
Is glycerol converted to pyruvate by E coli als929?
We report the conversion of glycerol to pyruvate by E. coli ALS929 containing knockouts in the genes encoding for phosphoenolpyruvate synthase, lactate dehydrogenase, pyruvate formate lyase, the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex, and pyruvate oxidase.
What is the yield of pyruvate from glycerol?
The presence of glucose significantly improved pyruvate productivity and yield from glycerol (0.72 g/g at 0.10 h (-1)). In fed-batch studies using exponential acetate/glucose-limited feeding at a constant growth rate of 0.10 h (-1), the final pyruvate concentration achieved was about 40 g/L in 36 h.
How do the substrates get converted to pyruvate in glucose synthesis?
The substrates get converted to pyruvate or other intermediates of the Citric acid cycle by various chemical reactions from which Gluconeogenesis begins. Which way does the process go if all the set of enzymes are same for both glucose synthesis and breakdown?
What are the precursors for glycerol 3-phosphate synthesis?
Glyceroneogenesis uses pyruvate, alanine, glutamine or any substances from the TCA cycle as precursors for glycerol 3-phosphate. Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPC-K), which is an enzyme that catalyzes the decarboxylation of oxaloacetate to phosphoenolpyruvate is the main regulator for this pathway.
Is glycerol a bioprocessing substrate?
Does E. coli produce pyruvate?
About this website
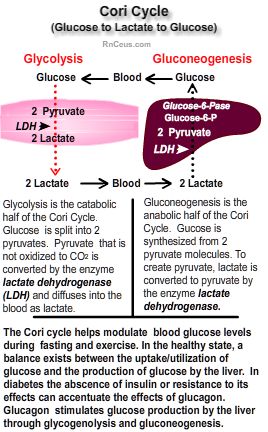
What can glycerol be converted into?
Glycerol can be converted to dihydroxyacetone phosphate that can be converted to glucose through the gluconeogenic pathway. Glycerol kinase converts glycerol to glycerol-3-phosphate that, in turn, can be converted to dihydroxyacetone phosphate by cytosolic (and/or mitochondrial) glycerol 3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
Can glycerol go into glycolysis?
In addition to its hepatic utilization for gluconeogenesis, in most tissues glycerol can be easily converted again to glycerol-3-P by glycerol kinases, to be used in the synthesis of acyl-glycerols. Glycerol is also a good substrate for energy, since it can be rapidly incorporated into the glycolytic pathway22.
Can glycerol be converted to ATP?
Lipid Metabolism in Plants Under High Temperature Thus a total of 2+4+15=21 ATPs are produced per glycerol molecule oxidized. However, there is consumption of one ATP molecule in the glycerol kinase catalyzed reaction. Therefore, the net gain is 21–1=20 ATPs per glycerol molecule oxidized.
How can a glycerol molecule enter the glycolysis pathway?
This process, called lipolysis, takes place in the cytoplasm. The resulting fatty acids are oxidized by β-oxidation into acetyl CoA, which is used by the Krebs cycle. The glycerol that is released from triglycerides after lipolysis directly enters the glycolysis pathway as DHAP.
Can glycerol be used in gluconeogenesis?
The major substrates of gluconeogenesis are lactate, glycerol, and glucogenic amino acids.
How is ATP formed from glycerol?
Glycerol. The anaerobic reactions of glycolysis accept glycerol as 3-phosphoglyceraldehyde, which then degrades to pyruvate to form ATP by substrate-level phosphorylation. Hydrogen atoms pass to NAD+, and the Krebs cycle oxidizes pyruvate.
Can glycerol be oxidized?
The glycerol partial oxidation in the liquid phase can lead to various products such as aldehydes (glyceraldehyde), ketones (dihydroxyacetone), and carboxylic acids (glyceric acid, tartronic acid, glycolic acid, etc.)
Can pyruvate be converted to glucose?
The process that coverts pyruvate into glucose is called gluconeogenesis. Another way organisms derive glucose is from energy stores like glycogen and starch.
What is the ATP yield for the conversion of glycerol to pyruvate?
two ATPsThis conversion of glycerol into pyruvic acid, which takes place in cytoplasm, yields two ATPs by substrate-level phosphorylation and two NADH which on reoxidation by terminal electron-transport chain via the external NADH dehydrogenase (located on the outer surface of the inner mitochondrial membrane in plants) ...
What is glycerol converted to in respiration?
Glycerol can be converted to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate, an intermediate of glycolysis, and continue through the remainder of the cellular respiration breakdown pathway. Fatty acids, on the other hand, must be broken down in a process called beta-oxidation, which takes place in the matrix of the mitochondria.
What is glycerol metabolism?
Glycerol is a major link between sugar and fatty acid metabolism (see Fig. 1). By reducing dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP, a key triose in glucose metabolism and energy generation) into glycerol-3-phosphate, it can be removed from glycolysis and used for lipid synthesis.
Can free fatty acids be converted to glucose?
Fatty acids and ketogenic amino acids cannot be used to synthesize glucose. The transition reaction is a one-way reaction, meaning that acetyl-CoA cannot be converted back to pyruvate. As a result, fatty acids can't be used to synthesize glucose, because beta-oxidation produces acetyl-CoA.
How does glycerol become glucose?
Glycerol derived from triacylglycerol in adipose tissue, and taken up by the liver is also converted to glucose via gluconeogenesis.
Is glycerol is a glycolysis intermediate?
The glycerol molecule can be converted to dihydroxyacetone phosphate (which is a glycolytic intermediate) during its metabolism. The first step is the conversion of glycerol to glycerol-3-phosphate by the enzyme glycerol kinase.
What happens to glycerol in metabolism?
Serum glycerol is mainly metabolized by the liver and kidneys. During the process glycerol kinase (GK) catalyzes glycerol into G3P, which can be used for lipid synthesis or enters glycolytic pathway after being oxidized into DHAP by FAD-dependent GPDH.
How can glycerol and fatty acids enter the citric acid cycle?
Through the process of phosphorylation, glycerol can be converted to glycerol-3-phosphate during the glycolytic pathway. When fatty acids are broken down into acetyl groups through beta-oxidation, the acetyl groups are used by CoA to form acetyl-CoA, which enters the citric acid cycle to produce ATP.
What is the process of converting glucose into glucose?
This process is called gluconeogenesis, and there are multiple pathways the body can use to achieve this conversion. Gluconeogenesis generally occurs only when the body cannot produce sufficient glucose from carbohydrates, such as during starvation or on a low-carbohydrate diet.
Which hormones control glycogenolysis?
Two hormones which control glycogenolysis are a peptide, glucagon from the pancreas and epinephrine from the adrenal glands. Glucagon is released from the pancreas in response to low blood glucose and epinephrine is released in response to a threat or stress.
What is the mechanism of glucose metabolism?
Gluconeogenesis is one of several main mechanisms used by humans and many other animals to maintain blood glucose levels, avoiding low levels (hypoglycemia). Other means include the degradation of glycogen (glycogenolysis) [1] and fatty acid catabolism.
How does fat become glycogen?
The amount of fat in the average diet and the amount of stored fat in the average body make the notion of converting that fat into usable energy appealing. Glycogen, a form of energy stored in muscles for quick use, is what the body draws on first to perform movements, and higher glycogen levels result in higher usable energy. It is not possible for fats to be converted directly into glycogen because they are not made up glucose, but it is possible for fats to be indirectly broken down into glucose, which can be used to create glycogen. Relationship Between Fats and Glycogen Fats are a nutrient found in food and a compound used for long-term energy storage in the body, while glycogen is a chain of glucose molecules created by the body from glucose for short-term energy storage and utilization. Dietary fats are used for a number of functions in the body, including maintaining cell membranes, but they are not used primarily as a source of fast energy. Instead, for energy the body relies mostly on carbohydrates, which are converted into glucose that is then used to form glycogen. Turning Fats Into Glucose Excess glucose in the body is converted into stored fat under certain conditions, so it seems logical that glucose could be derived from fats. This process is called gluconeogenesis, and there are multiple pathways the body can use to achieve this conversion. Gluconeogenesis generally occurs only when the body cannot produce sufficient glucose from carbohydrates, such as during starvation or on a low-carbohydrate diet. This is less efficient than producing glucose through the metabolizing of carbohydrates, but it is possible under the right conditions. Turning Glucose Into Glycogen Once glucose has been obtained from fats, your body easily converts it into glycogen. In gl Continue reading >>
How do plants use energy in their metabolism?
Metabolism: Transformations and Interactions Chemical Reactions in the Body Plants use the sun’s energy to make carbohydrate from carbon dioxide and water. This is called photosynthesis. Humans and animals eat the plants and use the carbohydrate as fuel for their bodies. During digestion, the energy-yielding nutrients are broken down to monosaccharides, fatty acids, glycerol, and amino acids. After absorption, enzymes and coenzymes can build more complex compounds. In metabolism they are broken down further into energy (ATP), water and carbon dioxide. Chemical Reactions in the Body Metabolic reactions take place inside of cells, especially liver cells. Anabolism is the building up of body compounds and requires energy. Catabolism is the breakdown of body compounds and releases energy. Chemical Reactions in the Body Enzymes and coenzymes are helpers in reactions. Enzymes are protein catalysts that cause chemical reactions. Coenzymes are organic molecules that function as enzyme helpers. Cofactors are organic or inorganic substances that facilitate enzyme action. Breaking Down Nutrients for Energy The breakdown of glucose to energy starts with glycolysis to pyruvate. Pyruvate may be converted to lactic acid anaerobically (without oxygen) and acetyl CoA aerobically (with oxygen). Eventually, all energy-yielding nutrients enter the TCA cycle or tricarboxylic acid cycle (or Kreb’s cycle) and the electron transport chain. Breaking Down Nutrients for Energy Glucose Glucose-to-pyruvate is called glycolysis or glucose splitting. Pyruvate’s Options Anaerobic – lactic acid Aerobic – acetyl CoA Pyruvate-to-Lactate Oxygen is not available or cells lack sufficient mitochondria Lactate is formed when hydrogen is added to pyruvate. Liver cells recycle Continue reading >>
What is the pathway that produces glucose?
Glucone ogenesis. Not to be confused with Glycogenesis or Glyceroneogenesis. Simplified Gluconeogenesis Pathway Gluconeogenesis ( GNG) is a metabolic pathway that results in the generation of glucose from certain non-carbohydrate carbon substrates.
How does the body get energy from fat?
Your body is an amazing machine that is able to extract energy from just about anything you eat. While glucose is your body's preferred energy source, you can't convert fat into glucose for energy; instead, fatty acids or ketones are used to supply your body with energy from fat. Video of the Day Fat is a concentrated source of energy, and it generally supplies about half the energy you burn daily. During digestion and metabolism, the fat in the food you eat is broken down into fatty acids and glycerol, which are emulsified and absorbed into your blood stream. While some tissues -- including your muscles -- can use fatty acids for energy, your brain can't convert fatty acids to fuel. If you eat more fat than your body needs, the extra is stored in fat cells for later use. Fat has more than twice as many calories per gram as carbs and protein, which makes it an efficient form of stored energy. It would take more than 20 pounds of glycogen -- a type of carbohydrate used for fuel -- to store the same amount of energy in just 10 pounds of fat. Your Body Makes Glucose From Carbs Almost all the glucose in your body originated from carbohydrates, which come from the fruit, vegetables, grains and milk in your diet. When you eat these carb-containing foods, your digestive system breaks them down into glucose, which is then used for energy by your cells. Any excess glucose is converted into glycogen, then stored in your muscles and liver for later use. Once you can't store any more glucose or glycogen, your body stores any leftover carbs as fat. Glucose is your brain's preferred source of energy. However, when glucose is in short supply, your brain can use ketones -- which are derived from fat -- for fuel. Since your brain accounts for approximately one-fifth of your daily calori Continue reading >>
Is glycerol a bioprocessing substrate?
There is increasing interest in the use of glycerol as a substrate for bioprocesses, primarily because of the increasing availability of crude material from biodiesel production [ 1 ]. Crude glycerol might be directly suitable as a microbial feedstock, particularly for the production of low-value commodity chemicals such as succinic acid, ethanol, and propionic acid [ 1 ]. One challenge in the use of this substrate, however, lies in its lower energy value compared with glucose and other 6-carbon carbohydrates. Although glycerol generates as much adenosine triphosphate (ATP) as glucose per mole of pyruvate formed, more ATP is required for the biochemical formation from glycerol of several precursor molecules needed for biomass, including glucose 6-phosphate, fructose 6-phosphate, ribose 5-phosphate, and erythrose 4-phosphate. Therefore, compared with glucose, use of glycerol as a sole carbon source would be expected to result in a lower yield of pyruvate and pyruvate-derived biochemicals. One means to redirect glycerol to the desired product would be to supply a limiting amount of an energy-rich substrate, ideally one which would also generate some of the needed precursor molecules, such as glucose itself.
Does E. coli produce pyruvate?
Escherichia coli containing the key gene mutations aceEF, ldhA, pfl, poxB, and pps accumulates pyruvate under aerobic conditions in a glucose and acetate medium [ 8 ]. By virtue of these mutations, the strain is unable to generate acetyl CoA from glycerol or glucose and has an absolute growth requirement for a secondary substrate which can generate acetyl CoA such as acetate (Fig. 1 ). However, acetate limitation forces a high rate of glycolysis and therefore pyruvate formation [ 9 ]. Glycerol should also serve as a biochemical source for pyruvate, and therefore we were interested in determining the rate of pyruvate formation from this substrate. Chemostats with E. coli ALS929 were used to compare dilution rates (i.e., growth rates).

Overview
Metabolic pathway
The main precursors of glyceroneogenesis are pyruvate, lactate, glutamine, and alanine. Glyceroneogenesis is also known as branched pathway of gluconeogenesis because the first few steps in glyceroneogenesis are exactly the same as gluconeogenesis (Figure 3).
When pyruvate or lactate is used as the precursor for glycerol 3-phosphate, gly…
Summary
In mammals, triglycerol or its backbone, glycerol 3- phosphate, is usually synthesized from glucose through glycolysis. Glucose will be degraded though glycolysis until fructose 1,6-bisphosphate is broken down to glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate and dihydroxyacetone phosphate. Dihydroxyacetone phosphate is significant in synthesizing triglycerides because it can be used to generate glycerol 3-phosphate. However, glycerol 3-phosphate is generated through a different p…
Regulation
Glyceroneogenesis can be regulated at two reaction pathways. First of all, it can be regulated at the decarboxylation of oxaloacetate to phosphoenolpyruvate. Secondly, TCA cycle can affect glyceroneogenesis when the glutamate or substrates in TCA cycle are being used as a precursor. Decarboxylation of oxaloacetate to phosphoenolpyruvate is catalysed by enzyme PEPC-K. PEPC-…
Location
Since glyceroneogenesis is related to lipid regulation, it can be found in adipose tissue and liver. In adipose tissue, glyceroneogenesis restrains the release of free fatty acids by re-esterifying them and in liver, triglycerides are being synthesized for lipid distribution.
White adipose tissue, also known as white fat, is one of the 2 types of adipose …
Disease
Failure in regulating glyceroneogenesis may lead to Type 2 diabetes. Type 2 diabetes is a metabolic disorder that results in high levels of blood glucose and blood lipid. Type2 diabetes is associated with over production of triglycerides in liver due to excessively active glyceroneogenesis and excess release of fatty acids from adipose tissues. Since the activity of glyceroneogenesis is mostly …
See also
• Gluconeogenesis
• Glycolysis
• TCA cycle
• Norepinephrine
• Glucocorticoid