What foods have high saturated fat content?
List of Foods High in Saturated Fat
- Whipped Cream. Nutrition Facts for Light Whipping Cream. ...
- Dried Coconut. Nutrition Facts for Dried Coconut (Unsweetened). ...
- Fatty Meats (Beef Short Ribs) Nutrition Facts for Braised Beef Shortribs. ...
- Processed Meats (Pepperoni) Nutrition Facts for Pepperoni. ...
- Desserts (Dulce De Leche) Nutrition Facts for Dulce De Leche. ...
- Palm Oil. ...
- Whole Milk. ...
What are the best saturated fats to eat?
Foods high in saturated fats
- milk and white chocolate, toffee, cakes, puddings and biscuits
- pastries and pies
- fatty meat, such as lamb chops
- processed meat, such as sausages, burgers, bacon and kebabs
- butter, lard, ghee, dripping, margarine, goose fat and suet
- coconut and palm oils and coconut cream
- full fat dairy products such as cream, milk, yogurt, crème fraiche and cheese
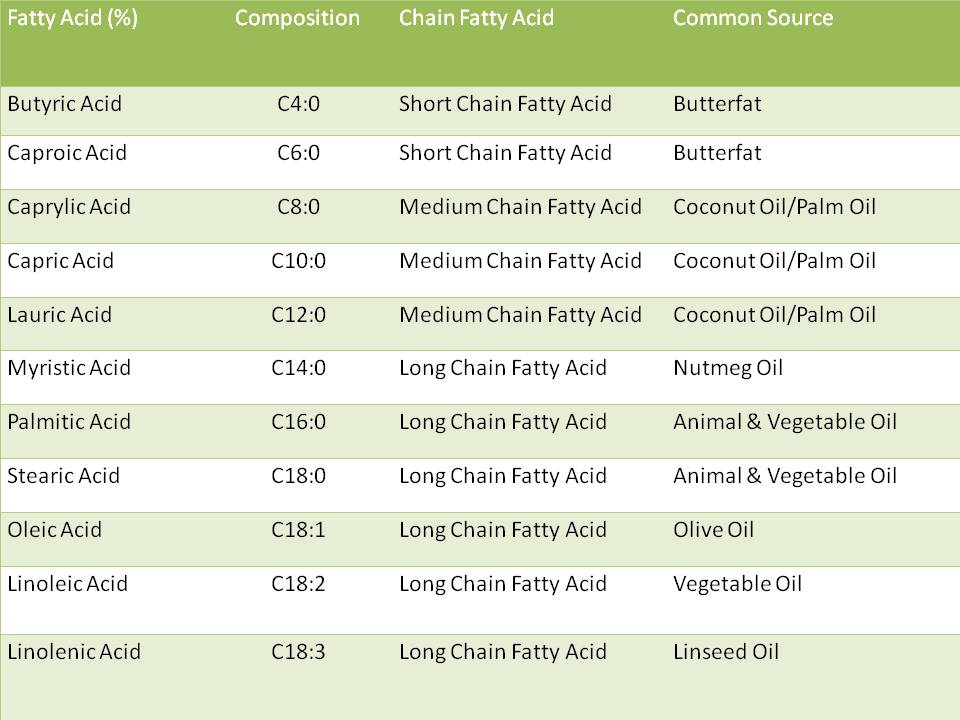
What foods are high in long chain fatty acids?
- Oleic acid (C18:1) (adrenoleukodistrophy, lowers blood pressure, stored in adipose tissue)
- Eicosenoic acid (C20:1)
- Erucic acid (C22:1) (in rapeseed, wallflower seed, and mustard seed)
- Nervonic acid (C22:1) (in treatment of adrenoleukodistrophy, MS)
What is saturated fat and is it unhealthy?
Saturated fat is a type of dietary fat. It is one of the unhealthy fats, along with trans fat. These fats are most often solid at room temperature. Foods like butter, palm and coconut oils, cheese, and red meat have high amounts of saturated fat. Too much saturated fat in your diet can lead to heart disease and other health problems.

Is saturated fat short-chain?
Saturated fatty acids that contain fewer than six carbon atoms are known as short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs).
Do saturated fats have long or short tails?
A saturated fat is a type of fat in which the fatty acid chains have all single bonds. A fat known as a glyceride is made of two kinds of smaller molecules: a short glycerol backbone and fatty acids that each contain a long linear or branched chain of carbon (C) atoms.
What chain do saturated fats have?
1: Fatty Acids: Saturated fatty acids have hydrocarbon chains connected by single bonds only. Unsaturated fatty acids have one or more double bonds. Each double bond may be in a cis or trans configuration. In the cis configuration, both hydrogens are on the same side of the hydrocarbon chain.
What fats are short-chain?
List of SCFAsLipid numberNameMass (g/mol)CommonC1:0Formic acid46.03C2:0Acetic acid60.05C3:0Propionic acid74.085 more rows
What fats are long chain?
Saturated long-chain fats include myristic acid, palmitic acid, stearic acid and arachidic acid. These are fatty acids found in dairy fat, coconut oil, palm kernel oil, peanut oil and other vegetable oils.
What are medium chain fats?
Overview. Medium chain triglycerides (MCTs) are fats that are made in a lab from coconut and palm kernel oils. Typical dietary fats are called long-chain triglycerides. MCTs are a fat source for people who cannot tolerate other types of fats.
What is the structure of saturated fatty acids?
Saturated fatty acids are compounds that consist of a hydrocarbon chain and a carboxylic acid group (-COOH) at the end of the chain. These fatty acids are referred to as saturated because the hydrocarbon chain is saturated with hydrogen atoms due to the absence of double bonds.
What is difference between saturated and unsaturated fats?
The difference between saturated and unsaturated fat lies in the number of double bonds in the fatty acid chain. Saturated fatty acids lack double bonds between the individual carbon atoms, while in unsaturated fatty acids there is at least one double bond in the fatty acid chain.
Are medium-chain fatty acids saturated?
Medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs) contain a mixture of fatty acids of 6–12 carbon saturated fatty acids.
What is short and medium-chain fatty acids?
Short-chain fatty acids (SCFA) are fatty acids with aliphatic tails of five or fewer carbons (e.g. butyric acid). Medium-chain fatty acids (MCFA) are fatty acids with aliphatic tails of 6 to 12 carbons, which can form medium-chain triglycerides.
How long are medium-chain fatty acids?
6–12 carbonsFatty acids can be categorized into several groups according to the length of the chains: short-chain fatty acids (SCFA) with aliphatic tails of 2-6 carbons; medium-chain fatty acids (MCFA) with aliphatic tails of 6–12 carbons; long-chain fatty acids (LCFA) 13 to 21 carbons in aliphatic tails and Very long chain fatty ...
What are long chain triglycerides?
Triglycerides. Long-chain triglycerides are the most important dietary lipids. Their digestion depends on an intricate interplay among pancreatic lipase, colipase, and bile acids. Pancreatic lipase hydrolyzes a triglyceride molecule to two fatty acid molecules and 2-monoacylglycerol.
What is a healthy, disease-protective diet?
What has been established through decades of research is that a healthy, disease-protective diet should be rich in nutritious, whole foods, especially high fiber plant foods, though it’s clear that nutritious foods high in saturated fat can be included as well .
What are saturated fats made of?
All fats are made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen molecules ( 2. Trusted Source. ). Saturated fats are saturated with hydrogen molecules and contain only single bonds between carbon molecules. On the other hand, unsaturated fats have at least one double bond between carbon molecules.
What is the most important thing to consider when choosing a healthy diet?
Remember, regardless of what dietary pattern you choose, the most important thing is balance and optimization — not omission. Summary. A healthy diet should be rich in whole, nutritious foods, regardless of macronutrient composition. Saturated fats can be included as part of a healthy diet.
What are the different types of saturated fats?
Keep in mind that there are different types of saturated fats depending on their carbon chain length, including short-, long-, medium-, and very-long-chain fatty acids — all of which have different effects on health.
Is APOB a protein?
ApoB is a protein and a main component of LDL. It’s considered a strong predictor of heart disease risk ( 8. Trusted Source. ). Saturated fat intake has been shown to increase both of these risk factors, as well as the LDL (bad) to HDL (good) ratio, which is another heart disease risk factor ( 9. Trusted Source.
Is high fat diet healthy?
Yet, current research supports the fact that nutritious high fat foods can indeed be included as part of a healthy, well-rounded diet. Although nutrition research tends to focus on individual macronutrients, it’s far more helpful to focus on the diet as a whole when it comes to overall health and disease prevention.
Does saturated fat affect heart health?
The effect of saturated fat on heart health. One of the main reasons for recommending that saturated fat intake be kept to a minimum is the fact that saturated fat consumption may increase certain heart disease risk factors, including LDL (bad) cholesterol.
How many carbon atoms are in a saturated fat?
Here are the most common saturated fatty acids in the human diet: Stearic acid: 18 carbon atoms long. Palmitic acid: 16 carbon atoms long.
What is the difference between saturated and unsaturated fats?
These groups differ slightly in their chemical structure and properties. For instance, saturated fat is generally solid at room temperature, while unsaturated fat is liquid.
What is the conversion rate of stearic acid to oleic acid?
However, according to some estimates, the conversion rate is only 14% and may not have much health relevance ( 12. Trusted Source.
Where are saturated fatty acids found?
They’re created in your gut from the fiber you eat and can also be found in trace amounts in some fermented food products. SUMMARY Saturated fatty acids are one of the two major categories of fat. Common dietary saturated fatty acids include stearic acid, palmitic acid, myristic acid, and lauric acid.
Is LDL cholesterol the same as heart disease?
High levels of LDL cholesterol are a well-known risk factor for heart disease. Still, not all LDL cholesterol is the same. More accurate markers of heart disease are the presence of a large number of LDL particles and of small, dense LDL particles ( 15. Trusted Source.
Does coconut oil have myristic acid?
Though coconut oil and palm kernel oil boast relatively high amounts of myristic acid, they also provide other types of fats, which may offset the effects of myristic acid on your blood lipid profile ( 26. Trusted Source. ). SUMMARY Myristic acid is a long-chain, saturated fatty acid.
Is stearic acid a saturated fat?
The levels of stearic acid are usually low in plant fat, with the exception of coconut oil, cocoa butter, and palm kernel oil. Stearic acid is considered a healthy saturated fat and does not appear to raise your risk of heart disease. ). SUMMARY Stearic acid is the second most common saturated fat in the American diet.
What are some examples of saturated fats?
Popular examples of foods rich in saturated fats are fatty cuts of beef and lamb, butter, heavy cream, cheese, coconut oil, and dark chocolate. Many of these foods carry a stigma simply because they are the top sources of saturated fat in our diets.
What is the difference between saturated and monounsaturated fats?
In contrast, polyunsaturated and monounsaturated fats, which are commonly known as the “healthy” fats, are typically the predominant fats found in nuts, seeds, olive oil, vegetable oils, and other plant foods/oil.
How do saturated fats get their name?
From a biochemical perspective, saturated fats get their name from the fact that their fatty acids consist of single-bonded carbon molecules that are entirely “saturated” with hydrogen atoms.
Why are fats and fatty acids used interchangeably?
In most cases, the terms “fatty acids” and “fats” are used interchangeably because the fatty acids are responsible for the properties and health effects of the triglycerides we consume. With this concept of mind, let’s add some more color to saturated fats. Here are the three categories of saturated fatty acids:
How many carbon atoms are in a saturated fatty acid?
Here are the three categories of saturated fatty acids: Short chain fatty acids (SCFAs) — These saturated fatty acids only contain 2-5 carbon atoms. They are produced when the friendly gut bacteria ferment fiber in your colon and are the primary source of energy for the cells lining your colon.
Where do keto fats come from?
For optimal health, the majority of these fats should come from fresh fatty meats and high-fat dairy rather than pure animal or dairy fat. Here are some examples of keto-friendly long-chain saturated fat food sources: Fatty cuts of beef and lamb.
How does the number of double bonds affect the body?
The number of double bonds ( or lack thereof) in the fatty acid significantly changes how the body processes it and what effect it has on health. The length of the fatty acid chain plays a crucial role as well. Different saturated fatty acids are named and categorized based on the number of carbons molecules they have.
What is the role of polyunsaturated fatty acids in the development of the brain?
A study of infants published in the journal "Pediatrics" in 2001 found that exposure to higher levels of long-chain fatty acids along with longer durations of breast-feeding played a beneficial role in brain development.
What are long chain saturated fats?
Long-chain saturated fatty acids are chains of carbon atoms that are fully saturated with hydrogen atoms. This creates straight and rigid chains, making saturated fats solid at room temperature. Sources of saturated fats in the diet include beef, pork, lamb, cheese, whole or reduced-fat milk and dairy products, palm oil, and coconut oil.
What is a long chain fatty acid?
What Is a Long-Chain Fatty Acid? Fatty acids are composed of carbon atom chains with hydrogen atoms joined at one end and an acid group attached to the other. These are the major components in dietary fats or triglycerides.
What are the health effects of Omega 3 fatty acids?
Each type of long chain fatty acid has its own health effects. Omega-3 fatty acids help lower blood pressure, regulate mood and decrease the risk of heart attacks. Polyunsaturated fatty acids play a crucial role in brain and visual development, especially in infants.
Where can I get DHA and ARA?
DHA and arachidonic acid -- ARA -- are the most abundant long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids in the brain. Infants can obtain DHA and ARA through breast milk or supplemented formula, while adults and children get them primarily from seafood and eggs.
How many carbons are in a long chain of unsaturated fat?
With unsaturated fats, a tail of up to 24 carbons is classified as long-chain. Very-long-chain unsaturated fatty acids are those with 25 or more carbons in their tails.
How many carbons are in a chain of fatty acids?
The number of carbon atoms in this chain is almost always even and consists of at least four carbons and a maximum of 28. Long-chain fatty acids have at least 14 carbon atoms in their tails.
What are polyunsaturated fats?
Polyunsaturated long-chain fats include linoleic acid, alpha-linolenic acid, arachidonic acid and eicosapentaenoic acid. ALA is a major component of seeds, nuts and some vegetable oils. Arachidonic is present in meat, eggs, fish and algae, while EPA is mostly found in oily fish and marine oils.
What is the basic building block of lipids?
Fat. By Elizabeth Brown Updated December 12, 2018. Fatty acids are the basic building blocks of lipids or fats. One of the ways fatty acids are classified is by the number of carbon atoms in their tails. Long-chain fatty acids are those with 14 or more carbons.
Is omega 3 fatty acid good for you?
Some long-chain fatty acids -- such as the omega-3 fatty acids ALA and EPA --have been shown to be very beneficial to human health. Others, such as the omega-6 arachidonic acid, are essential in small quantities but can be dangerous and pro-inflammatory in larger amounts. av-override. ‒‒:‒‒. /.
Who is Elizabeth Brown?
Elizabeth Brown is a journalist who covers health, nutrition, culture and current events. She has written for a variety of web and print publications, including health sites such as Well + Good NYC, Alignyo, and HuffPo Healthy Living.
