Yes. A note payable is an interest bearing debt. Where is notes payable on balance sheet? A note payable is shown under either current or long term liabilities on the balance sheet.
Are most notes not interest bearing?
Most notes are not interest bearing. Unearned revenues are received before goods are delivered or services are rendered. Material gains or losses on bond redemption are reported as part of other gains/losses on the income statement. equal to the note's face value.
Is notes payable an asset or a liability?
While Notes Payable is a liability, Notes Receivable is an asset. Notes Receivable record the value of promissory notes that a business owns, and for that reason, they are recorded as an asset. NP is a liability which records the value of promissory notes that a business will have to pay.
Are notes payable considered current liabilities?
The “Notes Payable” line item is recorded on the balance sheet as a current liability – and represents a written agreement between a borrower and lender specifying the obligation of repayment at a later date. Also contained within the notes payable are the terms stipulated between the two parties, such as:
Is notes payable a current liability?
On a balance sheet, notes payable appear as liabilities. The financial statements are key for accounting as well as for financing modeling. Furthermore, if the amounts owed within a year are late, the remaining amounts will be counted as current liabilities.
Is notes payable a non-interest bearing debt?
A non-interest bearing note payable is a note in which the interest is deducted from the face value of the note when it is issued. It is called non-interest bearing because no interest rate is stated on the note.
Do notes payable carry interest?
Notes payable almost always require interest payments. The interest owed for the period the debt has been outstanding that has not been paid must be accrued. Accruing interest creates an expense and a liability.
Are notes interest bearing?
What is an Interest Bearing Note? An interest bearing note represents funds loaned by a lender to a borrower, on which interest is accrued in accordance with the terms of the agreement. These notes have many applications.
How do you record interest bearing notes payable?
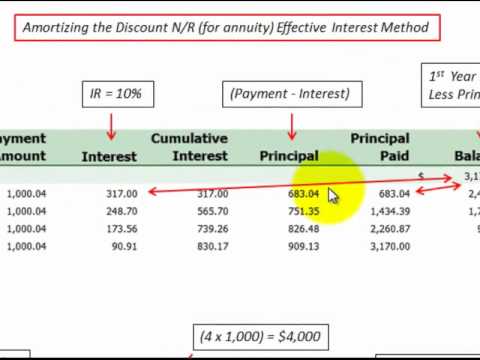
3:3914:49Notes Payable (Interest Bearing Note, Effective Interest Method ... - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipEquals the present value of the note here ninety five thousand two hundred dollars so that's what uhMoreEquals the present value of the note here ninety five thousand two hundred dollars so that's what uh corp b is gonna receive on this note when they exchange it here at the beginning of year one here.
What is a note payable?
Notes payable are long-term liabilities that indicate the money a company owes its financiers—banks and other financial institutions as well as other sources of funds such as friends and family. They are long-term because they are payable beyond 12 months, though usually within five years.
What is included in notes payable?
Definition of notes payable Recording notes payable includes specifying details of the matter. Information in the written statement generally includes the principal amount borrowed, the due date of payment and the interest to be paid.
What are non interest bearing assets?
Non-interest bearing liabilities represent a debt, an amount of money that a company owes, without any interest or penalties accruing while the company holds the debt.
What is a non interest bearing account?
The term “noninterest-bearing transaction account” includes a traditional checking or demand deposit account on which the insured depository institution pays no interest.
What is interest bearing and non interest bearing?
Interest bearing notes are debt instruments that require the issuer to pay interest at a predetermined interest rate, periodically till maturity of the note. Zero interest-bearing notes are debt instruments that do not require the issuer to make actual periodic interest payments to the investors.
What are non interest bearing liabilities?
A non-interest bearing current liability is an item in a corporate balance sheet that reflects short-term expenses and debts that are not accruing interest. Corporate balance sheets distinguish between obligations to pay debts with interest and obligations to pay ordinary expenses such as account receivables.
How do you record a non interest bearing note payable?
Multiply the market rate of interest by the present value of the note to arrive at the amount of interest income. Record the interest income as a credit to interest income and a debit to an asset account for the investment in the note.
What are interest bearing liabilities?
Interest-bearing liabilities are debts that cost money to hold. They include most financial liabilities that businesses commonly have, including bank loans and corporate bonds.
How do you calculate interest on a note payable?
The company can calculate the interest on note payable by multiplying the face value of the note payable with the interest rate and the time in the note maturity. The interest rate and the time in the note maturity need to be matched.
What is accrued interest on notes payable?
Interest that has occurred, but has not been paid as of a balance sheet date, is referred to as accrued interest. Under the accrual basis of accounting, the amount that has occurred but is unpaid should be recorded with a debit to Interest Expense and a credit to the current liability Interest Payable.
How do you account for notes payable?
If your company borrows money under a note payable, debit your Cash account for the amount of cash received and credit your Notes Payable account for the liability. When you repay the loan, you'll debit your Notes Payable account and credit your Cash account.
What's the difference between notes payable and accounts payable?
Notes payable are written contracts that typically serve the purpose of paying debts through credit companies and financial institutions, whereas accounts payable involves the suppliers of goods and services.
What is interest bearing note?
An interest-bearing note is a promissory note with a stated interest rate on its face. This note represents the principal amount of money that a lender lends to the borrower and on which the interest is to be accrued using the stated rate of interest.
What is a note payable?
The note payable is a written promissory note in which the maker of the note makes an unconditional promise to pay a certain amount of money after a certain predetermined period of time or on demand. The purpose of issuing a note payable is to obtain loan form a lender (i.e., banks or other financial institution) or buy something on credit.
What is the difference between the face value of a note and the amount lent by the lender to the borrower?
Thus, the difference between the face value of the note and the amount lent by the lender to the borrower is the interest charged by the lender .
Why are short term notes payable?
The short term notes payable are classified as short-term obligations of a company because their principle amount and any interest thereon is mostly repayable within one year period. They are usually issued for purchasing merchandise inventory, raw materials and/or obtaining short-term loans from banks or other financial institutions. The short-term notes may be negotiable which means that they may be transferred in favor of a third party as a mode of payment or for the settlement of a debt.
Why is the discount on notes payable debited?
The discount on notes payable account normally has a debit balance because it is a contra account to notes payable account (a liability account). When financial statements are prepared, the balance of discount on notes payable account is deducted from notes payable in the balance sheet.
What is a zero interest note?
A zero-interest-bearing note (also known as non-interest bearing note) is a promissory note on which the interest rate is not explicitly stated. When a zero-interest-bearing note is issued, the lender lends to the borrower an amount of money which is less than the face value of the note.
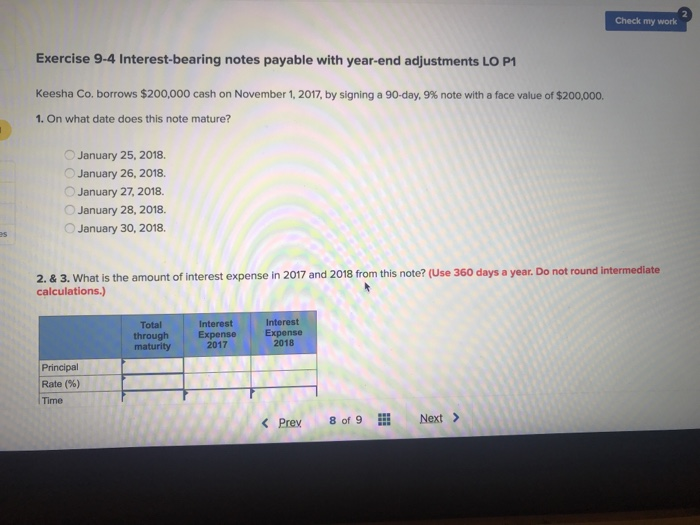
When is a journal entry required for a national company?
For National Company, prepare: a journal entry required at the time of issuing the note on November 1, 2018. an annual adjusting entry required to accrue the interest on December 31, 2018. a journal entry required at the time of repayment of principal as well as interest on February 1, 2019.
What are Notes Payable?
A note payable is a written promissory note. Under this agreement, a borrower obtains a specific amount of money from a lender and promises to pay it back with interest over a predetermined time period. The interest rate may be fixed over the life of the note, or vary in conjunction with the interest rate charged by the lender to its best customers (known as the prime rate ). This differs from an account payable, where there is no promissory note, nor is there an interest rate to be paid (though a penalty may be assessed if payment is made after a designated due date).
What happens if a note is payable?
Legal Issues Pertaining to Notes Payable. The lender may require restrictive covenants as part of the note payable agreement, such as not paying dividends to investors while any part of the loan is still unpaid. If a covenant is breached, the lender has the right to call the loan, though it may waive the breach and continue to accept periodic debt ...
What is the proper classification of a note payable?
The proper classification of a note payable is of interest from an analyst's perspective, to see if notes are coming due in the near future; this could indicate an impending liquidity problem.
When a company borrows money under a note payable, it debits a cash account for the amount of?
When a company borrows money under a note payable, it debits a cash account for the amount of cash received , and credits a notes payable account to record the liability. For example, a bank loans ABC Company $1,000,000; ABC records the entry as follows:
What does ABC wire to the bank?
ABC wires funds to the bank to pay for the interest expense, and records the following entry:
Is a note payable a short term liability?
A note payable is classified in the balance sheet as a short-term liability if it is due within the next 12 months, or as a long-term liability if it is due at a later date. When a long-term note payable has a short-term component, the amount due within the next 12 months is separately stated as a short-term liability.
How to calculate interest on a note payable?
The company can calculate the interest on note payable by multiplying the face value of the note payable with the interest rate and the time in the note maturity.
Why do companies sign promissory notes?
Sometimes, the company may sign a promissory note to borrow money from the creditor or the bank, which usually comes with the interest on the note payable. In this case, the company needs to calculate interest on note payable in order to prepare sufficient money to pay its creditor or bank when it is due (either interest or principal plus interest).
Why is there nothing recorded on the income statement?
The income statement will have nothing recorded because no time has passed for the interest to accrue. On June 30, your balance sheet will show $10,900 of cash and $10,900 of notes payable. The discount on note payable will have been amortized, increasing the value of our note payable.
Why is implicit interest rate implicit?
Even though the bank is not charging you direct interest, there is an implicit interest rate because they will give you slightly less than $10,900 today. It's like asking your brother for money. If you ask him for $100 today and say that you will return $100 in 20 years, he won't be happy. If you gave him back $300 in 20 years, he may lend you the money. There is an implicit interest rate in this transaction - $200. This compensates him for that fact that you will have the $100 and he will not.
What happens if you borrow $10,000?
If you borrow the money starting today, you will receive $10,000 and will record a liability, or a note payable, to reflect the fact. As the months go on, you will accrue interest. This basically means you have use of the $10,000 and need to pay 'rent' for it. In our case, this 'rent' is called interest.
When will the 2015 balance sheet show $10,000?
On Oct. 1, 2015, your balance sheet will show $10,000 of cash and $10,000 of notes payable. The income statement will have nothing recorded because no time has passed for the interest to accrue.
What is the obligation of a zero interest note?
In the case of zero interest-bearing notes, the issuing company is not obligated to make any periodic interest payments. His obligation is restricted to repayment of the face value at the time of maturity.
What is the difference between interest bearing and zero interest?
Meaning. Interest bearing notes are debt instruments that require the issuer to pay interest at a predetermined interest rate, periodically till maturity of the note.
What is zero interest bearing?
Zero interest-bearing notes are debt instruments that do not require the issuer to make actual periodic interest payments to the investors. 2. Issue price. Interest bearing notes are generally issued at face value. Zero interest-bearing notes are issued at a deep discount to their face value. 3.
What is the obligation of a company to pay periodic interest?
In the case of interest-bearing notes, the issuing company is obligated to make periodical interest payments to the investors. The interest payments are made at the attached coupon rate, at periodical intervals set out in the issuing terms.
How does XYZ borrow money?
XYZ Inc borrows money from a lender by issuing non-interest-bearing notes. It issues 100 notes of face value $1,000 each @ $914.24 each, with a term of 12 months. Thus, each bond is issued at a discount of $85.76.
What happens to a company's interest on a bond when it matures?
Once this is done, the obligation to pay interest ceases.
When to issue zero interest notes?
Companies prefer issuing zero interest notes when they do not wish to bear the expense of annual periodic payments. Companies that expect cash inflows from their business to materialize after several years can opt to issue such notes.
Definition and Explanation
Format of Note Payable
- A simple format of interest-bearing note payable is given below: The above note has been made on March 12, 2015. In this note, the Western Products Inc. is the maker of the note that makes an unconditional promise to pay Southern Company an amount of fifty thousand dollars plus 6% interest after six month of the date of preparation of the note. The note has been signed by A.B. …
Classification of Notes Payable
- The notes payable are usually classified in two ways. These are: 1. short-term and long-term notes payable and 2. interest-bearing and zero-interest-bearing notes payable.
Example 1 – Journal Entries For Interest-Bearing Note
- On November 1, 2018, the National Company obtains a loan of $100,000 from City Bank by signing a $100,000, 6%, 3 month note. The National Company prepares its financial statements on December 31, each year. Required: For National Company, prepare: 1. a journal entry required at the time of issuing the note on November 1, 2018. 2. an annual adjusting entryrequired to accr…
Example 2 – Journal Entries For Zero-Interest-Bearing Note
- On November 1, 2018, the National Company obtains a loan of $100,000 from City Bank by signing a $102,250, 3 month, zero-interest-bearing note. The National Company prepares its financial statements on December 31, each year. Required: For National Company, prepare: 1. a journal entry to be made on November 1, 2018. 2. an adjusting journal entry to be made on Dec…
Solution
- 1. Journal entry at the time of issuing the note on November 1, 2018: The company obtains a loan of $100,000 against a note with a face value of $102,250. The difference between the face value of the note and the loan obtained against it is debited to discount on notes payable. The discount on notes payable in above entry represents the cost of obtaining a loan of $100,000 for a period …