Which foods increase melanin production?
- Many of these foods also contain Vitamin A, an antioxidant that helps support the production of melanin.
- Mix dark green vegetables like broccoli, spinach, and some lettuce varieties into your diet. ...
- Cooking these vegetables won’t decrease the amount of beta-carotene you ingest, so feel free to get creative in the kitchen. ...
What makes the skin produce more melanin and why.?
When you spend time out in the sun, your body produces more melanin. The substance absorbs light from UV rays and redistributes it toward the upper layers of skin. It also protects the genetic material stored in your cells by keeping out harmful UV rays.
Are pigment melanin produced by the cells called melanocytes?
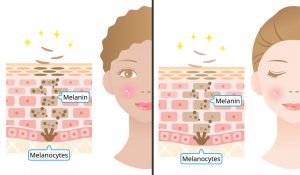
The basal cell layer contains cells called melanocytes. Melanocytes produce the skin coloring or pigment known as melanin, which gives skin its tan or brown color and helps protect the deeper layers of the skin from the harmful effects of the sun.
How to naturally increase melanin in your skin?
- Most sunscreens take a while to soak into your skin and start working, so wait 20 minutes after applying sunscreen before going outside. ...
- Repeat this process a couple of times per week and you’ll start to notice your skin tone gradually deepening.
- Skin cells produce melanin as a way of protecting their DNA from UV damage. ...
What specialized cells produce melanin?
melanocyte, specialized skin cell that produces the protective skin-darkening pigment melanin. Birds and mammals possess these pigment cells, which are found mainly in the epidermis, though they occur elsewhere—e.g., in the matrix of the hair.
Are specialized cells in the skin which produce melanin quizlet?
Terms in this set (13) Specialized cells known as melanocytes produce this, a dark pigment in the deeper layer of the epidermis.
What produces melanin?
Melanin is produced in melanocytes. These cells are located in different areas of your body, including: Your hair. The innermost layer of your skin.
Which skin layer produces melanin?
The basal cell layer contains cells called melanocytes. Melanocytes produce the skin coloring or pigment known as melanin, which gives skin its tan or brown color and helps protect the deeper layers of the skin from the harmful effects of the sun.
Are skin cells specialized cells?
The most common type of skin cell is the keratinocyte, whose primary function is to form a tough, waterproof layer against UV radiation, harmful chemicals, and infectious agents. However, the skin also contains highly specialized cells with important immunological, photoprotective, and sensory functions.
What are the specialized cells of the epidermis?
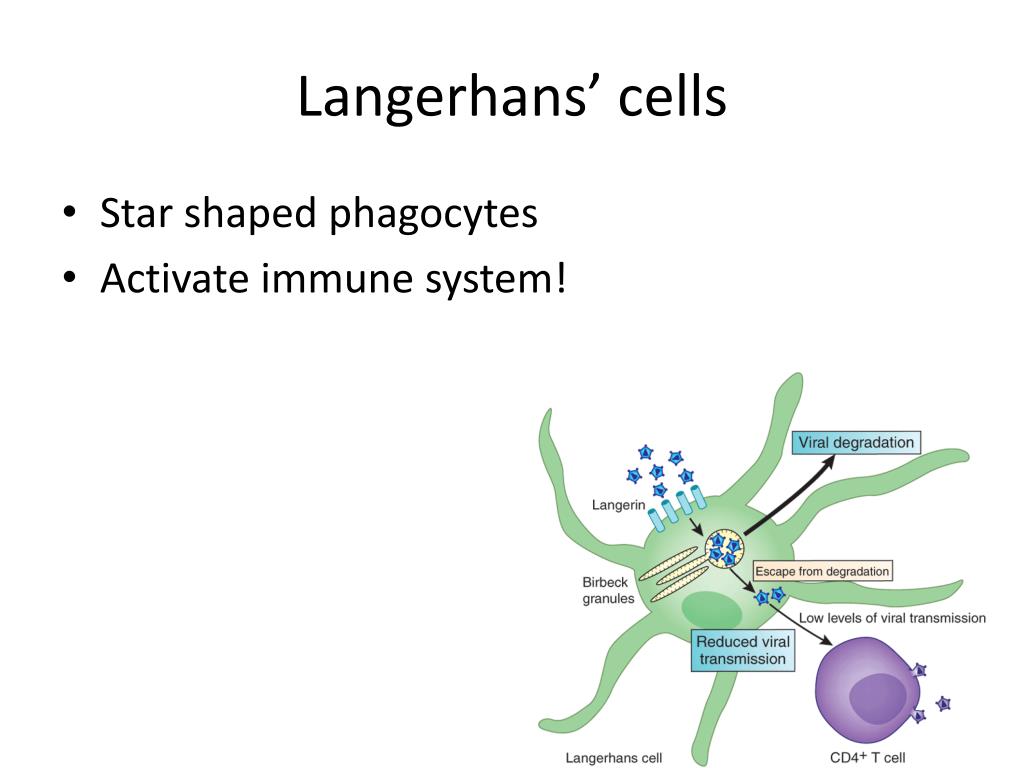
The epidermis has three main types of cell: Keratinocytes (skin cells) Melanocytes (pigment-producing cells) Langerhans cells (immune cells).
Which of the following are functions of the skin quizlet?
Functions of the skin include the following: regulates body temperature, prevents invasion of microorganisms, and assists in the production of vitamin D. Skin helps in thermoregulation by adjusting heat through the sweat glands and subcutaneous insulation.
What is the skin also known as?
Epidermis. The epidermis is the thin outer layer of the skin. It consists of 3 types of cells: Squamous cells. The outermost layer is continuously shed is called the stratum corneum.
What helps produce melanin?
Vitamin A. Studies suggest vitamin A is important to melanin production and is essential to having healthy skin. You get vitamin A from the food you eat, especially vegetables that contain beta carotene, such as carrots, sweet potatoes, spinach, and peas.
Where is melanin produced in the epidermis?
basal layerMelanin is produced in melanocytes—the cells, which at normal conditions are localized in the basal layer of the epidermis.
Why does skin produce melanin?
Melanin helps protect the cells of the epidermis, or outer layer of the skin, from UV light. This protection extends to all forms of UV light (UVC, UVB, and UVA) as well as blue light. It does this by absorbing the UV light before it's able to damage the sensitive DNA of the skin cells.
Which layer of the skin produces melanin quizlet?
The topmost layer, the stratum corneum, consists of dead cells that shed periodically and is progressively replaced by cells formed from the basal layer. The stratum basale also contains melanocytes, cells that produce melanin, the pigment primarily responsible for giving skin its color.
Does skin produce melanin?
Melanin is a natural pigment that gives your skin its color. It's produced in cells called melanocytes.
What are melanocytes?
(meh-LAN-oh-site) A cell in the skin and eyes that produces and contains the pigment called melanin. Enlarge. Anatomy of the skin, showing the epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous tissue. Melanocytes are in the layer of basal cells at the deepest part of the epidermis.
What is an example of a specialized cell?
Examples of specialized animal cells include nerve cells, sperm cells, egg cells, muscle cells, ciliated cells, and red blood cells. Specialized cells possess adaptations, special structures and features, which make them adapted to a particular function.
What does specialized cells mean?
Specialised cells are cells designed to carry out a particular role in the body, such as red blood cells which are designed to carry oxygen. Nerve cells help contraction of muscles or the relaxation of muscles according to what specific job you need them to do.
What type of cell is found in the skin?
Keratinocytes are the predominant cell type of epidermis and originate in the basal layer, produce keratin, and are responsible for the formation of the epidermal water barrier by making and secreting lipids.
Is guard cell a specialized cell?
Guard cells are highly specialized cells that form tiny pores called stomata on the leaf surface. The opening and closing of stomata control leaf gas exchange and water transpiration as well as allow plants to quickly respond and adjust to new environmental conditions.
What are the specialized cells in the integumentary system?
The integumentary system has four different specialized cells: keratinocytes, melanocytes, Merkel cells, and Langerhans cells.
What are the 4 types of cells found in the epidermis?
The most abundant epidermal cell type is the keratinocyte (approximately 90% of cells). Keratinocytes are continually renewing cells that are roughly divided into four types: basal (stratum germinativum), spinous (stratum spinosum), granular (stratum granulosum), and cornified (stratum corneum) keratinocytes.
Which hormone is responsible for skin Colour?
Melanocytes in the basal epidermis control skin pigmentation through synthesis of melanin, a complex process thought to be primarily regulated by alpha-melanocyte stimulating hormone (αMSH) (Figure 1—figure supplement 1A and B).
Which of the following parts of the body is known as the integumentary system?
The integumentary system is an organ system consisting of the skin, hair, nails, and exocrine glands.
What layer of the skin contains muscle cells glands blood vessels and sensory receptors?
The reticular layer is the deeper layer, thicker, less cellular, and consists of dense connective tissue/ bundles of collagen fibers. The dermis houses the sweat glands, hair, hair follicles, muscles, sensory neurons, and blood vessels.
What is the process of hardening old skin cells called?
The rods of cells move upward through the skin as new cells form beneath them. As they move up, they're cut off from their supply of nourishment and start to form a hard protein called keratin. This process is called keratinization (ker-uh-tuh-nuh-ZAY-shun).
What is melanin pigment?
What is melanin? Melanin is a type of complex pigment that, in humans, is responsible for producing the pigmentation in our hair, skin, and eyes. Although melanin is usually discussed as a single pigment, there are two types of melanin that contribute to pigmentation in the hair, skin, and eyes of humans and animals: Eumelanin.
Why is melanin important?
Trusted Source. against damage from the sun. Protection against UV light. Melanin helps protect the cells of the epidermis, or outer layer of the skin, from UV light.
What is the pigment that is responsible for our beautiful variety of skin tones and shades, eye colors, and hair colors?
Melanin is the pigment that is responsible for our beautiful variety of skin tones and shades, eye colors, and hair colors. However, when we discuss melanin, that discussion rarely includes its actual biological benefits.
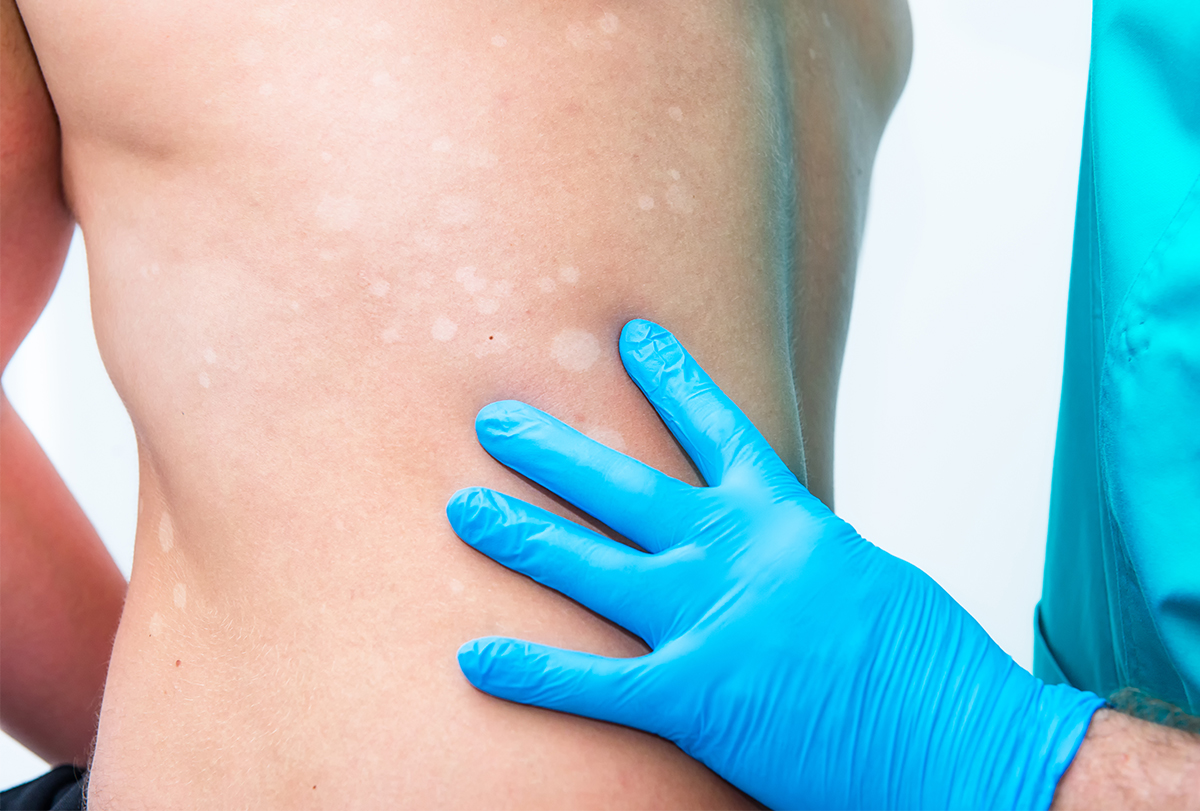
What causes melanin to be low?
Genetics generally determine the amount of melanin in your hair, skin, and eyes, but there are two conditions that can happen when your body lacks melanin: 1 Vitiligo. Vitiligo is an autoimmune condition that occurs when the body doesn’t produce enough melanocytes. This causes a lack of pigment that can appear as white patches on the skin or hair. Vitiligo affects between 1 and 2 percent of people around the world. 2 Albinism. Albinism is a rare genetic condition that occurs when the body doesn’t produce enough melanin. This may happen because of a reduced number of melanocytes or reduced melanin production from melanosomes. There are various types of albinism, but most cause a moderate to severe lack of pigment in the skin, hair, and eyes.
What is it called when you don't produce enough melanin?
Albinism. Albinism is a rare genetic condition that occurs when the body doesn’t produce enough melanin. This may happen because of a reduced number of melanocytes or reduced melanin production from melanosomes. There are various types of albinism , but most cause a moderate to severe lack of pigment in the skin, hair, and eyes.
What causes white spots on the skin?
Vitiligo. Vitiligo is an autoimmune condition that occurs when the body doesn’t produce enough melanocytes. This causes a lack of pigment that can appear as white patches on the skin or hair. Vitiligo affects between 1 and 2 percent of people around the world.
How does the sun affect DNA?
During sun exposure. Trusted Source. , harmful UV rays from the sun penetrate through the skin and begin to damage the DNA in the skin cells. In response to this cellular damage, the body attempts to produce more melanin to protect the cells.
Answer
Melanocytes produce the protective skin-darkening pigment melanin. Melanocyte, specialized skin cell that produces the protective skin-darkening pigment melanin. Birds and mammals possess these pigment cells, which are found mainly in the epidermis, though they occur elsewhere like in the matrix of the hair.
New questions in Biology
American apple cells contain an enzyme that turns the tissues brown when an apple is peeled and left for a time. Boiled apple does not go brown. Expla …
Where are skin cells produced?
Skin cells make up the skin and are mostly produced in the epidermis. Learn about the skin's different layers as well as the different types of skin cells and their respective functions. Updated: 09/23/2021
How does melanin affect skin color?
You might be wondering how your skin can be colored by melanin if these cells aren't on the surface. The answer is that melanocytes only make the melanin. They then transfer the pigments to keratinocytes on the surface of the epidermis. There are different types of melanin that produce different colors. Some, for instance, cause the darker colors of freckles and moles. Cancer of melanocytes is called melanoma and can be deadly if not treated early.
What are the different types of skin cells?
Within the epidermis are layers of four different kinds of skin cells: keratinocytes, melanocytes, Merkel cells, and Langerhans cells. A thin layer called the basement membrane separates the epidermis from the lower layer of the skin, called the dermis.
What happens to skin cells when you grow into an adult?
We're done at that point. There are a few exceptions, however, and one of those is skin cells. You may have noticed that when your skin is dry, it gets flaky and pieces fall off.
What happens to the cells in the epidermis?
From here, the new cells get pushed up into the epidermis. Once in the epidermis, the cells no longer receive blood or nutrients. They begin the slow process of dying and sloughing off to be replaced by yet more new cells. Your outermost layer of skin is nothing but dead cells.
What is the outer layer of the skin?
The outer layer of your skin that you see and feel and with which you sense the world is called the epidermis. Within the epidermis are layers of four different kinds of skin cells: keratinocytes, melanocytes, Merkel cells, and Langerhans cells.
Which cell makes up the epidermis?
Four types of cells make up the skin, and they are produced mainly in the epidermis near the basement membrane. Keratinocytes contain structural keratin and make up the bulk of the epidermis. Melanocytes produce melanin, the pigment that gives skin color.
Where are melanocytes found?
In the human skin, melanocytes are present in the epidermis and hair follicles. The basic features of these cells are the ability to melanin production and the origin from neural crest cells. This last element is important because there are other cells able to produce melanin but of different embryonic origin (pigmented epithelium of retina, some neurons, adipocytes). The life cycle of melanocyte consists of several steps including differentiation of melanocyte lineage/s from neural crest, migration and proliferation of melanoblasts, differentiation of melanoblasts into melanocytes, proliferation and maturation of melanocytes at the target places (activity of melanogenic enzymes, melanosome formation and transport to keratinocytes) and eventual cell death (hair melanocytes). Melanocytes of the epidermis and hair are cells sharing some common features but in general they form biologically different populations living in unique niches of the skin.
Where are melanocytes located in the hair?
Melanocyte localization in the hair between cells covering the hair papilla in the hair bulb. Stem cells for melanocytes are located in the region named the hair bulge
What is the simplified scheme of melanin synthesis in melanocytes during melanogenesis?
Simplified scheme of the melanin synthesis in melanocytes during melanogenesis. Tyrosine under influence of the basic enzymes such as tyrosinase (TYR), tyrosine- related protein 1 (TYRP1) and 2 (TYRP2) changes into a polymer of melanin, a mixture of pigments named eumelanin (black-brown) and pheomelanin (yellow-red)
What is the process of melanin synthesis?
Melanogenesis is a biochemical path way responsible for melanin synthesis [37]. It takes place in melanocytes, in separate cytoplasmic organelles called melanosomes [11]. Two major types of melanin are produced – pheomelanin and eumelanin. They differ in color and the way of synthesis. Melanin has numerous properties which are beneficial to the body: UV light absorption and scattering, free radical scavenging, coupled oxidation-reduction reactions and ion storage [23, 38, 39]. The availability of substrates and the function of melanogenesis enzymes decide about the types of melanins produced (Figure 4). Tyrosinase (TYR) carries out tyrosine hydroxylation to L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (DOPA) which is rapidly oxidized to DOPAquinone [40]. In the presence of cysteine DOPAquinone react with it, yielding 3- or 5-cysteinylDOPAs, which then oxidize and polymerize, giving rise to yellow-red soluble melanin – pheomelanin [37, 41]. In the absence of thiols (cysteine, glutathione or thioredoxin) brown-black eumelanin is produced. DOPAquinone spontaneously undergoes cyclization to DOPAchrome [42]. The DOPAchrome spontaneously loses carboxylic acid and generates 5,6-dihydroxyindole (DHI), which rapidly oxidizes and polymerizes to form dark brown-black, insoluble DHI-melanin. However, if DOPAchrome tautomerase (TYRP2/DCT) is present, DOPAchrome will form DHI-2-carboxylic acid (DHICA) [43]. Tyrosinase and TYRP1 catalyze further conversions obtaining finally a lighter brown color DHICA-melanin [30, 37]. Human skin contains a mixture of all melanin types, and the ratio of those in part determines visible pigmentation [19]. Diversity of skin pigmentation among different ethnic groups is preserved and depends on eumelanin content. The ratio of eumelanin to total melanin decide about skin color [30]. Pheomelanin does not correlate with skin pigmentation, a similar amount of this pigment is observed in the dark and light skin. While in hair, the ratio of eumelanin to pheomelanin decides about the color [35]. Eumelanin comparing to pheomelanin has better photoprotecting properties – higher resistance to degradation and ability to reactive oxygen species (ROS) neutralization [44]. Eumelanins are considered to be more effective in terms of photoprotection than the reddish pheomelanin. As a consequence, the risk of skin cancer in lighter skin is 30-40-fold higher than in the darker one [41]. Products of genes regulating melanogenesis act at subcellular, cellular, tissue and environmental levels [21]. During melanogenesis, as intermediate products, cytotoxic molecules are synthesized (quinones, hydrogen peroxide). Thus, melanocyte protects itself by separating areas of melanogenesis in melanosomes and increases the level of antiapoptotic protein Bcl-2 [1, 21].
How long do melanocytes live?
Epidermal melanocytes are long-living cells while hair melanocytes live as the hair cycle lasts (median: 3-5 years) [31]. Density of melanocytes in the skin depends on the environment (mainly UVR) and factors secreted by keratinocytes and fibroblasts. After 30 years of age 10-20% of epidermal melanocytes are lost every decade [51]. In the older people, apart from a decreased number of melanocytes morphology is changed (melanocytes are larger, more dendritic) and tyrosinase activity is reduced [19, 31, 52]. The relationships between ageing and the proliferative activity of melanocytes have been observed. In vitro, adult melanocytes proliferate less times than fetal and neonatal melanocytes [53]. Also, melanocytes from patients with a premature ageing disorder have reduced proliferative potential [50]. Terminally differentiated melanocyte proliferative potential is inhibited by changes in the cell cycle control elements, e.g. accumulation of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors (p27Kip1, p16INK4aand p21Cip1), hypophosphorylation of pRB (retinoblastoma protein), decrease level of cyclin D1 [50, 53]. Table 3lists basic cell cycle regulators involved in the regulation of melanocytic senescence (based on [53]).
What are the factors that control melanocytes?
Melanocytes’ biology is controlled also by dermal fibroblasts secreted factors, e.g. stem cell factor (SCF), neuregulin 1 (NRG1) [23, 26]. These cytokines influence not only the growth and pigmentation of melanocytes, but also their shape, dendricity, mobility and adhesive properties [23, 27]. In the epidermal melanin unit melanocyte is a very active element that secrets a number of signal molecules targeting not only keratinocytes but also skin immunological system cells [28, 29]. The proinflammatory cytokines (IL-1α, IL-2, IL-3, IL-6, IL-10 and TNF-α), chemokines (IL-8, CCL2), transforming growth factor (TGF-β), catecholamines, eicosanoids, serotonin, melanocyte stimulating factor (α-MSH) and nitric oxide (NO) are included as factors released by stimulated melanocytes [28, 29]. Secreted substances act also as autocrine factors, e.g. IL-1, IL-6 and TNF-α inhibit melanogenesis while under the influence of eicosanoids and α-MSH the level of melanin synthesis is elevated [30]. Thus, melanocytes and cooperating keratinocytes form well-organized units in the epidermis. The stable element in each unit is the melanocyte that lives long, keratinocytes die and are shedding. It is an open question how long melanocyte lives in the human skin.
How many stages of melanosome development are there?
There are four stages in melanosome development (Table 2). Premelanosomes (Stage I) are a round, small vesicles with an amorphous matrix. Melanosomes at Stage II have an organized, structured fibrillar matrix (mainly from gp100 family) and tyrosinase is present but pigment synthesis has not been noted. The beginning of melanin production takes place at Stage III, where pigment is deposited on protein fibrils. At the last Stage IV pigment fills the whole melanosome [41, 47]. Fully melanized melanosomes lose tyrosinase activity and are transported to surrounding keratinocytes by elements of the cytoskeletal system (Figure 1) [48].
Which cell is located in the basal layer of the epidermis?
These cells attach themselves to antigens that invade damaged skin and alert the immune system to their presence. Melanocyte. A melanocyte is a cell that produces melanin, and is located in the basal layer of the epidermis. Merkel Cells.
What are the layers of the skin?
Basically, the skin is comprised of two layers that cover a third fatty layer. These three layers differ in function, thickness, and strength. The outer layer is called the epidermis; it is a tough protective layer that contains the melanin -producing melanocytes. The second layer (located under the epidermis) is called the dermis;
What is the outermost layer of the epidermis?
Stratum Corneum. The stratum corneum is outermost layer of the epidermis, and is comprised of dead skin cells. It protects the living cells beneath it by providing a tough barrier between the environment and the lower layers of the skin.
What nerves are in the epidermis?
Sensory Nerves. The epidermis is innervated with sensory nerv es. These nerves sense and transmit heat, pain, and other noxious sensations. When they are not functioning properly sensations such as numbness, pins-and-needles, pain, tingling, or burning may be felt.
What is the second layer of the skin called?
The second layer (located under the epidermis) is called the dermis; it contains nerve endings, sweat glands, oil glands, and hair follicles. Under these two skin layers is a fatty layer of subcutaneous tissue, known as the subcutis or hypodermis. The skin contains many specialized cells and structures: Basket Cells.
Where is the hair follicle located?
It is located in the epidermis and the dermis. Hair Shaft. The hair shaft is the part of the hair that is above the skin. Langerhans Cells.
What are the two types of skin?
There are two general types of skin; thin and hairy, which is more prevalent on the body, and thick and hairless , which is found on parts of the body that are used heavily and endure a large amount of friction, like the palms of the hands or the soles of the feet. Basically, the skin is comprised of two layers that cover a third fatty layer.
Where is melanin found in the body?
Melanin is also found in the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye (the retina), where it plays a role in normal vision. Melanocytes make two forms of melanin, eumelanin and pheomelanin. The relative amounts of these two pigments help determine the color of a person's hair and skin.
Why do people with pheomelanin have red hair?
People who produce mostly pheomelanin tend to have red or blond hair, freckles, and light-colored skin that tans poorly. Because pheomelanin does not protect skin from UV radiation, people with more pheomelanin have an increased risk of skin damage caused by sun exposure.
What is the function of the melanocortin 1 receptor?
The melanocortin 1 receptor controls which type of melanin is produced by melanocytes. When the receptor is activated, it triggers a series of chemical reactions inside melanocytes that stimulate these cells to make eumelanin. If the receptor is not activated or is blocked, melanocytes make pheomelanin instead of eumelanin.
What is the role of MC1R in hair color?
Although MC1R is a key gene in normal human pigmentation, researchers believe that the effects of other genes also contribute to a person's hair and skin coloring.