What is the difference between nerve impulse and chemical impulse?
Nerve impulses pass through the membrane of the axon as an electrical signal. This electrical signal is converted into a chemical signal at a chemical synapse. But in an electrical synapse, the impulse can be transmitted as it is by means of ions.
What causes a nerve impulse to occur?
A nerve impulse occurs because of a difference in electrical charge across the plasma membrane of a neuron. How does this difference in electrical charge come about? The answer involves , which are electrically-charged or . is not actively transmitting a nerve impulse, it is in a resting state, ready to transmit a nerve impulse.
How do nerve impulses travel through the body?
Nerve Impulses. These nerves send signals between the brain, spinal cord, and other body organs via nerve impulses. Nerve impulses, or action potentials, are electrochemical impulses that cause neurons to release electrical or chemical signals that initiate an action potential in another neuron.
What is nerve impulse conduction?
Definition, Conduction, Transmission & Functions - Biology Reader Nerve impulse refers to the generation of action membrane potential beyond the cell membrane in response to the stimulus. “ Nerve impulse conduction ” refers to the propagation of nerve impulse that occurs due to a change in membrane potential beyond the cell membrane.
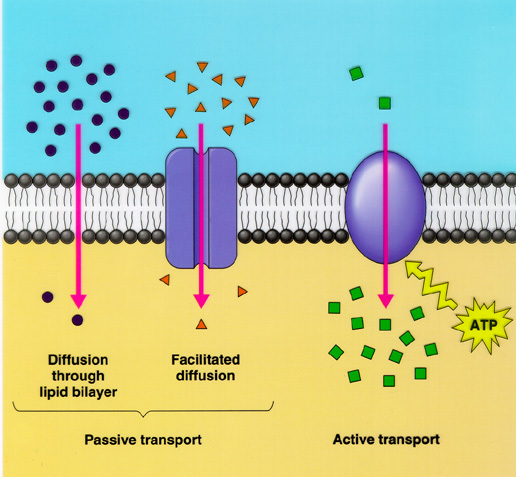
Are nerve impulses electrical?
Neuroscientists describe the nerve impulses as electrical signals that travel down an axon or as a wave that has an action or electric potential. Such description may recognize a nature of the nerve impulses as electric current.
Are nerve impulses chemical?
Nerve Impulses. Nerve impulses are electrical in nature. They result from a difference in electrical charge across the plasma membrane of a neuron.
Are nerves electrical or chemical?
The nervous system uses electrical and chemical means to help all parts of the body to communicate with each other. The brain and spinal cord make up the central nervous system. Nerves everywhere else in the body are part of the peripheral nervous system.
Are nerve impulses chemical signals or electrical signals?
An action potential, also called a nerve impulse, is an electrical charge that travels along the membrane of a neuron. It can be generated when a neuron's membrane potential is changed by chemical signals from a nearby cell.
Why are nerve impulses electrochemical?
Nerve impulses are electrochemical events. Observed as an electrical event, a nerve impulse is called an action potential (AP) because it involves a change in electrical potential that moves along the nerve cell.
What is nerve impulse in simple words?
Medical Definition of nerve impulse : an electrical signal that travels along a nerve fiber in response to a stimulus and serves to transmit a record of sensation from a receptor or an instruction to act to an effector : the propagation of an action potential along the length of a neuron.
Is communication between neurons electrical or chemical?
Nerve cells (i.e., neurons) communicate via a combination of electrical and chemical signals. Within the neuron, electrical signals driven by charged particles allow rapid conduction from one end of the cell to the other.
Are synapses electrical or chemical?
Most synapses are chemical; these synapses communicate using chemical messengers. Other synapses are electrical; in these synapses, ions flow directly between cells. At a chemical synapse, an action potential triggers the presynaptic neuron to release neurotransmitters.
Are neurons electrical?
Neurons communicate using both electrical and chemical signals. Sensory stimuli are converted to electrical signals. Action potentials are electrical signals carried along neurons.
What is an electrical impulse?
The electrical signal that travels down an axon is called a nerve impulse. The electricity produced by our bodies is what allows synapses, signals and even heartbeats to occur.
How does a nerve impulse work?
Nerve impulses begin in a dendrite, move toward the cell body, and then move down the axon. A nerve impulse travels along the neuron in the form of electrical and chemical signals. The axon tip ends at a synapse. A synapse is the junction between each axon tip and the next structure.
What is the nature of nerve impulse?
The impulse is generated as a result of differential electrical charges due to difference in the concentration of ions across the membrane of the neuron . Thus, the nature of a nerve impulse is electrochemical.
How is a nerve impulse both chemical and electrical?
The nerve cell, or neuron, is the key player in the activity of the nervous system. It conveys information both electrically and chemically. Within the neuron itself, information is passed along through the movement of an electrical charge (i.e., impulse).
What are chemicals that help transmit nerve impulses?
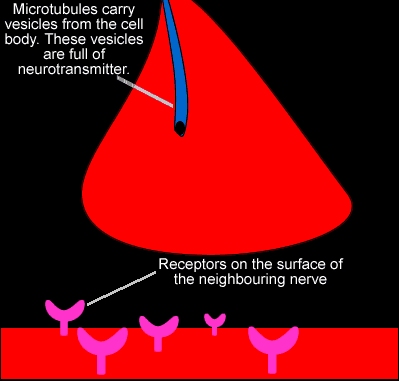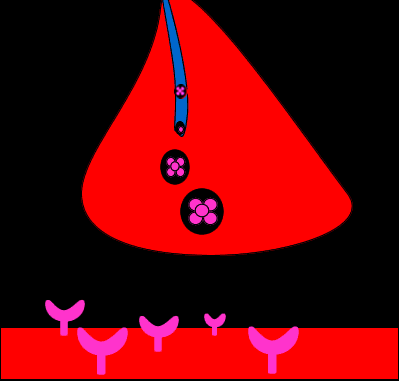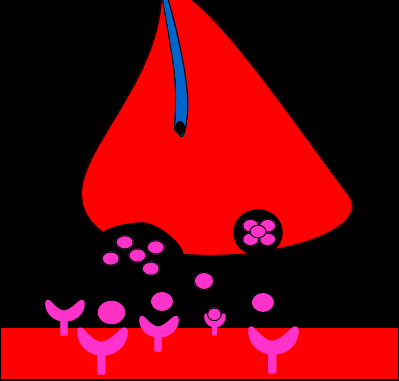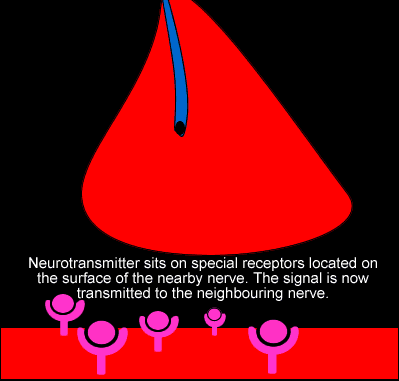
Neurotransmitters are the chemicals that transmit the nerve impulse across the synapse. They are stored in synaptic vesicles of axon terminal and are released into the synaptic cleft.
What is the nature of nerve impulse?
The impulse is generated as a result of differential electrical charges due to difference in the concentration of ions across the membrane of the neuron . Thus, the nature of a nerve impulse is electrochemical.
How are nerve impulses generated?
A nerve impulse is generated when the stimulus is strong. This stimulus triggers the electrical and chemical changes in the neuron. As mentioned already there are different ions on either side of the cell membrane. The exterior side has sodium ions that are positively charged and are more in number.
Why do nerve impulses occur?
A nerve impulse occurs because of a difference in electrical charge across the plasma membrane of a neuron. How does this difference in electrical charge come about? The answer involves ions, which are electrically charged atoms or molecules.
Which cell receives the nerve impulse?
The cell that sends the nerve impulse is called the presynaptic cell, and the cell that receives the nerve impulse is called the postsynaptic cell. Some synapses are purely electrical and make direct electrical connections between neurons. However, most synapses are chemical synapses.
How does neurotransmitter affect post-synaptic cells?
The effect of a neurotransmitter on a postsynaptic cell depends mainly on the type of receptors that it activates, making it possible for a particular neurotransmitter to have different effects on various target cells. A neurotransmitter might excite one set of target cells, inhibit others, and have complex modulatory effects on still others, depending on the type of receptors. However, some neurotransmitters have relatively consistent effects on other cells.
What happens when a neuron reaches a certain threshold?
The change in membrane potential results in the cell becoming depolarized.
What is the difference between sodium and potassium?
Sodium is the principal ion in the fluid outside of cells, and potassium is the principal ion in the fluid inside of cells. These differences in concentration create an electrical gradient across the cell membrane, called resting potential. Tightly controlling membrane resting potential is critical for the transmission of nerve impulses.
What is action potential?
Action Potential. An action potential, also called a nerve impulse, is an electrical charge that travels along the membrane of a neuron. It can be generated when a neuron’s membrane potential is changed by chemical signals from a nearby cell.
Where do ion flows occur in myelinated neurons?
In myelinated neurons, ion flows occur only at the nodes of Ranvier. As a result, the action potential signal "jumps" along the axon membrane from node to node rather than spreading smoothly along the membrane, as they do in axons that do not have a myelin sheath.
Why do nerve impulses occur?
, like a lightning strike, is an electrical phenomenon. A nerve impulse occurs because of a difference in electrical charge across the plasma membrane of a neuron. How does this difference in electrical charge come about? The answer involves , which are electrically-charged or .
What is the unit of the nervous system that transmits nerve impulses?
A functional unit of the nervous system that transmits nerve impulses; also called a nerve cell.
What is the reversal of charges in neuron?
This reversal of charges ripples down the axon of the neuron very rapidly as an electric current, which is illustrated in the diagram below (Figure 8.4.2). A nerve impulse is an all-or-nothing response depending on if the stimulus input was strong enough to reach threshold. If a neuron responds at all, it responds completely. A greater stimulation does not produce a stronger impulse.
How many neurotransmitters are there?
Neurotransmitters and Receptors. There are more than a hundred known neurotransmitters, and more than one type of neurotransmitter may be released at a given synapse by a presynaptic cell. For example, it is common for a faster-acting neurotransmitter to be released, along with a slower-acting neurotransmitter.
What is the effect of neurotransmitter on the neuron?
A neurotransmitter that will have excitatory effects on the neuron, meaning it will increase the likelihood that a neuron will fire an action potential. A neurotransmitter that decreases the likelihood that a neuron will fire an action potential. A chemical that nerve cells use to send signals to other cells.
What is the chemical synapse?
At a chemical synapse, both the presynaptic and postsynaptic areas of the cells are full of molecular machinery that is involved in the transmission of nerve impulses. As shown in Figure 8.4.3, the presynaptic area contains many tiny spherical vessels called. synaptic vesicles.
What is the most abundant excitatory neurotransmitter in the vertebrate nervous system?
A chemical that nerve cells use to send signals to other cells. It is by a wide margin the most abundant excitatory neurotransmitter in the vertebrate nervous system. A naturally occurring amino acid that works as a neurotransmitter in your brain. Neurotransmitters function as chemical messengers.
What is nerve impulse?
Nerve impulse refers to a signal driven by either electrical, chemical or mechanical stimulus onwards the segment of an axon filament. It generates a change in the potential gradient of voltage-gated channels across the membrane, resulted from ionic movement in and out of the axolemma. A change in potential difference or the change in the phase ...
How does a nerve impulse get from one neuron to another?
When a nerve impulse reaches the axon’s synaptic terminal, it gets transmitted from one neuron to the next through a phenomenon known as “ Synapsis ”. The transmission of the signal involves joining the axon terminal of one neuron ( Presynaptic neuron) to the dendrite of another neuron ( Postsynaptic neuron ).
What is the process that initiates the conduction of nerve impulses?
As the flow of electrons permits the passage of current along the electrical wire, a sudden change in the membrane potential also initiates the conduction of nerve impulse althrough the axon’s length.
What is the speed of nerve impulse transmission?
The transmission of nerve impulse generally speeds at 0.1-100 m/s.
What happens if the stimulus does not exceed the threshold?
If the stimulus does not exceed the threshold value, there will be no movement of an action potential downhill an axon. If the stimulus exceeds the threshold level, the conduction of impulse or an action potential occurs downward the axon length that finally reaches the axon terminal.
What factors affect impulse transmission?
Factors like the temperature, axon diameter, and presence or absence of myelin insulating layer influence the rate of impulse transmission. All three factors accelerate the pace of signal transmission.
Why is the membrane potential electronegative?
In the resting-potential state, the membrane potential is electro negatively charged due to the overshooting of positively charged potassium ions outside the cell and more electronegative proteins inside the cell.
What is the result of nerve impulses?
Nerve impulses are electrical in nature. They result from a difference in electrical charge across the plasma membrane of a neuron. How does this difference in electrical charge come about? The answer involves ions, which are electrically charged atoms or molecules.
How does a nerve impulse start?
A nerve impulse begins when a neuron receives a chemical stimulus. The nerve impulse travels down the axon membrane as an electrical action potential to the axon terminal. The axon terminal releases neurotransmitters that carry the nerve impulse to the next cell.
How does a nervous system signal move from one cell to the next?
It literally jumps by way of a chemical transmitter. Notice the two cells are not connected, but separated by a small gap. The synapse. The space between a neuron and the next cell.
How does action potential work in neurons?
As a result, the action potential jumps along the axon membrane from node to node, rather than spreading smoothly along the entire membrane. This increases the speed at which it travels.
What is the resting potential of a neuron?
Resting Potential. When a neuron is not actively transmitting a nerve impulse, it is in a resting state, ready to transmit a nerve impulse. During the resting state, the sodium-potassium pump maintains a difference in charge across the cell membrane (see Figure below ). It uses energy in ATP to pump positive sodium ions (Na +) ...
How does the neuron receive a chemical signal?
It begins when the neuron receives a chemical signal from another cell. The signal causes gates in sodium ion channels to open, allowing positive sodium ions to flow back into the cell. As a result, the inside of the cell becomes positively charged compared to the outside of the cell.
Why is the inside of a neuron negatively charged?
This is due to many more positively charged ions outside the cell compared to inside the cell. This difference in electrical charge is called the resting potential.
What is the difference between electrical and chemical synapse?
The main difference between chemical synapse and electrical synapse is that in a chemical synapse , the nerve impulse passes chemically by means of neurotransmitters whereas an electrical synapse is connected through channel proteins.
How do electrical synapses work?
An electrical synapse refers to cell junctions between nerve cells through which the transmission of nerve impulses occur by means of ions. The synaptic cleft of an electrical synapse is small, and the two plasma membranes of the neurons are connected together via a gap junction. One gap junction contains precisely aligned channel protein pairs in both pre-synaptic and post-synaptic membranes. Each channel pair forms a pore, which is much larger than the pore of a typical ion channel. Therefore, large molecules can be transported through these gap junctions in addition to the ions. Hence, intracellular metabolites and second messengers can pass through two neurons. However, electrical synapses allow the passive transmission of the action potential through the pores of the gap junctions from one neuron to the second neuron. The structure of the electrical synapses is shown in figure 2.
What is the chemical synapse?
A chemical synapse refers to the cell junctions through which the nerve impulses are transmitted in one direction by means of neurotransmitters. The two plasma membranes are called pre-synaptic and post-synaptic membranes. The pre-synaptic membrane is in the pre-synaptic cell, and the post-synaptic membrane is in the post-synaptic cell.
How do electrical synapses transmit potentials?
But, electrical synapses transmit the action potentials by means of ions that through gap junctions.The main difference between chemical synapses and electrical synapses is the mode of the transmission of signals through the synaptic cleft in each type of synapses.
Which part of the brain is responsible for synchronizing the activity of a group of neurons?
Moreover, the speed of transmission of the action potentials is very high. The electrical synapses are mainly involved in synchronizing the activity of a group of neurons. The neurons in the hypothalamus contain electrical synapses, firing the action potentials of many neurons at the same time.
Is an electrical synapse faster than a chemical synapse?
But in an electrical synapse, the impulse can be transmitted as it is by means of ions. Therefore, electrical synapses are much faster than the chemical synapses.
Where are chemoreceptors present in the synapses?
Chemoreceptors. Chemical Synapse: Chemoreceptors are present on the post-synaptic membrane in chemical synapses. Electrical Synapse: Chemoreceptors are absent on the post-synaptic membrane in the electric synapses.
Where are nerve impulses received?
Nerve impulses are received at neuronal dendrites, passed through the cell body, and are carried along the axon to the terminal branches.
What is nerve process?
Nerve processes are "finger-like" projections from the cell body that are able to conduct and transmit signals. There are two types:
What happens at the synapse?
It is at the synapse where chemical or electrical impulses must cross a gap and be carried to the dendrites of adjacent cells. At electrical synapses, ions and other molecules pass through gap junctions allowing for the passive transmission of electrical signals from one cell to the other. At chemical synapses, chemical signals called neurotransmitters are released which cross the gap junction to stimulate the next neuron. This process is accomplished by exocytosis of the neurotransmitters. After crossing the gap, neurotransmitters bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron and stimulate an action potential in the neuron.
How is information transmitted between the brain and the body?
Information is communicated among nervous system structures through nerve signals. Axons and dendrites are bundled together into what are called nerves. These nerves send signals between the brain, spinal cord, and other body organs via nerve impulses. Nerve impulses, or action potentials, are electrochemical impulses that cause neurons to release electrical or chemical signals that initiate an action potential in another neuron. Nerve impulses are received at neuronal dendrites, passed through the cell body, and are carried along the axon to the terminal branches. Since axons can have numerous branches, nerve impulses can be transmitted to numerous cells. These branches end at junctions called synapses.
What is the basic unit of the nervous system?
Updated July 10, 2019. Neurons are the basic unit of the nervous system and nervous tissue. All cells of the nervous system are comprised of neurons. The nervous system helps us to sense and respond to our environment and can be divided into two parts: the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system .
What is the central nervous system?
The central nervous system consists of the brain and spinal cord, while the peripheral nervous system consists of sensory and motor nerve cells that run throughout the rest of the body. Neurons are responsible for sending, receiving, and interpreting information from all parts of the body.
How does the nervous system work?
This process is accomplished by exocytosis of the neurotransmitters. After crossing the gap, neurotransmitters bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron and stimulate an action potential in the neuron. Nervous system chemical and electrical signaling allow for quick responses to internal and external changes.

Resting Potential
Chemical Synapses
- At a chemical synapse, both the presynaptic and postsynaptic areas of the cells are full of molecular machinery that is involved in the transmission of nerve impulses. As shown in Figure 8.4.3, the presynaptic area contains many tiny spherical vessels called that are packed with chemicals called . When an reaches the axon terminal of the presynapti...
Neurotransmitters and Receptors
- There are more than a hundred known neurotransmitters, and more than one type of neurotransmitter may be released at a given synapse by a presynaptic cell. For example, it is common for a faster-acting neurotransmitter to be released, along with a slower-acting neurotransmitter. Many neurotransmitters also have multiple types of to which they can bind. Re…
Attributions
- Figure 8.4.1 Lightening/ Purple Lightning, Dee Why by Jeremy Bishop on Unsplash is used under the Unsplash License(https://unsplash.com/license). Figure 8.4.2 Action Potential by CNX OpenStax, Biology on Wikimedia Commons is used under a CC BY 4.0(https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/deed.en) license. Figure 8.4.3 Chemical_synap…
References
- Amoeba Sisters. (2020, January 29). Sodium potassium pump. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7NY6XdPBhxo&feature=youtu.be CNX OpenStax. (2016, May 27) Figure 4 The action potential is conducted down the axon as the axon membrane depolarizes, then repolarizes [digital image]. In Open Stax, Biology(Section 35.2). OpenStax CNX. https://cnx…
Resting Potential
Chemical Synapses
- At a chemical synapse, both the presynaptic and postsynaptic areas of the cells are full of molecular machinery that is involved in the transmission of nerve impulses. As shown in Figure 8.4.3, the presynaptic area contains many tiny spherical vessels called that are packed with chemicals called . When an reaches the axon terminal of the presynapti...
Neurotransmitters and Receptors
- There are more than a hundred known neurotransmitters, and more than one type of neurotransmitter may be released at a given synapse by a presynaptic cell. For example, it is common for a faster-acting neurotransmitter to be released, along with a slower-acting neurotransmitter. Many neurotransmitters also have multiple types of to which they can bind. Re…
Attributions
- Figure 8.4.1 Lightening/ Purple Lightning, Dee Why by Jeremy Bishop on Unsplash is used under the Unsplash License(https://unsplash.com/license). Figure 8.4.2 Action Potential by CNX OpenStax, Biology on Wikimedia Commons is used under a CC BY 4.0(https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/deed.en) license. Figure 8.4.3 Chemical_synap…
References
- Amoeba Sisters. (2020, January 29). Sodium potassium pump. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7NY6XdPBhxo&feature=youtu.be CNX OpenStax. (2016, May 27) Figure 4 The action potential is conducted down the axon as the axon membrane depolarizes, then repolarizes [digital image]. In Open Stax, Biology(Section 35.2). OpenStax CNX. https://cnx…