See more

How long can you live with cor pulmonale?
If a person does not seek treatment for cor pulmonale, it can be life threatening. The overall 5-year survival rate for cor pulmonale with COPD is around 50%.
Can you live with cor pulmonale?
For example, patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) who develop cor pulmonale have a 30% chance of surviving 5 years. However, whether cor pulmonale carries an independent prognostic value or is simply reflecting the severity of underlying COPD or other pulmonary disease is not clear.
What is the primary treatment for cor pulmonale?
Treatment strategies for cor pulmonale include supplemental oxygen, assisted mechanical ventilation, digoxin, and diuretics. Pulmonary vasodilator compounds should be used with caution because they can compromise gas exchange in cor pulmonale from secondary pulmonary hypertension.
Is cor pulmonale permanent?
Cor pulmonale is usually chronic but may be acute and reversible. Primary pulmonary hypertension. It has many secondary causes; some cases are idiopathic.
How common is cor pulmonale?
Cor pulmonale is estimated to account for 6% to 7% percent of all types of adult heart disease in the United States. The incidence of cor pulmonale is widely variant among countries. It depends on air pollution, the prevalence of cigarette smoking and other risk factors for various lung diseases.
What are common signs of cor pulmonale?
SymptomsFainting spells during activity.Chest discomfort, usually in the front of the chest.Chest pain.Swelling of the feet or ankles.Symptoms of lung disorders, such as wheezing or coughing or phlegm production.Bluish lips and fingers (cyanosis)
Is cor pulmonale the same as right-sided heart failure?
Right-sided heart failure is also known as cor pulmonale or pulmonary heart disease.
Can right-sided heart failure be reversed?
Treatment is directed at the cause of your heart failure, and not all causes of right-sided heart failure are curable. But you can treat heart failure and improve your symptoms. Often, a combination of lifestyle changes, medications and heart devices can help you manage heart failure and live an active life.
What can cause cor pulmonale?
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. It is the most common cause of cor pulmonale. It is often caused by smoking or being exposed to smoky or poorly ventilated environments. Its symptoms include wheezing, chest pain, trouble breathing, respiratory infections, lethargy, weight loss, and swelling of the lower limbs.
What is the difference between cor pulmonale and pulmonary hypertension?
In the case of primary pulmonary hypertension, this is due to disease of the pulmonary vasculature while cor pulmonale is related to diseases of the pulmonary vasculature, airways, or interstitium.
What happens when you have right-sided heart failure?
So when you have right-side heart failure, the right chamber has lost its ability to pump. That means your heart can't fill with enough blood, and the blood backs up into the veins. If this happens, your legs, ankles, and belly often swell.
What ECG finding is suggestive of cor pulmonale?
The S1Q3T3 sign (prominent S wave in lead I, Q wave and inverted T wave in lead III) is a sign of acute cor pulmonale (acute pressure and volume overload of the right ventricle because of pulmonary hypertension) and reflects right ventricular strain.
Is cor pulmonale the same as right sided heart failure?
Right-sided heart failure is also known as cor pulmonale or pulmonary heart disease.
What is cor pulmonale chronic?
Chronic cor pulmonale: key points Cor pulmonale can be defined as pulmonary arterial hypertension resulting from diseases affecting the structure and/or function of the lungs. Pulmonary hypertension results in right ventricular enlargement and may lead with time to right heart failure.
What are the risk factors of cor pulmonale?
Globally, the incidence of cor pulmonale is widely variable due to air pollution, tobacco use, and toxic exposure. An estimated 10–30% of heart failure admissions in the United States are the result of cor pulmonale, most commonly related to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
What is the difference between cor pulmonale and pulmonary hypertension?
In the case of primary pulmonary hypertension, this is due to disease of the pulmonary vasculature while cor pulmonale is related to diseases of the pulmonary vasculature, airways, or interstitium.
A.K.A. Right-Sided Heart Failure
Deborah Leader RN, PHN, is a registered nurse and medical writer who focuses on COPD.
Causes
This type of right-sided heart disease can develop slowly or suddenly, and it is always caused by lung disease. COPD is the most common cause of cor pulmonale, but there are others as well. 1 Often, cor pulmonale is more severe if you also have other types of heart disease, such as an arrhythmia or a history of a heart attack.
Symptoms
The early symptoms of cor pulmonale can go unnoticed because the causative lung disease also causes symptoms, and some effects may be similar. To make matters even more confusing, symptoms of cor pulmonale often develop as the underlying lung condition worsens. 2
Diagnosis
The diagnosis for cor pulmonale is usually made in the healthcare provider’s office. A physical exam typically picks up any abnormal heart sounds or rhythm, fluid retention, or protruding neck veins.
Treatment
Treatment for cor pulmonale is focused on addressing the underlying illness. There are also a few treatments that can alleviate some effects of heart failure.
Acute cor pulmonale
This condition develops suddenly and is most often caused by a massive pulmonary embolism. This occurs when part of a blood clot breaks away and travels to the lungs through the bloodstream. The clot can cause a blockage and damage the lungs.
Chronic cor pulmonale
This condition develops over time. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is the most common cause of chronic cor pulmonale. COPD is a chronic and progressively disabling disease that results in persistent respiratory symptoms. It is usually caused by significant exposure to noxious agents via breathing.
Causes
It is best to think of cor pulmonale as a response to another primary condition that can then cause other symptoms.
Testing and Diagnosis
Under normal conditions, the right side of the heart pumps in a more relaxed, low-pressure way at about one-tenth of the power that other parts of the systemic arteries.
Treatment
Usually, treatment for cor pulmonale aims to treat the primary condition that causes it.
What is cor pulmonale?
Cor pulmonale is a condition that occurs when the right ventricle of your heart cannot pump properly. The right side of your heart pumps blood from your body into your lungs to get oxygen. Cor pulmonale is caused by pulmonary hypertension (PH). PH is high blood pressure in the arteries of your lungs.
What increases my risk for cor pulmonale?
Acute lung diseases, such as acute respiratory distress syndrome or a blood clot in your lungs
How is cor pulmonale diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will ask about your symptoms and any health problems you have. He or she will listen to your heart and lungs. He or she will check for swelling in your abdomen, ankles, and feet. You may need any of the following tests:
How is cor pulmonale treated?
Diuretics are given to decrease excess fluid that collects in a part of your body, such as your legs. Diuretics can also remove excess fluid from around your heart or lungs and decrease your blood pressure. It is often called water pills. You will urinate more often when you take this medicine.
How can I manage my cor pulmonale?
Limit your liquids as directed. Ask your healthcare provider how much liquid you should drink each day. Too much liquid can increase your risk for swelling and make your cor pulmonale worse.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
Etiology of Cor Pulmonale
Acute cor pulmonale has few causes. Chronic cor pulmonale is usually caused by COPD Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is airflow limitation caused by an inflammatory response to inhaled toxins, often cigarette smoke. Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency and various occupational...
Symptoms and Signs of Cor Pulmonale
Initially, cor pulmonale is asymptomatic, although patients usually have significant symptoms (eg, dyspnea, exertional fatigue) due to the underlying lung disorder.
Diagnosis of Cor Pulmonale
Cor pulmonale should be suspected in all patients with one of its causes. Chest x-ray shows RV and proximal pulmonary artery enlargement with distal arterial attenuation. ECG evidence of RV hypertrophy (eg, right axis deviation, QR wave in lead V1, and dominant R wave in leads V1 to V3) correlates well with degree of pulmonary hypertension.
Treatment of Cor Pulmonale
Treatment is difficult; it focuses on the cause (see elsewhere in THE MANUAL), particularly alleviation or moderation of hypoxia. Early identification and treatment are important before structural changes become irreversible.
Key Points
Cor pulmonale is RV enlargement and eventually failure secondary to a lung disorder that causes pulmonary artery hypertension.
Drugs Mentioned In This Article
In temperate climates, which of the following is the most common infectious cause of dilated cardiomyopathy?
Merck and the Merck Manuals
Merck & Co., Inc., Kenilworth, NJ, USA is a global healthcare leader working to help the world be well. From developing new therapies that treat and prevent disease to helping people in need, we are committed to improving health and well-being around the world. The Merck Manual was first published in 1899 as a service to the community.
Group 2 PH
Group 2 PH is caused by conditions that affect the left side of the heart and carry over to the right side of the heart. This includes mitral valve disease and long-term systemic high blood pressure.
Group 3 PH
Group 3 PH is associated with certain lung and breathing conditions, including:
Group 4 PH
Blood clots in the lungs and other clotting disorders are associated with Group 4 PH.
Other medications and treatments
Other medications used to treat PH include digoxin (Lanoxin), which helps the heart pump stronger. Digoxin is also used in some to treat heart failure or other heart disease.
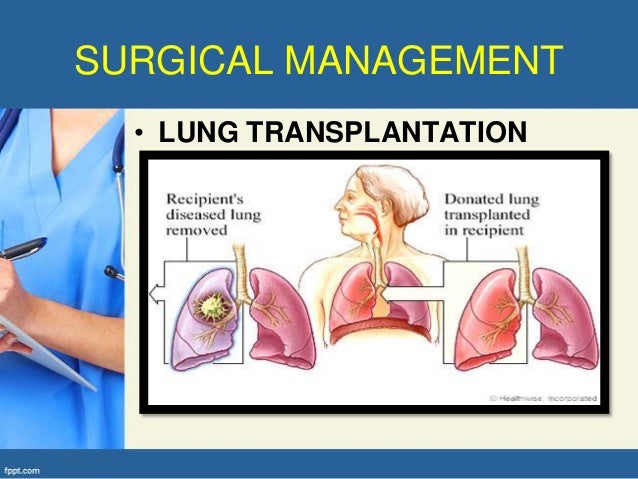
Transplantation
Lung or heart-lung transplantation is used for the most serious cases of PH. A lung transplant is performed on people who have severe PH and lung disease, but heart function is deemed adequate. A heart-lung transplant may be necessary if both the heart and lungs can no longer function well enough to keep you alive.