Can Staphylococcus aureus be killed by heat?
Staph bacteria are killed by cooking, but the toxins are not destroyed and will still be able to cause illness. Foods that are not cooked after handling, such as sliced meats, puddings, pastries, and sandwiches, are especially risky if contaminated with Staph.
What kills Staphylococcus aureus?
Hydrogen peroxide kills Staphylococcus aureus by reacting with staphylococcal iron to form hydroxyl radical. J Biol Chem.
What temperature can Staph survive in?
The temperature range for growth of S. aureus is 7–48°C, with an optimum of 37°C. S. aureus is resistant to freezing and survives well in food stored below -20°C; however, viability is reduced at temperatures of -10 to 0°C.
Is Staphylococcus aureus resistant to high temperatures?
Staphylococcal toxins are very resistant to heat [7]. Enterotoxins retain some of their biological activity in milk after pasteurization or heating at 121°C for 28 min [8].
How do I get rid of Staphylococcus aureus permanently?
Antibiotics commonly prescribed to treat staph infections include cefazolin, nafcillin, oxacillin, vancomycin, daptomycin and linezolid. For serious staph infections, vancomycin may be required. This is because so many strains of staph bacteria have become resistant to other traditional antibiotics.
How long can Staphylococcus aureus live on surfaces?
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) can survive on some surfaces, like towels, razors, furniture, and athletic equipment for hours, days, or even weeks. It can spread to people who touch a contaminated surface, and MRSA can cause infections if it gets into a cut, scrape, or open wound.
What temp water kills Staph?
One study, done in Britain and published 12 years ago, showed that washing the very dirty clothes of hospital staff members at approximately 100 degrees Fahrenheit in a home washing machine was just as effective at killing one type of bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus) as washing it at a much higher temperature. Dr.
How does Staphylococcus aureus survive?
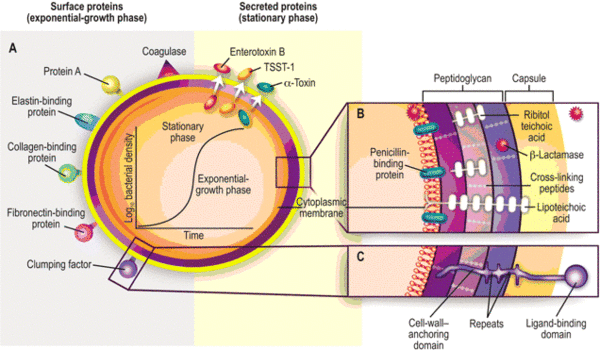
Staphylococcus aureus grows best in an aerobic (oxygen-rich) environment but it can also live in anaerobic conditions (without oxygen). The bacterium has a diameter of about 0.8 µm, 60 times smaller than a hair's breadth.
Where is Staphylococcus aureus most commonly found?
Staphylococcus aureus or “staph” is a type of bacteria found on human skin, in the nose, armpit, groin, and other areas.
How did Staphylococcus aureus become resistant?
Staphylococcus aureus can become drug-resistant by genetic mutations that alter the target DNA gyrase or reduce outer membrane proteins, thereby reducing drug accumulation (Kime et al., 2019; Yang et al., 2019).
How can you prevent Staphylococcus aureus from spreading?
PreventionWash your hands. Thorough hand washing is your best defense against germs. ... Keep wounds covered. Keep cuts and scrapes clean and covered with sterile, dry bandages until they heal. ... Reduce tampon risks. ... Keep personal items personal. ... Wash clothing and bedding. ... Take food safety precautions.
Why is S. aureus not resistant to antibiotics?
Staphylococcus aureus is naturally susceptible to virtually every antibiotic that has ever been developed. Resistance is often acquired by horizontal transfer to genes from outside sources, although chromosomal mutation and antibiotic selection are also important. This exquisite susceptibility of S.
What kills staph naturally?
Alternative Remedies Some people apply substances with reported antimicrobial properties, such as tea tree oil, apple cider vinegar, coconut oil, eucalyptus essential oil, oregano essential oil, and others to skin infections to help them heal.
What is the most effective way to control Staphylococcus aureus?
Some experts recommend combination therapy with a penicillinase-resistant penicillin or cephalosporin (in case the organism is methicillin-sensitive S aureus [MSSA]) and clindamycin or a quinolone. Others suggest use of clindamycin, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (TMP-SMX), rifampin, doxycycline, or a quinolone.
What is the best home remedy for Staphylococcus aureus?
Most small staph skin infections can be treated at home:Soak the affected area in warm water or apply warm, moist washcloths. ... Put a heating pad or a hot water bottle to the skin for about 20 minutes, three or four times a day.Apply antibiotic ointment, if recommended by your doctor.More items...
Does vinegar help Staphylococcus aureus?
Antibacterial apple cider vinegar eradicates methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus and resistant Escherichia coli | Scientific Reports.
What is the cause of Staphylococcus aureus?
Staphylococcus aureus is a bacterium that causes staphylococcal food poisoning, a form of gastroenteritis with rapid onset of symptoms. S. aureus is commonly found in the environment (soil, water and air) and is also found in the nose and on the skin of humans.
What are the factors that affect the growth of S. aureus?
The growth and survival of S. aureus is dependent on a number of environmental factors such as temperature, water activity (aw), pH, the presence of oxygen and composition of the food (refer to Table 1). These physical growth parameters vary for different S. aureus strains (Stewart 2003).
How long does it take to recover from food poisoning?
Individuals may not demonstrate all the symptoms associated with the illness. In severe cases, headache, muscle cramping and transient changes in blood pressure and pulse rate may occur. Recovery is usually between 1–3 days (Stewart 2003; FDA 2012). Fatalities are rare (0.03% for the general public) but are occasionally reported in young children and the elderly (4.4% fatality rate) (Montville and Matthews 2008).
Is food poisoning a disease in Australia?
Staphylococcal food poisoning is not a notifiable disease in Australia or New Zealand. There were two reported outbreaks of staphylococcal food poisoning in Australia in 2011 and two outbreaks reported in 2010. In New Zealand there were no outbreaks of staphylococcal food poisoning in 2011 and two outbreaks reported in 2010 (Lim et al. 2012; OzFoodNet 2012a; OzFoodNet 2012b). It is generally recognised that there may be significant under reporting of staphylococcal food poisoning due to the short duration of illness and self-limiting symptoms. In Australia it is estimated that S. aureus accounts for 1% of foodborne illness caused by known pathogens (Hall et al. 2005).
Is S. aureus a Gram positive bacterium?
S. aureus is a Gram-positive, non-spore forming spherical bacterium that belongs to the Staphylococcus genus. The Staphylococcus genus is subdivided into 32 species and subspecies. S. aureus produces staphylococcal enterotoxin (SE) and is responsible for almost all staphylococcal food poisoning (Montville and Matthews 2008; FDA 2012).
Is staphylococcus spp. a food poisoning?
All people are believed to be susceptible to staphylococcal food poisoning. However, the severity of symptoms may vary depending on the amount of SE consumed in the food and the general health of individuals. The young and elderly are more likely to develop more serious symptoms (FDA 2012).
How long does it take for heat to kill bacteria?
Most bacteria and viruses that are dangerous to humans, on the other hand, may be destroyed by heat of 165 degrees Fahrenheit or greater within minutes of cooking. " span >Bacteria are sensitive to heat; a few minutes at a high temperature will kill most bacteria found in food."
Can heat kill bacterial infections?
Most bacteria can be killed by hot temperatures of at least 140 degrees Fahrenheit. Most bacteria flourish at temperatures ranging from 40 to 140 degrees Fahrenheit, which is why it is critical to keep food refrigerated or to cook it at high temperatures. However, some bacteria are able to survive at lower temperatures. For example, some strains of E. coli can live in frozen vegetables that have not been thoroughly washed.