
What is the most common cause of obstructive jaundice?
Obstructive jaundice may be due to a number of causes, all of which narrow or block the bile ducts in some way: Gallstones. Pancreatic cancer, when it occurs near the tube connecting the pancreas to the intestines. Swelling of lymph glands near the bile duct.
Does hepatitis cause obstruction?
Mechanical or intrahepatic causes are most commonly hepatitis and cirrhosis. Drugs may also cause direct damage to hepatocytes and metabolic obstruction. Note the following: Hepatitis is inflammation of the liver characterized by diffuse or patchy necrosis.
What type of jaundice can be found in patients with hepatitis?
Sometimes there are no symptoms of hepatitis in the first weeks after infection -- the acute phase. But when they happen, the symptoms of types A, B, and C may include fatigue, nausea, poor appetite, belly pain, a mild fever, or yellow skin or eyes (jaundice).
How does hepatitis cause jaundice?
Hepatitis damages the liver, making it less able to move bilirubin into the bile ducts. Hepatitis may be acute (short-lived) or chronic (lasting at least 6 months). Acute viral hepatitis is a common cause of jaundice, particularly jaundice that occurs in young and otherwise healthy people.
What is the difference between hemolytic jaundice and obstructive jaundice?
The most common cause of pre-hepatic jaundice is hemolytic anemia which causes excess heme breakdown. In post-hepatic jaundice or obstructive jaundice, there is an impediment to the flow of bile due to a partial or complete obstruction of the extrahepatic biliary passage between the liver and duodenum.
What is elevated in obstructive jaundice?
Background: Obstructive jaundice is believed to be characterized by abnormalities of alkaline phosphatase (ALP), rather than aspartate transaminase (AST).
What is the difference between hepatitis A and hepatitis B?
Hepatitis B is a blood-borne pathogen; its primary mode of transmission is through direct blood-to-blood contact with an infected person. In contrast, hepatitis A can be spread by fecal-oral transmission or by consuming food or water that has been contaminated.
What is the difference between hepatitis B and jaundice?
Jaundice and hepatitis: what's the difference? Hepatitis is a viral infection that causes an inflammation (swelling) of the liver tissue. Jaundice, on the other hand, is caused due to high levels of bilirubin pigment in the liver, which in turn results in a yellow colouration of the skin.
Which bilirubin is elevated in hepatitis?
Bilirubin values of 2.5–3.0 mg/dl or greater establish the presence of the icteric phase of hepatitis. Bilirubin levels in excess of 30 mg/dl suggest hemolysis (over production of bilirubin) or renal failure (failure of excretion). Serum bilirubin levels are not always of clinical value.
Is jaundice a symptom of hepatitis?
Symptoms of hepatitis A include flu-like symptoms, such as fever, nausea, loss of appetite, and diarrhea. Hepatitis A may also cause jaundice, a condition that makes the skin and eyes look yellow and causes stool to become light in color and urine to become dark.
Is jaundice a symptom of hepatitis B?
If patients with chronic hepatitis B progress to cirrhosis (when the liver becomes severely scarred) they will develop signs and symptoms of liver failure, including: Jaundice.
Which virus is responsible for jaundice?
Conditions that can cause jaundice include: Infections of the liver from a virus (hepatitis A, hepatitis B, hepatitis C, hepatitis D, and hepatitis E) or a parasite. Use of certain drugs (such as an overdose of acetaminophen) or reactions to other medicines or or exposure to poisons (for example, poisonous mushrooms)
What complications can hepatitis cause?
Having a chronic HBV infection can lead to serious complications, such as:Scarring of the liver (cirrhosis). The inflammation associated with a hepatitis B infection can lead to extensive liver scarring (cirrhosis), which may impair the liver's ability to function.Liver cancer. ... Liver failure. ... Other conditions.
What are some complications of hepatitis?
If fibrosis develops and becomes more extensive, then it is described as cirrhosis.Cirrhosis of the Liver. Extensive fibrosis is called cirrhosis. ... Cancer of the Liver. Liver cancer is a complication of cirrhosis. ... Liver Failure. ... Glomerulonephritis. ... Cryoglobulinemia. ... Hepatic Encephalopathy. ... Portal Hypertension. ... Porphyria.More items...
What symptoms does hepatitis cause?
Symptoms of hepatitis can include: fever, fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, dark urine, light-colored stools, joint pain, and jaundice.
Does hepatitis cross the placenta?
Summary. Evidence that hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg) can pass through the human placenta has been questioned. We investigated 15 HBeAg-positive mothers who were hepatitis B carriers and their newborn babies, and found that HBeAg does indeed cross the human placenta.
What are the other types of jaundice?
Jaundice is typically classified as pre-hepatic, hepatic, or post-hepatic. Bile flow obstruction is an example of post-hepatic jaundice. Hepatic ja...
What are the complications of obstructive jaundice?
One implication of having obstructive jaundice is the potential for the underlying cause to be malignant, or cancerous. Moreover, whenever there is...
What markers do doctors use to diagnose obstructive jaundice?
Liver enzymes from blood work can reveal specific patterns that sometimes suggest an obstructive jaundice picture in somebody who has jaundice. Wha...
Can you prevent obstructive jaundice?
Any attempts at preventing obstructive jaundice would, in theory, be directed at preventing underlying, potentially modifiable risk factors. For ga...
What is the cause of jaundice?
1 . Jaundice is most commonly associated with liver diseases, including viral hepatitis, but can also be caused by alcohol abuse, medication overuse, and certain autoimmune disorders.
How to tell if you have jaundice?
The most obvious way to diagnose jaundice is by physical appearance. While it may be more noticeable in some people than others, most will recognize the subtle—and sometimes not-so-subtle—changes in their skin or eye color. Moreover, the yellowing will often be accompanied by extreme exhaustion as well as darkened urine ...
How does jaundice develop?
How Jaundice Develops. Jaundice is the consequence of having too much bilirubin in the blood. 2 Bilirubin is a yellow-pigmented substance derived from metabolized red blood cells. As old red blood cells enter the spleen, they are broken down and formed into bilirubins which the liver uses to create bile .
What is jaundice in medical terms?
Jaundice is an abnormal symptom characterized by the yellowing of the skin and/or the whites of the eyes (sclera).
How does the body avoid bilirubin accumulation?
The body avoids the accumulation of bilirubin by excreting any excess through urine or in stools. However, if the system is disrupted, there may be more bilirubin in the blood than the body can handle. If this happens, the accumulation can saturate cells and manifest with the yellowing we recognize as jaundice. 3
How many people have hepatitis B and C?
And for good reason. According to statistics from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, as many as 5.7 million Americans may be chronically infected with hepatitis B and C, while 3.9 million are believed to be suffering from some form of chronic liver disease. 4 .
Why do newborns have hyperbilirubinemia?
Hyperbilirubinemia may be caused by the excessive production and breakdown of red blood cells (as can happen with newborns) or when the ducts of the liver become obstructed and are less capable of processing bilirubin. In this latter case, viral hepatitis and advanced liver disease (such as cirrhosis or liver cancer) are the two top conditions a doctor would explore. 3
Why is bilirubin increased in pre-hepatic jaundice?
In pre-hepatic jaundice, the unconjugated bilirubin markedly increased in the serum because the production of bilirubin exceeds the conjugation capacity of the liver. In hepatocellular jaundice, the unconjugated and conjugated bilirubin is increased because of leakage of bilirubin from affected hepatocytes.
What is the clinical case of icteric jaundice?
Clinical case 1: A 52-year-old man presented with a history of nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain and icteric jaundice for one week. A physical examination revealed stable vital signs, and there was no evidence of hepatic encephalopathy. He had icteric sclera and right upper quadrant abdominal tenderness to palpation.The laboratory investigation results are presented below.
What is the clinical case presentation and biochemical test results suggestive of acute hepatitis?
Case 1: The clinical case presentation and biochemical test results are suggestive of acute hepatitis. The total and direct bilirubin are markedly increased. The transaminases are also elevated with ALT >20 times upper reference limit shows that the viral infection may be caused lysis of hepatocytes and leakage of bilirubin and transaminases. In addition, serum albumin and prothrombin time are within normal reference interval suggesting the acute nature of the disease. To confirm the etiology and type of infected virus, the antibody detection assay against different class hepatitis virus, serological test and PCR identification of virus serotype are recommended.
What happens if you have obstructive jaundice?
Untreated, obstructive jaundice can lead to serious infection that spreads to other parts of the body. Seek immediate medical care (call 911) for serious symptoms such as high fever (higher than 101 degrees Fahrenheit), severe abdominal pain, abdominal swelling, and nausea with or without vomiting.
What are the potential complications of obstructive jaundice?
You can help minimize your risk of serious complications by following the treatment plan that you and your health care professional design specifically for you. Complications of obstructive jaundice include:
What are some examples of bile duct surgery?
Examples include: Antibiotic therapy (if indicated for infection) Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP), an imaging procedure that allows treatment of some bile duct problems, including removal of gallstones that are causing obstruction. Intravenous fluids and pain medications. Nutritional support.
What causes jaundice in the liver?
Symptoms of obstructive jaundice include yellow eyes and skin, abdominal pain, and fever. Any type of obstruction that blocks the flow of bile from the liver can cause obstruct ive jaundice. Most commonly, gallstones create the blockage.
What is a condition in which there is blockage of the flow of bile out of the liver?
Obstructive jaundice is a condition in which there is blockage of the flow of bile out of the liver. This results in redirection of excess bile and its by-products into the blood, and bile excretion from the body is incomplete. Bile contains many by-products, one of which is bilirubin, a pigment derived from dead red blood cells.
Why is bile yellow?
Bilirubin, a component of bile, is yellow, which gives the characteristic yellow appearance of jaundice in the skin, eyes, and mucous membranes . The most common cause of obstructive jaundice is the presence ...
What is the yellow substance in the body?
Bile contains many by-products, one of which is bilirubin, a pigment derived from dead red blood cells. Bilirubin is yellow, and this gives the characteristic yellow appearance of jaundice in the skin, eyes, and mucous membranes. Symptoms of obstructive jaundice include yellow eyes and skin, abdominal pain, and fever.
Why is jaundice painful?
The reason for this difference is that stones tend to harbour bacteria and cause bile duct infection, resulting in pain and fever.
What is a hemolytic jaundice?
Haemolytic jaundice (blood disorder) - a result of increased breakdown of red blood cells due to underlying conditions such as thalassaemia, autoimmune disease or malaria.
What does it mean when your urine is yellow?
Yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes, light-coloured stools and dark urine could be signs of obstructive jaundice – a condition where normal drainage of bile from the liver to the small intestines is blocked.
Why does jaundice turn yellow?
Patients with medical jaundice will have yellowing of the skin, without dark urine or light-coloured stools. Medical jaundice can be related to: Hepatocellular jaundice - caused by a liver condition such as hepatitis and liver cirrhosis; and. Haemolytic jaundice (blood disorder) - a result of increased breakdown of red blood cells due ...
What is the function of the liver?
The liver produces bile to digest food and deliver waste products to the intestines for elimination. When bile drainage is obstructed, bilirubin – a byproduct of red cell recycling – builds up in the liver and spills over to the bloodstream, causing the skin and whites of eyes to turn yellowish.
Is obstructive jaundice a disease?
Obstructive jaundice is not a disease in itself but a symptom of an underlying condition involving the liver, the gallbladder or the pancreas. It will usually require surgical intervention, and is also known as surgical jaundice. “The most common cause of obstructive jaundice here is gallstones causing a blockage in the drainage of pathway ...
Is obstructive jaundice malignant or benign?
As mentioned above, there are both benign and malignant causes of obstructive jaundice. Benign causes: Gallstones or cysts in the bile ducts (choledochal cyst), narrowing of the bile ducts (bile duct strictures), pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas).
What causes obstructive jaundice?
Causes of obstructive jaundice. Cholelithiasis/choledocholithiasis. Gall Stones- the most common cause. There are cholesterol stones or mixed stones that form in the gall bladder, migrate via the cystic duct. Pancreatic head carcinoma. Common bile duct strictures are mostly iatrogenic-ERCP and cholecystectomy. Cholangiocarcinoma.
What is the name of the condition that causes a yellowish discoloration of the duodenum?
Obstructive Jaundice: Causes, Symptoms and Treatment. Obstructive jaundice is the type of jaundice resulting from obstruction of bile flow to the duodenum from the biliary tract. Also called mechanical, cholestatic jaundice or surgical jaundice. As a reminder, Jaundice, or icterus refers to the yellowish discoloration of the skin, sclerae, ...
What is the term for the retention of bilirubin in the hepatocytes?
Histologically, the retention of bilirubin in the hepatocytes, bile canaliculi, or bile ducts causes bilirubinostasis and is clinically manifested as jaundice.
What is cholestasis in hepatocytes?
Cholestasis is defined as stagnation, or at least a marked reduction, in bile secretion and flow. Cholestasis can be due to a functional impairment of the hepatocytes in the secretion of bile and/or due to an obstruction at any level of the excretory pathway of bile, from the level of the hepatic parenchymal cells at the basolateral (sinusoidal) ...
Is cholestasis intrahepatic or extrahepatic?
Cholestatic jaundice can thus be classified into intrahepatic or extrahepatic cholestasis, depending upon the level of obstruction to bile flow. Intrahepatic cholestasis or functional cholestasis can be due to a disease involving the liver parenchymal cells and/or the intrahepatic bile ducts. Intrahepatic cholestasis can be further subclassified as ...
Is bilirubin level normal in cholestasis?
As the excretion of bilirubin follows hepatocellular pathways different from those of bile acids, serum bilirubin level may be normal in certain cases of severe cholestasis (anicteric cholestasis), and the patient may present with only pruritus but no jaundice.
Overview
Causes
- Jaundice is yellowing of your eyes and skin. It is caused by too much bilirubin in your blood. Bilirubin is a yellow substance found in red blood cells. It is released when the body breaks down old red blood cells. Bilirubin usually leaves the body through bowel movements. Jaundice happens because your body breaks down cells correctly, but it cannot remove the bilirubin.
- Jaundice may be caused by several different disease processes. It is helpful to understand the different causes of jaundice by identifying the problems that disrupt the normal bilirubin metabolism and/or excretion. This form of jaundice occurs when the breastfed newborn does not receive adequate breast milk intake. This may occur because of delayed or insufficient milk pro…
- Normally, large amounts of blood flow each minute through the liver, which may be thought of as the body's chemical processing plant. The liver breaks down old, inefficient red blood cells in a process called hemolysis. This releases large amounts of bilirubin. The liver also manufactures the other components of bile.Bile is a greenish-yellow fluid secreted by the liver that contains ch…
- This type of jaundice is often associated with physiologic jaundice but is a result of a lower blood plasma volume in the baby. This increases the concentration of bilirubin in the blood but subsides once the baby is feeding for a period of time. It is often complicated by a low breast milk supply as the mothers breast tissue begins to produce milk in the first few days of the babys life. Breas…
Diagnosis
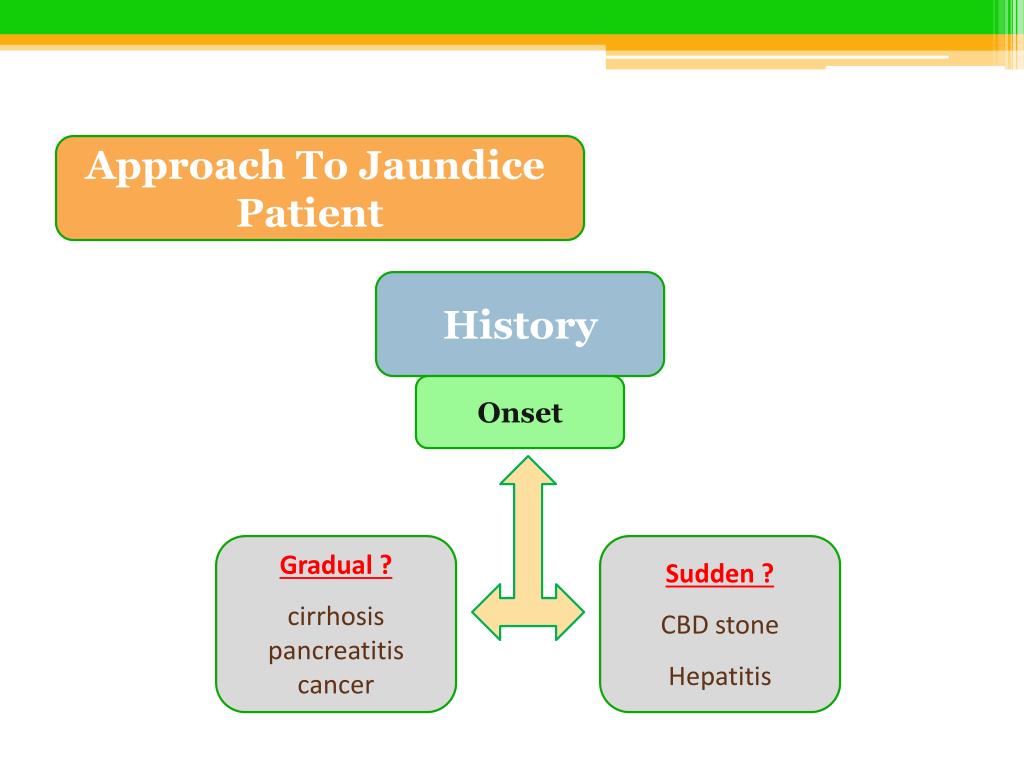
- Your healthcare provider will ask how long you have had symptoms. He or she will ask what medicines you take and how much alcohol you drink. He or she will also ask if you recently had surgery, an injury, or a blood transfusion. Tell him or her if you or anyone in your family has a history of liver disease. Your healthcare provider will order blood and urine tests to measure you…
- These may initially include a complete blood count (CBC), liver function tests (including a bilirubin level), lipase/amylase level to detect inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis), and an electrolytes panel. In women, a pregnancy test may be obtained. Additional blood tests may be required depending upon the initial results and the history provided to the practitioner.
- Difficulties can arise with overlapping of diseases such as autoimmune hepatitis with primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC) and autoimmune hepatitis with hepatitis C.
- Your doctor will take a medical history and perform a physical exam. Your doctor will ask how suddenly the jaundice came on, what other symptoms accompanied it, and how the stool and urine look. A blood sample will also be taken and checked for hepatitis virus antibodies, abnormal red blood cells, bilirubin levels, and various other substances that give clues about liver function…
Pathophysiology
- Jaundice in these cases is caused by rapid increase in the breakdown and destruction of the red blood cells (hemolysis), overwhelming the liver's ability to adequately remove the increased levels of bilirubin from the blood. Jaundice in these cases, also termed obstructive jaundice, is caused by conditions which interrupt the normal drainage of conjugated bilirubin in the form of bile fro…
- 1. Bilirubin is produced from the breakdown of haemoglobin in the reticuloendothelial system. 95% of the circulating bilirubin is unconjugated and bound to albumin. 2. The bilirubin-albumin complex is broken down by hepatocytes leaving free albumin circulating. The bilirubin is excreted in bile but only when made water-soluble by conjugation with glucuronic acid in the liver. 3. Bile i…
- Free bilirubin is constantly circulating in the blood stream and averages about 0.5mg/dL in a normal state. Any disruption increases the free and conjugated bilirubin in the blood. The yellowish discoloration of the skin that is typical of jaundice becomes evident when the bilirubin level reaches 1.5mg/dL. Hepatocellular jaundice is the result of defective uptake or excretion of …
- Severe Malaria In cases of severe, untreated malaria, plasmodium cells attack and infect both the liver and red blood cells. The breakdown of red blood cells and liver function produce excessive bilirubin which causes the tell-tale yellowing of the skin, eyes, and mucus cells in the mouth.
Treatment
- Your healthcare provider will try to find and treat the cause of your jaundice. Medicine may be given to decrease bilirubin levels. Your provider may have you stop taking a medicine if it is causing your symptoms. You may need one or more procedures to find or remove a blockage in your pancreas or gallbladder.
- There's no treatment for jaundice as such, since it's not a disease but a sign of a medical problem. The approach is to treat the underlying cause, if possible. Some of the medical problems that cause jaundice are curable, like malaria. Others, like thalassemia, are treatable. Many, like hepatitis A, newborn jaundice, or cholestasis of pregnancy, aren't curable but go away on their o…
Signs And Symptoms
- Jaundice is a yellow discoloration of the skin, mucous membranes, and the whites of the eyes caused by increased amounts of bilirubin in the blood. Jaundice is a sign of an underlying disease process.
- When you are jaundiced, your skin and the whites of your eyes are yellow. Sometimes, people who eat a lot of carrots or beta-carotene tablets take on a yellowish colour. This is called carotenemia, and can be easily distinguished from jaundice because the whites of the eyes don't turn yellow.Other symptoms depend on the cause of jaundice. If a fever or flu-like illness comes befo…
- Jaundice in newborn babies are a common occurrence and is evident as a yellowish discoloration of the skin, mouth and whites of the eye (sclera). In babies, the discoloration of the sclera is often more prominent than it is in jaundiced adults. Jaundice is due to an elevated level of bilirubin in the blood (hyperbilirubinemia).
- Severe Alcoholism Alcoholism leading to cirrhosis of the liver may also cause jaundice since the disease interferes with the healthy operation of the liver and an imbalance in the processing of bilirubin.
Definition
- Jaundice is the medical term for yellow discoloration of the skin, sclera (whites of the eye) and deeper tissues like the mucus membrane of the mouth usually as a result of high levels of bilirubin in the blood. The word jaundice essentially means yellow color (Latin ~ glabinus, French ~ jaunisse). It is commonly referred to as yellow jaundice but this makes the term redundant (yel…
Management
- This will depend on the diagnosis and cause of the jaundice in each individual case but factors to consider here include managing any pruritus that may be present - including lifestyle and dietary advice and cholestyramine treatment.
Classification
- Neonatal jaundice (newborns) is also a form of non-hemolytic jaundice but is not related to any pathology and is also known as physiologic jaundice. Bilirubin from a fetus enters the mothers blood stream and is metabolized by the mothers liver. Once the baby is born, the liver is not able to conjugate bilirubin in the first few days to week of life, resulting in an increase of bilirubin in th…
Clinical Significance
- Urinalysis is an analysis of the urine and is a very useful test in the diagnosis of screening many diseases.
- A type of hemolytic jaundice seen in newborns is known as erythroblastosis fetalis. It arises when a baby inherits Rh-positive red blood cells from the father while the mother is Rh-negative. The process begins in the fetus and antibodies produced in the mothers body crosses the placental barrier where it destroys the babys red blood cells. In erythroblastosis fetalis, the baby is often b…
- Sickle Cell Anemia This blood condition results in abnormally shaped and defective red blood cells, which can lead to the production of excessive bilirubin and jaundice.