
What is the limiting mass of a white dwarf star?
This limiting mass, known as the Chandrasekhar limit, is on the order of 1.4 solar masses. Both predictions are in excellent agreement with observations of white dwarf stars. The central region of a typical white dwarf star is composed of a mixture of carbon and oxygen.
Why don't All Stars become white dwarfs?
Such a star will not become a white dwarf, because the mass of its central, non-fusing core, initially supported by electron degeneracy pressure, will eventually exceed the largest possible mass supportable by degeneracy pressure.
What happens when a white dwarf star goes supernova?
The thermonuclear flame consumes much of the white dwarf in a few seconds, causing a Type Ia supernova explosion that obliterates the star.
What is an example of a white dwarf star?
White dwarfs can also exist as binaries or multiple star systems that only consist of white dwarfs. An example of a resolved triple white dwarf system is WD J1953-1019, discovered with Gaia DR2 data. One interesting field is the study of remnant planetary systems around white dwarfs.
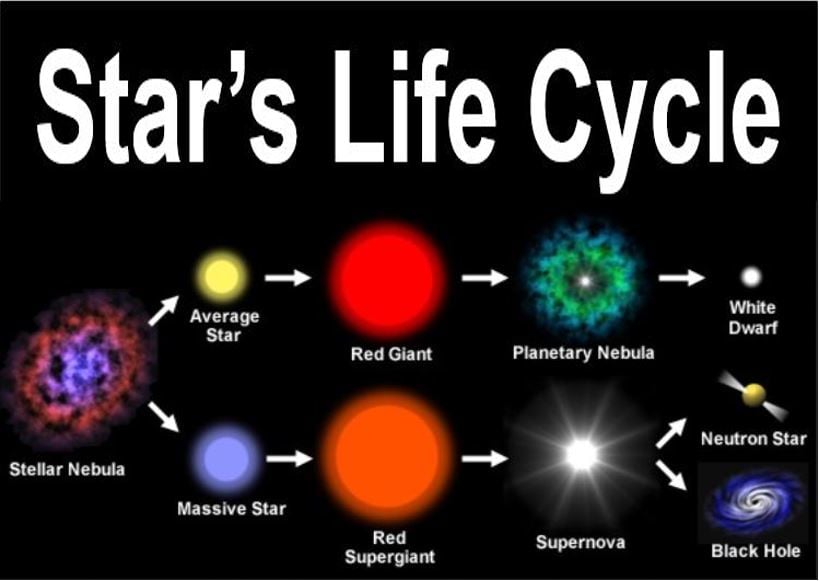
What turns a star into a white dwarf?
A white dwarf is what stars like the Sun become after they have exhausted their nuclear fuel. Near the end of its nuclear burning stage, this type of star expels most of its outer material, creating a planetary nebula. Only the hot core of the star remains.
Can a star of 2.5 solar masses ever become a white dwarf?
Even for these more massive stars, however, if the residual mass in the core is less than 1.4 solar masses (the Chandrasekhar limit), the stellar remnant will become a white dwarf.
Do white dwarfs have high mass?
Although white dwarfs are known with estimated masses as low as 0.17 M ☉ and as high as 1.33 M ☉, the mass distribution is strongly peaked at 0.6 M ☉, and the majority lie between 0.5 and 0.7 M ☉. The estimated radii of observed white dwarfs are typically 0.8–2% the radius of the Sun; this is comparable to the Earth's ...
Can a star of 4 solar masses ever become a white dwarf?
White dwarfs evolve from stars with an initial mass of up to three or four solar masses or even possibly higher. After quiescent phases of hydrogen and helium burning in its core—separated by a first red-giant phase—the star becomes a red giant for a second time.
What would happen if mass is added to a 1.4 solar mass white dwarf?
What would happen if mass is added to a 1.4 solar mass white dwarf? The star would eventually become a black hole.
What would happen if a white dwarf gained enough mass to reach the 1.4 solar mass white dwarf limit?
A) If enough mass is accreted by a white-dwarf star so that it exceeds the 1.4-solar-mass limit, it will undergo a supernova explosion and leave behind a black-hole remnant.
How does red giant become white dwarf?
In a red giant, the inner helium core contracts while the outer layers of hydrogen expand. When the helium is gone, the stars become white dwarfs.
Can a white dwarf become a star again?
Because the white dwarf remains intact, it can repeat the process several times when it reaches that critical point, breathing life back into the dying star over and over again.
Do red dwarfs become white dwarfs?
The end of the line Tiny red dwarfs may have an extended lifetime, but like all other stars, they'll eventually burn through their supply of fuel. When they do, the red dwarfs become white dwarfs — dead stars that no longer undergo fusion at their core.
Why is there an upper mass limit for white dwarfs?
2)Why is there an upper limit to the mass of a white dwarf? A)The more massive the white dwarf, the higher its temperature and hence the greater its degeneracy pressure. At about 1.4 solar masses, the temperature becomes so high that all matter effectively melts, even individual subatomic particles.
Will the Sun become a black dwarf?
The Sun won't become a black dwarf for trillions of years, and even the oldest white dwarfs have not had time to cool enough to become black dwarfs yet. Q: When will the Sun become a black dwarf? Black dwarfs are the very last stage of Sun-like stars.
Will the Sun become a red giant?
A red giant is a dying star in the final stages of stellar evolution. In about five billion years, our own sun will turn into a red giant, expand and engulf the inner planets — possibly even Earth.
How many solar masses does a white dwarf have?
White dwarfs evolve from stars with an initial mass of up to three or four solar masses or even possibly higher. After quiescent phases of hydrogen and helium burning in its core—separated by a first red-giant phase—the star becomes a red giant for a second time.
Why are white dwarf stars called white dwarf stars?
White dwarf stars, so called because of the white colour of the first few that were discovered, are characterized by a low luminosity, a mass on the order of that of the Sun, and a radius comparable to that of Earth . Because of their large mass and small dimensions, such stars are dense and compact objects with average densities approaching ...
What temperature does a white dwarf star have?
…be smaller and are termed white dwarf stars. Surface temperatures of white dwarfs typically range from 10,000 to 12,000 K (18,000 to 21,000 °F), and they appear visually as white or blue-white.….
What is the name of the object that stops radiating?
Following the complete exhaustion of this reservoir of thermal energy, a process that takes several additional billion years, the white dwarf stops radiating and has by then reached the final stage of its evolution and becomes a cold and inert stellar remnant. Such an object is sometimes called a black dwarf.
What are the different types of stars?
Learn about the different types of stars categorized according to their mass and temperature - red dwarfs, red giants, supergiants, white, and brown dwarf stars. Overview of several types of stars, notably the red dwarf, red giant, supergiant, white dwarf, and brown dwarf. Unlike most other stars that are supported against their own gravitation by ...
How long does it take for a star to lose its mass?
This is the planetary-nebula phase. During the entire course of its evolution, which typically takes several billion years , the star will lose a major fraction of its original mass through stellar winds in the giant phases and through its ejected envelope.
Do white dwarfs have nuclear energy?
White dwarfs have exhausted all their nuclear fuel and so have no residual nuclear energy sources. Their compact structure also prevents further gravitational contraction. The energy radiated away into the interstellar medium is thus provided by the residual thermal energy of the nondegenerate ions composing its core.
Why is a white dwarf hot?
A white dwarf is very hot when it forms, but because it has no source of energy, it will gradually cool as it radiates its energy. This means that its radiation, which initially has a high color temperature, will lessen and redden with time.
What is the density of a white dwarf?
A typical white dwarf has a density of between 10 4 and 10 7 g/cm 3. White dwarfs are composed of one of the densest forms of matter known, surpassed only by other compact stars such as neutron stars, quark stars (hypothetically), and black holes .
Why do white dwarfs have metal lines?
Around 25–33% of white dwarfs have metal lines in their spectra, which is notable because any heavy elements in a white dwarf should sink into the star's interior in just a small fraction of the star's lifetime. The prevailing explanation for metal-rich white dwarfs is that they have recently accreted rocky planetesimals. The bulk composition of the accreted object can be measured from the strengths of the metal lines. For example, a 2015 study of the white dwarf Ton 345 concluded that its metal abundances were consistent with those of a differentiated, rocky planet whose mantle had been eroded by the host star's wind during its asymptotic giant branch phase.
How many white dwarfs are there?
There are currently thought to be eight white dwarfs among the hundred star systems nearest the Sun. The unusual faintness of white dwarfs was first recognized in 1910. The name white dwarf was coined by Willem Luyten in 1922.
How long does it take for a white dwarf to reach its current age?
Because the length of time it takes for a white dwarf to reach this state is calculated to be longer than the current age of the known universe (approximately 13.8 billion years), it is thought that no black dwarfs yet exist. The oldest white dwarfs still radiate at temperatures of a few thousand kelvins .
What would happen if a white dwarf exceeded the Chandrasekhar limit?
If a white dwarf were to exceed the Chandrasekhar limit, and nuclear reactions did not take place, the pressure exerted by electrons would no longer be able to balance the force of gravity, and it would collapse into a denser object called a neutron star.
How does compression affect a white dwarf?
Compression of a white dwarf will increase the number of electrons in a given volume. Applying the Pauli exclusion principle, this will increase the kinetic energy of the electrons, thereby increasing the pressure. This electron degeneracy pressure supports a white dwarf against gravitational collapse.
What do scientists study about white dwarfs?
Center for Astrophysics | Harvard & Smithsonian scientists study many different aspects of white dwarfs and neutron stars: Observing the way white dwarfs interact with other astronomical objects, including stars and planets. White dwarfs produce a great deal of radiation, which can profoundly impact any nearby object.
What are white dwarfs made of?
These white dwarfs are made of helium. Despite their name, white dwarfs can range in color from blue-white to yellow, depending on how hot they are. They are common: most stars will eventually become white dwarfs.
What are binary systems with two white dwarfs?
Monitoring binary systems containing two white dwarfs in very close orbits. These systems are radiating gravitational waves that aren’t detectable by LIGO, but which astronomers measure indirectly by how the white dwarfs are increasing in speed.
What is the brightest gravitational wave?
One white dwarf binary , which orbits once every 12.75 minutes, will be potentially the “brightest” gravitational wave source for LISA. Space-Warping White Dwarfs Produce Gravitational Waves. Using NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory and other telescopes to find X-ray sources created by neutron stars in binary systems with ordinary stars.
Why are neutron stars important?
For all these reasons, white dwarfs and neutron stars are important laboratories for physics at the extremes of strong gravity, density, ...
How often do neutron stars spin?
Most known neutron stars are pulsars. Pulsars spin anywhere between once every few seconds to hundreds or — in the case of millisecond pulsars — thousands of times per second, depending on their environment and how they formed. Some millisecond pulsars spin so precisely they can be used as interstellar clocks.
What is the Harvard Astronomical Glass Plate Collection?
The Harvard Astronomical Glass Plate Collection is an archive of roughly 500,000 images of the sky preserved on glass photographic plates, the way professional astronomers often captured images in the era before the dominance of digital technology. These plates are more than historical curiosities: they provide over a century’s worth of data that can be used by contemporary astronomers to trace how objects in the night sky change over periods from years to decades.#N#For that reason, researchers with the DASCH (Digital Access to a Sky Century @ Harvard) project are scanning the plates for digital storage and analysis. The process can also lead to new discoveries in old images, particularly of events that change over time, such as variable stars, novas, or black hole flares. The Harvard Astronomical Plate Collection is housed at the Harvard College Observatory (HCO), part of the Center for Astrophysics | Harvard & Smithsonian.
What is the difference between a neutron star and a white dwarf?
White dwarfs are formed from the collapse of low mass stars , less than about 10 time the mass of the Sun. This star loses most of its mass in a wind, leaving behind a core that is less than 1.44 solar mass. On the other hand, neutron stars are formed in the catastrophic collapse of the core of a massive star.# N#Other differences follow:
Which star has a stronger gravitational field?
A neutron star has a stronger gravitational field -about 400,000 times. 5. Finally, neutron stars have higher temperatures at birth, spin faster, and have stronger magnetic fields, among other things.
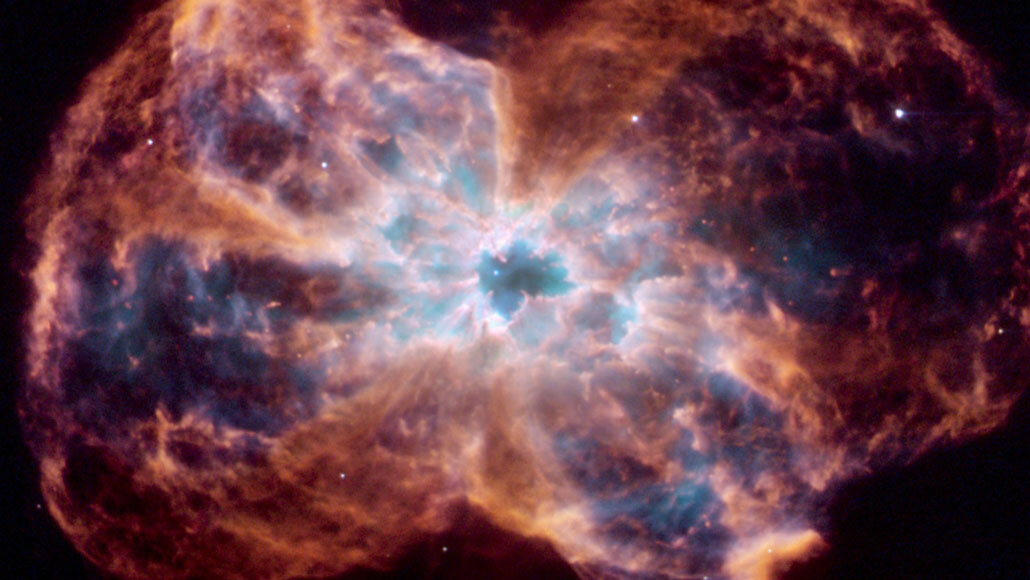

Overview
A white dwarf, also called a degenerate dwarf, is a stellar core remnant composed mostly of electron-degenerate matter. A white dwarf is very dense: its mass is comparable to that of the Sun, while its volume is comparable to that of Earth. A white dwarf's faint luminosity comes from the emission of residual thermal energy; no fusion takes place in a white dwarf. The nearest known whi…
Discovery
The first white dwarf discovered was in the triple star system of 40 Eridani, which contains the relatively bright main sequence star 40 Eridani A, orbited at a distance by the closer binary system of the white dwarf 40 Eridani B and the main sequence red dwarf 40 Eridani C. The pair 40 Eridani B/C was discovered by William Herschel on 31 January 1783. In 1910, Henry Norris Russell, Edward Charles Pickering and Williamina Fleming discovered that, despite being a dim star, 40 Eridani B w…
Composition and structure
Although white dwarfs are known with estimated masses as low as 0.17 M☉ and as high as 1.33 M☉, the mass distribution is strongly peaked at 0.6 M☉, and the majority lie between 0.5 and 0.7 M☉. The estimated radii of observed white dwarfs are typically 0.8–2% the radius of the Sun; this is comparable to the Earth's radius of approximately 0.9% solar radius. A white dwarf, then, packs m…
Variability
Early calculations suggested that there might be white dwarfs whose luminosity varied with a period of around 10 seconds, but searches in the 1960s failed to observe this. The first variable white dwarf found was HL Tau 76; in 1965 and 1966, and was observed to vary with a period of approximately 12.5 minutes. The reason for this period being longer than predicted is that the variability of HL Tau 76, like that of the other pulsating variable white dwarfs known, arises from …
Formation
White dwarfs are thought to represent the end point of stellar evolution for main-sequence stars with masses from about 0.07 to 10 M☉. The composition of the white dwarf produced will depend on the initial mass of the star. Current galactic models suggest the Milky Way galaxy currently contains about ten billion white dwarfs.
If the mass of a main-sequence star is lower than approximately half a solar mass, it will never b…
Fate
A white dwarf is stable once formed and will continue to cool almost indefinitely, eventually to become a black dwarf. Assuming that the Universe continues to expand, it is thought that in 10 to 10 years, the galaxies will evaporate as their stars escape into intergalactic space. White dwarfs should generally survive galactic dispersion, although an occasional collision betwee…
Debris disks and planets
A white dwarf's stellar and planetary system is inherited from its progenitor star and may interact with the white dwarf in various ways. Infrared spectroscopic observations made by NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope of the central star of the Helix Nebula suggest the presence of a dust cloud, which may be caused by cometary collisions. It is possible that infalling material from this may cause …
Habitability
It has been proposed that white dwarfs with surface temperatures of less than 10,000 Kelvins could harbor a habitable zone at a distance of c. 0.005 to 0.02 AU that would last upwards of 3 billion years. This is so close that any habitable planets would be tidally locked. The goal is to search for transits of hypothetical Earth-like planets that could have migrated inward and/or formed there. As a white dwarf has a size similar to that of a planet, these kinds of transits woul…