
Do basal cells turn into squamous cells?
Basal cells: These cells are in the lower part of the epidermis, called the basal cell layer. These cells constantly divide to form new cells to replace the squamous cells that wear off the skin's surface. As these cells move up in the epidermis, they get flatter, eventually becoming squamous cells.
Can you have basal cell and squamous cell carcinoma?
Therefore, when determining the diagnosis and surgical treatment of patients with skin cancer, we should not rule out the possibility that BCC and SCC may coexist and that basosquamous cell carcinoma may develop even if patients are referred to plastic surgeons after being diagnosed with BCC and SCC in other hospitals ...
Can basal cell carcinoma turn malignant?
Basal cell carcinoma does not progress into melanoma. Each is a separate and distinct type of skin cancer. Basal cell carcinoma is the most common form of skin cancer and one of two major nonmelanoma skin cancer types (the other is squamous cell carcinoma).
Which grows faster basal cell or squamous cell carcinoma?
Squamous cell skin cancer SCC is generally faster growing than basal cell cancers. About 20 out of every 100 skin cancers (20%) are SCCs. They begin in cells called keratinocytes, which are found in the epidermis. Most SCCs develop on areas of skin exposed to the sun.
Can you have two different cancers at the same time?
For example, someone who was treated for a certain type of colorectal cancer can get another type of colorectal cancer as a second cancer.
How quickly does squamous cell carcinoma spread?
Squamous cell carcinoma rarely metastasizes (spreads to other areas of the body), and when spreading does occur, it typically happens slowly. Indeed, most squamous cell carcinoma cases are diagnosed before the cancer has progressed beyond the upper layer of skin.
How do you know if basal cell carcinoma has spread?
Ask your doctor if your lymph nodes will be tested. Basal and squamous cell cancers don't often spread to other parts of the body. But if your doctor thinks your skin cancer might spread, you might need imaging tests, such as MRI or CT scans.
What's worse basal cell or squamous?
Though not as common as basal cell (about one million new cases a year), squamous cell is more serious because it is likely to spread (metastasize).
How long does it take for basal cell carcinoma to spread?
The tumors enlarge very slowly, sometimes so slowly that they go unnoticed as new growths. However, the growth rate varies greatly from tumor to tumor, with some growing as much as ½ inch (about 1 centimeter) in a year. Basal cell carcinomas rarely spread (metastasize) to other parts of the body.
What does the beginning of squamous cell carcinoma look like?
Squamous cell carcinoma initially appears as a skin-colored or light red nodule, usually with a rough surface. They often resemble warts and sometimes resemble open bruises with raised, crusty edges. The lesions tend to develop slowly and can grow into a large tumor, sometimes with central ulceration.
How does squamous cell carcinoma start?
Most squamous cell carcinomas of the skin result from prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, either from sunlight or from tanning beds or lamps. Avoiding UV light helps reduce your risk of squamous cell carcinoma of the skin and other forms of skin cancer.
How long can you wait to treat squamous cell carcinoma?
The median patient delay was 2 months. The highest quartile patients reported > 9 months between noticing the lesion and the first visit, defined as long patient delay. The median treatment delay was 2 months. The highest quartile patients reported > 4 months treatment delay, defined as long treatment delay.
How can you tell the difference between basal cell and squamous cell carcinoma?
Basal cell carcinoma most commonly appears as a pearly white, dome-shaped papule with prominent telangiectatic surface vessels. Squamous cell carcinoma most commonly appears as a firm, smooth, or hyperkeratotic papule or plaque, often with central ulceration.
What is Stage 4 squamous cell carcinoma?
Stage 4 SCC indicates cancer spread to distant sites, such as organs, distant lymph nodes and other structures.
What organs does squamous cell carcinoma affect?
If left untreated, squamous cell carcinoma can spread to nearby lymph nodes, bones or distant organs (such as the lungs or liver). Normal squamous tissue usually appears flat. When this tissue develops cancer it can appear as round masses that are can be flat, raised, or ulcerated.
How can you tell if squamous cell carcinoma has spread?
How to Tell If Squamous Cell Carcinoma Has SpreadThe tumor is thicker than 2 millimeters.The tumor has grown into the lower dermis or subcutis layers of the skin.The tumor has grown into the nerves in the skin.The tumor is present on the ear or on a hair-bearing lip.
Are There Different Kinds of Skin Cancer?
There are many types of skin cancer. Some are very rare. Your doctor can tell you more about the type you haveThe two most common kinds of skin can...
How Does The Doctor Know I Have Skin Cancer?
You may not know you have a skin cancer until it’s really big. Then it can itch, bleed or even hurt. But before it can be seen or felt you may noti...
How Serious Is My Cancer?
If you have skin cancer, the doctor will want to find out how far it has spread. This is called staging. You may have heard other people say that t...
What Kind of Treatment Will I Need?
There are many ways to treat skin cancer. The main types of treatment are surgery (SUR-jur-ee), radiation ( RAY-dee-A-shun), targeted therapy, and...
What Will Happen After Treatment?
You’ll be glad when treatment is over. Your doctor will want you to check your skin at least once a month. It will be very important to protect you...
What is basal cell carcinoma?
Overview. Basal cell carcinoma is a type of skin cancer that most often develops on areas of skin exposed to the sun. This photograph shows a basal cell carcinoma that affects the skin on the lower eyelid. Basal cell carcinoma is a type of skin cancer.
When does basal cell carcinoma become more common?
But it can also affect younger adults and is becoming more common in people in their 20s and 30s. A personal or family history of skin cancer.
What is the name of the cancer that is most often found on the face?
Basal cell carcinoma is a type of skin cancer that most often develops on areas of skin exposed to the sun, such as the face. On brown and Black skin, basal cell carcinoma often looks like a bump that's brown or glossy black and has a rolled border.
What is the name of the cancer that occurs when a cell moves upward?
As new cells move upward, they become flattened squamous cells, where a skin cancer called squamous cell carcinoma can occur. Melanoma, another type of skin cancer, arises in the pigment cells (melanocytes). Basal cell carcinoma occurs when one of the skin's basal cells develops a mutation in its DNA.
What are the factors that increase the risk of basal cell carcinoma?
Factors that increase your risk of basal cell carcinoma include: Chronic sun exposure. A lot of time spent in the sun — or in commercial tanning beds — increases the risk of basal cell carcinoma. The threat is greater if you live in a sunny or high-altitude location, both of which expose you to more UV radiation.
What is the most common type of basal cell carcinoma?
The most common type of basal cell carcinoma, this lesion often appears on the face and ears. The lesion may rupture, bleed and scab over. A brown, black or blue lesion — or a lesion with dark spots — with a slightly raised, translucent border.
Where does skin cancer develop?
Where skin cancer develops. Skin cancer begins in the cells that make up the outer layer (epidermis) of your skin. One type of skin cancer called basal cell carcinoma begins in the basal cells, which make skin cells that continuously push older cells toward the surface. As new cells move upward, they become flattened squamous cells, ...
How many stages of squamous cell carcinoma are there?
According to the Moffitt Cancer Center, squamous cell carcinoma is classified into stages from 0-4 according to how far it has spread throughout the body. Stage 0 means it hasn’t spread beyond the top layer of skin. Stage 1 squamous cell has spread deeper into the skin but has not spread into healthy tissue or lymph nodes.
What is the difference between stage 3 and 4 squamous cell?
Stage 3 means that the cancer has spread to lymph nodes, and Stage 4 squamous cell has spread to at least one organ, such as a separate area of the skin, the lungs, or the brain.
What is the second most common type of skin cancer?
The second most common type of skin cancer is squamous cell carcinoma. Squamous cell carcinoma is also frequently caused by sun exposure or tanning bed use. Like basal cells, squamous cells can grow deep into the skin.
Can basal cell carcinoma spread?
Basal cell carcinoma is a slow-growing cancer, but early treatment is important because, if left untreated, basal cell carcinoma can spread and grow deep into the skin. My surgeon told me many years ago that, what appears to be a small area of basal cell carcinoma on the surface of the skin, can actually be as large as a silver dollar in other layers of the skin.
Where does basal cell carcinoma start?
Basal cell carcinoma begins in the basal cells —a type of cell within the skin that produces new skin cells as old ones die off. Basal cell carcinoma often appears as a slightly transparent bump on the skin, though it can take other forms.
Where does squamous cell carcinoma occur?
Squamous cell carcinoma develops in the thin, flat squamous cells that make up the outer layer of the skin. Squamous cells are found all over the body, and this type of cancer can occur anywhere squamous cells are found. Though this form of skin cancer is not usually life-threatening, one major difference between basal cell and squamous cell cancers is that squamous cell cancer are more likely to grow deeper into the layers of your skin and spread to other parts of the body. While still relatively uncommon, it is considered an aggressive form of cancer, if left untreated.
What is the treatment for basal cell carcinoma?
There are several basal cell carcinoma treatment options available to patients, including Mohs micrographic surgery, excisional surgery, electrosurgery, cryosurgery, and laser surgery. These treatments all have one thing in common: the word surgery.
What is the most common type of skin cancer?
Basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma are the two most common types of skin cancers. According to the American Cancer Society, over 5 million cases of basal cell and squamous cell cancers are diagnosed every year.
Why do basal cells have mutations?
Most basal cell carcinomas are thought to be caused by long-term exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from sunlight and commercial tanning beds.
Is basal cell cancer life threatening?
Though this form of skin cancer is not usually life-threatening, one major difference between basal cell and squamous cell cancers is that squamous cell cancer are more likely to grow deeper into the layers of your skin and spread to other parts of the body.
Is squamous cell carcinoma invasive?
Traditional treatment options—including Mohs—has involved invasive incisions that cut through healthy tissue, leading to a lengthy recovery and unsightly scarring. Sensus Healthcare is changing all that with a non-surgical treatment option— the SRT-100™.
What does squamous skin cancer look like?
Basal and squamous skin cancer may look like: Flat, firm, pale or yellow areas that look a lot like a scar. Raised reddish patches that might itch. Rough or scaly red patches, which might crust or bleed. Small, pink or red, shiny, pearly bumps, which might have blue, brown, or black areas.
What is the cancer that starts in the top layer of the skin?
Squamous cell cancer, which starts in the top layer of the skin. Another kind of skin cancer is called melanoma. These cancers start from the color-making cells of the skin (called melanocytes). You can read about melanoma in If You Have Melanoma Skin Cancer.
How serious is my cancer?
If you have skin cancer, the doctor will want to find out how far it has spread. This is called staging.
How to treat skin cancer without cutting?
Some of these use freezing, chemo or other drugs put right on the skin, light therapy (PDT), or lasers to kill cancer cells .
What is it called when cancer spreads to another part of the body?
Cancer is always named based on the place where it starts. So if skin cancer spreads to another part of the body, it’s still called skin cancer .
How to tell if you have skin cancer?
In a biopsy, the doctor takes out a small piece of tissue to check it for cancer cells. A biopsy is the only way to tell for sure if you have skin cancer and what kind it is.
Can basal cell cancer spread to lymph nodes?
Basal and squamous cell cancers don' t often spread to other parts of the body.
Where does squamous cell carcinoma occur?
But it can occur anywhere on your body, including inside your mouth, the bottoms of your feet and on your genitals.
Which area of the body is most likely to develop squamous cell carcinoma?
Sun-exposed areas such as the lips and ears are especially likely to develop s quamous cell carcinoma of the skin.
What is the risk of precancerous skin lesions?
Having a precancerous skin lesion, such as actinic keratosis or Bowen's disease, increases your risk of squamous cell carcinoma of the skin.
What are the factors that increase the risk of squamous cell carcinoma?
Factors that may increase your risk of squamous cell carcinoma of the skin include: Fair skin. Anyone, regardless of skin color, can get squamous cell carcinoma of the skin. However, having less pigment (melanin) in your skin provides less protection from damaging UV radiation.
How to tell if you have squamous cell carcinoma?
Signs and symptoms of squamous cell carcinoma of the skin include: A firm, red nodule. A flat sore with a scaly crust. A new sore or raised area on an old scar or ulcer. A rough, scaly patch on your lip that may evolve to an open sore. A red sore or rough patch inside your mouth.
What is the name of the cancer that starts in the basal cells?
One type of skin cancer called basal cell carcinoma begins in the basal cells, which make skin cells that continuously push older cells toward the surface. As new cells move upward, they become flattened squamous cells, where a skin cancer called squamous cell carcinoma can occur. Melanoma, another type of skin cancer, ...
Where does skin cancer develop?
Where skin cancer develops. Skin cancer begins in the cells that make up the outer layer (epidermis) of your skin. One type of skin cancer called basal cell carcinoma begins in the basal cells, which make skin cells that continuously push older cells toward the surface. As new cells move upward, they become flattened squamous cells, ...
Where does basal cell carcinoma occur?
Studies reveal that 80% of skin cancers develop from basal cancer cells. The basal cell skin cancer generally develops on the neck and head while also being found anywhere on the skin. Furthermore, the disease is usually caused by the sun’s ultraviolet rays or develops in people who have taken radiation therapy many years ago. Basal cell carcinoma grows relatively slowly and hardly spreads to other parts of the body.
How long does squamous cell carcinoma last?
Also, the condition may be fatal sometimes. If detected early, the five-year squamous cell carcinoma survival rate is 99%. Even if the cancer is spread to the nearby organs, the squamous cell carcinoma treatment can be done through a combination of surgery and radiation treatment.
What are the different types of skin cancer?
Primarily, there are four types of skin cancer: basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, Merkel cell cancer, and melanoma, but basal and squamous cell cancer are the most common types. Let’s find out more about these diseases.
What causes skin cancer?
The mutations that occur in the skin cell DNA causes skin cancer. Such changes cause abnormal cells to multiply uncontrollably. When this occurs in squamous cells, it gives rise to squamous cell cancer. DNA mutations are generally caused by UV radiation found in the sun, tanning lamps, and beds.
Does UV light cause cancer?
As we read, exposure to UV radiation increases the risk of cancer. Still, it is pretty shocking to know that less exposure to sunlight or tanning lamps also increases the risk of squamous cell carcinoma.
Can a scaly patch grow?
Flat and scaly spots: Such patches can be seen with raised edges. Also, they can grow quite large over a period of time.
Does radiation cause skin cancer?
Studies also reveal that people with a weak immune system are likely to develop skin cancer. Radiation therapy also increases the risk of squamous cell carcinoma.
What are the signs of basal cell carcinoma?
Signs and Symptoms. The most common warning sign of skin cancer is a change on the skin, especially a new growth or a sore that doesn't heal. The cancer may start as a small, smooth, shiny, pale or waxy lump. It also may appear as a firm red lump.
Where can basal cell cancer be found?
Both basal and squamous cell cancers are found mainly on areas of the skin that are exposed to the sun — the head, face, neck, hands and arms. But skin cancer can occur anywhere.
How many people have actinic keratosis?
These precancerous lesions affect more than 10 million Americans. People with one actinic keratosis usually develop more. Up to 1 percent of these lesions can develop into a squamous cell cancer. Actinic keratoses are most common in people older than 40, but can appear in younger individuals with extensive sun exposure.
What is the second most common skin cancer after basal cell?
Pearly or waxy appearance. Sunken center. Irregular blood vessels on surface. Tendency to bleed easily after injury. Squamous cell carcinoma is the second most common skin cancer after basal cell. It's rarely deadly, but may spread or recur if not caught early.
What is the color of actinic keratosis?
These lesions are typically pink or red in color and rough or scaly to the touch. They occur on sun-exposed areas of the skin such as the face, scalp, ears, backs of hands or forearms. Actinic keratoses may start as small, red, flat spots but grow larger and become scaly or thick, if untreated.
Is basal cell carcinoma fatal?
Basal cell carcinoma is rarely fatal and doesn't typically spread, but it's important to catch it in the early stages so the surgical removal is as non-invasive as possible. It generally occurs on sun-exposed areas and often looks like pink bumps with the following features: Pearly or waxy appearance. Sunken center.
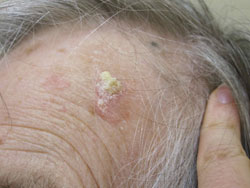
Overview
Symptoms
- Basal cell carcinoma usually develops on sun-exposed parts of your body, especially your head and neck. Less often, basal cell carcinoma can develop on parts of your body usually protected from the sun, such as the genitals. Basal cell carcinoma appears as a change in the skin, such as a growth or a sore that won't heal. These changes in the skin (lesions) usually have one of the fo…
Causes
- Basal cell carcinoma occurs when one of the skin's basal cells develops a mutation in its DNA. Basal cells are found at the bottom of the epidermis — the outermost layer of skin. Basal cells produce new skin cells. As new skin cells are produced, they push older cells toward the skin's surface, where the old cells die and are sloughed off. The process of creating new skin cells is c…
Risk Factors
- Factors that increase your risk of basal cell carcinoma include: 1. Chronic sun exposure. A lot of time spent in the sun — or in commercial tanning beds — increases the risk of basal cell carcinoma. The threat is greater if you live in a sunny or high-altitude location, both of which expose you to more UVradiation. Severe sunburns also increase your risk. 2. Radiation therapy.R…
Complications
- Complications of basal cell carcinoma can include: 1. A risk of recurrence.Basal cell carcinomas commonly recur, even after successful treatment. 2. An increased risk of other types of skin cancer.A history of basal cell carcinoma may also increase the chance of developing other types of skin cancer, such as squamous cell carcinoma. 3. Cancer that ...
Prevention
- To reduce your risk of basal cell carcinoma you can: 1. Avoid the sun during the middle of the day.In many places, the sun's rays are strongest between about 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. Schedule outdoor activities for other times of the day, even during winter or when the sky is cloudy. 2. Wear sunscreen year-round.Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30, even on clou…