Explore
Pseudoaneurysms can also occur in other arteries throughout the body as a result of: A small pseudoaneurysm of a femoral artery due to cardiac catheterization may go undetected and not cause any complications. You may not notice it until days or weeks after the procedure.
Can pseudoaneurysms occur without any complications?
You may need any of the following to treat a pseudoaneurysm that does not close: Debridement is a procedure used to remove dead tissue. You may need this if the area around your pseudoaneurysm becomes infected. Compression is a procedure that may be used if the pseudoaneurysm is in your leg.
How do you treat a pseudoaneurysm that does not close?
A pseudoaneurysm typically develops close to the insertion spot where the narrow, flexible catheterization tube is threaded up toward the heart. If the catheter is inserted in your groin area, the pseudoaneurysm may develop there.
Where does a pseudoaneurysm develop?
Your healthcare provider may want to monitor the pseudoaneurysm for up to 4 weeks to see if it closes. He or she may tell you to limit your activity to lower your risk for rupture. Do not smoke. Nicotine and other chemicals in cigarettes and cigars can cause blood vessel and lung damage.
How long does it take for a pseudoaneurysm to close?
What happens when a pseudoaneurysm ruptures?
A rupture carries a risk of internal bleeding that can be life-threatening. A pseudoaneurysm is due to an artery injury that pierces the wall of a blood vessel. The opening in the blood vessel allows blood to leak out and pool in the surrounding tissue.
How long does it take for a pseudoaneurysm to dissolve?
How is a pseudoaneurysm diagnosed and treated? Your healthcare provider will use an ultrasound to check the artery for leaking blood. A small pseudoaneurysm may close on its own in about 4 weeks.
How long can you live with a pseudoaneurysm?
Methods: 10 patients with postinfarction left ventricular pseudoaneurysm were followed up over a mean (SD) period of 3.8 (5.2) years. Results: In those treated conservatively (n = 9), cumulative survival was 88.9 (10.5)% and 74.1 (16.1)% at one and four years, respectively.
Can a false aneurysm rupture?
Pseudoaneurysms result from traumatic arterial injury. With the increasing utilization of percutaneous arterial interventions, iatrogenic arterial injury has become the predominant cause of pseudoaneurysm formation. Rupture of the pseudoaneurysm comprises a vascular emergency.
What is a traumatic pseudoaneurysm?
Traumatic pseudoaneurysm of the STA is a rare lesion. It manifests as a painless pulsatile mass in the temporal region following trauma. The unusual incidence and confusing presentation require the clinicians to have a thorough knowledge of its presentation and diagnosis.
How do you cure pseudoaneurysm?
Currently the treatment options for pseudoaneurysms include ultrasound guided compression (USGC), thrombin therapy, arterial embolisation, endovascular stent graft insertion and surgery.
What does pseudo aneurysm feel like?
Symptoms of pseudoaneurysm include pain due to increased pressure from swelling or nerve compression, and extremity swelling due to venous compression. Further complications of pseudoaneurysms include deep venous thrombosis or rupture, the risk of which increases with increasing pseudoaneurysm size (1).
How can you tell the difference between an aneurysm and a pseudoaneurysm?
A saccular-shaped aneurysm bulges or balloons out only on one side. A pseudoaneurysm, or false aneurysm, is not an enlargement of any of the layers of the blood vessel wall. A false aneurysm may be the result of a prior surgery or trauma.
Can a pseudoaneurysm heal?
Some pseudo-aneurysms heal without treatment. Those that continue to grow larger may need treatment. The doctor may inject medicine through a needle to make the blood clot in the pseudo-aneurysm. He or she may also use pressure (compression) to make the blood clot.
What is false pseudoaneurysm?
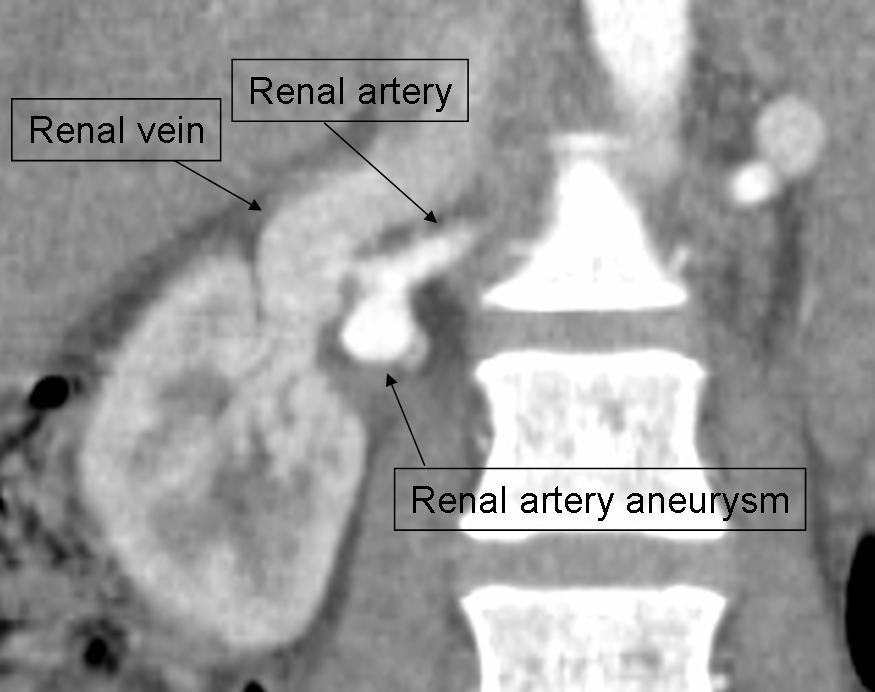
False aneurysms, also known as pseudoaneurysms, are abnormal outpouchings or dilatation of arteries which are bounded only by the tunica adventitia, the outermost layer of the arterial wall. These are distinguished from true aneurysms, which are bounded by all three layers of the arterial wall.
Which blood vessel is most commonly damaged resulting in pseudoaneurysm?
Pseudoaneurysms can develop in any artery, but they're most common in the femoral artery, especially if you've undergone a cardiac catheterization procedure. A pseudoaneurysm can also be caused by: trauma. surgical procedures.
What is the difference between a hematoma and a pseudoaneurysm?
By definition a pseudoaneurysm communicates with the feeding artery. In contrast a hematoma does not have a "neck.” "Yin-Yang” sign – indicates bidirectional flow within the lesion from arterial blood flowing into the lesion, which may resemble its namesake.
What Is A Pseudoaneurysm?
A pseudoaneurysm, or false aneurysm, is swelling of the wall of the artery. The swelling is caused by a small hole that has not sealed. A pseudoane...
What Causes Or Increases My Risk For A Pseudoaneurysm?
1. Heart catheterization or a heart attack 2. An injury that damages an artery 3. An infection, such as tuberculosis or pneumonia 4. A blood clot i...
How Is A Pseudoaneurysm Diagnosed and Treated?
Your healthcare provider will use an ultrasound to check the artery for leaking blood. A small pseudoaneurysm may close on its own in about 4 weeks...
What Can I Do to Manage Or Prevent A Pseudoaneurysm?
1. Limit activity if the pseudoaneurysm has not ruptured. Your healthcare provider may want to monitor the pseudoaneurysm for up to 4 weeks to see...
When Should I Seek Immediate Care?
1. You have shortness of breath. 2. You cough up blood. 3. You have swelling or pain near the artery site. 4. You have numbness or pain in your arm...
When Should I Contact My Healthcare Provider?
1. You have sudden or more pain in your groin. 2. Your skin over the pseudoaneurysm is cool to the touch, pale, or changes color. 3. You have tingl...
What is a pseudoaneurysm?
As you might guess from the name, a pseudoaneurysm is a false aneurysm. It occurs when the wall of a blood vessel is damaged. This can cause blood to leak out of the blood vessel and to collect in the surrounding tissue. If you have a pseudoaneurysm, it’s important to get a diagnosis and the appropriate treatment because some pseudoaneurysms, ...
Why do pseudoaneurysms occur?
Trauma. Trauma or damage to the aorta from an accident or wound can cause blood to start leaking, causing a pseudoaneurysm to form in the surrounding tissues. Surgical complication.
What are the symptoms of pseudoaneurysm?
Your healthcare provider might suspect a pseudoaneurysm if you develop the following symptoms: swelling or tenderness in a particular area, especially if you’ve recently undergone a procedure. a painful mass or lump.
Where does a pseudoaneurysm develop?
A pseudoaneurysm typically develops close to the insertion spot where the narrow, flexible catheterization tube is threaded up toward the heart.
What is the most commonly used diagnostic tool for detecting a pseudoaneurysm?
Ultrasonography is the most commonly used diagnostic tool for detecting a pseudoaneurysm.
Can a pseudoaneurysm develop after a cardiac catheterization?
It’s not uncommon for a pseudoaneury sm to develop after a person undergoes a cardiac catheterization procedure. In fact, research suggests that a pseudoaneurysm is a common occurrence when the femoral artery (a large artery in your groin area) has been repeatedly punctured during a catheterization.
Why is it important to get a diagnosis for a pseudoaneurysm?
If you have a pseudoaneurysm, it’s important to get a diagnosis and the appropriate treatment because some pseudoaneurysms, if left untreated, may rupture. Let’s take a closer look at what causes pseudoaneurysms, where they develop, as well as their symptoms, risk factors, diagnosis, and treatment.
What is a pseudoaneurysm?
Answer From Francisco Lopez-Jimenez, M.D. A pseudoaneurysm, or pseudoaneurysm of the vessels, occurs when a blood vessel wall is injured and the leaking blood collects in the surrounding tissue. It is sometimes called a false aneurysm. In a true aneurysm, the artery or vessel weakens and bulges, sometimes forming a blood-filled sac.
What is the treatment for a pseudoaneurysm?
Ultrasound-guided medication. In this treatment, your doctor uses ultrasound imaging to locate and inject a blood clot-forming medication (thrombin) into the pseudoaneurysm. The medication causes the pooled blood to clot.
How long does it take to see if a pseudoaneurysm is a femoral?
You may not notice it until days or weeks after the procedure . Your doctor may recommend a watchful-waiting approach and an occasional duplex ultrasound test to see if it goes away on its own.
What to do if your doctor doesn't think ultrasound will work?
Surgery. If your doctor doesn't think either ultrasound-guided treatment will work, he or she may recommend surgery to correct it.
What is a pseudoaneurysm?
A pseudoaneurysm, or false aneurysm, is swelling of the wall of the artery. The swelling is caused by a small hole that has not sealed. A pseudoaneurysm can happen in any artery. It may become a medical emergency because the pseudoaneurysm can rupture.
How to prevent pseudoaneurysms?
Reach or maintain a healthy weight. Extra weight increases your risk for a pseudoaneurysm. Ask your healthcare provider what a healthy weight is for you. He or she can help you create a healthy weight loss plan if you are overweight.
What can I do to manage or prevent a pseudoaneurysm?
Limit activity as directed. Your healthcare provider may want to monitor the pseudoaneurysm for up to 4 weeks to see if it closes. He or she may tell you to limit your activity to lower your risk for rupture.
How long to monitor for pseudoaneurysm?
Your healthcare provider may want to monitor the pseudoaneurysm for up to 4 weeks to see if it closes. He may tell you to limit your activity to lower your risk for rupture. Do not smoke. Nicotine and other chemicals in cigarettes and cigars can cause blood vessel and lung damage.
What is debridement surgery?
Debridement is a procedure used to remove dead tissue. You may need this if the area around your pseudoaneurysm becomes infected.
Can you take salt for pseudoaneurysms?
Your healthcare provider may recommend that you limit the amount of sodium (salt) you have every day. You may also need to take your blood pressure and keep a record of the numbers. You may also need to take medicine to control your blood pressure.
How to treat pseudoaneurysms?
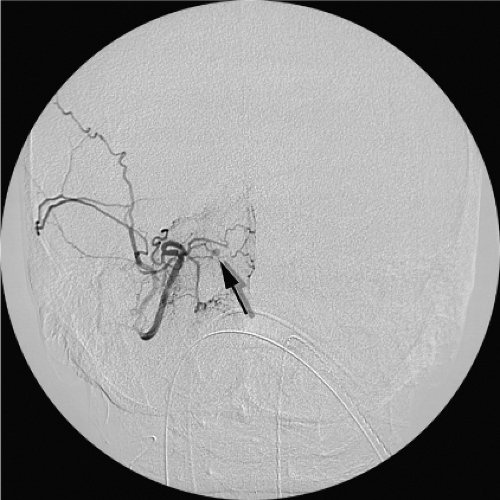
Visceral artery pseudoaneurysms are typically treated by endovascular means first, with surgery reserved for failure; this is highly effective, with one study reporting a 98% success rate in control of pseudoaneurysms and ruptured true aneurysms.[11] Techniques include coiling, injections of procoagulant materials, and covered stent deployment to seal the origin of the pseudoaneurysm.
What is an arterial pseudoaneurysm?
An arterial pseudoaneurysm, AKA false aneurysm, is caused by damage to the arterial wall, resulting in locally contained hematoma with turbulent blood flow and a neck that typically does not close spontaneously once past a certain size .
What is the surgical management of femoral pseudoaneurysm?
Surgical management of femoral pseudoaneurysm is reserved for those who fail at least one unsuccessful duplex-guided compression or thrombin injection, [1]or for those with anastomotic disruptions. If surgical repair is required, blood should be typed and crossed, and available as inadvertent entry into the pseudoaneurysm before achieving proximal and distal control can result in massive bleeding.
What is the incidence of a femoral pseudoaneurysm?
Femoral pseudoaneurysms typically result from access for catheter-based interventions and carry an incidence of 0.6 to 4.8% .[1] With the increasing use of ultrasound for access, some society guidelines quote that the acceptable rate of pseudoaneurysm after percutaneous access should be less than 0.2%.
What causes a pseudoaneurysm in the femoral area?
The most common cause of femoral pseudoaneurysm is iatrogenic.
What is the most common presentation of a pseudoaneurysm?
The most common clinical presentation of a pseudoaneurysm is a femoral pseudoaneurysm following access for endovascular procedures. Other less common presentations include visceral pseudoaneurysms and aortic pseudoaneurysms. This article will focus on these three entities.
How to diagnose aortic pseudoaneurysm?
The diagnosis of aortic pseudoaneurysms is most commonly via CTA or conventional arteriography. They may have a history of previous open repair of dissection or aneurysm, blunt or penetrating trauma, infection, or genetic disorders which predispose to aneurysmal degeneration of the aorta such as Marfan syndrome or Ehlers-Danlos syndrome.
What Are the Causes of a Pseudoaneurysm?
A pseudoaneurysm is often a complication of cardiac catheterization. Cardiac catheterization is a procedure for diagnosing heart conditions. Your doctor will insert a flexible tube with a camera into the artery in your leg and thread it through your blood vessels to your heart.
What Are the Symptoms of a Pseudoaneurysm?
The symptoms of a pseudoaneurysm are usually pain and swelling at the site of the blood vessel damage. You might feel a lump under your skin where the blood is pooling in the tissue. It may feel tender or painful to the touch. It may feel like it's throbbing.
What Is the Treatment for a Pseudoaneurysm?
If you suspect you have a pseudoaneurysm, you should talk to your doctor, especially if you’ve recently had a cardiac catheterization. You will need to have an ultrasound of the area to get a firm diagnosis. Your doctor will be able to decide on treatment after seeing the details of the pseudoaneurysm.
Does a Pseudoaneurysm Have Health Risks?
If you think you might have a pseudoaneurysm, you should call your doctor. If you don't have the condition treated, you're at risk of severe complications. The buildup of blood can damage circulation in the area and cause tissue death.