
What is cartilage in the spine?
Cartilage is a firm, flexible connective tissue found in many areas of the body, primarily around bones and joints. In the spine, it helps joints and discs move without friction.
What is the spine made up of?
The spine is made up of a series of bones that are stacked like blocks on top of each other with cushions called discs in between to help absorb shock/load. The spine is divided into three regions: Cervical spine — The cervical spine (or neck) is the uppermost part of the spine.
What is the function of the spinal disc?
Spinal Discs. They act as a shock absorbers in the spine, positioned between each bony vertebra. They act as tough ligaments that hold the vertebrae of the spine together. They are cartilaginous joints that allow for slight mobility in the spine. There are a total of twenty-three vertebral discs in the spinal column.
What causes cartilage to degenerate on the spine?
Causes and Symptoms of Spinal Cartilage Degeneration. Some of the more common spinal conditions that can result as a direct cause of degenerating spinal disc cartilage include a herniated or bulging disc, degenerative disc disease, and spinal stenosis.

What is a spinal disk made of?
The intervertebral disc is made up of two components: the annulus fibrosus and thenucleus pulposus. The annulus fibrosus is the outer portion of the disc. It is composed of layers of collagen and proteins, called lamellae.
What is the difference between cartilage and disc?
Discs are the cushions between the vertebrae in the spine. They are made up of cartilage – soft cartilage on the inside with an outer layer of tough cartilage.
What type of cartilage is Spinal discs?
The intervertebral disk end plate comprises a thin layer of hyaline cartilage that is bonded to an underlying layer of perforated cortical bone.
What happens when the discs in your back wear away?
Degenerative disk disease occurs when your spinal disks break down. When these disks wear out, people typically experience back pain and stiffness. You may find pain relief with nonsurgical treatments such as physical therapy and spinal injection.
Can a degenerative disc ever heal?
No, degenerative disc disease cannot heal on its own. Many treatments for degenerative disc disease focus on reducing symptoms. Some people experience more severe or longer-lasting symptoms than others.
Are spinal discs bones?
Your spine is made up of 24 small bones (vertebrae) that are stacked on top of each other to create the spinal column. Between each vertebra is a soft, gel-like cushion called a disc that helps absorb pressure and keeps the bones from rubbing against each other.
What tissue is the intervertebral discs made of?
FibrocartilageFibrocartilage is the tough, very strong tissue found predominantly in the intervertebral disks and at the insertions of ligaments and tendons; it is similar to other fibrous tissues but contains cartilage ground substance and chondrocytes.
What type of tissue is the intervertebral disc?
fibrocartilage2.1 Introduction. Intervertebral discs are pads of fibrocartilage which lie between the vertebrae of the spine.
Can you rebuild cartilage in your spine?
A: Though it is made of cells and tissues, cartilage cannot repair itself due to the lack of blood vessels and enough blood supply to create and duplicate new cells.
How do they repair cartilage in the spine?
6 treatment options to repair damaged cartilageArthroscopic debridement. ... Microfracture. ... Autologous chondrocyte implantation (ACI) ... Articular cartilage repair: Matrix-induced autologous chondrocyte implantation (MACI) ... Osteochondral autograft transplantation. ... Stem cell therapy.
What causes cartilage loss in the spine?
Cartilage loss caused by a direct injury can result from blunt trauma to the joint. This can be from a severe car accident or even a very bad fall where the joint makes direct impact with the ground. If you're an athlete, sporting injuries are also a cause of cartilage loss.
Can cartilage be replaced in spine?
Without cartilage, the integrity of bones will wear down, and they may eventually need to be replaced through a joint replacement procedure. However, some patients qualify for a surgery in which the cartilage can be replaced in hopes of preventing/prolonging the need for a replacement.
What causes degeneration of disc cartilage?
Inhibited gait. Some of the more common spinal conditions that can result as a direct cause of degenerating spinal disc cartilage include a herniated or bulging disc, degenerative disc disease, and spinal stenosis.
What to do if cartilage degeneration is confirmed?
Once cartilage degeneration is confirmed, your doctor will walk you through your treatment options. In most cases, conservative treatment options will be the first choice, where things like physical therapy, targeted exercise routines, pain medications or strength training and stretching will be used to see if pain alleviates.
Why does cartilage hurt?
Unfortunately, due to acute injury or natural degeneration, cartilage can wear down, which can inhibit movement or make it painful.
What is the best test for cartilage damage?
The most common test for checking for cartilage damage is an MRI , which uses a magnetic field and radio waves to create a detailed picture of the body. Another common diagnostic tool is called an arthroscopy, which is better able to diagnose cartilage damage in joints like the knee or elbow.
What to do when you walk into a spinal doctor?
However, the first thing a good spinal specialist will do when you walk into their office is to conduct a physical exam. This will allow the doctor to get a better understanding of which areas of your spine are hurting, and they’ll ask you about your symptoms and what makes pain worse or better.
What can help with pain caused by a loss of cartilage?
Surgical procedures like artificial disc replacement or spinal fusion can help to prevent pain caused by a loss of spinal cartilage. Your surgeon can walk you through the specifics should your pain progress this far, but it’s worth noting that many of these surgeries have very high success rates. Comments are closed.
Does exercise help with cartilage?
You might think that movement of these discs and joints serves to break down the cartilage, but movement and exercise can actually help strengthen these areas. Lack of movement or spinal exercise can actually be worse for your cartilage than overworking the spine, but a healthy medium is best.
What are the different types of spines?
From the side, the spine has an S-shaped curve, which acts like a spring to absorb shock, maintain balance and allow movement. The sections of the spine are: 1 Cervical (neck) – supports head and allows the neck to move 2 Thoracic (mid back) – holds the rib cage and protects the heart and lungs 3 Lumbar (lower back) – carries the weight of the trunk 4 Sacrum – connects the spine to the hip bones (iliac); forms the pelvic girdle with the iliac bones 5 Coccyx – attaches to the ligaments and muscles of the pelvic floor
What is the ring of the pelvic floor called?
A disc that acts like a cushion and stops the bones rubbing together separates each vertebra. The outer ring of the discs, called the annulus, has criss-crossing bands that attach to each vertebra. The discs have a gel-filled centre called the nucleus.
Which section of the spine supports the head and allows the neck to move?
The sections of the spine are: Cervical (neck) – supports head and allows the neck to move. Thoracic (mid back) – holds the rib cage and protects the heart and lungs. Lumbar (lower back) – carries the weight of the trunk. Sacrum – connects the spine to the hip bones (iliac); forms the pelvic girdle with the iliac bones.
What is the function of the spine?
It also protects the spinal cord, which transmits information between the body and brain via the nerves. From the side, the spine has an S-shaped curve, which acts like a spring to absorb shock, maintain balance and allow movement. The sections of the spine are:
How many discs are there in the spine?
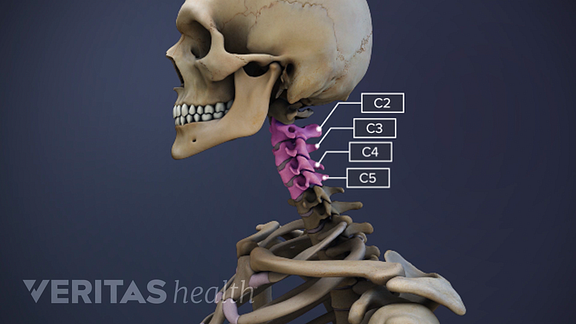
There are 23 discs in the human spine: 6 in the neck ( cervical) region, 12 in the middle back ( thoracic) region, and 5 in the lower back ( lumbar) region Discs are named by the vertebral body above and below. For example, the disc between the fifth and sixth cervical vertebrae is designated "C5-6".
How many discs are there between vertebrae?
There is one disc between each pair of vertebrae, except for the first cervical segment, the atlas. The atlas is a ring around the roughly cone-shaped extension of the axis (second cervical segment). The axis acts as a post around which the atlas can rotate, allowing the neck to swivel.
What is the structure of the Cervical vertebra?
Structure. Cervical vertebra with intervertebral disc. Intervertebral discs consist of an outer fibrous ring, the anulus fibrosus disci intervertebralis, which surrounds an inner gel-like center, the nucleus pulposus. The anulus fibrosus consists of several layers (laminae) of fibrocartilage made up of both type I and type II collagen.
What is the space between adjacent vertebrae?
Intervertebral disc space . The intervertebral disc space is typically defined on an X-ray photograph as the space between adjacent vertebrae. In healthy patients, this corresponds to the size of the intervertebral disc.
What is the intervertebral disc?
Anatomical terminology. An intervertebral disc (or intervertebral fibrocartilage) lies between adjacent vertebrae in the vertebral column. Each disc forms a fibrocartilaginous joint (a symphysis ), to allow slight movement of the vertebrae, to act as a ligament to hold the vertebrae together, and to function as a shock absorber for the spine.
Which type of intervertebral disc is concentrated toward the edge of the ring?
The stiff laminae can withstand compressive forces. The fibrous intervertebral disc contains the nucleus pulposus and this helps to distribute pressure evenly across the disc.
What is a herniated disc?
Herniation. Stages of spinal disc herniation. Main article: Spinal disc herniation. A spinal disc herniation, commonly referred to as a slipped disc, can happen when unbalanced mechanical pressures substantially deform the anulus fibrosus, allowing part of the nucleus to obtrude.
What is the ring of the pelvic girdle?
The sacrum and hip bones form a ring called the pelvic girdle. Coccyx (tailbone): Four fused vertebrae make up this small piece of bone found at the bottom of the spine. Pelvic floor muscles and ligaments attach to the coccyx.
What are the parts of the spine?
Key parts of your spine include vertebrae (bones), disks, nerves and the spinal cord. The spine supports your body and helps you walk, twist and move. The disks that cushion vertebrae may compress with age or injury, leading to a herniated disk. Exercises can strengthen the core muscles that support the spine and prevent back injuries and back pain.
What are bone spurs?
Bone spurs (jagged edges on vertebrae that put pressure on the spinal cord and nerves). Curvatures of the spine ( scoliosis and kyphosis ). Neuromuscular diseases, such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Nerve injuries, including spinal stenosis, sciatica and pinched nerves. Osteoporosis (weak bones).
What causes spine pain?
Other conditions that affect spine health include: Arthritic conditions, such as ankylosing spondylitis (AS). Back strains and sprains. Birth defects such as spina bifida. Bone spurs (jagged edges on vertebrae that put pressure on the spinal cord and nerves).
How to prevent back pain?
Exercises can strengthen the core muscles that support the spine and prevent back injuries and back pain. The spine has three normal curves: cervical, thoracic and lumbar. There are seven cervical vertebrae in the neck, 12 thoracic vertebrae in the torso and five lumbar vertebrae in the lower back.
Which part of the spine supports the upper part of the spine?
Lumbar (lower back): Five vertebrae (L1 to L5) make up the lower part of the spine. Your lumbar spine supports the upper parts of the spine.
Which vertebrae allow you to turn, tilt and nod your head?
These neck vertebrae allow you to turn, tilt and nod your head. The cervical spine makes an inward C-shape called a lordotic curve. Thoracic (middle back): The chest or thoracic part of the spine has 12 vertebrae (T1 to T12). Your ribs attach to the thoracic spine.
How to treat spinal degeneration?
Severe degeneration may be treated with an arthroscopic procedure that involves removing damaged parts of cartilage. Surgery may also be an option if there is a related issue contributing to your discomfort, such as a herniated disc that’s compressing nerves. Cartilage damage is sometimes minimized with artificial disc replacement or a fusion if the spine has become unstable. There are also a wide variety of spinal fusion alternatives.
How do you know if you have cartilage degeneration?
Signs and Symptoms. Symptoms associated with spinal cartilage degeneration can vary based on which part of the spine is affected. Localized pain may be felt in the lower back or neck if only the area where cartilage is worn is affected.
What causes cartilage degeneration in the spine?
The onset of spinal cartilage degeneration is sometimes hastened by underlying issues like spinal osteoarthritis or issues with the discs and joints of the spine. In some cases, the reverse is true and worn or damaged cartilage is what contributes to degenerative disc disease and disc herniation. It may also play a role in the severity ...
What are the symptoms of spinal cartilage degeneration?
If this happens, symptoms associated with spinal cartilage degeneration may include: Radiating pain felt in arms, shoulders, hips, or legs. Numbness and tingling sensations. Noticeable reduction in range of motion. Difficulty walking.
Why does cartilage wear down?
Over time, cartilage can wear down, a process that’s sometimes hastened by an injury or progressive condition such as arthritis that affects tissues around bones and joints. When this happens, bones, joints, and discs of the spine are more susceptible to damage since there’s less cushioning from cartilage.
Does exercise help with cartilage degeneration?
However, avoiding exercise can weaken muscles that provide some type of support to the spine, which forces the backbone and its discs to absorb more pressure from daily movements. Most patients with spinal cartilage degeneration respond well to conservative (non-surgical) treatments, which may include: Massage therapy.
Can a CT scan show spinal degeneration?
Since the symptoms typically experienced with spinal cartilage degeneration can also be associated with other sources of back, neck, or radiating pain, diagnosis usually involves an examination, a review of medical history, and image testing. X-rays won’t show cartilage damage, so an MRI or CT scan is often done to make a positive diagnosis.
What is a Bulging Disc?
Bulging discs occur when the disc becomes dehydrated and its circumference increases. Think of a hamburger that is too big for the bun. Only the outside, tough cartilage layer is affected.
What is a Herniated Disc?
Herniated discs, also called ruptured or slipped discs, are typically much more painful than bulging discs. This is because herniated discs occur when there is a crack in the outer cartilage, exposing the inner, soft cartilage.
What is the spine made of?
Your spine is made up of bones called vertebrae that are stacked on top of each other. Disks between the vertebrae work like cushions to allow the vertebrae to rotate and move without the bones rubbing against each other. The lumbar vertebrae and disks are at the bottom of your spine. Lumbar disk replacement involves replacing a worn ...
What happens during lumbar disk replacement?
What happens during a lumbar disk replacement? You will have an IV line put into a vein in your hand or arm through which an anesthetic is given. The medicine will put you into a deep sleep and keep you from feeling pain during the surgery. You will be lying on your back for this surgery.
Why do I need a lumbar replacement?
Why might I need a lumbar disk replacement? The main reason you would need a lumbar disk replacement is to treat low back pain. Still, not everyone with low back pain is a good candidate for a lumbar disk replacement surgery. Your doctor will need to do some tests to see if it’s the right procedure for you.
What are the risks of a spinal stenosis surgery?
Some of the potential risks of this surgery include: Infection of the artificial disk or the area around it. Dislocation or dislodging of the artificial disk. Implant failure or fracture (break) Implant loosening or wear. Narrowing of the spine (stenosis) because of the breakdown of spinal bones.
How long does it take to recover from lumbar disc replacement?
You’ll need to avoid any jarring activities or motions for quite a while. Your recovery may take from a few weeks to a few months. A lumbar disk replacement generally improves pain, but it does not eliminate it completely. Talk with your doctor to get a realistic idea about what you can expect after this surgery.
Where is the lumbar disc?
The lumbar vertebrae and disks are at the bottom of your spine. Lumbar disk replacement involves replacing a worn or degenerated disk in the lower part of your spine with an artificial disk made of metal or a combination of metal and plastic. Lumbar disk replacement is generally seen as an alternative to the more common spinal fusion surgery.
Why is my spine narrowing?
Narrowing of the spine (stenosis) because of the breakdown of spinal bones. Problems due to a poorly positioned implant. Stiffness or rigidity of the spine. Blood clots in your legs due to decreased activity. There may be other risks, depending on your specific medical condition.
Overview
Clinical significance
Anything arising from the intervertebral disc may be termed discogenic in particular when referring to associated pain as discogenic pain.
A spinal disc herniation, commonly referred to as a slipped disc, can happen when unbalanced mechanical pressures substantially deform the anulus fibrosus, allowing part of the nucleus to obtrude. These events can occur during peak physical performance, during traumas, or as a resu…
Structure
Intervertebral discs consist of an outer fibrous ring, the anulus fibrosus disci intervertebralis, which surrounds an inner gel-like center, the nucleus pulposus. The anulus fibrosus consists of several layers (laminae) of fibrocartilage made up of both type I and type II collagen. Type I is concentrated toward the edge of the ring, where it provides greater strength. The stiff laminae can withstand compressive forces. The fibrous intervertebral disc contains the nucleus pulposus an…
Function
The intervertebral disc functions to separate the vertebrae from each other and provides the surface for the shock-absorbing gel of the nucleus pulposus. The nucleus pulposus of the disc functions to distribute hydraulic pressure in all directions within each intervertebral disc under compressive loads. The nucleus pulposus consists of large vacuolated notochord cells, small chondrocyte-like cells, collagen fibrils, and aggrecan, a proteoglycan that aggregates by binding to
Etymology
The Latin word anulus means "little ring"; it is the diminutive of anus ("ring"). The misspelling annulus is also common.
See also
• Back pain
• Degenerative disc disease
• Spinal decompression
• Lumbar spinal stenosis
External links
• Intervertebral Discs
• Spinal Disc Summary
• Cross section image: pembody/body12a—Plastination Laboratory at the Medical University of Vienna