What are the colony characteristics of Escherichia coli on mannitol salt agar?
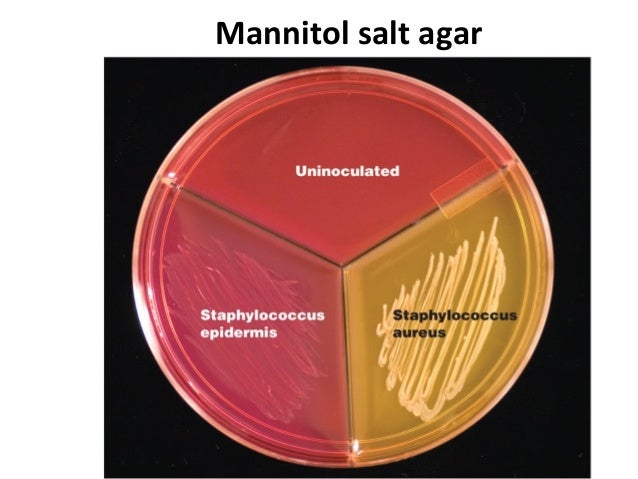
Expected colony characteristics of organism in Mannitol Salt Agar Escherichia coli: Does not grow Staphylococcus epidermidis: Colorless to pink colonies Staphylococcus aureus: Yellow colonies; may have yellow halo around colonies.
What does MSA plate test for mannitol?
Mannitol Salt Agar (MSA) Plate. Mannitol Salt Agar (MSA) is used to determine if the bacteria is halophilic (salt loving) and if the bacteria can ferment mannitol. If the bacteria is able to grow then it is a halophilic bacteria, due to it's ability to grow in a high salt environment. A positive result for mannitol fermentation would be...
What is the color of media around Staphylococcus aureus in MSA?
As MSA contains phenol red as a pH indicator, at pH levels below 6.9, the medium is a yellow color. But if coagulase-negative staphylococci (CONS) grows, they cant ferment mannitol, so the color of the media around the bacterial colony does not change to yellow, it appears pink.
Is Enterococcus faecalis salt tolerant?
Enterococcus faecalis and Enterococcus faecium (most common enterococcal species that has been isolated from human infections) are salt tolerant bacteria. They can ferment mannitol and produce lactic acid, producing yellow colored colonies on MSA.

Does E coli grow on MSA media?
Gram-negative bacteria like E. coli and P. aeriginosa are not tolerant to salt (not halophilic) and will not grow colonies on MSA (see quadrants II and IV).
What bacteria grows on MSA?
Mannitol Salt Agar (MSA) is used as a selective and differential medium for the isolation and identification of Staphylococcus aureus from clinical and non-clinical specimens.
What color is E coli on MSA?
Results on Mannitol Salt Agar (MSA)OrganismsResultsStaphylococcus aureusYellow colonies surrounded by the yellow zoneStaphylococcus epidermidisPink or Red coloniesMicrococciRed coloniesEscherichia coliNo growthJan 5, 2022
What can grow on MSA plate?
Mannitol Salt Agar (MSA) The high salt concentration (7.5%) is the selective ingredient. Staphylococcus species, which commonly inhabit human skin, can grow on this high salt concentration (left plate in picture below).
What bacteria Cannot Grow on mannitol salt agar?
Most non-pathogenic staphylococci will not ferment mannitol. The Staphylococcus aureus ferments mannitol and turns the medium yellow. The Serratia marcescens does not grow because of the high salt content.
Does Salmonella grow on mannitol salt agar?
Selective medium xylose lysine deoxycholate agar (XLD) and Mannitol salt agar were used for the identification of Salmonella sp. and S. aureus. Staphylococcus aureus produced yellow colonies with yellow zones on Mannitol salt agar.
What genus bacteria grows best on MSA?
Members of the genus Staphylococcus can tolerate high salt concentration (7.5%) and grow on mannitol salt agar.
Does E. coli grow on Mac?
Pink-red colonies: Pink-red colonies on MAC medium indicate the presence of lactose fermenting bacteria. Examples include Escherichia coli, Klebsiella spp, Citrobacter, Enterobacter, etc.
Which bacteria can ferment mannitol?
concluded that the most common mannitol-fermenting isolates were S. aureus (48.9%) followed by S. hemolyticus (46.2%), Staphylococcus simulans, and Staphylococcus warneri.
Will E coli grow on MacConkey agar?
Streak plate of Escherichia coli and Serratia marcescens on MacConkey agar. Both microorganisms grow on this selective media because they are gram-negative non-fastidious rods.
Can gram-negative bacteria grow on mannitol salt agar?
Principle of Mannitol Salt Agar. ◈ The selectivity of this medium is based on the presence of sodium chloride (7.5%) which inhibits most Gram negative and Gram positive bacteria.
What does growth on MSA indicate?
Mannitol Salt Agar (MSA) is used to determine if the bacteria is halophilic (salt loving) and if the bacteria can ferment mannitol. If the bacteria is able to grow then it is a halophilic bacteria, due to it's ability to grow in a high salt environment.
Can gram-negative bacteria grow on Mannitol Salt Agar?
Principle of Mannitol Salt Agar. ◈ The selectivity of this medium is based on the presence of sodium chloride (7.5%) which inhibits most Gram negative and Gram positive bacteria.
Does Streptococcus grow on MSA?
MSA contains a high concentration of salt (NaCl), and therefore, selects for the growth of microbes that can tolerate high salt concentrations. Staphylococcus species are halotolerant, whereas Streptococcus species and many other organisms are inhibited by high concentrations of NaCl.
Does Bacillus grow on MSA?
The large colonies at the center of the plate are Bacillus cereus. Although these organisms grow well on nutrient agar, they are not halophiles so will not grow on mannitol salt agar.
Does Pseudomonas grow on MSA?
Psuedomonas aeruginosa (Gram negative) - no growth Mannitol Salt Agar (MSA) is used to determine if the bacteria is halophilic (salt loving) and if the bacteria can ferment mannitol. If the bacteria is able to grow then it is a halophilic bacteria, due to it's ability to grow in a high salt environment.
What is the color of MSA?
As MSA contains phenol red as a pH indicator, at pH levels below 6.9, the medium is a yellow color. But if coagulase-negative staphylococci (CONS) grows, they cant ferment mannitol, so the color of the media around the bacterial colony does not change to yellow, it appears pink. So, MSA is also a differential medium.
Why is 7.5% sodium chloride used in MSA?
The incorporation of 7.5% sodium chloride in the medium helps to select only those bacteria which can tolerate high salt concentrations. MSA helps to demonstrate the ability of a bacterium to grow in a 7.5% salt environment (growth indicates tolerance for a high salt environment – no growth means intolerance).
What bacteria can ferment mannitol?
Enterococcus faecalis and Enterococcus faecium (the most common enterococcal species that has been isolated from human infections) are salt-tolerant bacteria. They can ferment mannitol and produce lactic acid, producing yellow-colored colonies on MSA. Catalase test can help to differentiate between Enterococcus (-ve) and Staphylococcus (+ve).
What is mannitol salt agar?
Mannitol salt agar (MSA) is a selective, differential, and indicator medium that is used to isolate and identify Staphylococcus aureus from the clinical specimen. As its name suggests mannitol salt agar (MSA) contains 1% mannitol (sugar), 7.5% salt, and agar as a solidifying agent.
What species of micrococcus is yellow?
Troubleshooting: When grown on mannitol salt agar some species of Micrococcus ( Micrococcus is a normal flora of human skin, mucosa, and oropharynx), such as M. luteus (yellow) can produce yellow colonies. M. roseus (red) produces pink colonies on MSA.
Can staphylococci tolerate salt?
Species of staphylococci are able to tolerate this salt concentration but other pathogenic bacteria may not. This concentration inhibits the growth of most other gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Thus MSA selectively isolates Staphylococcus spp i.e. selective media for Staphylococcus spp.
Does Escherichia coli grow?
Escherichia coli: Does not grow. Staphylococcus epidermidis: Colorless to pink colonies. Staphylococcus aureus: Yellow colonies; may have a yellow halo around colonies. Note: Do not perform coagulase test from the colonies isolated from mannitol salt agar.
