What are 10 examples of prokaryotic cells?
What are 5 examples of prokaryotic cells?
- Escherichia Coli Bacterium (E. coli)
- Streptococcus Bacterium.
- Streptomyces Soil Bacteria.
- Archaea.
What types of cells are prokaryotic?
What are 4 examples of prokaryotic cells?
- Escherichia Coli Bacterium (E. coli)
- Streptococcus Bacterium.
- Streptomyces Soil Bacteria.
- Archaea.
Why do prokaryotic cells have no nucleus?
They have no nucleus; instead their genetic material is free-floating within the cell. They also lack the many membrane-bound organelles found in eukaryotic cells. Thus, prokaryotes have no mitochondria. How do prokaryotic cells survive in the absence of important organelles like mitochondria and nucleus?
Which organisms are prokaryotic?
What is a Prokaryotic Cell?
- Prokaryotic cells are microorganisms that are known to be the earliest on earth.
- Kingdom Monera includes the prokaryotic cells. ...
- Prokaryotic cell refers to the cell which is unicellular, i.e. ...
- Prokaryotic means “pro” = primitive and “karyos” = nucleus, i.e. ...
- Bacteria and Archaea come under prokaryotes.
What is a prokaryotic cell?
What are some examples of unicellular prokaryotes?
How many layers does the mitochondria have?
Why don't we see prokaryotic cats?
How do mitochondria reproduce?
Which organisms are unicellular and multicellular?
What is the difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic?
See 4 more
About this website

Do unicellular organisms have prokaryotic cells?
Unicellular organisms can be prokaryotes or eukaryotes. Prokaryotes do not have cell nuclei: their structures are simple. Bacteria and archaea are all unicellular prokaryotes. Eukaryotes do have cell nuclei and their structures are more complex.
Are prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells multicellular or unicellular?
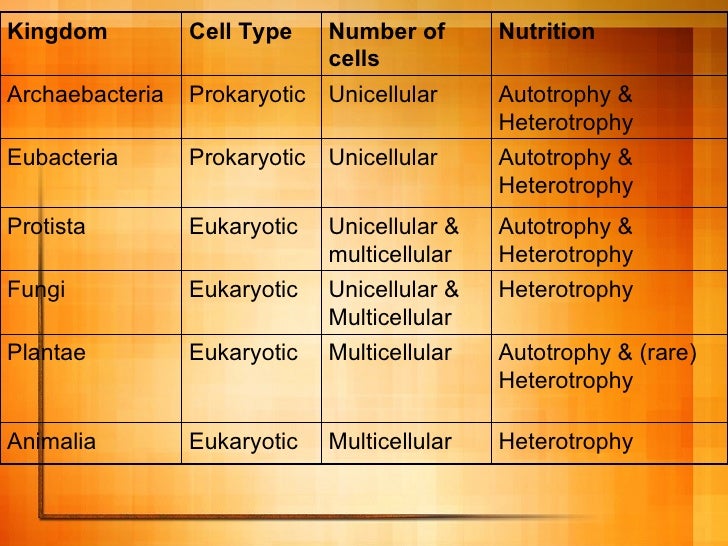
Prokaryotes are always unicellular, while eukaryotes are often multi-celled organisms. Additionally, eukaryotic cells are more than 100 to 10,000 times larger than prokaryotic cells and are much more complex. The DNA in eukaryotes is stored within the nucleus, while DNA is stored in the cytoplasm of prokaryotes.
Where prokaryotic cells are found?
bacteriaProkaryotic cells are characterized as cells that lack a well-defined nucleus and no membrane-bound organelles. In primitive unicellular organisms like bacteria and archaea, prokaryotic cells are found.
Do prokaryotic cells have multicellular?
These organisms carry out all functions required for their maintenance and survival using one cell. Therefore, prokaryotes are unicellular and not multicellular.
Why are prokaryotes not multicellular?
Prokaryotes are simple, single-celled organisms such as bacteria and archaea. There are no multicellular prokaryotes in existence. The prokaryotic cell structure of these organisms are too simple and lack the organelles that can sustain the complex cellular functions of multicellular organisms.
Why are all prokaryotes unicellular?
Complete answer: All prokaryotes are unicellular and do not have a well-developed nucleus. Prokaryotes are divided into bacteria and archaea. Prokaryotes lack cellular compartments and therefore do not have membrane-bound organelles and lack mitochondria.
Where are prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells found?
Prokaryotic cells are found in single-celled organisms, such as bacteria. Eukaryotic cells are found mainly in multicellular organisms.
Are eukaryotic cells multicellular?
Eukaryotes may be either single-celled or multicellular. Eukaryotes are differentiated from another class of organisms called prokaryotes by way of the presence of internal membranes that separate parts of the eukaryotic cell from the rest of the cytoplasm. These membrane-bound structures are called organelles.
Which is true about prokaryotic cells?
Prokaryotic cells do not have a true nucleus that contains their genetic material as eukaryotic cells do. Instead, prokaryotic cells have a nucleoid region, which is an irregularly-shaped region that contains the cell's DNA and is not surrounded by a nuclear envelope.
Which cells can be multicellular?
All species of animals, land plants and most fungi are multicellular, as are many algae, whereas a few organisms are partially uni- and partially multicellular, like slime molds and social amoebae such as the genus Dictyostelium.
Which is not true about prokaryotes?
This is Expert Verified Answer Evolutionary origin is about 1.2 million years ago is the right answer which is option d. this fact is not true about prokaryotes. Looking at Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells. Prokaryotes are single-celled life forms of the areas Bacteria and Archaea.
Are any bacteria multicellular?
Many bacteria have a multicellular phase of their lifecycle, which fall into three broad categories based on shape and mechanism of formation. A number of pressures may have selected for multicellularity, including physicochemical stress, nutrient scarcity, predation, and environmental variability.
Are eukaryotic cells multicellular or unicellular?
Eukaryotes can be unicellular. While prokaryotes are always unicellular organisms, eukaryotes can be either unicellular or multicellular. For example, most protists are single-celled eukaryotes!
Are eukaryotes multicellular or unicellular or both?
Eukaryotes may be either single-celled or multicellular. Eukaryotes are differentiated from another class of organisms called prokaryotes by way of the presence of internal membranes that separate parts of the eukaryotic cell from the rest of the cytoplasm. These membrane-bound structures are called organelles.
What cells are unicellular and multicellular?
Unicellular organisms are made up of only one cell that carries out all of the functions needed by the organism, while multicellular organisms use many different cells to function. Unicellular organisms include bacteria, protists, and yeast.
Which type of cell is multicellular?
Organisms that are composed of more than one cell are called multicellular organisms. Multicellular organisms are almost always eukaryotes.
What are 4 examples of prokaryotic cells?
Examples of prokaryotic cells are: 1. bacterial cells like Escherichia Coli Bacterium, Streptococcus Bacterium 2. cyanobacteria, 3. archaea, 4. myc...
What is a prokaryotic cell simple definition?
Prokaryotic cell refers to the unicellular cell which lacks well-defined nucleus and other membrane bound organelles.
What are 2 examples of prokaryotic cells?
Examples of prokaryotic cells are Bacteria and cyanobacteria.
What is a prokaryotic cell example?
An example of a prokaryotic cell is a bacterial cell.
Which are prokaryotes?
Prokaryotes refers to the unicellular organisms lacking well-defined nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles.
What is a Prokaryotic Cell?
Prokaryotic cells are microorganisms that are known to be the earliest on earth.
What are the characteristics of a prokaryotic cell?
Characteristics of Prokaryotic Cell. Prokaryotic cells have no organized nucleus, i.e. their genetic material is not surrounded by a nuclear membrane and that type of nucleus is called nucleoid. The cell is surrounded by a plasma membrane. Surrounding plasma membrane is a cell wall which is usually made of carbohydrates and small proteins.
Why do prokaryotic cells have flagella?
6. Prokaryotic cells may have flagella used for locomotion and pili for attachment to surfaces or else can be passively transported by wind, water, etc. 7. Pilli can also be used to transfer DNA molecules to other bacteria.
How do flagella cells move?
These cells move by the simple beating of flagella or by gliding.
Which cell contains all the genes that code for all the proteins of the prokaryotic cell?
Nucleoid- It contains all the genes that code for all the proteins of the prokaryotic cell which have structural and functional roles. Plasmid – It may contain genes that code for proteins or enzymes that can protect the cell from toxic substances. Figure showing Nucleoid (bacterial DNA) and Plasmids. 4.
How does circular DNA replicate?
In this method of reproduction, circular DNA replicates followed by cell expansion. Due to this the duplicated DNA is pulled apart. Then there is a constriction in the middle which results in separating the two cells apart from each other, resulting in the formation of two daughter cells.
How do spores reproduce?
Their reproduction is by spore formation or binary fission.
What is a prokaryotic cell?
Prokaryotic cells are unicellular organisms. Prokaryotic cells (also known as prokaryotes): Prokaryotes are simple, small (1-10 µ in size) and primitive type of cells. Prokaryotic cells consist of no ‘well defined nucleus’ and the genetic material is found scattered within the cytoplasm of cell, called nucleoid.
What are some examples of unicellular prokaryotes?
Some examples of unicellular prokaryotes are as follows: Organisms having prokaryotic cellular organisations are both unicellular as well as multicellular. Bacteria and cyanobacteria are the typical representatives of prokaryotic cells. Bacteria are unicellular but cyanobacteria have multicellular forms also.
How many layers does the mitochondria have?
Prokaryotes have a cell wall and a cell membrane, further the cell wall is divided in three layers. But the mitochondria has only two membranes the outer and inner membrane.
Why don't we see prokaryotic cats?
There are two reasons why we do not see prokaryotic cats and dogs around. One is due to evolution. Only one species can fill a specific niche. Between fungi, animals, and plants, we have most of the niches for multicellular life filled up.
How do mitochondria reproduce?
7. Both Chloroplast and Mitochondria can reproduce by binary fission while Prokaryotes can reproduce by conjugation (sexual) and asexually.
Which organisms are unicellular and multicellular?
Organisms having prokaryotic cellular organisations are both unicellular as well as multicellular. Bacteria and cyanobacteria are the typical representatives of prokaryotic cells. Bacteria are unicellular but cyanobacteria have multicellular forms also.
What is the difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic?
Eukaryotic means “with real nucleus”. The term prokaryotic has been used to denote organisms that do not have a nucleus. A better term is “akaryotic”, meaning “without nucleus”, as that term does not make any assumption about the origins.

What Are Eukaryotic cells?
What Are Prokaryotic cells?
- Prokaryotic cells do not have a nucleus, mitochondria or any other membrane boundorganelles. In other words, neither their DNA nor any other of their metabolic functions are collected together in a discrete membrane enclosed area. Instead everything is openly accessible within the cell. Though some bacteria have internal membranes as sites of metabolic activity, these membrane…
How Multicellular and Unicellular Organisms Work
- All the Prokaryotes (Bacteria and Archaea) are unicellular. Only Eukaryotes – the Protista, some Fungi and some Plants – are multicellular. In most single celled organisms, the cells are all the same (most of the time, in any given species). In multicellular organisms, individual groups of cells have become specialized to perform particular roles i...
Small Cells – Big Organisms
- Most cells are tiny… too small to be seen with the naked eye. Yet we can easily see trees, flies and elephants – which are made up of trillions of cells working together. Where do all the cells come from? One cell becomes two cells by slowly dividing in half. These halves then grow to full size before they themselves divide. This is called binary fission. This is the golden rule, whether you …
What Exactly Is A Cell Anyway?
- OK, so now we know a bit about how important cells are. But what really is a cell? The three images above are all examples of plant cells while the 3 below are all animal cells. The simplest answer is that a cell is a container… like a box or a bottle or a jar. It has an inside and an outside… and something like a wall in between – to let us know where the outside begins and the inside e…
What Next?
- Well now you know the difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells, perhaps you should look into which kingdoms are eukaryotic and prokaryotic.