
Medication
Normal thorough cooking (pasteurisation: 70°C 2min or equivalent) will kill Cl.botulinum bacteria but not its spores. To kill the spores of Cl.botulinum a sterilisation process equivalent to 121°C for 3 min is required. The botulinum toxin itself is inactivated (denatured) rapidly at temperatures greater than 80°C.
Therapy
Key takeaways:
- Botulism is a rare but life-threatening illness that causes your muscles to become paralyzed. It’s also highly preventable.
- Botulism is caused by different things like eating foods that are not properly preserved or feeding honey to infants.
- The treatment for botulism usually involves managing the symptoms caused by muscle paralysis.
Nutrition
C. botulinum spores can be killed by heating to extreme temperature (120 degrees Celsius) under pressure using an autoclave or a pressure cooker for at least 30 minutes. The toxin itself can be killed by boiling for 10 minutes. Answer 2:
Specialist To Consult
- Use a recommended pressure canner that holds at least four one-quart jars sitting upright on the rack.
- Be sure the gauge of the pressure canner is accurate. ...
- Clean lid gaskets and other parts according to the manufacturer’s directions.
- Vent the pressure canner before pressurizing and follow recommended cooling steps.
Does cooking kill botulism toxin?
How deadly is botulism?
Can you kill botulism by boiling?
How to avoid botulism when Canning at home?
Can you survive botulism poisoning?
People can die from botulism poisoning because of breathing failure. Someone with severe botulism may need a breathing machine and medical care for several months. Those who survive botulism poisoning may have tiredness and shortness of breath for years.
Can botulism heal itself?
But nerves can repair themselves. Many people recover fully. But recovery may take months and typically involves extended rehabilitation therapy. A different type of antitoxin, known as botulism immune globulin, is used to treat infants.
How long does it take for botulism to go away?
Depending on the severity of your case, recovery from botulism can take weeks, months or even years. Most people who receive prompt treatment recover completely in less than two weeks.
How do you know if you've got botulism?
Symptoms of botulism usually start with weakness of the muscles that control the eyes, face, mouth, and throat. This weakness may spread to the neck, arms, torso, and legs. Botulism also can weaken the muscles involved in breathing, which can lead to difficulty breathing and even death.
What is the survival rate of botulism?
Mortality rates vary based on the age of the patient and the type of botulism. Foodborne botulism carries an overall mortality rate of 5-10%. Wound botulism carries a mortality rate that ranges from 15-17%. The risk of death due to infant botulism is usually less than 1%.
What kills botulism?
To kill the spores of Cl. botulinum a sterilisation process equivalent to 121°C for 3 min is required. The botulinum toxin itself is inactivated (denatured) rapidly at temperatures greater than 80°C .
Does all honey contain botulism?
Honey can contain the bacteria that causes infant botulism, so do not feed honey to children younger than 12 months. Honey is safe for people 1 year of age and older. Learn more about infant botulism from the Infant Botulism Treatment and Prevention Program.
What temperature kills botulism?
Botulism spores die at 250 F. 3. Botulisum toxin that is the cause of the disease dies at 185 F (below boiling) or boiling for 10min.
What happens if botulism goes untreated?
If untreated, the disease may progress and symptoms may worsen to cause full paralysis of some muscles, including those used in breathing and those in the arms, legs, and trunk (part of the body from the neck to the pelvis area, also called the torso).
How do adults usually get botulism?
Botulism does not spread from person to person. A person can get foodborne botulism from eating food that contains botulism toxin if the food is not heated or processed properly. Foodborne botulism is most frequently caused by eating improperly processed home-canned, preserved or fermented foods.
Why is botulism so rare?
The bacteria that make botulinum toxin are found naturally in many places, but it's rare for them to make people sick. These bacteria make spores, which act like protective coatings. Spores help the bacteria survive in the environment, even in extreme conditions.
What two organ systems are primarily affected by botulism?
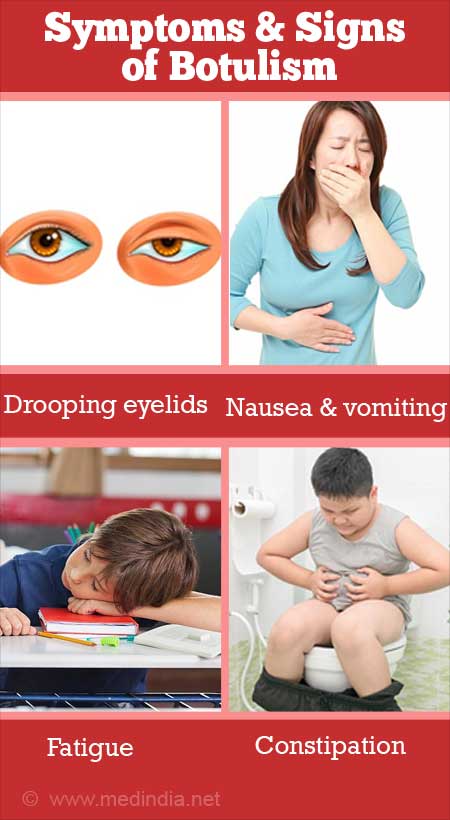
Botulism caught from food usually affects the stomach and intestines, causing nausea, vomiting, constipation, diarrhoea and abdominal cramps.
What happens if botulism goes untreated?
If untreated, the disease may progress and symptoms may worsen to cause full paralysis of some muscles, including those used in breathing and those in the arms, legs, and trunk (part of the body from the neck to the pelvis area, also called the torso).
Can you have a mild case of botulism?
Some botulism patients may have mild illness without progression and may not require BAT; however, the clinical features that predict which patients will progress and should be treated with BAT are unknown.
How quickly does botulism progress?
Symptoms generally begin 12-36 hours after eating contaminated food, but may occur as early as a few hours and as late as 10 days. Symptoms of botulism in infants may occur up to 14 days later.
What are the long term effects of botulism?
Even several years after acute illness, patients who had had botulism were more likely than control subjects to experience fatigue, generalized weakness, dizziness, dry mouth, difficulty lifting things, and difficulty breathing caused by moderate exertion.
What is the best treatment for botulism?
Antibiotics. Antibiotics are recommended for the treatment of wound botulism. However, these medications are not advised for other types of botulism because they can speed up the release of toxins.
How to treat foodborne botulism?
Treatment. For cases of foodborne botulism, doctors sometimes clear out the digestive system by inducing vomiting and giving medications to induce bowel movements. If you have botulism in a wound, a doctor may need to remove infected tissue surgically.
How long does it take to diagnose botulism?
Analysis of blood, stool or vomit for evidence of the toxin may help confirm an infant or foodborne botulism diagnosis. But because these tests may take days, your doctor's exam is the main way to diagnose botulism.
What to ask a doctor about botulism?
In cases of possible infant botulism, the doctor may ask if the child has eaten honey recently and has had constipation or sluggishness. Analysis of blood, stool or vomit for evidence ...
Can antitoxins reverse nerve damage?
The antitoxin cannot , however, reverse the damage that's been done. Fortunately, nerves do regenerate. Many people recover fully, but it may take months and extended rehabilitation therapy. A different type of antitoxin, known as botulism immune globulin, is used to treat infants.
What is botulism 3D?
About Botulism. This illustration depicts a three-dimensional (3D) computer-generated image of a group of anaerobic, spore-forming, Clostridium sp. organisms. Botulism (“BOT-choo-liz-um”) is a rare but serious illness caused by a toxin that attacks the body’s nerves and causes difficulty breathing, muscle paralysis, and even death.
What conditions can make a spore a toxin?
The conditions in which the spores can grow and make toxin are: Low-oxygen or no oxygen (anaerobic) environment. Low acid. Low sugar. Low salt. A certain temperature range. A certain amount of water.
Can botulinum toxin be made in food?
These bacteria can produce the toxin in food, wounds, and the intestines of infants. The bacteria that make botulinum toxin are found naturally in many places, but it’s rare for them to make people sick. These bacteria make spores, which act like protective coatings.
What is botulism in the body?
Related Pages. Botulism is a rare but serious illness caused by a toxin that attacks the body’s nerves. Symptoms of botulism usually start with weakness of the muscles that control the eyes, face, mouth, and throat. This weakness may spread to the neck, arms, torso, and legs.
Can botulism cause death?
Botulism also can weaken the muscles involved in breathing, which can lead to difficulty breathing and even death. If you or someone you know has symptoms of botulism, see your doctor or go to the emergency room immediately.
Can canned foods cause botulism?
Foodborne botulism is often caused by eating home-canned foods that have not been canned properly. Commercially canned foods are much less likely to be a source of botulism because modern commercial canning processes kill C. botulinum spores.
Can botulism be infected?
Sometimes a wound can get infected with C. botulinum. The most common way this happens is when a contaminated illicit drug, such as black tar heroin, is injected into muscle or skin. Wound botulism also has been reported following traumatic injuries, such as motorcycle crashes and surgeries.
Can babies have botulism?
We don’t know how most babies with infant botulism came into contact with C. botulinum spores, but we do know that these spores can be found in honey. Do not feed honey to children younger than 12 months because it has been linked to some cases of infant botulism.
How to prevent botulism?
To prevent wound botulism, do not use recreational injected drugs. Report deep wounds promptly to a physician.
How long does botulism last?
Most paralysis symptoms of botulism last for several weeks and then slowly go away in the following months. Sometimes fatigue and shortness of breath can last for years.
What is Botulism?
Botulism is a form of poisoning caused by exposure to Clostridium botulinum bacteria. These bacteria manufacture a chemical poison known as botulinum toxin that interferes with muscle function in many areas of the body, causing paralysis of individual muscles or groups of muscles. Exposure to this toxin is life threatening, since one of the muscles it can paralyze is the diaphragm, the muscle that controls breathing.
What foods can cause botulism?
Home-canned vegetables that are not highly acidic (asparagus, green beans, peppers, beets and corn) are good incubators for botulism bacteria unless they are heat-treated appropriately to kill the spores during the canning process and eaten quickly after opening. The bacteria can release large quantities of toxin into the canned food jar, causing botulism symptoms in people who sample the produce. Home-canned, smoked or fermented fish is also a risk. Recent outbreaks have been reported from commercial carrot juice and home-canned bamboo shoots. In the United States, roughly 100 people become ill with botulism each year. About a quarter are due to consumption of contaminated food. Most cases today (about 70%) occur in infants. Babies less than 1 year old, especially those that are breast feeding, have a different intestinal system than adults. Spores swallowed by an adult with a mature digestive tract usually will remain in their hibernating, inactive state. But spores ingested by a young infant can reproduce and can form toxin that is absorbed into the bloodstream, causing botulism.
How long does it take for botulism to show up?
All of the symptoms of botulism are the result of nerve paralysis during exposure to the toxin. Symptoms usually begin within one to two days after eating contaminated food. Symptoms of infant botulism and wound botulism also appear suddenly.
How to diagnose botulism?
Botulism is uncommon enough that your doctor will consider other explanations for your symptoms. In most cases, several other tests will be ordered: 1 A brain scan, such as a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan, to check for other diagnoses such as stroke 2 Blood tests to check for Lyme disease 3 A lumbar puncture to help to distinguish botulism from a similar illness called Guillain-Barre syndrome 4 An electromyogram, a test of nerve and muscle function, to determine if the problem might be another muscle-weakening disease such as polymyositis or myasthenia gravis
What lab test is used to test for botulism?
If your doctor suspects botulism after asking you about your medical history and examining you, both blood and stool samples may be tested to check for the presence of botulinum toxin. Generally these tests are done in a government laboratory that specializes in detecting botulism. Sometimes botulism bacteria can be grown from a stool sample.
How long does it take to recover from botulism?
In severe cases, recovery from botulism can take weeks, or even months. The after-effects – which can include fatigue and shortness of breath – can last for years.
What is botulism?
Botulism is a serious, potentially fatal illness caused by a type of poison. The poison – known as botulinum toxin – is produced by a kind of bacteria. Botulinum toxin is the strongest poison known to science.
Why is botulism considered a possible terror weapon?
And people who develop botulism require prolonged, intensive care. A large outbreak of botulism would create a major disruption of normal activity.
When did botulism become a weapon?
Attempts to use botulism as a weapon go back at least to World War II. Since the 1970s, a number of nations have developed – or are believed to be developing – the capability to use botulism as a weapon. A Japanese religious cult tried to release botulism poison into the air at several locations in the Tokyo area, at least three times, between 1990 and 1995.
Can botulism be used as a weapon?
It is also believed that the botulism poison could be used as a weapon – by deliberately putting it in food, or by releasing it into the air, so people inhale it.
Can you get botulism from other people?
No. Again, botulism is a type of poison. It isn’t caused by a living organism, and it can’t be passed from one person to another.
How long does it take for a botulism to heal?
It turns out, herb-infused oil is one of the twelve foods, or more precisely, food groups, that can cause botulism, a rare, but life-threatening food-borne illness that causes paralysis and may take weeks, even months to recover.
What is botulism?
Botulism is a deadly food-borne disease caused by the bacterium C. botulinum. This rod-like bacteria lives in the soil and can be found in many plants and animals.
How many forms of botulism are there?
In addition to these, MedScape, which lists six forms of botulism, includes inhalational botulism and adult intestinal colonization botulism.
How many foods carry C. botulinum?
Reports from the FDA, as well as the CDC, name twelve foods, or food groups that may carry C. Botulinum to humans. They break it up into three foods for infants under one year, and nine that may pose a risk to all the rest of us.
Is botulism preventable?
But also, the Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), in “ Botulism prevention: Many cases of botulism are preventable “ , tells us that new sources of botulism poisoning are found nearly every decade.
Is C botulinum deadly?
While it is deadly, C. botulinum needs a specific environment to grow . We can lessen our chances of getting this disease if we remember these three facts.
Does C botulinum need oxygen?
Fortunately for humans, C. botulinum needs a near-oxygen-free environment to grow, and doesn’t like acid. Air and acids such as vinegar, lemon and lime juice help to keep us safe from food-borne botulism. That’s one reason people preserve foods by pickling them in vinegar.
