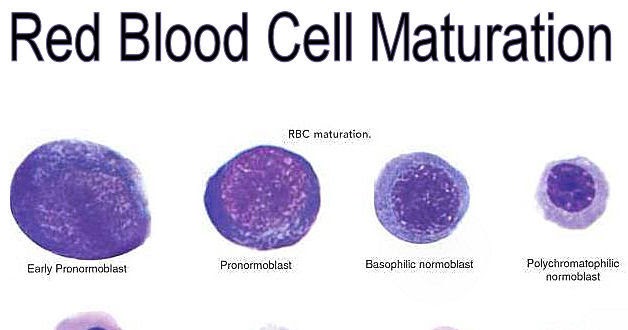
Blood cells are like animal cells they don’t have walls because the cell membrane allows them to take any shape so they can live through that environment. Do white blood cells have a cell membrane? Plasma membranes enclose the borders of cells, but rather than being a static bag, they are dynamic and constantly in flux.
Full Answer
Why do immune cells poke holes in blood vessels?
How do immune cells keep blood in?
Why do blood vessel cells open?
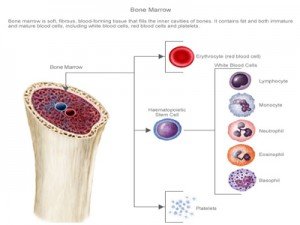
Do blood cells have a cell wall?
The red blood cell is enclosed in a thin membrane that is composed of chemically complex lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates in a highly organized structure.
In which cell we can see cell wall?
The cell wall surrounds the plasma membrane of plant cells and provides tensile strength and protection against mechanical and osmotic stress. It also allows cells to develop turgor pressure, which is the pressure of the cell contents against the cell wall.
Can you see cells in blood?
You should see hundreds of tiny red blood cells; there are billions circulating throughout our blood stream. Red blood cells contain no nucleus, which means they can't divide. Red blood cells are constantly produced by the bone marrow and the spleen. You should also be to find a few white blood cells.
Is cell wall found in all cells?
All cells have a cell membrane, but not all cells have a cell wall. Cell walls are very rigid, which makes the cell harder to move. They can be made up of a variety of substances, so cell walls in plant cells are different than those found in bacterial cells.
Where are cell walls not found?
Cell walls are absent in many eukaryotes, including animals, but are present in some other ones like fungi, algae and plants, and in most prokaryotes (except mollicute bacteria).
Can you see cell walls under a microscope?
Note: The nucleus, cytoplasm, cell membrane, chloroplasts and cell wall are organelles which can be seen under a light microscope.
What can be seen in blood?
Some blood tests can help your doctor determine how different organs in your body are working. Examples of organs whose malfunctions can be visible in a blood test include your thyroid, liver, or kidneys....What does a blood test show?diabetes.HIV.anemia.cancer.coronary heart disease.
What can they see in your blood?
The tests can give providers information about your organs, such as the heart, kidneys, and liver. The BMP includes blood glucose, calcium, and electrolyte tests, as well as blood tests that measure kidney function. Some of these tests require you to fast (not eat any food) before the test, and others don't.
What can be found in blood cells?
Red blood cells contain a protein called hemoglobin, which carries oxygen from the lungs to all parts of the body. Checking the number of red blood cells in the blood is usually part of a complete blood cell (CBC) test. It may be used to look for conditions such as anemia, dehydration, malnutrition, and leukemia.
Is cell wall only in plant cell?
Plant cells have a cell wall, as well as a cell membrane. In plants, the cell wall surrounds the cell membrane. This gives the plant cell its unique rectangular shape. Animal cells simply have a cell membrane, but no cell wall.
Is cell wall only found in plant cells?
Cell wall is present in both animal and plant cell.
What cell type has no cell wall?
Protista. Protists are single-celled and usually move by cilia, flagella, or by amoeboid mechanisms. There is usually no cell wall, although some forms may have a cell wall. They have organelles including a nucleus and may have chloroplasts, so some will be green and others won't be.
Is cell wall available in animal cell?
The cell wall is present only in plants and some other organisms, not in animals.
Is cell wall in plant and animal cells?
Plant cells have a cell wall, as well as a cell membrane. In plants, the cell wall surrounds the cell membrane. This gives the plant cell its unique rectangular shape. Animal cells simply have a cell membrane, but no cell wall.
Is cell wall seen in all prokaryotes?
All prokaryotic cells are encased by a cell wall. Many also have a capsule or slime layer made of polysaccharide. Prokaryotes often have appendages (protrusions) on their surface. Flagella and some pili are used for locomotion, fimbriae help the cell stick to a surface, and sex pili are used for DNA exchange.
Why do blood vessel cells open?
The long-standing question has been whether these openings form because the blood vessel cells are contracting like small muscles in response to their interactions with arrested and crawling leukocytes. The Alon study, which was based on both in vitro and animal models, suggests that the openings in fact involve an active process imposed by the nuclei of the squeezing leukocytes: these nuclei are pushed forward by the leukocyte's own motors bending and snapping the various filaments that comprise the cytoskeleton of the endothelial cells breached by the squeezing leukocyte.
How many microns are in a leukocyte?
Shortly after arresting, leukocytes use additional chemoattractive signals to crawl, protrude and squeeze their bodies, generating pores or gaps with a diameter of 4 to 5 microns, which is about the diameter of their bulky nuclei.
What is the effect of blood vessel walls?
In general, the thin blood vessel walls crossed by infiltrating immune cells at most tissues are effective at keeping blood and circulating immune cells in and anything that doesn't belong out.
Why do immune cells poke holes in blood vessels?
In any given second, thousands of immune cells are poking holes in your blood vessels as they travel out of the blood stream to survey your organs for problems or join the fight against a pathogen.
Is cancer more efficient than leukocytes?
The research is also relevant to cancer physiology, as tumor cells are much less efficient than leukocytes in their ability to move their nucleus forward and squeeze it through blood vessels at sites of metastasis.
Why do immune cells poke holes in blood vessels?
In any given second, thousands of immune cells are poking holes in your blood vessels as they travel out of the blood stream to survey your organs for problems or join the fight against a pathogen. Despite the constant assault, the damage is negligible, and in a study, appearing January 17 in Cell Reports, researchers may reveal why: as immune cells squeeze their nuclei through blood vessel walls, the force breaks thin filaments that make up the cytoskeleton—the scaffold proteins that give a cell its shape—of individual endothelial cells that hold the wall together. These filaments are known to quickly be replaced.
How do immune cells keep blood in?
In general, the thin blood vessel walls crossed by infiltrating immune cells at most tissues are effective at keeping blood and circulating immune cells in and anything that doesn't belong out. When subsets of immune cells, white blood cells (leukocytes), encounter specific signals on blood vessels at nearby sites of infection or inflammation, these chemicals guide the immune cells to stop and exit the blood vessels. Shortly after arresting, leukocytes use additional chemoattractive signals to crawl, protrude and squeeze their bodies, generating pores or gaps with a diameter of 4 to 5 microns, which is about the diameter of their bulky nuclei.
Why do blood vessel cells open?
The long-standing question has been whether these openings form because the blood vessel cells are contracting like small muscles in response to their interactions with arrested and crawling leukocytes. The Alon study, which was based on both in vitro and animal models, suggests that the openings in fact involve an active process imposed by the nuclei of the squeezing leukocytes: these nuclei are pushed forward by the leukocyte's own motors bending and snapping the various filaments that comprise the cytoskeleton of the endothelial cells breached by the squeezing leukocyte.
