What is flue gas condensation?
Flue gas condensation is a process, where flue gas is cooled below its water dew point and the heat released by the resulting condensation of water is recovered as low temperature heat. Cooling of the flue gas can be performed either directly with a heat exchanger or indirectly via a condensing scrubber .
What is the heat recovery potential of flue gas condensation?
The heat recovery potential of flue gas condensation is highest for fuels with a high moisture content (e.g. biomass and municipal waste ), and where heat is useful at the lowest possible temperatures.
Do you have flue condensation problems on your furnace?
Flue condensation problems have been observed on all kinds of furnaces including gas and oil furnaces. If you have this problem or see it on your furnace heating system please consult a professional. If not repaired, eventually the corrosive condensation dripping down the flue will cause a flue or ventilation failure.
What causes condensation on the inside of a chimney?
This problem is caused by hot gases cooling too quickly in the flue. As the hot gasses cool, the moisture in the gases condenses and starts dripping back down the flue. Typically, there is a combustion issue or bad flue design.

How do you stop flue condensation?
How to Mediate Flue CondensationAdjust the furnace temperature: Make sure that the furnace temperature is hot enough for the gases to freely flow through the flue and out into the atmosphere.Improve the flue design: Have a professional HVAC tech look at your flue and recommend improvements to the flue's design.
At what temperature does a condensing boiler condense?
If the return temperature is kept below approximately 55°C (131°F), the boiler will be in condensing mode and working at its most efficient. What else helps the boiler to condense?
What is flue gas dew point?
The acid dew point of flue gas is the temperature at which the acidic elements in your flue gas start to condense. Many different types of fuel are used in combustion processes. Used fuels are natural gas, off-gases, LPG, but also naphtha, fuel oils, biogas and solid fuels like coal are applied.
What causes a boiler to condensate?
Condensate is what gets produced when your boiler is being used to heat your home or produce hot water. This is because when your boiler burns fuel, a chemical reaction causes produces carbon dioxide and water vapour by-products. Once enough heat is produced from this vapour, it's condensed back into water form.
At what temperature does water start to condensate?
Water condenses at the boiling point; this is the condensation point or dew point. The condensation point of water is 100 ° C or 212 ° F.
At what temperature does steam condensate into water?
As temperature drops, steam turns into liquid, then ice From the graph, when steam at 125°C cools, its temperature starts to drop (E) until it reaches 100 °C (D). At 100 °C, the steam condenses and turns into liquid water.
What is a good flue gas reading?
Many burner manufacturers look for a reading of between 8 1/2% to 10% in the flue gas. Carbon dioxide, when mixed with water, forms carbonic acid, which could damage the standard efficiency boiler or chimney.
What is the moisture in flue gas?
The flue gases moisture content is between 150 to 108 grams per kilogram of dry gas (g/kg. d.g), depending on the excess air ratio (D =1÷1.4). Heat recovery process by cooling the flue gases to the dew point precedes the water vapor condensation. Obtained heat amount depends on the initial flue gases temperature.
How do you reduce the temperature of a gas flue?
Using an integrated or downstream economiser, the flue gas temperature can be reduced to 120 – 140°C, depending on the economiser design, which reduces the flue gas loss significantly. During this process, the heat in the flue gases is transferred to the boiler feed water flowing in countercurrent.
How much condensate does a gas boiler produce?
How Much Condensate Water Does a Condensing Boiler Produce? According to the HHIC (Heating & Hot Water Industry Council), a condensing boiler that's working efficiently will produce around two litres of condensate water every hour.
How much condensation is normal in a boiler?
How much water does a condensate boiler produce? A condensing boiler will produce about 2 litres of condensate an hour at an average temperature of 30-40℃. This condensate needs to drain into your waste water outlet or to a drain via your condensate pipe.
How much condensate does a boiler produce per day?
An efficient condensing boiler will generate around 2 litres of condensate water an hour at a temperature of around 30-40°c.
How much condensation is normal in a boiler?
How much water does a condensate boiler produce? A condensing boiler will produce about 2 litres of condensate an hour at an average temperature of 30-40℃. This condensate needs to drain into your waste water outlet or to a drain via your condensate pipe.
How much condensate does a condensing boiler produce?
An efficient condensing boiler will generate around 2 litres of condensate water an hour at a temperature of around 30-40°c. This needs to be safely disposed of, within the buildings waste water system.
What temperature should a grant condensing boiler be set at?
To ensure maximum efficiency, the boiler return temperature should be 55° C or less, this will enable the latent heat to be condensed out of the flue gases. The boiler will achieve nett thermal efficiencies of 100%.
How do I know if my boiler is condensing properly?
In the meantime you can look at the flue emissions. Contrary to popular belief, a sign that your boiler is condensing is an invisible discharge from the flue. A boiler is NOT condensing when white plumes are exiting the flue. This is a sign that the energy is not being recovered as the heat is lost to outside.
Flue gas dew point temperatures and condensation of water vapor
Flue gas dew point temperature is the temperature where condensation of water vapor in the flue gas starts.
Engineering ToolBox - SketchUp Extension - Online 3D modeling!
Add standard and customized parametric components - like flange beams, lumbers, piping, stairs and more - to your Sketchup model with the Engineering ToolBox - SketchUp Extension - enabled for use with the amazing, fun and free SketchUp Make and SketchUp Pro .Add the Engineering ToolBox extension to your SketchUp from the SketchUp Pro Sketchup Extension Warehouse!.
Privacy
We don't collect information from our users. Only emails and answers are saved in our archive. Cookies are only used in the browser to improve user experience.
Advertise in the ToolBox
If you want to promote your products or services in the Engineering ToolBox - please use Google Adwords. You can target the Engineering ToolBox by using AdWords Managed Placements.
Citation
Engineering ToolBox, (2010). Flue Gases - Dew Point Temperatures. [online] Available at: https://www.engineeringtoolbox.com/dew-point-flue-gases-d_1583.html [Accessed Day Mo. Year].
Why does my furnace have condensation?
This picture shows furnace flue condensation problems. This problem is caused by hot gases cooling too quickly in the flue. As the hot gasses cool, the moisture in the gases condenses and starts dripping back down the flue. Typically, there is a combustion issue or bad flue design.
Can you vent up the flue before the moisture condenses?
This problem can be solved by making sure the gases are hot enough to be vented into the atmosphere. Vented up the flue before the moisture condenses in the gases. It could be a problem that requires a slight adjustment at the burner. Furthermore, it is a good idea when you observe a furnace flue condensation problem where ...
Can a flue duct rot?
Flue condensation problems, if left alone, can cause the flue duct to rot and vent hot gases in an area where it could be hazardous to the occupants of the building. Furthermore, there is carbon monoxide present in these gases, and carbon monoxide is very dangerous.
What is the flue gas temperature?
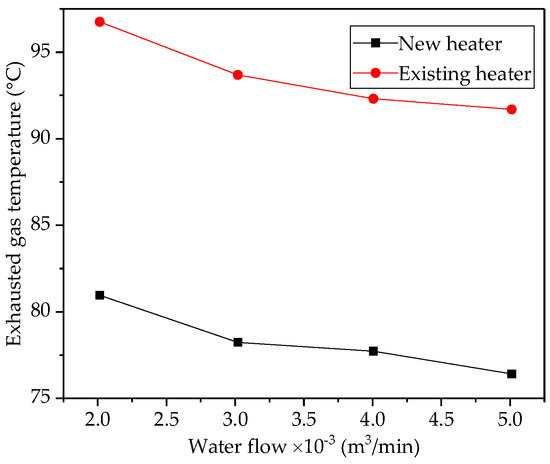
At an operating pressure of 10 bar, which corresponds to a saturated steam temperature of 185°C, the flue gas temperature is therefore roughly 245°C. This corresponds to a flue gas loss of roughly 11%. As shown in the graphic ( Fig. „Efficiency gain for various exemplary sizes of economiser“ ), the flue gas loss can be reduced by roughly 1 percentage point, or the boiler efficiency increased accordingly, with each 20°C reduction in flue gas temperature.
When using condensing technology, not only the sensible heat which is directly linked to the temperature but also the condensation?
When using condensing technology, not only the sensible heat which is directly linked to the temperature but also the condensation heat latent in the water vapour is partially removed from the flue gas. Liquid flue gas condensate is produced which must be removed from the flue gas path, neutralised and introduced into the sewer system.
How does an integrated economiser reduce flue gas?
During this process, the heat in the flue gases is transferred to the boiler feed water flowing in countercurrent. The heat removed from the flue gas flow is fed to the boiler via the heated feed water . This increases the combustion efficiency by 5 – 7%.
What happens when you use condensing technology?
When using condensing technology, not only the sensible heat which is directly linked to the temperature but also the condensation heat latent in the water vapour is partially removed from the flue gas. Liquid flue gas condensate is produced which must be removed from the flue gas path, neutralised and introduced into the sewer system.
Why is low water inlet temperature important?
The low water inlet temperature allows extensive flue gas condensation and therefore optimum use of condensing technology. With this application, the diversity factor between waste heat availability and heat energy demand is also available during routine operation which means this benefit always exists.
What is the minimum temperature required for a condensing heat exchanger?
To operate a condensing heat exchanger efficiently, a sufficiently large (>30% of the boiler steam output) and cool (temperature <35°C) water flow is required as a low temperature heat sink. This should be available when the steam boiler is in operation.
How hot can a boiler feed water?
heating of the make-up water of the steam boiler system, a building heating system or process water heating system, the feed water temperature can be reduced from 103°C down to 65°C using a simple inexpensive plate heat exchanger. Owing to the larger difference between the flue gas and feed water temperature, the flue gas can now also be further cooled to roughly 85°C without requiring further investment in the economiser. This increases the combustion efficiency and achieves up to 1.8% fuel savings.
What temperature should a flue gas vent be?
I hired a HVAC pro to diagnose the problems. He used an analyser and found that the flue gas temperature is only around 225F and this low temperature results in condensation in the b-vent pipe. He mentioned that it should be around 300F for the proper venting of flue gases without condensation.
What does it mean when a furnace says "too much heat"?
He means you have too much heat availble and no place to use it. Your condensation problems will likely continue and you will sooner or later be replacing it anyway as that furnace doesnt like water.
Where is the temperature rise measured?
Temp rise is measured between the supply duct temperature and the return duct temperature, near the furnace. If it's not right, the duct size doesn't matcgh the furnace size someplace.
Does turning down the gas pressure increase or decrease the amount of water that I collect in my attic?
Now, it is definitely running longer than it used to be. But, I am still collecting the same amount of water in my attic. So, turning down the gas pressure didn't increase or decrease the amount of water that I collect in my attic.
