Chestnut Trees thrive in heat and humidity, making it the perfect tree to grow in Canada. The hotter, the better. Expect your chestnut tree to grow over 50 feet tall providing amazing shade for your yard. If you want to plant a tree that will produce food then planting a Chestnut Tree is a MUST!
How many species of chestnuts are native to Canada?
Of 10 known species, one, American chestnut (C. dentata), is indigenous to Canada. Chestnut (Castanea), genus of trees of beech family (Fagaceae). Of 10 known species, one, American chestnut (C. dentata), is indigenous to Canada.
Can I grow chestnut trees in my area?
As long as your soil drains well and is somewhat acidic (pH of 4.5 to 6.5), you may be able to grow chestnut trees. If you soil is clay, or if your land is low-lying, poor drainage may be a problem when growing chestnut trees. At their peak, American chestnut trees existed as far north as Maine and Southern Ontario, and as far south as Mississippi.
What kind of tree is a chestnut?
Chestnut (Castanea), genus of trees of beech family (Fagaceae). Of 10 known species, one, American chestnut (C. dentata), is indigenous to Canada. Chestnut (Castanea), genus of trees of beech family (Fagaceae). Of 10 known species, one, American chestnut (C. dentata), is indigenous to Canada.
Why is the chestnut tree so rare?
This species is now rare because of the chestnut blight. A hardiness zone is a geographically defined area where a given plant is capable of growing. Hardiness zones are based largely on climate, particularly minimum temperatures.
See more
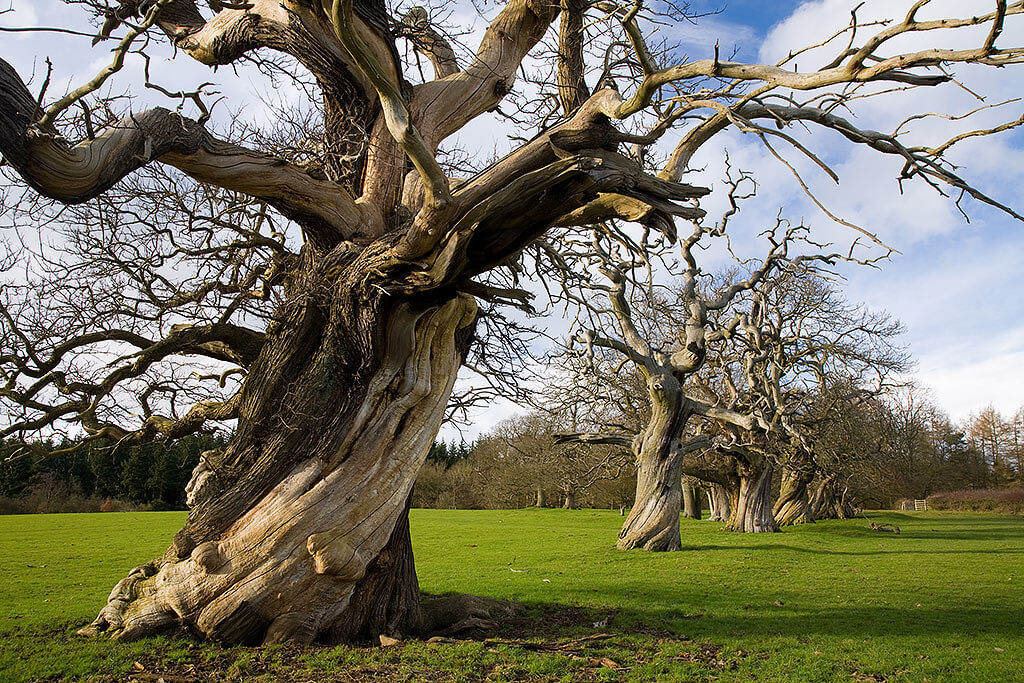

How far north can chestnut trees grow?
Chestnuts are a group of hardwood, deciduous trees, native to the temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere where they thrive in USDA Hardiness Zones 4 to 8, with some variation in range depending on the species.
Are all chestnuts Edible Canada?
A: Two different chestnut species grow here. One kind is edible, the other is poisonous. The toxic kind (the Horse Chestnut) is the one that is most frequently grown here and its very likely this is the one your mother picked.
Are there chestnut trees in Toronto?
Horsechestnut IN TORONTO Some of the horsechestnuts planted in Queen's Park at that time may still stand there today. Horsechestnut is a popular urban-tolerant ornamental tree that can live more than 100 years. Its large canopy requires considerable space, so it should only be planted in open, sunny sites.
Will chestnut trees grow in Alberta?
Horse chestnuts (Aesculus hippocastanum) will grow in the Edmonton area. I have seen specimens get as large as 10 metres high and four metres wide.
Are there American chestnut trees in Canada?
In Canada, the American Chestnut is restricted primarily to southwestern Ontario. Based on information available in 2004, it was estimated that there are 120 to 150 mature trees and 1,000 or more small, young trees in the province.
Do you need two chestnut trees to produce fruit?
Make sure you have enough space for at least two giant trees before committing to grow chestnuts. You'll also need to plan to have at least two chestnut trees planted within ~100 feet of each other (or less). This ensures that your chestnuts will be able to cross-pollinate in order to produce nuts.
Are chestnut trees protected in Ontario?
American Chestnut has been protected from being killed, harmed, harassed, captured or taken since 2008. In addition, the habitat of American Chestnut has been protected from being damaged or destroyed since 2013.
What is the difference between a chestnut tree and a horse chestnut tree?
while sweet chestnut trees grow in woods, forests or orchards; each horse chestnut leaf consists of several oval "leaflets", which give the whole leaf a palm-shaped appearance, whereas sweet chestnut leaves are simple and elongated without leaflets.
Why are chestnut trees extinct?
Mature American chestnuts have been virtually extinct for decades. The tree's demise started with something called ink disease in the early 1800s, which steadily killed chestnut in the southern portion of its range.
Are chestnut trees invasive?
Like many other invasive species (see our post on the Spotted Lantern Fly) the fungus was accidentally brought to the United States, probably through imported Asian Chestnut trees. Shortly after the fungi's arrival it spread rapidly, devastating billions of American chestnut trees.
Can chestnut trees grow in Manitoba?
They are noted for attracting pollinating insects such as bumble and honey bees. The Ohio buckeye and its sister tree, the European horse chestnut (which can also grow in warmer areas of Manitoba including Winnipeg), do have a feature that may not appeal to everyone.
What zones do chestnut trees grow in?
Chestnut trees are hardy to USDA zones 4-9, unless otherwise noted.
Are all chestnuts edible?
Edible chestnuts belong to the genus Castanea and are enclosed in sharp, spine-covered burs. The toxic, inedible horse chestnuts have a fleshy, bumpy husk with a wart-covered appearance. Both horse chestnut and edible chestnuts produce a brown nut, but edible chestnuts always have a tassel or point on the nut.
Are Vancouver chestnuts edible?
They are a beautiful, shiny brown nuts but inedible. However, there are in Vancouver a few Spanish Chestnut or Sweet Chestnut trees (Castanea saliva), the nuts of which are edible, and elderly Asian and European residents are quick to harvest them as they fall to the ground.
Do edible chestnuts grow in Ontario?
They are suited to the mild areas of zone 6 to 7 (close to Lakes Erie and Ontario) in Southwestern Ontario and the Niagara Peninsula. They are best grown on well drained sandy and light clay loams with a pH of 5 to 6. Generally, the peach soils are well suited to commercial chestnut orchards.
How do you identify a chestnut tree?
The American chestnut tree has recognizable long, pointed, lanceolate leaves with coarsely serrated margins and sharp, spiky burs that fall from the tree in late summer. You can identify American chestnuts in landscapes by their broad, spreading rounded crown, twigs with a reddish hue, and bumpy, ridged bark.
How Fast Do Chestnut Trees Grow?
Chinese chestnut trees can grow 1 to 2 feet per year, ultimately reaching a height of 40 to 60 feet tall at maturity.
How cold can chestnut trees withstand?
This means that they can withstand temperatures down to -5 degrees Fahrenheit (-20.6 degrees Celsius). Chestnut trees can withstand frost, and some varieties can withstand temperatures down to -10 degrees Fahrenheit or lower!
What Kind Of Soil Do Chestnut Trees Like?
According to the Chestnut Hill Tree Farm, chestnut trees prefer well-draining soil with a pH between 5.0 and 6.5. This means that sandy soil is ideal for growing chestnut trees, since it drains very well.
How Long Does It Take For A Chestnut Tree To Bear Fruit?
According to Chestnut Hill Tree Farm, a chestnut tree will bear fruit 3 to 5 years after planting.
What is the temperature of chestnut trees?
American chestnut trees are hardy to USDA Zone 3, down to -35 degrees Fahrenheit (-37.2 degrees Celsius). However, their lack of resistance to chestnut blight means that the disease will likely kill them instead of the cold.
What caused the decimation of chestnut trees?
According to the Michigan State University Extension, “This important tree for food and lumber was decimated by a fungal blight that was introduced into the New York area on imported chestnut trees around 1904. The chestnut blight fungus, Cryphonectria parasitica, quickly spread across the eastern half of the United States, killing more than three billion trees by the 1930s.”
Why is chestnut blight so bad?
Chestnut blight was caused by an Asian bark fungus, and the disease destroyed billions of American chestnut trees between 1904 and 1930.
What are chestnut trees?
Printer Friendly Version. Image by ribeiroantonio. Chestnut trees have been cultivated for their starchy nuts for thousands of years, at least since 2,000 BC. The nuts have been an important source of food for humans in the past , used to make flour as well as a substitute for potatoes.
How long do chestnut trees live?
Most chestnut tree types only begin to produce nuts after they are three to 7 years old. Still, keep in mind that some chestnut tree types can live up to 800 years. Printer Friendly Version.
What are the leaves of a chestnut tree?
The leaves are a fresh green, darker on the top than the bottom. They are oval or lance-shaped and edged by widely separated teeth. The flowers of the chestnut tree are long, drooping catkins that appear on the trees in spring. Each tree bears both male and female flowers, but they cannot self-pollinate.
How many types of chestnut trees are there?
Currently, nine different chestnut tree types grow in temperate areas around the world. All are deciduous trees belonging to the family Fagaceae, like oaks and beeches. If you are thinking of growing chestnut trees, read on for information about chestnut tree care.
What type of soil do chestnut trees need?
All chestnut tree types require well-drained soil to thrive. They can grow in partially clay soil if the land is on a slope, but they will grow best in deep, sandy soils. Be sure your soil is acidic before growing chestnut trees. If you aren’t sure, get the pH tested. You need a pH of between 4.5 and 6.5.
Can chestnut trees grow in deep soil?
If you read up on chestnut tree information, you’ll find that growing chestnut trees is not difficult if they are planted in an appropriate site. When planted on good, deep soil, the trees are very drought tolerant when established. Young seedlings require regular irrigation.
Is a chestnut tree edible?
Additionally, it is important to note that these are not the same trees as horse chestnuts ( Aesculus) – of which the nuts are not edible. The size of chestnut trees depends on the species, but, generally, chestnuts are big trees. The tallest species is the American chestnut that scrapes the sky at 100 feet (30+ m.).
When do chestnut trees start to grow?
Chestnuts usually begin to develop roots in early to mid February. If you want to give the tree a head start, you can plant the seed early indoors once these roots poke through. Poke a few drainage holes in the bottom of a half-gallon (2 L) cardboard milk carton. Cut the top off the carton, as well.
What kind of soil do chestnut trees like?
The best soil for chestnut trees be well-draining and slightly acidic. Chestnut trees thrive in deep, sandy loam soils. Soils that contain rocks and gravel are also acceptable. Avoid heavy clay soils. The only way a chestnut tree can survive in a clay soil is if it is planted at the top of a downward slope.
How long does it take for a chestnut tree to produce nuts?
Give the tree plenty of time. Chestnut trees don't produce any nuts during their first few years. If there is at least one other chestnut tree nearby and the trees remain healthy during these years, they should eventually produce nuts. Chinese chestnut trees usually produce nuts after five years.
How to get rid of a nutshell on a tree?
Twist off the old shell. Carefully remove the seedling from its container and find the old nutshell clinging to the roots. Use your fingers to gently twist or break it off without damaging the roots. Many animals will be attracted to the scent of the nutshell and may dig up you seedling trees looking for that shell.
What is the problem with chestnut weevils?
Protect the tree against insect pests, as well. There are several different insect pests that may attack your tree, but the biggest problem is usually the chestnut weevil. Adult weevils lay eggs in developing nuts. When the eggs hatch, the larvae consumes the meat inside of the nut.
Why plant two different chestnut varieties?
Plant two different chestnut varieties to promote cross-pollination.
How much space do chestnut trees need?
Give the tree plenty of space. Make sure that each chestnut tree you plant has 40 feet (12.2 m) (12 m) of free soil space in all directions to allow for adequate growing room.
Where do chestnut trees grow?
A chestnut is the edible nut of the chestnut fruit, produced by thechestnut tree (Castanea sativa, Castanea dentata, Castanea mollissima).Chestnuts are native to the Mediterranean areas of Europe, China, andNorth American continent. Unlike most nuts, chestnuts contain primarily sugars and starches instead of oils and fats, ...
How big do chestnut trees get?
Size. Chestnut trees vary in size from the very large American species that grow over 80' tall, to the mid-range European cultivars that reach around 65' in height, and the smaller Chinese species that top out around 40' at maturity.
How long does it take for chestnuts to ripen?
Chestnuts don’t ripen at the same time and chestnut harvest time can span as much as five weeks, although the nuts generally ripen in a 10 to 30 day span of time in mid-to-late summer. Allow the nuts to fall from the tree naturally. Avoid trying to pick the nuts; aside from the spines, the unripe nuts will not release easily, ...
What are the different types of chestnut trees?
Chestnut trees are usually divided into three different types: American, European, and Chinese . American chestnut trees tend to be the tallest with the sweetest nut meat, but tend to be vulnerable to chestnut blight and should be grown only in area that do not have chestnut blight (typically west of the Rocky Mountains).
Which is larger, Chinese or European chestnut?
European chestnuts are mid-sized trees with larger nuts and more disease resistance than American chestnuts. Chinese chestnuts are much smaller trees than either the European or American species, but produce large nuts and considerably more pollen making them valuable as pollenizer trees.
What is the best zone for chestnut trees?
Chestnut trees are hardy to USDA zones 4-9, unless otherwise noted. This rating tells you the minimum winter temperature the plants typically survive when properly hardened off. Make sure you consult the USDA Hardiness Maps website, which provides information on the average minimum winter temperature in your location, by zip code. Your USDA Plant Hardiness Zone does not reflect the many of the other factors in successfully growing apple trees, including length of growing season, rainfall amounts, soil quality, and chill hours. Consult your local extension service for more detailed information about your local growing region and the factors you will need to know when selecting fruit trees for your home orchard.
Why do nuts ripen in the sun?
Nut ripening and flavor development are also benefited by the carbohydrate production stimulated by the sun, as well as it’s heat.
Where was the Bent Creek Experimental Forest?
The study sites were along forested slopes in the Bent Creek Experimental Forest in the Southern Appalachian Mountains.
Do chestnuts have blight?
Like all pure American chestnuts, the seedlings are susceptible to blight, but before becoming infected can inform the researchers about how chestnut seedlings respond to different light conditions.
Is shelterwood part of the Forest Service?
The findings are timely, as the shelterwood regeneration treatment is part of the Forest Service’s national management plans for the southeastern United States.
Is chestnut blight resistant?
To date, chestnut restoration has mostly meant breeding blight -resistant trees. Now, thanks to collaboration between the U.S. Forest Service , The American Chestnut Foundation ...
What is the most common setback in chestnut growing?
In Pennsylvania and New Jersey, the most common setback in chestnut growing is browse by deer. In many areas of both states, es-pecially urban areas, deer populations are out of control.
Can you start chestnut seeds indoors?
Starting seeds indoors is a very reliable method of propagating chestnuts. It can be easier to protect your stock from would-be seed predators. Still, starting your chestnuts indoors carries with it its own pitfalls. Be sure to keep these things in mind when planting your seed inside.
