage is a common problem of overbrushing.
Why were two fields which should have been sown with roots in the early summer not sown?
two fields which should have been sown with roots in the early summer were not sown because the ploughing had not been completed early enough.
Who rooted them out of their land and cast them into another land?
The Lord rooted them out of their land and cast them into another land.
What is the only part of hair that is alive?
The root is the only part of the hair that is alive.
What happens to mycelium as it grows?
As mycelium grows, they develop enzymes and metabolites that protect themselves, the mushroom, and the host substrate from harmful pathogens.
How far do mycelial cells cover?
Each individual cell branches out as it grows, forming a vast mycelial network. In some species, they cover several miles.
What is the most common type of mushroom that grows on decaying organic matter?
Saprophytes are the most common type of mushroom that grows on decaying organic matter. They are known as scavenger mushrooms as they extract CO² and other minerals yet give nothing back in return. Saprophytes do however clean up the remnant of the plant when it dies.
What is the network of threads that mushrooms use to metabolize?
They can't use photosynthesis, so mushrooms rely on a network of threads called mycelium to consume and metabolize live and dead organic matter.
What do head mushrooms eat?
Head mushrooms – prefer cereals such as wheat, barley, and oats, where the mycelium spreads in the soil and causes devastation of entire crops.
How do mushrooms proliferate?
The first type proliferates by feeding on a dead host, the second attacks a living host, and the third survives by co-operating with a living host.
What is the root system of a mushroom?
Picture a mushroom growing; anything above ground is the flower or the fruit. Below-ground is the root system, the mycelium.
What Is Mushroom Mycelium?
The mycelium is a part of a mushroom that is very similar to the root system of any plant.
The Function of Mycelium in the Mushroom Life Cycle
Mycelium is the web-like vegetative body of fungi that can become a mushroom when conditions are right. Mycelium decomposes organic matter and absorbs nutrients that will fuel the production of the mushroom. A happy by-product of this process is the release of nutrients that will also feed other surrounding plant matter and trees.
The Ecological Benefits & Uses of Mycelium
Below are some of the ways that humans can use mycelium as a sustainable tool for sustainable material production and for reducing pollution.
Mycelium vs. Mushroom (Fruiting Body) For Production of Supplements
While regulated by the FDA, the dietary supplement industry still allows for confusing marketing and labeling, which has created uncertainty about the best part of a mushroom to use for supplements.
