
Who Can Diagnose and Treat Eye Problems?
What are the eye problems that adults experience?
Why is my vision blurry?
What are the eyes that protect the eyes?
What is the third layer of the eye?
What is the outermost layer of the eye?
What is the purpose of the eye?
See 4 more
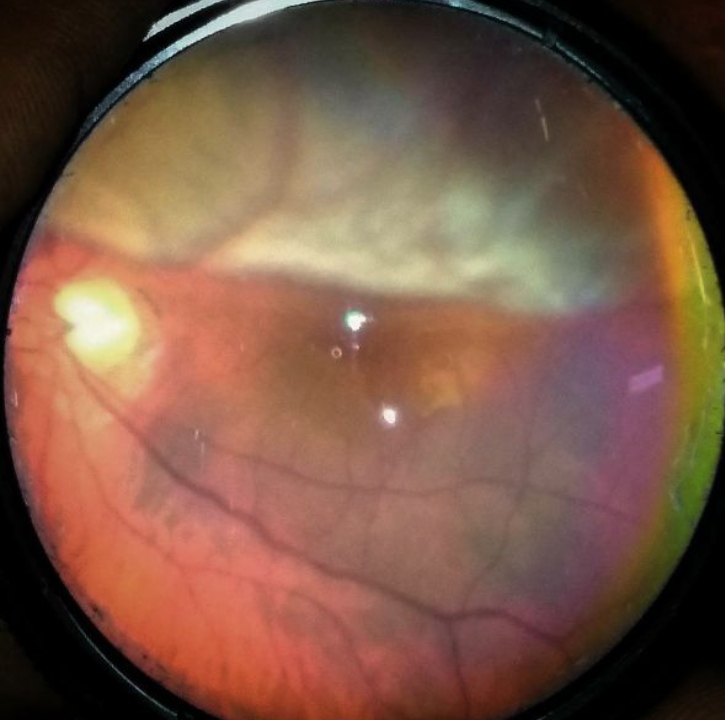
Do Optometrists examine the retina?
The second type of vision assessment involves the use of a retinoscopy. The optometrists use a retinoscopy to measure the patient's eyes to see if there are any refractive errors.
How do optometrists check for retinal detachment?
Your doctor will give you some eye drops to dilate (widen) your pupil and then look at your retina at the back of your eye. This exam is usually painless. The doctor may press on your eyelids to check for retinal tears, which may be uncomfortable for some people.
How do doctors check for retinal tears?
Retinal examination. The doctor may use an instrument with a bright light and special lenses to examine the back of your eye, including the retina. This type of device provides a highly detailed view of your whole eye, allowing the doctor to see any retinal holes, tears or detachments.
How do you know if you have a retinal tear?
Symptoms. A patient with an acute retinal tear may experience the sudden onset of black spots or “floaters” in the affected eye. This can have the appearance of someone shaking pepper in your vision. Flashes of light (Photopsia) are another common symptom.
Can an optician spot detached retina?
Retinal detachment diagnosis If you're experiencing symptoms, an optician should be able to confirm whether you have a retinal tear or detachment. They can make an urgent referral to a hospital ophthalmologist for specialist assessment and treatment.
How common are retinal tears?
The retina is a thin layer of light-sensitive tissue that lines the back of the eye cavity like wallpaper. Retinal tears and holes are quite common. In fact, they´re found in about 10% of the population.
How long before a retinal tear become a detachment?
The rate of progression of a retinal detachment can vary from days to weeks depending on many factors such as patient age as well as the size and the number of retinal tears. Gradual loss of peripheral vision in the form of a shadow, curtain, or cloud (this corresponds to the retina detaching.)
How long can retinal tear go untreated?
A retinal detachment may cause permanent blindness over a matter of days and should be considered an eye emergency until evaluated by a retina specialist. Most retinal detachments occur suddenly and can threaten the central vision within hours or days.
What does your vision look like with a retinal tear?
Signs and Symptoms of Retinal Tears Black spots in field of vision. Flashes of light. Blurry vision. Darker/dimmer vision.
What is the most common cause of retinal tear?
Aging is the most common cause of rhegmatogenous retinal detachment. As you get older, the vitreous in your eye may change in texture and may shrink. Sometimes, as it shrinks, the vitreous can pull on your retina and tear it.
Can you feel a torn retina?
Retinal detachment itself is painless. But warning signs almost always appear before it occurs or has advanced, such as: The sudden appearance of many floaters — tiny specks that seem to drift through your field of vision. Flashes of light in one or both eyes (photopsia)
How can you check your retina at home?
0:152:14How to See Your Retina - TRY THIS EXPERIMENT - AAPT FilmsYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAny bright light will do but it will be much dimmer as seen through the eyelids. Yep there it isMoreAny bright light will do but it will be much dimmer as seen through the eyelids. Yep there it is take the flashlight and hold it gently against the top of your eyelid when it is closed.
Can a normal eye exam detect retinal detachment?
You need an eye exam to diagnose retinal detachment. Your eye care provider will use a dilated eye exam to check your retina. They'll put eye drops in your eyes. The drops dilate, or widen, the pupil.
What are the warning signs of a detached retina?
Detached retina (retinal detachment)dots or lines (floaters) suddenly appear in your vision or suddenly increase in number.you get flashes of light in your vision.you have a dark "curtain" or shadow moving across your vision.your vision gets suddenly blurred.
How does retinal detachment feel?
Retinal detachment itself is painless. But warning signs almost always appear before it occurs or has advanced, such as: The sudden appearance of many floaters — tiny specks that seem to drift through your field of vision. Flashes of light in one or both eyes (photopsia)
Can ophthalmologist see retinal detachment?
Retinal problems Tears can go unnoticed until the retina detaches. As a result, it is hard to just “feel” or “know” that there is a problem with your retina. An ophthalmologist can take a look at your eye and determine whether there are any tears.
An Optometrist Can Treat Serious Eye Health Problems
Some problems with eye health are more serious than others and as an optometrist, we can diagnose each one in turn. Regardless of whether a patient has poor vision or is suffering from a serious eye disease, we can treat the problem. Here is what you need to know about some of the more serious eye conditions.. Cataracts
Can optometrists treat glaucoma, or should I go to an ... - FindaTopDoc
I am biased, being a Neuro-ophthalmologist. I would seek the attention of a general Ophthalmologist and follow up visual field and intraocular pressure testing (and optical coherence tomographic scans should also be done at least twice yearly if not 3 times a year) possibly could be done by a good Optometrist but I would at least see an MD once a year.
What Kind of Doctor Can Treat an Eye Infection?
What Kind of Doctor Can Treat an Eye Infection? While there are three types of doctors that specialize in treating eyes, only two are deemed qualified to treat eye infections. Eyes are sensitive and not every doctor can treat the different types of injuries or conditions that eyes experience. If you are looking to get a
Can Optometrists Diagnose Cataracts? - American Academy of ...
Free Newsletter. Get ophthalmologist-reviewed tips and information about eye health and preserving your vision.
Who Can Diagnose and Treat Eye Problems?
Health professionals who are qualified to diagnose and treat eye diseases are optometrists and ophthalmologist. Ophthalmologists complete 4 years of medical school and perform 4 years of residency training. Optometrists complete 4 years of optometry school and 1 year of residency training. Ophthalmologists have the title MD (a doctor of medicine) attached to their name and optometrists have the title DO (a doctor of osteopathic medicine) attached to their name. Optometrists can diagnose conditions, prescribe medications and treat most eye diseases.
What are the eye problems that adults experience?
Adults experience a wider range of potential eye problems as they grow older or get sick. Minor eye problems that adults are usually afflicted with are refractory disorders like astigmatism, farsightedness, nearsightedness, and presbyopia. More serious eye problems associated with adults are macular degeneration, cataracts, and glaucoma. Macular Degeneration is a condition where part of the retina (called the macula) becomes atrophic. This eye disease can cause permanent loss of vision. Those with high blood pressure, high cholesterol, poor blood sugar control, and those who smoke are prone to getting macular degeneration.
Why is my vision blurry?
blurred vision. Blurred vision can be caused by astigmatism or another type of refractive error. Nearsightedness is the most common type of eye disorder that school-age children experience. Lazy eye, also known as amblyopia, occurs when the eyes and brain do not work together.
What are the eyes that protect the eyes?
The eyeball rests in an orbit, also known as the eye socket. The eye socket is made of bone and encases the entire eyeball. Tears produced in the eyes help protect the eyes from an internal standpoint.
What is the third layer of the eye?
The choroid is made up of blood vessels that help bring essential nutrients and oxygen to the internal parts of the eyes. The third layer is known as the retina. The retina is the innermost layer of the eye that helps convert light into something your brain can recognize. The retina is located near the optic nerve.
What is the outermost layer of the eye?
The Anatomy of Human Eyes. The eye is composed of 3 layers. The white, outermost layer of the eye is called the sclera . The sclera is the protective clear film on top of the eyes. It is made up of fibrous, strong tissues and is fixed to the cornea. The second layer of the eye is called the choroid.
What is the purpose of the eye?
Your eyes are a vital part of your body that help you see the things and people around you. Of the five senses, it is considered one of the most often used. This important organ works to take in and process visual images so that the brain can comprehend and gauge the distance of objects. The size of a human eye is equivalent to a ping pong ball. ...
How can retinal holes and tears be prevented?
There is no way to avoid retinal holes and tears other than protecting your eyes from harm, such as avoiding high contact sports like football and ice hockey.
What causes retinal holes and tears?
This gel is attached to the retina at birth, but it separates from the retina as we become older, resulting in a posterior vitreous detachment (PVD). In most cases, this does no harm.
Is there a difference between retinal holes and retinal tears?
The terms retinal hole and tears may often be used interchangeably, but there is a clinical difference.
Should I unfocus my eye?
I can unfocus my eye and vision on command. I am not sure if this is healthy for the eye and it's muscle. Should I continue to do this or will this cause eye strain or other eye problems? Does doing this rapidly work our the eye muscle or does it make it worse.
Can normal (regular) astigmatism cause multiple ghosting image (polyopia)?
For last 3-4 weeks, i started to see triple sometimes. The triple (new appeared) ghosting image is placed usually between the center of the original and old 1 ghosting image. They sometimes appeared as clearly visible triple image or sometimes the newly appeared ghosting image merge with the old ghosting image. I also asked the doctor about keratoconus and doctor told me that I have no keratoconus. Can normal (regular) astigmatism cause multiple ghosting image (polyopia)?
What happens if you don't see a retinal specialist?
Retinal detachments are serious and need to be seen by a retinal specialist right away.Failure to do so will often lead to blindness in the eye the detachment occurs in.
Why is there no one time period for the treatment of all retinal detachments?
There is no one time period for the treatment of all retinal detachments, because they are all different and all have different risks for loss of functional vision. Sooner is always better than later. Central is more urgent that peripheral and superior is more urgent than inferior.
What is the difference between an ophthalmologist and an optometrist?
Ophthalmologists are medical doctors that specialize in the treatment and surgery of a diseased eye, and know some Optometry. Optometrists are doctors that specialize in vision and the visual systems of the eye, and can diagnose and treat some of Ophthalmology. Ocularist make artificial eyes.
How long does it take for a retina to detach?
In a worst case scenario, the retina could detach within hours of tearing.
What is an optician?
Opticians are typically involved with ophthalmic appliances. Making, mounting, selecting and fitting the proper eyeglass lenses and frames, dispensing contact lenses. Oculists is an old term that refers to Ophthalmologists and Optometrists.
What is an ophthalmologist?
Ophthalmologists are medical doctors that specialize in the treatment and surgery of a diseased eye, and know some Optometry.
Can you see a pupil with a dilated pupil?
On a good day, yes. Some are easy to see- looking inside the eye it is like a curtain waving in the wrong place. Others are much more difficult and the patient’s symptoms and history will be enough to justify an exam with dilated pupils. Some optoms (depends where you are in the world) will routinely dilate all patient’s pupils unless it is unsafe. In most parts of world optometrists will have the training and equipment to detect most retinal detachments. Some ret.dets. are annoying elusive and may require an Optos machine (nice kit but very expensive) or scleral indentation to detect. Scleral
Question (s) For Expert Witness
1. Do you routinely treat patients like the one described in this case?
Expert Witness Response E-011072
It’s important to evaluate someone with flashes very carefully because this can sometimes be a sign of a retinal tear, that can lead to retinal detachment, and that can lead to loss of vision. This is what I do everyday and we work to avoid this outcome, however sometimes retinal detachment results in loss of vision even with proper treatment.
What Are the Signs of a Retinal Tear?
There’s no pain associated with this condition, but here are the tell-tale symptoms of a tear you should look out for:
How to tell if you have a tear in your eye?
There’s no pain associated with this condition, but here are the tell-tale symptoms of a tear you should look out for: 1 Floaters. Small particles of debris in the vitreous gel that might appear as spots, squiggles, or threads that float about in your vision. It is natural to have them, but a sudden increase in the size and number of floaters in your vision is a cause for concern. 2 Sudden flashes. Do you experience brief light flashes in your peripheral vision? These flashes typically occur while the eye is moving. 3 A shadow in your peripheral vision. 4 A grey curtain that moves across your field of vision, or a sudden decrease in vision.
What is the lining of the eye?
The lining is made up of a thin layer of tissue that generates vision. Light enters the eye through the pupil, passes through the lens, then passes through the vitreous gel filling the eye, falling on the retina. A retinal tear can occur when the retina pulls away from the outer layers of the eye. Although a tear can usually be repaired ...
What are the risk factors for retinal tear?
These risk factors include: Middle and older age: at birth, the vitreous gel is attached to the retina.
How to avoid permanent loss of vision due to a tear?
The best way to avoid permanent loss of vision due to a tear is to book regular appointments for eye exams. At Eyelux Optometry, we include digital retinal imaging (DRI) without any additional fee as part of every comprehensive eye exam. DRI allows for analysis over time, ensuring we detect early signs of retinal degeneration or a retinal tear before lasting damage occurs.
Why does my retina tear?
When we age, the gel separates from the retina, which may cause the retina to tear. Being extremely nearsighted. Previous eye surgery. Trauma, such as a blow to the eye. Diabetes, especially if it is poorly controlled. Hereditary risks: If a close relative has a tear, you could be at risk.
Can you have a retinal tear without treatment?
If you suspect you have a retinal tear, it’s important to make an appointment with your optician for an eye exam. It is possible that tears that haven’t progressed to retinal detachment may not require treatment: an eye care professional may be able to observe such tears without providing treatment as they heal themselves.
What is the procedure to repair a retinal tear?
Surgery is almost always used to repair a retinal tear, hole or detachment. Various techniques are available. Ask your ophthalmologist about the risks and benefits of your treatment options. Together you can determine what procedure or combination of procedures is best for you.
What type of eye exam is used to see the retina?
This type of device provides a highly detailed view of your whole eye, allowing the doctor to see any retinal holes, tears or detachments. Ultrasound imaging.
What is the procedure called when you inject air into your eye?
Injecting air or gas into your eye. In this procedure, called pneumatic retinopexy (RET-ih-no-pek-see), the surgeon injects a bubble of air or gas into the center part of the eye (the vitreous cavity). If positioned properly, the bubble pushes the area of the retina containing the hole or holes against the wall of the eye, stopping the flow of fluid into the space behind the retina. Your doctor also uses cryopexy during the procedure to repair the retinal break.
How to prevent retinal detachment?
When a retinal tear or hole hasn't yet progressed to detachment, your eye surgeon may suggest one of the following procedures to prevent retinal detachment and preserve vision. Laser surgery (photocoagulation). The surgeon directs a laser beam into the eye through the pupil. The laser makes burns around the retinal tear, ...
What is the procedure called when you put silicone on your eye?
This procedure, called scleral (SKLAIR-ul) buckling, involves the surgeon sewing (suturing) a piece of silicone material to the white of your eye (sclera) over the affected area. This procedure indents the wall of the eye and relieves some of the force caused by the vitreous tugging on the retina.
What is the procedure called to remove the vitreous?
Draining and replacing the fluid in the eye. In this procedure, called vitrectomy (vih-TREK-tuh-me), the surgeon removes the vitreous along with any tissue that is tugging on the retina. Air, gas or silicone oil is then injected into the vitreous space to help flatten the retina.
What test is used to check for retinal bleeding?
Ultrasound imaging. Your doctor may use this test if bleeding has occurred in the eye, making it difficult to see your retina.
What are the symptoms of retinal disorders?
Most retinal disorders share similar symptoms, such as blurred vision or vision loss. These disorders include floaters, retinal tear or detachment, macular degeneration, diabetic retinopathy, and epiretinal membrane.
What do optometrists do?
The job itself is varied, from conducting eye exams, evaluating vision, and assessing eye conditions to writing prescriptions, recommending further treatments, and providing preoperative and postoperative care.
What is the difference between an optometrist and an ophthalmologist?
Ophthalmologist. Optician. Summary. An optometrist is an eye doctor capable of examining the eyes for vision defects, signs of injury, ocular conditions, and problems with general eye health. Optometrists are primary healthcare specialists. They differ from both ophthalmologists and opticians.
How much does an optometrist make in 2019?
Statistics show that just under 40,000 people held jobs as optometrists in 2019, with a mean annual wage of $122,980.
What are the different types of optometrists?
An optometrist may work in many different environments. These include: 1 a solo or group private practice 2 a community health center, Veterans Affairs medical center, or hospital 3 an academic setting 4 a research facility 5 a retail, optical, or corporate setting 6 the military
What is the name of the condition that causes blindness in the eye?
Glaucoma. Glaucoma refers to damage to the optic nerve, which connects the eye to the brain. It is a leading cause of irreversible blindness in the U.S., affecting more than 3 million people. An optometrist can diagnose glaucoma and devise a treatment plan.
What happens when the lens in the eye develops cloudy patches?
Cataracts occur when the lens in the eye develops cloudy patches. These can grow larger, seriously affecting vision and potentially causing blindness.
Who Can Diagnose and Treat Eye Problems?
Health professionals who are qualified to diagnose and treat eye diseases are optometrists and ophthalmologist. Ophthalmologists complete 4 years of medical school and perform 4 years of residency training. Optometrists complete 4 years of optometry school and 1 year of residency training. Ophthalmologists have the title MD (a doctor of medicine) attached to their name and optometrists have the title DO (a doctor of osteopathic medicine) attached to their name. Optometrists can diagnose conditions, prescribe medications and treat most eye diseases.
What are the eye problems that adults experience?
Adults experience a wider range of potential eye problems as they grow older or get sick. Minor eye problems that adults are usually afflicted with are refractory disorders like astigmatism, farsightedness, nearsightedness, and presbyopia. More serious eye problems associated with adults are macular degeneration, cataracts, and glaucoma. Macular Degeneration is a condition where part of the retina (called the macula) becomes atrophic. This eye disease can cause permanent loss of vision. Those with high blood pressure, high cholesterol, poor blood sugar control, and those who smoke are prone to getting macular degeneration.
Why is my vision blurry?
blurred vision. Blurred vision can be caused by astigmatism or another type of refractive error. Nearsightedness is the most common type of eye disorder that school-age children experience. Lazy eye, also known as amblyopia, occurs when the eyes and brain do not work together.
What are the eyes that protect the eyes?
The eyeball rests in an orbit, also known as the eye socket. The eye socket is made of bone and encases the entire eyeball. Tears produced in the eyes help protect the eyes from an internal standpoint.
What is the third layer of the eye?
The choroid is made up of blood vessels that help bring essential nutrients and oxygen to the internal parts of the eyes. The third layer is known as the retina. The retina is the innermost layer of the eye that helps convert light into something your brain can recognize. The retina is located near the optic nerve.
What is the outermost layer of the eye?
The Anatomy of Human Eyes. The eye is composed of 3 layers. The white, outermost layer of the eye is called the sclera . The sclera is the protective clear film on top of the eyes. It is made up of fibrous, strong tissues and is fixed to the cornea. The second layer of the eye is called the choroid.
What is the purpose of the eye?
Your eyes are a vital part of your body that help you see the things and people around you. Of the five senses, it is considered one of the most often used. This important organ works to take in and process visual images so that the brain can comprehend and gauge the distance of objects. The size of a human eye is equivalent to a ping pong ball. ...
