
Could gluten be ruining your skin?
Inflammation can show itself in a number of ways on the skin. A few examples of allergic response are acne, eczema, or dermatitis. Along with the skin allergy, people with gluten sensitivity may experience some of many digestive issues that prevent our body from absorbing essential nutrients.
What are bumps on skin that itch and spread?
Hives or urticaria is one of the skin conditions that may cause itchy bumps all over body. Hives is a sudden outbreak of swollen, pale red bumps on the skin. These bumps or plagues sometimes result from allergic reactions. This condition causes burn, sting and itchiness.
What causes gluten problems?
These include:
- Atypical serotonin levels. Serotonin is a neurotransmitter that allows cells to communicate. ...
- Gluten exorphins. These peptides are formed during the digestion of some of the gluten proteins. ...
- Changes in the gut microbiota. ...
What causes dark bumps on skin?
What Are Black Spots on Skin?
- Dark or black marks on the skin that are due to hyperpigmentation caused by melanin in the skin.
- Very dark skin growths that are usually harmless (like skin tags or normal moles) but can sometimes be the start of skin cancer.
- Clogged pores that turn black when the air oxidizes the sebum (oil the skin produces) plug in the pore.
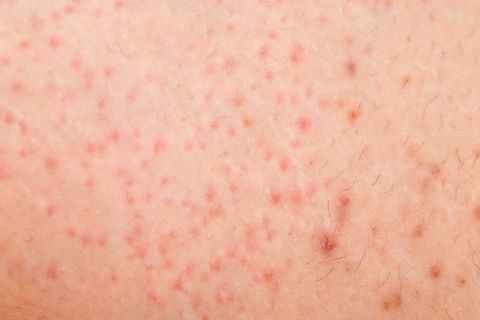
What does a rash from gluten look like?
What Does Gluten Rash Look Like? Dermatitis herpetiformis can occur anywhere on the body, but it is most commonly seen on the knees, elbows, buttocks, lower back, and the back of the neck. The rash typically takes the form of myriad tiny reddish-purple bumps that can take several days to heal.
Can gluten intolerance cause skin issues?
Gluten intolerance can also affect your skin. A blistering skin condition called dermatitis herpetiformis is one manifestation of celiac disease ( 9 ). Although everyone who has celiac disease is sensitive to gluten, some people with the condition do not experience digestive symptoms that indicate celiac disease (10).
How long do gluten bumps last?
Most people manage the condition with a gluten-free diet and with medications to treat the rash. If you rely on diet alone, it can take 6 to 24 months after removing gluten from your diet for the rash to disappear.
How do you get rid of gluten bumps?
Treatments for gluten rash typically involve removing gluten from your diet and taking antibiotics such as dapsone. Although dapsone can improve symptoms within a few hours, it may take several months for you to notice the effects of removing gluten from your diet.
What are the warning signs of gluten intolerance?
People may experience the following symptoms for several hours or days after they consume gluten:Abdominal pain.Anemia.Anxiety.Bloating or gas.Brain fog, or trouble concentrating.Depression.Diarrhea or constipation.Fatigue.More items...•
What are the first signs of being gluten intolerant?
Seven symptoms of a gluten intoleranceDiarrhea and constipation. Symptoms of gluten intolerance may include constipation, fatigue, headaches, and nausea. ... Bloating. Another very common symptom that people report in cases of gluten intolerance is bloating. ... Abdominal pain. ... Fatigue. ... Nausea. ... Headaches. ... Other symptoms.
What does gluten face look like?
A typical gluten face will present with red, puffy cheeks, with spots of hyperpigmentation around the chin. Some people will also have pimples spread out over the chin. Your face can also become bloated or swollen.
How long after cutting out gluten Will you notice a difference?
Many people report digestive symptom improvement within a few days of dropping gluten. Fatigue and brain fog often start getting better in the first week or two. This is a gradual process, though. Other symptoms, such as the itchy rash dermatitis herpetiformis , may take much longer to clear up.
How quickly will gluten affect you?
When patients are exposed to gluten, they show an immune reaction within two hours, more quickly than previously believed. Even the symptoms are different from what many expect.
Can eating gluten cause keratosis pilaris?
Keratosis Pilaris And Gluten There are no studies indicating a direct correlation between gluten and keratosis pilaris ( chicken skin). However, it can be caused by vitamin A deficiency or essential fatty acid deficiency, both of which can occur with gastrointestinal absorption problems.
What foods cause keratosis pilaris?
Can your diet cause keratosis pilaris? Despite what you might see on the internet, your diet does not cause keratosis pilaris. While doctors point to several reasons why someone might develop this skin condition, your diet is typically not one of them.
What does gluten face look like?
A typical gluten face will present with red, puffy cheeks, with spots of hyperpigmentation around the chin. Some people will also have pimples spread out over the chin. Your face can also become bloated or swollen.
What are the five common symptoms of gluten allergy?
According to the Celiac Disease Foundation, common symptoms of gluten intolerance may include:Constipation or diarrhea.Excessive bloating.Abdominal pain.Headaches.Bone or joint pain.Fatigue.Unexplained mood changes.“Brain fog,” or having trouble thinking clearly.
Does a gluten free diet improve skin?
Some people believe that eating gluten can inflame the skin and, therefore, cutting it out will help relieve red, inflamed skin or other skin conditions, such as psoriasis or eczema. But in reality, cutting gluten from your diet will only help if you actually have celiac disease or a hypersensitivity to gluten.
What part of the body does gluten sensitivity affect?
Celiac disease, sometimes called celiac sprue or gluten-sensitive enteropathy, is an immune reaction to eating gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley and rye. If you have celiac disease, eating gluten triggers an immune response in your small intestine.
What are the conditions that affect celiac disease?
Eczema. Alopecia Areata. Chronic Urticaria (Hives) Acne. Keratosis Pilaris. Dry Skin. Celiac disease and non-celiac gluten sensitivity can affect far more than just your digestive system—they also may affect your skin, in the form of several distinct skin conditions. Around 15% to 25% of people with celiac have dermatitis herpetiformis, ...
What percentage of people with celiac disease have dermatitis?
Around 15% to 25% of people with celiac have dermatitis herpetiformis, a rash considered the skin manifestation of celiac disease. 1 But this is by no means the only skin problem people with celiac disease and gluten sensitivity may have.
What is the condition where your hair falls out?
Alopecia Areata. This photo contains content that some people may find graphic or disturbing. DermNet / CC BY-NC-ND. Alopecia areata , an autoimmune condition in which your body attacks your hair follicles and causes your hair to fall out, also has been linked in research studies to celiac disease. 5 .
What is the purple rash on celiac?
Dermatitis herpetiformis, a rash that people with celiac get when they eat gluten, appears as tiny, reddish-purple bumps. As one outbreak heals, another might erupt, and severe rashes may include blisters. Purple marks could remain for weeks. 9 The extremely itchy outbreaks often appear on the elbows, knees, buttocks, back, and neck.
How long does it take for hives to disappear?
Once the children in the study were diagnosed with celiac disease and adopted the gluten-free diet, all saw their chronic urticaria disappear within five to 10 weeks. 6
Does psoriasis cause high levels of antibodies?
People with psoriasis often have high levels of antibodies to gluten circulating in their bloodstreams, which indicates that they're reacting to gluten in their diets even if they haven't been diagnosed with celiac disease.
Can celiac disease cause eczema?
Besides dermatitis herpetiformis, people with celiac disease may have eczema, psoriasis, acne, chronic dry skin, hives, and alopecia areata. For some reason, they affect those with celiac disease more often than the general population.
What other symptoms might occur with gluten rash?
Because a gluten rash can be a symptom of celiac disease, you might experience digestive symptoms along with the rash. These symptoms might include:
What are the risk factors for gluten rash?
Having an autoimmune disease increases your risk of other autoimmune diseases. People at risk for gluten rash include those with lupus, type 1 diabetes, thyroid disease, and Sjögren syndrome.
What are the potential complications of gluten rash?
When a gluten rash heals, it can leave behind scars or discolored skin. The celiac disease that may underlie a gluten rash can cause serious complications left untreated, including:
What causes a gluten rash on the back of the butt?
Intestinal cancers. Multiple sclerosis and other types of autoimmune disorders. Neurological conditions like migraine. Osteoporosis. Adults and children who develop a gluten rash on the elbows, knees, back, buttocks, or hairline should be evaluated promptly by a medical professional for diagnosis.
How long does it take for a gluten rash to subside?
Dapsone has a dramatic effect, relieving itching and preventing new lesions. However, it can take several months or longer for the rash to fully subside. Following a lifelong, gluten-free diet will prevent additional bouts of gluten rash.
What is gluten rash?
What is a gluten rash? The rash that most people call a “gluten allergy rash” or “gluten rash” is an autoimmune disorder, most closely associated with celiac disease. Gluten rash also is known as “dermatitis herpetiformis.”. It generally does not occur in conjunction with gluten intolerance or sensitivity, though a wheat allergy can cause ...
Why does gluten cause a rash?
Gluten rash is caused by an abnormal immune system response to consuming gluten, a protein found in wheat. A small percentage of people with celiac disease also develop a gluten rash, and it’s possible to have the skin rash without having the digestive symptoms of celiac disease (such as bloating and diarrhea ).
What skin conditions are related to gluten?
However, the most common skin problems diagnosed as directly related to gluten include dermatitis herpetiformis and Linear IgA disease.
What are the conditions that can be avoided in the first year of life?
A study published in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology in 1989 suggested that if a mother and her infant avoided all the most common allergens (including wheat) in the infant’s first year of life, skin conditions such as eczema, psoriasis and urticaria were far less likely to develop.
What vitamins are good for celiac disease?
Nutrients such as vitamin A, vitamin C, vitamin K and protein play a strong role in the health of your skin.
Can gluten cause skin inflammation?
All forms of untreated gluten intolerance involve increased pro-inflammatory cytokines in the blood. This trigger of systemic inflammation may also contribute to skin manifestation of gluten intolerance. When you combine poor nutrition with systemic inflammation, you open a pandora’s box of potential skin problems.
Is Dermatitis herpetiformis a celiac disease?
Dermatitis herpetiformis is almost always a skin manifestation of celiac disease, while Linear Iga disease is only rarely related to gluten. Sometimes the diagnosis of these two different conditions are confused, because the location of the skin biopsy can lead to misdiagnosis.
Does gluten cause dermatitis?
For example, dermatitis herpetiformis doesn’t occur immediately after consuming gluten. It occurs after gluten antibodies continue to course through your veins over time and attack skin cells. It also doesn’t occur if you held gluten against your skin. It happens when you ingest gluten.
Is gluten intolerance a skin condition?
Common Skin Conditions Related To Gluten Intolerance. Gluten intolerance is both closely related to certain skin conditions and loosely related to several different forms of rashes. However, the emphasis of this post is not on allergic reactions.
What is the most common rash associated with gluten intolerance?
The most common rash associated with gluten intolerance is dermatitis herpetiformis (also known as Duhring’s disease). Dermatitis herpetiformis manifests through pinkish to redish blisters that occur most often on the outside of joints (knees and elbows) and from the back of the neck down to the buttocks along the spine.
Why does my skin rash from gluten?
In addition, a gluten skin rash might be a manifestation of an allergy or an autoimmune response that involves some kind of gluten intolerance not diagnosed as celiac disease or a wheat allergy.
What is the term for a rash on the skin?
Eczema is a broad term applied to a broad range of dermatitis diagnoses. It may appear differently in different people, but symptoms often include blisters, cracking skin, patches of crusty, dry skin, itchy spots, pinkish skin blotches and skin edema (skin swelling). Urticaria is basically what most of us call hives.
What is a hive that is swollen and red?
Urticaria is basically what most of us call hives. It manifests itself as blotches of swollen, pale red and itchy raised bumps. Most cases of urticaria involve some kind of allergy, though some cases of chronic urticaria are either categorized as idiopathic (basically, the cause is unknown) or they have a correlation with an autoimmune disease (similar to how I described psoriasis above).
Why is it important to understand how an autoimmune disease is different from an allergy?
It isn’t that simple, and it is important to understand how an autoimmune disease is different from an allergy because you won’t always have an immediate reaction to something that your body treats as toxic.
Is Dermatitis herpetiformis linear IgA?
Dermatitis herpetiformis and linear IgA disease look and feel very similar, so accurate lab work is necessary to differentiate these two skin rashes.
Can you test for gluten allergy?
The appropriate gluten allergy tests should help you determine whether or not the rash you’ve developed was triggered by gluten. For more detailed information on the different types of tests, including the industry standards, read my article on gluten intolerance testing.
Does Gluten Cause Keratosis Pilaris (a.k.a. Chicken Skin)?
Chicken skin is a term commonly used for the skin condition keratosis pilaris. According to “Dr. Google,” this rash on the backs of arms, cheeks, and thighs is made worse by eating gluten. Can cutting gluten from the diet help? Is there truth to this claim, or is it another internet myth?
What causes keratosis pilaris?
Causes of Keratosis Pilaris. Although it is known to have a genetic factor, scientists do not know the true cause of keratosis pilaris. It is seen more commonly in inflammatory conditions such as asthma and allergies. It associated with dry skin, vitamin A and essential fatty acid deficiency.
Why does keratosis pilaris worsen in cold weather?
Keratosis pilaris occurs more often in people with eczema or dry skin and worsens in cold or dry weather. It is associated with other inflammatory conditions such as allergies and asthma.
What is the best treatment for keratosis pilaris?
Hydration of the skin is an important part of treatment for keratosis pilaris. Mild cases can be treated with over-the-counter lubricating creams. There is a laundry list of dermatologic therapies such as alpha-hydroxy creams, retinoic acid therapies, and steroids. Dermatologists may prescribe personalized therapies that can be formulated.
What is the best treatment for chicken skin rash?
The most common alternative treatment for a ” chicken skin rash ” are omega-3 fatty acids ( fish oil supplements). In addition to providing the essential fatty acids that may be lacking, these supplements also have a strong anti-inflammatory effect.
What foods can help with a rash?
Increasing essential fatty acid intake by consuming more coldwater fish such as sardines, mackerel, and salmon may lessen the rash. Walnuts are a great vegan source of essential fatty acids. There are many people who do say their rash is affected by other diet changes but no studies to back up those claims.
How to improve KP?
Lifestyle changes such as stress reduction, mindfulness techniques, and proper sleep hygiene might also improve KP by decreasing inflammation .
What is a canker sore?
Canker sores. One of the lesser known symptoms of Celiac Disease (and gluten sensitivity), canker sores are a sign that something is typically wrong . Several GI diseases are linked to this symptom (like Crohn’s and ulcerative colitis) along with autoimmune diseases too.
What is Prurigo Nodularis?
Prurigo nodularis is named for thickened, intensely itchy, crusted skin that has no current known cause. While you won’t find as much research on prurigo nodularis as eczema, there are case reports that connect prurigo nodularis to gut malabsorption.
What causes psoriasis to be gluten sensitive?
Triggers can include infections, Ibuprofen, genetics, stress, and even food like gluten. About 25% of people diagnosed with psoriasis also are gluten sensitive.
What is the name of the disease that causes hives?
Commonly known as hives, urticaria has links to both celiac disease and gluten.
Why do dermatologists use probiotics on rosacea?
As a result, some dermatologists are using probiotics applied directly to the skin in addition to those taken orally.
What are the risk factors for AD?
There are certain risk factors that may cause you to be more prone to develop AD such as a genetic SNP of filaggrin (which I discuss at length HERE) as well as gut infections and food sensitivities (most definitely including gluten).
How many people have psoriasis?
A truly frustrating chronic skin issue, over 7.5 million people have been diagnosed with some form of psoriasis. Patches of dead skin form due to excessive multiplication of skin cells typically on knees, elbows and even the scalp (though it is possible to develop it elsewhere such as your finger and toenails and even the inside of your mouth).

Epidemiology
Treatment
- Although there's currently little clear medical evidence that consuming gluten actually causes these skin conditions, in some cases people have found relief by following the gluten-free diet. If you have dermatitis herpetiformis, you're considered to also have celiac disease as long as your celiac blood tests also are positive. Although your physician can prescribe the medication dapso…
Signs and symptoms
- The skin conditions associated with celiac disease run the gamut from itchy rashes to hair loss, but most seem to be at least in part autoimmune or genetic in nature. Here's a summary of the most common skin conditions currently associated with celiac disease, plus links to additional information:
Symptoms
- Dermatitis herpetiformis, a skin rash caused by gluten consumption, is usually (but not always) one of the itchiest rashes you'll ever experience, and lesions can sting and burn as well as itch. Lesions can appear anywhere but occur most often on the elbows, knees, buttocks, lower back and the back of the neck and head.
Causes
- Several studies show that the skin condition psoriasis, which causes thick, scaly red plaques to develop on your skin, shares a strong link with gluten consumption. Psoriasis patients often have high levels of antibodies to gluten circulating in their bloodstreams, which indicates that they're reacting to gluten in their diets even if they haven't been diagnosed with celiac disease. It's not cl…
Overview
- Eczema, another itchy rash, causes scaly, whitish patches on your skin. Eczema occurs most often in children, but adults also can suffer from the skin condition. Although the primary treatment for eczema is topical corticosteroids, there's some evidence that for some people, eczema may be linked to celiac disease. For these people, a gluten-free diet may help to treat th…
Research
- Most of the research that shows a link between celiac disease and alopecia areata also reports that people with both celiac and alopecia areata found their hair grew back when they adopted a gluten-free diet. Still, some non-celiacs with alopecia areata also can experience seemingly random hair regrowth, as well.
Prognosis
- A 2005 study found that 5% of children with chronic urticaria (colloquially known as hives) also had celiac disease. Once the children in the study were diagnosed with celiac disease and adopted the gluten-free diet, all saw their chronic urticaria disappear within five to 10 weeks.
Prevention
- Again, while there's no research that links celiac with keratosis pilaris, a skin condition that causes tiny goosebump-like bumps to form, mainly on the backs of your upper arms, many people report that the condition disappears once they adopt a gluten-free diet. Keratosis pilaris is more common in those with eczema and seems to run in families.