
Who should get irradiated blood?
• All patients undergoing autologous bone marrow transplant or peripheral blood stem cell transplant should receive irradiated cellular blood components from initiation of conditioning chemo/radiotherapy until 3 months post-transplant (6 months if total body irradiation was used in conditioning).
What are the reasons for elevated platelets?
- infectious disease
- inflammatory disease
- neoplasms
- non-malignant haematological conditions e.g. acute blood loss, iron deficiency anaemia
- functional and surgical hyposplenism
- tissue damage, e.g. recent trauma or surgery
- exercise
- reaction to medications e.g. steroids, adrenalin
- pregnancy
- allergic reactions
When is the immune system attacks the platelets?
Your body may produce enough platelets on its own, but some conditions and medicines may destroy them or stop them from working correctly (dysfunction). 3 When you have an autoimmune condition, your immune system attacks healthy cells. Diseases like lupus and rheumatoid arthritis may cause the immune system to destroy platelets.
Who requires irradiated blood products?
Who requires irradiated blood products? Patients presenting for surgery who are immunocompromised may require a blood transfusion. Some of these patients will require irradiated blood (Table 1). Transfusion with irradiated blood prevents these patients from develop-ing transfusion-associated graft versus host disease (TA-GVHD), which is
Are all platelets irradiated?
Is all blood routinely irradiated? Red cell and platelet transfusions are not routinely irradiated and need to be irradiated 'on demand' for patients at risk of TA-GvHD. It is important that you remind your medical team of your need for irradiated blood as they have to order it specially.
Which blood product should be irradiated?
All red cells and platelets for intrauterine transfusion (IUT) must be irradiated. For exchange transfusions where there has been a previous intrauterine transfusion, irradiated cellular components are essential. For other exchange transfusions, irradiation is recommended provided this doesn't delay transfusion.
Does plasma need to be irradiated?
Irradiation of thawed plasma and cryoprecipitate are not necessary as they have never been associated with TA-GVHD. Fresh liquid plasma (never frozen) may have a small amount of viable lymphocytes and should be irradiated if the patient has indications for irradiated cellular blood products.
How long are irradiated platelets good for?
The FDA says that an irradiated product expires 28 days from irradiation OR the product's regular expiration date, whichever comes first. Obviously, irradiating a unit of platelets has no effect whatsoever on that unit's expiration time (since platelets only have a five day shelf-life anyway).
Why are platelets irradiated?
Irradiation of platelet products is generally used to prevent transfusion-associated graft-versus-host disease (TA-GvHD) as well as transfusion-transmitted infections. As an essential prerequisite, gamma-irradiation of blood products prior to transfusion is required in patients who may develop TA-GVHD.
Is FFP and platelets the same?
One unit of FFP has a concentration of coagulation factors similar to that of 4 to 5 units of platelet concentrates, 1 apheresis unit of platelets, and 1 unit of fresh whole blood; 1 mL/kg of FFP raises most factor levels by approximately 1%.
Does FFP have to be irradiated?
Fresh Frozen Plasma (FFP), cryoprecipitate, frozen washed red cells and fractionated plasma products do not need to be irradiated as the lymphocytes will not, or are extremely unlikely to survive the freezing/fractionation process.
Which apheresis platelets product should be irradiated?
Which apheresis platelets product should be irradiated? d. a directed donation given by an unrelated family friend. Blood products from blood relatives containing viable lympocytes must be irradiated to inhibit the proliferation of T cells and subsequent GVHD.
What is the difference between irradiated and non irradiated blood?
Irradiated or non-irradiated transfusions have many risks involved including elevated potassium levels and graft versus host disease (TA-GVHD). Irradiated blood is able to destroy the leukocytes responsible for TA-GVHD, but it adversely causes elevated extracellular potassium due to hemolysis of the RBC's.
Who irradiated platelets?
Why is Blood Irradiated?Fetal and neonatal recipients of intrauterine transfusions.Selected immunocompromised recipients.Recipients of cellular components known to be from a blood relative.Recipients who have undergone marrow or peripheral blood progenitor cell transplantation.More items...
When do you need irradiated blood?
Why is blood irradiated? Irradiated blood is used to prevent a very rare but serious complication of blood transfusions called 'transfusion-associated graft-versus-host disease' (TA-GvHD). This is when donor white blood cells attack your own tissues.
Is blood always irradiated?
Is all blood irradiated? No. Blood is only irradiated for patients at risk of TA-GvHD.
Which apheresis platelet product should be irradiated?
Which apheresis platelets product should be irradiated? d. a directed donation given by an unrelated family friend. Blood products from blood relatives containing viable lympocytes must be irradiated to inhibit the proliferation of T cells and subsequent GVHD.
Which type of transfusion reaction can be prevented by using irradiated blood products?
TA-GVHD is a transfusion-transmitted disease and is preventable with irradiation of blood products.
Why are blood products Leukoreduced and irradiated?
Irradiated Blood: Irradiation is needed to destroy all nucleated cells and living leukocytes (white blood cells), particularly lymphocytes that could cause transfusion associated graft versus host disease (TAGVD).
Is CMV negative irradiated?
CMV antibody negative products are recommended for all immuno-deficient patients and pregnant women negative for CMV antibody. Irradiated blood products are used in the treatment of immuno-deficient patients receiving large amounts of blood, and in all severely immuno-compromised patients.
How long does it take for a rash to appear after a blood transfusion?
Typically the condition presents 10-14 days after transfusion with rash (erythroderma), pancytopenia and abnormal liver function. There is a longer time between transfusion and presentation in neonates.
What are some examples of large volume transfusions?
Examples include large volume neonatal transfusion such as exchange transfusion, ECLS or rapid large volume transfusion. Irradiation of platelets has not been shown to cause any clinically significant change in platelet function. Platelets may be irradiated at any stage during their 5 day storage life.
Do platelets get irradiated in Victoria?
In Victoria all platelets are irradiated by ARCBS prior to issue. Irradiation of granulocytes. There is conflicting evidence of irradiation damage to granulocytes. Granulocytes should be transfused as soon as possible after collection and irradiation.
What causes a refractory platelet count?
There are clinical and immunological causes of platelet refractoriness. Clinical causes include fever, sepsis, bleeding, DIC and some drugs.
What is a platelet transfused?
Platelets are commonly transfused to patients with low platelet counts or patients with platelet dysfunction who are bleeding or at high risk of bleeding. All platelet components are leucodepleted and irradiated prior to release to the hospital.
What is the role of platelets in blood clots?
Platelets are small, disc shaped cells that have a critical role in helping our blood clot and stop bleeding. When there is a break in the vascular endothelium, a process of platelet activation occurs and the platelets change shape and aggregate to form a platelet plug. Platelets are commonly transfused to patients with low platelet counts ...
Can you use platelet products with both donor and recipient?
Where possible, a platelet product compatible with both donor and recipient should be used . At RCH the platelet product choice for each transplant recipient will be specified by their transplant physician and will be listed on the Transplant Protocol
Can you transfuse blood after a red blood cell?
Do not transfuse though the same blood administration filter after red blood cell transfusion as some platelets may get caught in fibrin strands/debris caught in filter (Exception: critical bleeding event, can continue to use the same blood administration filter unless flow is impeded by debris caught in the filter).
Do you need pooled platelets for apheresis?
Certain patient groups may require pooled platelets as the first choice. The ratio of plasma to platelets is less in pooled components than apheresis products and therefore the exposure to plasma is less. This becomes significant for those patient groups who have mild – moderate allergic reaction to apheresis platelets.
Why is Blood Irradiated?
As described in the Technical Manual ( 20th Edition) and Circular of Information ( October 2017 ), cellular blood components are irradiated prior to transfusion to prevent the proliferation of viable T lymphocytes which are the immediate cause of Transfusion Associated-Graft Versus Host Disease (TA-GVHD).
Where Can I Find More Clinical Information?
The Circular of Information for Human Blood and Blood Components has detailed information on indications for use, safety and hazards.
What Type of Blood Irradiation Devices are FDA Cleared?
The following devices are FDA-approved/cleared “for use in the irradiation of blood and blood products (packaged in transfusion bags) to inactivate T-lymphocytes for the prevention of Graft Versus Host Disease...”:
US Government Efforts: Risk Reduction and Elimination of Gamma Irradiators
INCREASED SECURITY MEASURES: The US NRC requires increased security measures to reduce the risk of unauthorized use of radioactive materials for gamma irradiators. The US Office of Radiological Security (ORS) offers federally funded security enhancements for radioisotope-based blood irradiators that are above and beyond the NRC’s Part 37 requirements – see Additional Resources section..
Recent Actions
04/12/12 The Radiological Devices Panel of the Medical Device Advisory Committee met to advise FDA on the device classification of blood irradiators. In its public statement, AABB recommended that no measures be added for use of blood irradiators and that the devices be classified as class I or II.
How is blood irradiated?
How Blood is Irradiated. Blood is irradiated by exposing the bags to gamma radiation from cobalt-60 or cesium-137 using an instrument called an irradiator. The minimum radiation dose to kill the T-lymphocytes of 25 Gy10. Another method uses X-rays generated by a linear accelerator.
What is irradiated blood used for?
Irradiated blood is used to prevent transfusion-associated graft-versus host disease (TA-GvHD) in people who received bone marrow transplants or transfusions of blood components.
What happens if you irradiate a T lymphocyte?
The irradiation process kills the donor’s T-lymphocytes which are the main cause of TA-GvHD. Unless the T-lymphocytes are destroyed, they will graft themselves in the recipient’s tissues. If the person’s own immune system is incapable of mounting an immune response to them, the T-lymphocytes get the upper hand and attack the recipient’s body as if it were a foreign invader.
Does blood become radioactive after irradiation?
Blood does not become radioactive after it is irradiated, and it does not present a danger to the recipient or their family members. The process does not damage healthy blood cells or platelets, but it does shorten the shelf life slightly because the cells lose some of their salt content.
When should I irradiate red cells?
Routine irradiation of red cells for transfusion to preterm or term infants (other than for EBT) is not required unless there has been a previous IUT, in which case irradiated components should be administered until 6 months after the expected delivery date (40 weeks gestation) (2/C).
How long should you wait to receive irradiated blood components before bone marrow harvest?
Patients (adult and paediatric) undergoing bone marrow or peripheral blood stem cell collections for future autologous re-infusion should receive irradiated cellular blood components for 7 days prior to and during the bone marrow/stem cell harvest to prevent the collection of viable allogeneic T lymphocytes, which can potentially withstand cryopreservation (1/C).
How long do red cells stay in the body?
intrauterine or neonatal EBT, or other large-volume transfusion of neonates and infants, it is recommended that red cells are transfused within 24 h of irradiation (1/C).
What is the purpose of blood component?
Purpose. To provide healthcare professionals with clear guidance on situations when the use of irradiated blood components is indicated. The term ‘blood component’ means the therapeutic constituents of human blood (red cells, white cells, platelets and plasma) that can be prepared by various methods ...
What is the minimum dose achieved in the irradiation volume?
The minimum dose achieved in the irradiation volume should be 25 Gy, with no part receiving >50 Gy (1/B). The irradiation procedure must be validated and there must be regular monitoring of dosimetry.
Can IUT be used for TA-GvHD?
A fatal case of TA-GvHD occurred following IUT of non-irradiated maternal blood in an emergency. 25 BSH guidelines recommended that maternal blood should not be used for IUT to avoid this risk. 40
Is irradiation a manufacturing process?
Irradiation of blood components constitutes a manufacturing process. The responsible institution is therefore expected to comply with relevant aspects of the European Commission Guide to Good Manufacturing Practice 55 and hold the appropriate licence as a Blood Establishment according to the Blood Safety and Quality Regulations 2005 56 .

Transfusion Associated Graft Versus Host Disease
Irradiation of Blood Products
- Irradiation of blood products is undertaken using a dedicated blood irradiator located onsite with a long half-life gamma emitting source. Irradiation of blood products will take a further 4 - 5 minutes to provide. If blood products are needed urgently or in the case of an MTP, the products may not be able to be irradiated in a timely manner. Un-ir...
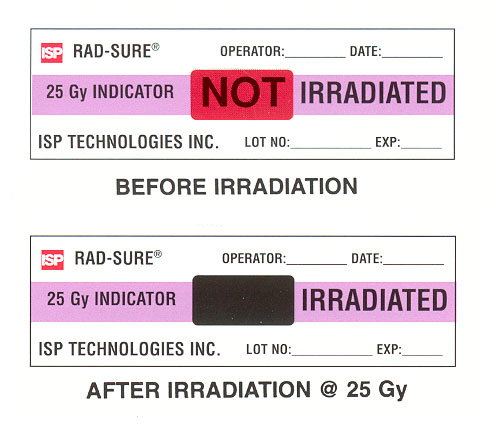
Labelling
- Blood product irradiation is identified using the Radsure™ system. A label is applied to the blood pack prior to irradiation. The words NOT IRRADIATED are visible. Once irradiation has taken place, the word IRRADIATEDremains visible.
Requests
- The clinician requesting the crossmatch or blood product is responsible for ensuring irradiated components are requested for appropriate patients. Tick the box on the request form indicating irradiated products are required. During the final bedside check prior to blood product administration, a check is made to ensure that appropriate blood product modifications such as …
Irradiation Policy at Rch
- At RCH a universal blood irradiation policy applies for patients in the following units: PICU, NICU and Children's Cancer Centre. Although not all patients in these units are at risk of TA-GVHD, this policy ensures patients who require irradiated products are not missed. (Note - haematopoietic stem cells and donor lymphocytes must notbe irradiated). In addition blood is irradiated at RCH i…