What is a bathyal zone ecosystem?
bathyal zone, marine ecologic realm extending down from the edge of the continental shelf to the depth at which the water temperature is 4° C (39° F). Both of these limits are variable, but the bathyal zone is generally described as lying between 200 and 2,000 m (660 and 6,600 feet) below the surface.
Is there sunlight in the bathyal zone?
The depths from 1,000-4,000 meters (3,300 - 13,100 feet) comprise the bathypelagic zone. Due to its constant darkness, this zone is also called the midnight zone. The only light at this depth (and lower) comes from the bioluminescence of the animals themselves.
What are the characteristics of the bathyal zone?
The bathyal zone or the bathypelagic zone, which means 'midnight zone. This is the part of the open ocean that extends from a depth of about 1,000 to 4,000 m (that is 3,300 to 13,100 ft) this lies below the ocean surface. This zone lies between the mesopelagic above and the abyssopelagic which lies below.
Which ocean zone has plants?
The top zone is the euphotic or sunlit zone. This is the ocean zone that sunlight penetrates. Because this zone gets sunlight, photosynthesis can occur and plants can grow here.
Is there life in the bathypelagic zone?
Animals living in the bathypelagic zone rely on detritus for food or on eating other animals in this zone. At this depth and pressure, the animals most commonly found are fish, mollusks, crustaceans, and jellyfish. Sperm whales will hunt at these depths on occasion to prey on giant squid.
What are the challenges of living in the bathypelagic zone?
The constraints of darkness, high pressure, cold temperatures, and large distance from the base of the food chain (plankton, which require sunlight) limit the amount of life that the bathypelagic zone can support. Therefore, finding food, while simultaneously conserving energy, presents a major challenge.
Why is there no plant life in the bathyal zone?
Sunlight does not reach this zone, meaning primary production, if any, is almost nonexistent. There are no known phytoplankton or aquatic plants in this zone because of the lack of sunlight necessary for photosynthesis.
What are the producers of the bathyal zone?
Answer and Explanation: There are no producers found in the bathypelagic zone. This is because producer organisms are autotrophic organisms that make their food using photosynthesis. There is no light that penetrates the bathypelagic zone, which is why it is also called the midnight zone.
Where are bathyal zone found?
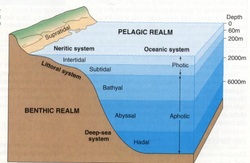
The bathyal zone lies along the slopes of continents and on seamounts and underwater rises. It extends from the edge of the shelf to the beginning of the abyss and is a substantial part of the ocean, being larger than the shallow shelf zone, including the sublittoral.
Where in the ocean do most plants live?
Euphotic ZoneAlmost all ocean plants grow in the Euphotic Zone, the upper 200 meters. This depth is referred to as the “Sunlight Zone” because sunlight penetrates through it. Plants make their food through photosynthesis, a process that requires 4 things: Water – Plenty of that in the oceans.
In what zone can photosynthesis not happen?
From 200 to 1000 metres lies the dysphotic zone, or the twilight zone (corresponding with the mesopelagic zone). There is still some light at these depths, but not enough to support photosynthesis. Below 1000 metres is the aphotic (or midnight) zone, where no light penetrates.
What ocean zone is the Titanic in?
The Titanic lies at 3,800 meters or about 12,500 feet. This area of the ocean is known as the Bathyal zone. The average temperature is 39° F. The pressure at this depth is 5,850 pounds per square inch.
Does the twilight zone receive sunlight?
660-3,300 feet below the surface of the ocean Just below the sunlight zone is the twilight zone. This zone still gets some sunlight, but is colder. Marine life at this layer often has larger eyes. Larger eyes allow more light into the eye and help these animals to see better.
Is there sunlight in the Epipelagic zone?
The epipelagic zone gets plenty of sunlight, with a slightly shaded effect in its lower regions that end at 200 meters below the surface. The abundance of sunlight is why photosynthetic organisms can survive in the epipelagic zone, where they cannot survive in the lower depth zones.
Does the mesopelagic zone receive sunlight?
This area is known as the twilight zone, as it sits between the epipelagic zone, which receives the most light, and the bathypelagic zone, which receives no light. The light that reaches the mesopelagic zone is dim and does not allow for photosynthesis.
Where is the sunlight zone located?
The upper 200 meters of the ocean is called the euphotic, or "sunlight," zone. This zone contains the vast majority of commercial fisheries and is home to many protected marine mammals and sea turtles. Only a small amount of light penetrates beyond this depth.
1. What are Equatorial Regions?
Ans. Equatorial regions are those regions that are located in a band that is around the Equator and this covers about 6% of the Earth's surface. Th...
2. What is Mesopelagic?
Ans. The mesopelagic zone is also known as the middle pelagic or the twilight zone, which is the part of the pelagic zone lying between the photic...
3. What Do You Mean By Bioluminescent?
Ans. Bioluminescence is the production and thereby the emission of light by a living organism. This is a form of chemiluminescence. The bioluminesc...
What is the bathyal zone?
The Bathyal zone is the marine ecologic realm that extends down from the continental shelf to the depth where the water temperature is 4°C (which is 39°F). Both these limits are variable number, but the bathyal zone is normally described as a surface which lies between 200 and 2,000 m (that is 660 and 6,600 feet) below the surface area.
What is the temperature of the bathyal zone?
In the bathyal zone, the marine ecologic realm extends down from the edge of the continental shelf towards the depth where the water temperature is 4° C (that is around 39° F). Both these temperature limits are quite variable, yet the bathyal zone is generally described as lying between the 200 and 2,000 m (which is 660 and 6,600 feet) below the surface area.
What is the mesopelagic zone?
The mesopelagic zone is also known as the middle pelagic or the twilight zone, which is the part of the pelagic zone lying between the photic epipelagic and the aphotic bathypelagic zones. The mesopelagic zone extends from 660-3,300 feet which are below the ocean surface.
Why is the single habitat species diversity higher for the bathyal fauna?
This condition is caused by the constancy of the bathyal environmental conditions, moreover about the temperature. The bottom dwellers in the zone with adequate circulation get adapted to the local substrate conditions. The terrigenous bottoms which are located near ...
How deep can sunlight penetrate the bathyal waters?
In these tropic regions, small amounts of sunlight can penetrate deep as 600 m (2,000 feet). The temperatures in higher latitudes range from approximately 3° to -1° C (that is 37° to 30° F). Except for this place, the normal temperatures range between 5° and 15° C (that is 41° and 59° F), the western oceanic margins are warmer, this is because of the current from the equatorial region and from the eastern margins which receives colder boreal currents and also experiences upwelling. The salinities typically range between 34 and 36 parts per thousand in the bathyal zone. While it varies with local conditions of water-mass formation. The Bathyal fauna reflects how the narrow ranges of temperature and salinity occur.
How deep is the bathyal water?
At the bathyal depths, here the currents are exceedingly slow, also in many areas, the bathyal waters are quite deeper than 1,000 m (that is 3,280 feet) this water is essentially stagnant, which results in low oxygen concentrations and impoverished faunal levels.
What is the salinity of the bathyal zone?
The salinities typically range between 34 and 36 parts per thousand in the bathyal zone. While it varies with local conditions of water-mass formation. The Bathyal fauna reflects how the narrow ranges of temperature and salinity occur.
What is the sublittoral zone?
Sublittoral zone—away from land, that is, low-tide mark to edge of the continental shelf. •. Bathyal zone—slopes and rises of the ocean floor. •. Abyssal zone—the region of ocean floor plains. •. Hadal zone—the region of deep trenches in ocean. The pelagic zone has two main subdivisions: neritic zone and oceanic zone.
What is the deep sea zone?
The slope, terraces, and plateaux from depths of 200 to 2000 m are referred to as the bathyal or deep-sea zone. The bathyal zone and the abyssal and hadal zones below it are referred to as the deep sea. In much of the hydrocarbon resource area of the North West Shelf, the sea bed lies in this depth zone.
What is the deep sea fauna of Australia?
The deep-sea benthic bathyal fauna of Australia, especially that of the North West Shelf, is little known. 19 A review of key ecological features in the Northwest Marine Region 12 provides a summary of knowledge of the deep-sea environment and identified databases of relevant information and specimens from the region. Two systematic accounts of benthic slope invertebrates in the region deal with ophiuroids 20 and azooxanthellate corals 21 and include references to species that inhabit this depth zone.
Why do benthic species have more phyla than pelagic species?
The number of phyla and the number of species of benthic animals exceeds those of pelagic species, at least partly because of the greater physical variety of benthic habitats.
What are sediments in the North West Shelf?
Sediments of the North West Shelf slope are carbonates, generally silty sands composed of skeletal remains of pelagic foraminifera. Ripple marks indicate bottom currents, but apart from these, the topography of the seabed is regular and featureless except for the high biohermic banks such as the Rowley Shoals and Scott and Seringapatam Reefs on the slope terraces. Typically, the physical conditions of these benthic bathyal habitats are relatively uniform and constant compared to the benthic shelf. However, reviews of the world’s deep-sea benthos 17 show that this ecosystem is patchy but with surprisingly high biomass in places and with high levels of species-richness that surpass that of many terrestrial and other marine systems that are commonly regarded as supporting high biodiversity.
How are the numbers of species in a benthic community determined?
The numbers and types of species making up any particular benthic community are determined by a variety of physical and biological factors. In shallow coastal communities, the types of species present and their relative abundance will be partly determined by tidal levels and degree of exposure to air, wave action, and range of salinity and temperature. At all depths, the type of sediment (e.g. sand, rock, mud) will dictate the relative proportions of epifauna and infauna. Biological factors that influence benthic community structure include competition for limited resources (e.g. food, space), predation, and type of development.
Where do brachiopods live?
At high latitudes, brachiopods range from intertidal depths to basinal environments at depths of over 6000 m. They are most common in fjord settings in Canada, Norway and Scotland and in the seas around Antarctica and New Zealand. The association between the horse mussel Modiolus and the brachiopod Terebratulina retusa is particularly widespread in the Northern Hemisphere. In the tropics, however, many species are micromorphic, exploiting cryptic habitats in reef crevices or in the shade of corals and sponges. Larger forms live in deeper-water environments, evading groups of predators that might graze on meadows of newly attached larvae.
What is bathyal sediment?
Bathyal sediments are terrestrial, pelagic, or authigenic (formed in place). Terrestrial (or land-derived) sediments are predominantly clays and silts and are commonly coloured blue because of accumulated organic debris as well as bacterially produced ferrous iron sulfides.
What is the depth of the abyssal zone?
…abyssal zone and the overlying bathyal zone is conveniently defined as the depth at which the water temperature is 4° C (39° F); this depth varies between 1,000 and 3,000 m. Waters deeper than 6,000 m are treated separately as the hadal realm by ecologists.…
Why do some species in the bathyal zone have no eyes?
Fun Fact! Primary production (the synthesis of organic compounds from atmospheric or aqueous carbon dioxide.) does not happen in this zone due to the lack of sunlight. Because of this, some of the species that inhabit the bathyal zone do not have eyes.
Why are there no plants?
There are no plants because of the lack of sunlight necessary for photosynthesis.