How do you treat hemoglobinopathies?
Supportive, rather than curative, treatment consists of periodic blood transfusions for life, combined with iron chelation. Drugs to treat the symptoms of sickle-cell disease include analgesics, antibiotics, ACE inhibitors and hydroxyurea. Blood transfusions should be given only when strictly indicated.
Is hemoglobinopathies a disease?
The hemoglobinopathies are a group of disorders passed down through families (inherited) in which there is abnormal production or structure of the hemoglobin molecule. Sickle cell disease (SCD) is one such blood disorder caused by the abnormal hemoglobin that damages and deforms red blood cells.
What are the causes of hemoglobinopathies?
The term hemoglobinopathy refers to a number of inherited disorders that result from mutations in the globin (alpha, beta, or gamma) genes. These mutations result in either reduced production or altered structure of the hemoglobin (Hb) molecule.
What is gene therapy for hemoglobinopathies?
Gene therapy for hemoglobinopathies is currently based on transplantation of autologous hematopoietic stem cells genetically modified with a lentiviral vector expressing a globin gene under the control of globin transcriptional regulatory elements.
How are hemoglobinopathies inherited?
Hemoglobinopathy is the medical term for a group of inherited blood disorders and diseases that primarily affect red blood cells. They are single-gene disorders and, in most cases, they are inherited as autosomal co-dominant traits....HemoglobinopathySpecialtyHematology3 more rows
How do you test for hemoglobinopathies?
A hemoglobinopathy evaluation typically involves tests that determine the types and amounts of hemoglobin. Information from these tests, along with results from routine tests such as a complete blood count (CBC) and blood smear, aid in establishing a diagnosis.
What are examples of hemoglobinopathies?
Hemoglobinopathy is a group of disorders in which there is abnormal production or structure of the hemoglobin molecule. It is passed down through families (inherited). This group of disorders includes hemoglobin C disease, hemoglobin S-C disease, sickle cell anemia, and thalassemias.
Can drinking too much water lower hemoglobin?
In this study, we found that water intake may improve anemia by increasing the hemoglobin index. In the experimental group, the increase in hemoglobin was not significant, although there were significant increases in MCH and MCHC, indicating that water assists hemoglobin synthesis.
What is Haemoglobinopathy blood test?
A haemoglobinopathy evaluation is used to detect abnormal forms and/or relative amounts of haemoglobin, the protein found in all red blood cells that transports oxygen. Testing may be used for: Screening. All newborns are screened for certain hemoglobin variants.
What is the most common Hemoglobinopathy?
Sickle cell disease, the most common hemoglobinopathy, occurs when at least one HbS variant is present with a second pathogenic beta globin variant; the variants result in abnormal Hb. For more information on pathogenic Hb variants, see the Human Hemoglobin Variants and Thalassemias database.
When was gene therapy for hemoglobinopathies?
In June 2007, the first successful gene therapy for a transfusion-dependent hemoglobin (Hb) βEβ0-thalassemia was done using an SIN LV-based βT87Q vector. A transduction efficiency of about 30% was reported.
What do you know about gene therapy?
Gene therapy is a technique that modifies a person's genes to treat or cure disease. Gene therapies can work by several mechanisms: Replacing a disease-causing gene with a healthy copy of the gene. Inactivating a disease-causing gene that is not functioning properly.
What does Haemoglobinopathy mean?
2. Haemoglobinopathies: an overview. Haemoglobinopathies are a group of recessively inherited genetic conditions affecting the haemoglobin component of blood. They are caused by a genetic change (mutation) in the haemoglobin [footnote 2] [footnote 3].
Is sickle cell disease hemoglobinopathy?
Sickle cell disease (SCD) is the most common inherited hemoglobinopathy worldwide. It results from a single-nucleotide substitution that leads to a propensity toward hemoglobin polymerization and sickling of red blood cells.
What blood disorders are hemoglobinopathies?
Hemoglobinopathy is a group of disorders in which there is abnormal production or structure of the hemoglobin molecule. It is passed down through families (inherited). This group of disorders includes hemoglobin C disease, hemoglobin S-C disease, sickle cell anemia, and thalassemias.
What are the most common hemoglobinopathies?
Sickle cell disease and beta thalassemia major are two common hemoglobinopathies worldwide.
What is haemoglobinopathy?
Haemoglobinopathy is a clinical term that describes a group of blood disorders that affect red blood cells. Blood cells contain haemoglobin, a protein that carries oxygen around the body and removes carbon dioxide.
Prognosis of the condition
At present, there is no cure for haemoglobinopathies. However, there are treatments that can relieve symptoms.
Symptoms of haemoglobinopathy
In very serious cases of a haemoglobinopathy, patients may experience the following symptoms:
Medical tests to diagnose haemoglobinopathy
After an abnormal result from a blood smear or complete blood count, a specialist may recommend a haemoglobinopathy evaluation. In this evaluation, a pathologist who has expertise in haematology, examines the results of several tests.
What are the causes?
Haemoglobinopathies are almost always genetically inherited. Many blood-affecting genetic mutations can cause different types of haemoglobinopathy.
Can it be prevented?
As it is genetically inherited, it cannot be prevented. The risk of a child inheriting the condition can be predicted by evaluating with genes the parents carry.
Treatments for haemoglobinopathy
Patients with haemoglobinopathies should receive regular specialist reviews and care. Treatment options and recommendations differ between types of condition.
Are you sure your patient has a hemoglobinopathy? What are the typical findings for this disease?
The term hemoglobinopathy refers to a number of inherited disorders that result from mutations in the globin (alpha, beta, or gamma) genes. These mutations result in either reduced production or altered structure of the hemoglobin (Hb) molecule.
What caused this disease to develop at this time?
Neonates produce mostly Hb F (composed of two alpha and two gamma globin molecules) rather than the adult form of Hb (composed of two alpha and two beta globin chains).
What laboratory studies should you request to help confirm the diagnosis? How should you interpret the results?
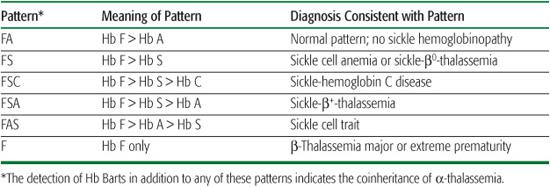
Mild anemia and microcytosis are seen when three alpha genes are missing and the mean corpuscular Hb is also reduced. Red blood cell morphologic analysis shows anisocytosis and hypochromia. The CBC may be normal in the neonatal period of show mild microcytosis with or without mild anemia when two alpha genes are missing (alpha-thalassemia trait).
Would imaging studies be helpful? If so, which ones?
Imaging studies are generally not helpful. Chest radiography and echocardiography may be used in the evaluation of a cyanotic infant to assess for cardiopulmonary disease.
If you are able to confirm that the patient has a hemoglobinopathy, what treatment should be initiated?
For sickle cell disease, penicillin prophylaxis (125 mg orally twice daily) should be initiated by the time the infant is 2-3 months old. The child should be referred to a sickle cell program if available.
What are the adverse effects associated with each treatment option?
Transfusion therapy carries the risk of infectious disease transmission, transfusion reactions, and fluid overload. The development of red blood cell alloantibodies are uncommon in the neonate. Repeated transfusions can lead to the development of iron overload over many years.
What are the possible outcomes of hemoglobinopathies?
Families can be reassured that cyanosis or hemolysis related to gamma globin gene mutations will resolve over the first couple of months of life.
Follow-Up Testing
Your baby’s doctor may ask you if your baby is showing any of the signs of a hemoglobinopathy (see Early Signs below). If your baby has certain signs, your baby’s doctor may need to treat him or her immediately.
About Hemoglobinopathies
The severity of conditions classified as “various other hemoglobinopathies” varies. Some children experience severe signs while others have no signs of the condition at all.
Support for Hemoglobinopathies
Support groups can help connect families who have a child or other family member affected with a hemoglobinopathy with a supportive community of people who have experience and expertise in living with the condition. These organizations offer resources for families, affected individuals, health care providers, and advocates.
ACT Sheets
Describes the short term actions a health professional should do following an abnormal newborn screen. This includes ordering confirmatory testing and communicating with the family about appropriate steps in the follow-up of the infant that has screened positive.
Slide 1
Hello, my name is Trefor Higgins. I am the Director of Clinical Chemistry at DynaLIFEDx, a large reference laboratory located in Edmonton, Alberta, Canada. I am also a Clinical professor at the University of Alberta in Edmonton. Welcome to this Pearl of Laboratory Medicine on “Hemoglobinopathies.”
Slide 2
Hemoglobin consists of 2 α and 2 non α globin chains forming a shell around a heme molecule. In the most common hemoglobin, Hb A, the globin chains are α and β, and forms about 80-90% of the total hemoglobin.
Slide 3
The majority of hemoglobinopathies arise from changes in the amino acid sequence of the either the α or β globin chains or both. This change in amino acid sequence may be due to the removal, addition, or substitution of a different amino acid, or a combination of these.
Slide 4
To date, over 1000 hemoglobinopathies have been found but fortunately, only a few have clinical significance.
Slide 5
There are 4 globin genes that are involved in the production of alpha chains. When one of these becomes mutated, a hemoglobinopathy is produced which usually forms 25% or less of the total hemoglobin. Hb G Philadelphia, found in blacks, is an example of an alpha chain variant.
Slide 6
Complex hemoglobinopathies arise when there is a thalassemia alongside the hemoglobinopathy or there are changes in both the alpha and beta chains. In blacks, the combination of the alpha chain Hb G Philadelphia with the beta chain Hb S is not uncommon.
Slide 7
Hemoglobinopathies are found in the quantitation of Hb A1c by HPLC or capillary electrophoresis or as part of a clinical investigation as to the reason for sickle, boat, or target cells in the peripheral blood film. A hemoglobinopathy investigation may be initiated in the presence of unexplained microcytosis in an iron replete person.
Cure versus remission
A cure means that the cancer has gone away with treatment, no more treatment is needed, and the cancer is not expected to come back. It’s rare that a doctor can be sure that cancer will never come back. In most cases it takes time to know if the cancer might come back.
What do survival statistics mean?
When told they have cancer, many people ask their doctor what their chance of survival is. While there are many factors that go into an answer, there are statistics that may help. Statistics are numbers that describe what happens to large groups of people with the same diagnosis.
What does it mean to be a cancer survivor?
There is more than one definition of cancer survivor. Some people use this term to refer to anyone who has ever been diagnosed with cancer. This is what the American Cancer Society means when we talk about survivorship or living as a cancer survivor.
What is Various other hemoglobinopathies
Hemoglobinopathies are a group of inherited (genetic) conditions that affect the hemoglobin in blood. Hemoglobin is a part of your red blood cells, which carry oxygen in your body.
Newborn Screening and Follow-Up
Newborn screening for hemoglobinopathies is done using a small amount of blood collected from your baby’s heel. To learn more about this process, visit the Blood Spot Screening page.
Condition Details
Newborn screening helps babies lead healthier lives. If your baby has an out-of-range result, follow up with your health care provider quickly. It is important to follow their instructions. Your baby may need to get treatment right away, even if they are not showing signs or symptoms.
Treatment and Management
It is important to talk to your health care provider about which treatment (s) are best for your baby. The goal of treatment is to prevent the health problems caused by this condition.
