Full Answer
Do some protists live in ponds?
Protists make their homes in aquatic environments such as oceans, ponds, lakes and streams. Some attach themselves to rocks and reside on the bottom, while others float on the surface of the water, taking advantage of photosynthesis. Protists also live in aquariums and birdbaths. See also what animal lives in south america
What organisms can be found in pond water?
What types of organisms can be found in pond water?
- Arthropods.
- Bacteria.
- Protozoa.
- Hydras.
- Algae.
What animals live in pond water?
What can live in an outdoor pond?
- Archerfish.
- Bluegills.
- Fathead Minnows.
- Golden Rainbow Trout.
- Goldfish.
- Koi.
- Pumpkinseeds.
- Redears.
What plants can be found in pond water?
Here is a list of the top aquatic flowering plants:
- Water iris. These are emergent aquatic flowering plants and their flowers are generally bright, sunny yellow in color.
- Lotus plants. These flowering water plants have exotic flowers can float on ponds or grow tall on long stems. ...
- Water lily plants. ...
- Water hawthorn plants. ...
- Mosaic flower. ...
- Flowering water poppies
What are the organisms in pond water?
What kingdoms are in a pond?
How many species of algae are there in the world?
Why do phytoplankton exist in rivers?
What are the arthropods?
What would happen if there were no microorganisms?
How do fungi help other organisms?
See 2 more
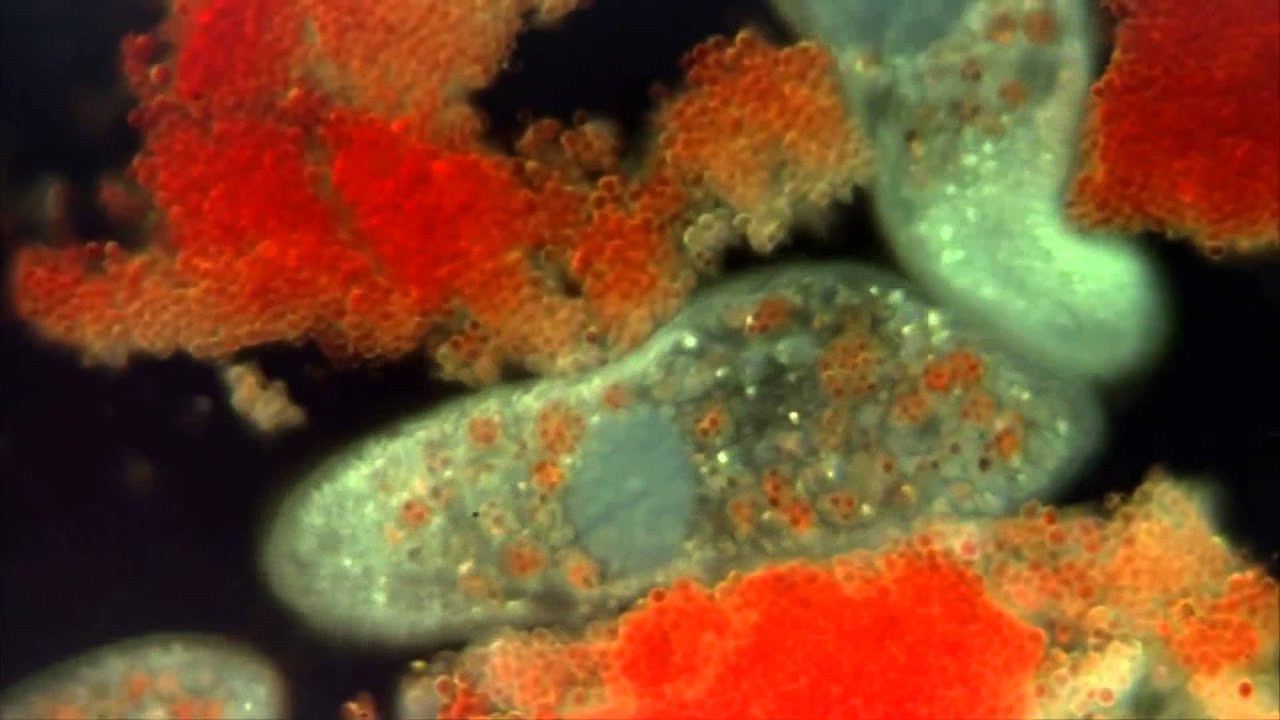
Are protists found in pond water?
Pond water can host organisms from different kingdoms including Kingdom Animalia and Plantae. Examples of protists found in pond water include water molds, green algae, euglena, diatoms, paramecium, amoeba, and heliozoa.
What protists live in ponds?
Paramecium and amoebae, as representatives of heterotrophic protists, are one of the main inhabitants of all ponds.
What are the most common microorganisms found in pond water?
The common bacterial species found in all the ponds and the water source were Aeromonas hydrophila, Citrobacter freundii, Escherichia coli, Enterobacter aerogenes, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas sp., Bacillus sp., Listeria monocytogenes, and Staphylo- coccus sp.
What is in my pond water?
Types of Pond Bacteria & Microorganisms1) Arthropods. A Water Mite. ... 2) Bacteria. Cyanobacteria. ... 3) Protozoa. Blepharisma japonicum. ... 4) Hydras. Hydras. ... 6) Phytoplankton. Image of phytoplankton under a microscope.7) Algae. Diatom Algae.
Where would you expect to find protists?
Where are protists found? Most protists can be found in moist and wet areas. They can also be found in tree trunks and other organisms.
Where do protists usually live?
Most protists are aquatic organisms. They need a moist environment to survive. They are found mainly in damp soil, marshes, puddles, lakes, and the ocean. Some protists are free-living organisms.
What color should pond water be?
That is typically considered "pigment." Water with abundant amounts of limestone is typically a beautiful, rich green color, top to bottom. Water with lots of iron is clear, sometimes with an orange tint. Soft, acidic water is the color of iced tea. Soft, really acidic water is cobalt blue, almost like the Caribbean.
What protists live in water?
Freshwater animal-like examples include amoeba, heliozoans, and paramecium. Plant-like protists are forms of algae, and they make their own food through photosynthesis. Examples include golden algae, diatoms, Euglena, and green algae.
What are 3 examples of protists?
Examples of protists include:Amoebas (including nucleariids and Foraminifera);choanaflagellates; ciliates;Diatoms;Dinoflagellates;Giardia;Plasmodium (which causes malaria);Oomycetes (including Phytophthora, the cause of the Great Famine of Ireland); and.slime molds.
What are aquatic protists?
Diversity, Distribution and Ecology of Aquatic Protists. In contrast to bacteria and archaea (prokaryotes), protists are single celled organisms that have real nuclei (eukaryotes), in most cases mitochondria or mitochondrial derivates and sometimes also chloroplasts.
What is the most common protist and why?
Algae: Algae are plant like photosynthetic protists carrying out probably 50→60% of all photosynthesis on earth.
What are the organisms in pond water?
1.1.5 5) Fungi. 1.1.6 6) Phytoplankton. 1.1.7 7) Algae. Healthy pond water is teeming with tiny organisms, but most can only been seen under a microscope. Microorganisms are single celled organisms that are found within four kingdoms – the plant kingdom, bacteria, fungi, and protozoa. While it may seem at first as though all microorganisms are ...
What kingdoms are in a pond?
Microorganisms are single celled organisms that are found within four kingdoms – the plant kingdom, bacteria, fungi, and protozoa. While it may seem at first as though all microorganisms are the same, ...
How many species of algae are there in the world?
The number of algae species is widely contested, ranging from estimates of 1 million to 350 million. Of course, some algae are helpful while others tend to be more harmful. Diatoms, for example, are never bad no matter how many there are. In fact, they’re responsible for producing anywhere from 25 to 40% of the world’s oxygen (more than all of the rainforests combined), and really don’t look like typical algae at all. They look more like tiny glasslike structures with intricate patterns in them.
Why do phytoplankton exist in rivers?
In streams and rivers, little to no phytoplankton exist because the faster flowing waters wash them away more quickly than they are able to reproduce.
What are the arthropods?
Arthropods include micro and macroinvertebrates such as tardigrades (water bears), crustaceans, some insect larvae, and water mites among others, and most are visible without the use of a microscope.
What would happen if there were no microorganisms?
These microorganisms are at the very base of food webs and ecological functions; without them, life simply would not be possible . From generating oxygen to facilitating decomposition to promoting the carbon cycle to releasing nutrients that otherwise would be bound up in nature and not available to the rest of us living things, the world as we know it today simply would not exist were it not for microorganisms and bacteria.
How do fungi help other organisms?
Through this, they aid in nutrient cycling, decomposition, and provide a valuable food source to other organisms.
What are the tiny cilia that propel protists through water called?
These critters are called Ciliates and have hundreds of tiny cilia which beat in unison to propel the protists through the water. Shown at left is a school classic, the Paramecium. Often cilia are fused together in rows or tufts (called cirri) and are used for special functions such as food gathering.
What protists move with a whip like extension called a flagella?
Phylum Mastigophora. These protists move with a whip like extension called a flagella. The flagella is a long fibril that is spirally wound and beats or rotates in the water to move the protozoan about. Included in this group is the Peranema (shown at left), the Euglena and the Volvox. View more Mastigophora here.
How are protozoans classified?
Protozoans are further classified according to how they move and there are four types . The phyla Mastigophora move with a long whip like extension called a flagella. The Ciliophora have hundreds of tiny little "hairs" which beat in unison like little oars to move them through the water. The Sarcodina includes the Amoebas and they move like a flowing blob of jelly using what is called a "pseudopod", or false foot. The last type of protozoan are the Sporazoans. They are very small spore-like with no apparent means of locomotion. Some are harmful like those that cause malaria.
What kingdom are multicellular animals?
Multicellular Animals. These critters don't belong to the Kingdom Protista but rather the Kingdom Anamalia. Some, like the rotifers look like protists and even have cilia but they are made of many cells and have organs like other animals. Shown at the left is a very common pond water critter called a Rotifer.
What is the name of the protozoan that moves like a jelly ball?
The Sarcodina includes the Amoebas and they move like a flowing blob of jelly using what is called a "pseudopod", or false foot. The last type of protozoan are the Sporazoans. They are very small spore-like with no apparent means of locomotion. Some are harmful like those that cause malaria.
What can you see in fresh water?
When you look at fresh water with a microscope you will likely see a variety of tiny living things. Sources of fresh water samples can include ponds, lakes, rivers, aquarium tanks or even an old rain puddle. You might see bacteria which belongs to the Kingdom Monera. You likely will see tiny animals like rotifers which belong to ...
Which kingdom is the bacteria?
You might see bacteria which belongs to the Kingdom Monera. You likely will see tiny animals like rotifers which belong to the Kingdom Animalia and of course, there are the Protozoans and Algae which belong to the Kingdom Protista. The algae are single celled plant-like protists and the protozoans are single celled animal-like protists. Remember, the Protists are neither animals or plants but in a Kingdom of their own!
What are the colors of algae in ponds?
Their chloroplasts contain both chlorophyll A and B, accounting for their typical bright green coloration, though they may also be various hues of yellow.
What kingdom is algae in?
Algae (or alga, singularly), belonging to the kingdom Protista, are largely aquatic organisms that are typically fully photosynthetic but differ from plants in that they lack true roots, stems, leaves, and gametes (the male and female parts of plants). Algae can vary in size from less than two micrometers (in the case of micromonas, ...
Why Is Identifying Algae Important?
Knowing which algae you have is important, as some types are beneficial to the ecos-system, whereas others can be harmful.
How to control filamentous algae?
You can control filamentous algae by utilizing naturally occurring microbes, vacuuming/raking out any mats that are present, and regularly monitoring your water quality to prevent algae overgrowth.
How many species of Euglena are there?
Euglena, belonging to the family euglenaceae and phyla euglenophyta, contains over 1,000 species and is incredibly diverse and resilient, able to exist in any water body around the world as well as most moist soil types. Typically green or red, this type of algae is often quite alarming – and for good reason.
How big is an algae?
Algae can vary in size from less than two micrometers (in the case of micromonas, a species of green algae) to over 200 feet tall (in the case of some species of giant sea kelps )! In total, there are eight main groups of algae: blue-green algae (also known as cyanobacteria), diatoms, chlorophyta (or green algae), euglenophyta, dinoflagellate, ...
Why is muskgrass used in waterfowl?
Muskgrass is commonly consumed by waterfowl and provides habitat for aquatic insects, which are in turn eaten by fish.
What are the producers of ponds?
Ponds are typically very productive, meaning there are many producers, including algae and plants. Producers carry out the process of photosynthesis.
What do plants do in ponds?
Some plants root into the pond sediment and produce leaves that reach the water surface.
Can you see internal organs of animals?
Small animals that are transparent so you can sometimes see internal organs, including what they have eaten.
Can photosynthetic bacteria extract nitrogen from water?
Photosynthetic bacteria can also extract nitrogen from water.
What are the organisms in pond water?
1.1.5 5) Fungi. 1.1.6 6) Phytoplankton. 1.1.7 7) Algae. Healthy pond water is teeming with tiny organisms, but most can only been seen under a microscope. Microorganisms are single celled organisms that are found within four kingdoms – the plant kingdom, bacteria, fungi, and protozoa. While it may seem at first as though all microorganisms are ...
What kingdoms are in a pond?
Microorganisms are single celled organisms that are found within four kingdoms – the plant kingdom, bacteria, fungi, and protozoa. While it may seem at first as though all microorganisms are the same, ...
How many species of algae are there in the world?
The number of algae species is widely contested, ranging from estimates of 1 million to 350 million. Of course, some algae are helpful while others tend to be more harmful. Diatoms, for example, are never bad no matter how many there are. In fact, they’re responsible for producing anywhere from 25 to 40% of the world’s oxygen (more than all of the rainforests combined), and really don’t look like typical algae at all. They look more like tiny glasslike structures with intricate patterns in them.
Why do phytoplankton exist in rivers?
In streams and rivers, little to no phytoplankton exist because the faster flowing waters wash them away more quickly than they are able to reproduce.
What are the arthropods?
Arthropods include micro and macroinvertebrates such as tardigrades (water bears), crustaceans, some insect larvae, and water mites among others, and most are visible without the use of a microscope.
What would happen if there were no microorganisms?
These microorganisms are at the very base of food webs and ecological functions; without them, life simply would not be possible . From generating oxygen to facilitating decomposition to promoting the carbon cycle to releasing nutrients that otherwise would be bound up in nature and not available to the rest of us living things, the world as we know it today simply would not exist were it not for microorganisms and bacteria.
How do fungi help other organisms?
Through this, they aid in nutrient cycling, decomposition, and provide a valuable food source to other organisms.