
Can solumedrol be given im?
SOLU-MEDROL may be administered by intravenous or intramuscular injection or by intravenous infusion, the preferred method for initial emergency use being intravenous injection. To administer by intravenous (or intramuscular) injection, prepare solution as directed. The desired dose may be administered intravenously over a period of several ...
Can Humalog be given IM and same with Lantus?
Yes you can take them at the same time, but not in the same syringe or the same exact injection site. You would usually take the Humalog a little before (or same time) as eating carbs/meals, and/or to correct a high bg. Lantus is usually taken either in the morning or at bedtime (and sometimes split into 2 doses per day).
Do I really need insulin?
“Why do I need insulin” is a very legitimate question. In this article we will talk about when insulin is absolutely necessary and why do you need insulin. Aside from treating diabetes with diet , exercise, and oral medications, insulin is sometimes an absolute necessity when everything else fails to achieve diabetes control.
Is there any type of insulin that can be given intravenously?
The only type of insulin that is given intravenously is human regular insulin. A rapid-acting insulin analog is unnecessary in intravenous insulin administration because the insulin is delivered directly into the bloodstream and takes immediate effect. An insulin analog is human insulin genetically altered in the laboratory to make them rapid-acting or long lasting.
See more
What happens if I give insulin IM?
Always work with your doctor Injecting insulin into muscle changes the way it's metabolized, can be more painful, and may cause more bruising. And be careful to never inject long-acting insulin into muscle, as that can ruin blood sugars and send you on a blood glucose rollercoaster for the next 24 hours.
Is insulin given IM or IV?
Human regular insulin may be injected directly into the vein in a hospital setting under close medical supervision only. Insulin is added to intravenous fluids, and the insulin dose and blood sugar are strictly monitored.
What routes can insulin be administered?
There are three primary methods to administer insulin: injections, inhalers (if you are at least 18 years old), and pumps.Injections. Many manage T1D it with multiple daily injections (MDI). ... Inhaler. Afrezza, a quick acting inhaled insulin, can be an alternative to injectable pre-meal insulin. ... Pumps.
Can you give IM injection with insulin syringe?
0:082:56How to Inject Insulin with a Syringe - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipYou may be prescribed insulin in a vial. And you will use a syringe to inject it. It also may beMoreYou may be prescribed insulin in a vial. And you will use a syringe to inject it. It also may be prescribed as a pen.
Can insulin be given in the deltoid?
Insulin is more readily absorbed from the abdomen and deltoid region compared to thigh and buttocks [111, 115, 118, 122–125, 130].
Why does insulin need to be administered subcutaneously?
The preferred tissue space for insulin injection is the subcutaneous layer, which is the fat layer just below the dermis and above the muscle1; it offers slow, stable and predictable absorption, whatever the fat tissue depth2. Stable and predictable absorption of insulin will support optimal blood glucose control.
Is insulin given IM or SubQ?
Insulin is given as a subcutaneous injection — or just under the skin — so the needle doesn't go into muscle, which could affect your blood sugar levels.
Where should you not inject insulin?
Do not inject near joints, the groin area, the navel, the middle of the abdomen, or scar tissue. You will also need to rotate, or switch, your injection sites. If you use the same injection site over and over again, you may develop hardened areas under your skin that keep the insulin from working properly.
Which insulin can only be given IV?
The only type of insulin that should be given intravenously is human regular insulin. There is no advantage to using rapid-acting analogs in preparing insulin infusions because the rate of absorption is no longer a factor when administering insulin intravenously and can only result in added costs to the institution.
How do you administer insulin?
The insulin needs to go into the fat layer under the skin.Pinch the skin and put the needle in at a 45º angle.If your skin tissues are thicker, you may be able to inject straight up and down (90º angle). ... Push the needle all the way into the skin. ... Leave the syringe in place for 5 seconds after injecting.
How can I get insulin without a needle?
Instead of a needle, a jet insulin injector uses a high-pressure blast of air or a spring to inject a dose of insulin through your skin.
Can you inject testosterone SUBQ?
Subcutaneous Injection of Testosterone Is an Effective and Preferred Alternative to Intramuscular Injection: Demonstration in Female-to-Male Transgender Patients.
Can insulin be given IV?
IV insulin delivery offers many advantages over subcutaneous insulin delivery. It eliminates the need for multiple injections, allows for more accurate dose administration, has more predictable kinetics, and provides a quick response to rapidly changing glucose levels.
Can you give regular insulin IV?
Intravenous insulin administration is as follows: Mix 250 units of regular human insulin in 250 mL of normal saline (1 U/mL). Flush approximately 30 mL through the line prior to administration. Do not use a filter or filtered set with insulin.
How is insulin administered?
The insulin dose is dialed on the pen, and the insulin is injected through a needle, much like using a syringe. Cartridges and pre-filled insulin pens only contain one type of insulin. Two injections must be given with an insulin pen if using two types of insulin.
When do you start IV insulin?
All four sets of guidelines recommend initiating insulin therapy in patients with persistent hyperglycemia (blood glucose > 180 mg/dl). After insulin is initiated, the target blood glucose range should be 140–180 mg/dl for the majority of patients.
What Do I Need to Know About Insulin syringes?
Insulin syringes come in different sizes depending on the dose of insulin you need. Your healthcare provider or pharmacist will help you find the r...
Where Do I Inject Insulin?
1. You can inject insulin into your abdomen, upper arm, buttocks, hip, and the front or side of the thigh. Insulin works fastest when it is injecte...
How Do I Inject The Insulin With A syringe?
1. Clean the skin where you will inject the insulin. You can use an alcohol pad or a cotton swab dipped in alcohol. 2. Grab a fold of your skin. Ge...
How Can I Decrease Pain When I Inject Insulin?
1. Inject insulin at room temperature. If the insulin has been stored in the refrigerator, remove it 30 minutes before you inject it. 2. Remove all...
Where Should I Get Rid of My Used syringes?
Ask your healthcare provider where to get rid of your syringes. He may tell you to place the syringe in a heavy-duty laundry detergent bottle or a...
When Should I Contact My Healthcare Provider?
1. You feel or see hard lumps in your skin where you inject your insulin. 2. You think you gave yourself too much or not enough insulin. 3. Your in...
Why Is Insulin Injected Instead Of Taken By Mouth?
Insulin cannot be taken orally because it would break down in the digestive process. Insulin is a poly-peptide protein, which can be broken down by enzymes in the digestive system. By the time it reaches the small intestine, where it is absorbed, it is only a single peptide and can no longer function as insulin. Besides the chemical reasons for not ingesting insulin, there are other reasons that have more to do with the management of diabetes. Why Injection Is Better Blood sugar levels are subject to great change throughout the day. What foods were consumed, exercise, stress, illness, even time of day – all of these impact glucose levels. If this were not so, there would be no need to monitor levels with a finger prick multiple times each day. Insulin is needed to ensure that glucose is properly utilized and that levels of glucose remain stable. In order to work properly, insulin must enter the bloodstream intact. By injecting it into the subcutaneous tissue in our bodies, it is designed to be absorbed into the bloodstream without changing its properties and within a proscribed amount of time. Insulin should not be injected directly into muscle or into the bloodstream, as both will increase the speed of absorption. How fast absorption happens is also a function of what type of insulin is being used: rapid-acting, short-acting, intermediate-acting, long-acting or a mix of some of these. Each is designed to be absorbed and active over certain time frames, in order to cope with different glucose control needs, like consuming a meal or sleeping all night. Possible New Alternatives There is active research to develop alternatives to injections. One of the most promising is inhaled insulin. There was an inhaled insulin product, Exubera, on the market for about a year betwee Continue reading >>
How does insulin work?
Insulin is a hormone that helps cells use glucose (sugar) for energy. It works as a “key,” allowing the sugar to go from the blood and into the cell. In type 1 diabetes, the body doesn’t make insulin. In type 2 diabetes, the body doesn’t use insulin correctly, which can lead to the pancreas not being able to produce enough — or any, depending on the progression of the disease —insulin to meet your body’s needs. Diabetes is normally managed with diet and exercise, with medications, including insulin, added as needed. If you have type 1 diabetes, insulin is required for life. This may seem difficult at first, but you can learn to successfully administer insulin with the support of your healthcare team, determination, and a little practice. There are different ways to take insulin, including syringes, insulin pens, insulin pumps, and jet injectors. Your doctor will help you decide which technique is best for you. Syringes remain a common method of insulin delivery. They’re the least expensive option, and most insurance companies cover them. Syringes Syringes vary by the amount of insulin they hold and the size of the needle. They’re made of plastic and should be discarded after one use. Traditionally, needles used in insulin therapy were 12.7 millimeters (mm) in length. Recent research shows that smaller 8 mm, 6 mm, and 4 mm needles are just as effective, regardless of body mass. This means insulin injection is less painful than it was in the past. Insulin is injected subcutaneously, which means into the fat layer under the skin. In this type of injection, a short needle is used to inject insulin into the fatty layer between the skin and the muscle. Insulin should be injected into the fatty tissue just below your skin. If you inject the insulin deeper int Continue reading >>
How is insulin secreted?
Insulin is a protein formed by two cross-linked peptide chains. Insulin is secreted in pulses by the pancreas and reaches the liver via the portal circulation. Some 80% of the insulin reaching the liver is cleared from the circulation, which means that insulin attains much higher concentrations in the liver than in the peripheral circulation. Insulin has a short plasma half-life (3-4 minutes), and choice of the route and timing of insulin administration is a major determinant of metabolic control. Conventional insulin injections are given into the thigh, abdomen or outer side of the buttock. Standard needles range from 0.8 - 1.6 cm in length, are used with a syringe or pen device and deliver insulin into the subcutaneous fat. Too long a needle or poor injection technique can result in injection into a muscle, which is painful and results in more rapid absorption of insulin. Many alternative routes of administration have been tested, but none can match direct injection or infusion. Subcutaneous insulin injection or infusion share the disadvantages of delivery into the systemic rather than portal circulation, and rates of appearance in the blood stream which are delayed and rendered somewhat erratic by the process of absorption from subcutaneous tissues. Characteristics of an ideal insulin administration system Nature has placed the pancreatic beta cell inside a digestive gland and astride an arterial supply that continuously samples the rate of nutrient absorption from the gut. It responds instantaneously to these blood-borne signals by releasing insulin in synchronised pulses, a pattern of secretion that maximises its effect on liver cells. Furthermore, it matches this insulin secretion with reciprocal suppression or release of its partner hormone pancreatic glucagon, t Continue reading >>
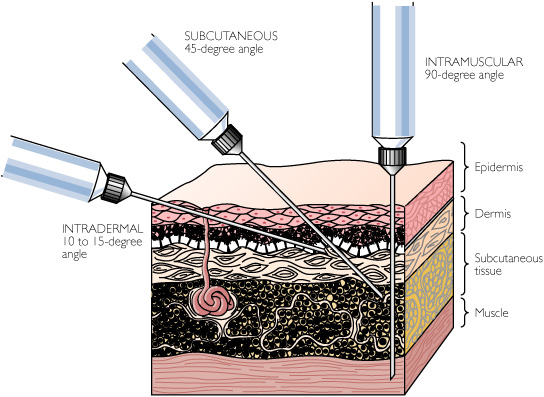
Where is the ID injection?
Intradermal injections (ID) are injections administered into the dermis, just below the epidermis. The ID injection route has the longest absorption time of all parenteral routes. These types of injections are used for sensitivity tests, such as TB (see Figure 7.13), allergy, and local anesthesia tests. The advantage of these tests is that the body reaction is easy to visualize, and the degree of reaction can be assessed. The most common sites used are the inner surface of the forearm and the upper back, under the scapula. Choose an injection site that is free from lesions, rashes, moles, or scars, which may alter the visual inspection of the test results (Lynn, 2011). Equipment used for ID injections is a tuberculin syringe calibrated in tenths and hundredths of a millilitre, and a 1/4 to 1/2 in., 26 or 27 gauge needle. The dosage of an ID injection is usually under 0.5 ml. The angle of administration for an ID injection is 5 to 15 degrees. Once the ID injection is completed, a bleb (small blister) should appear under the skin. Checklist 56 outlines the steps to administer an intradermal injection. Disclaimer: Always review and follow your hospital policy regarding this specific skill. Do not aspirate. It is not necessary to aspirate because the dermis is relatively without vessels. Always take steps to eliminate interruptions and distractions during medication preparation. If the patient expresses concerns about the medication or procedure, stop and explore the concerns. Re-verify order with physician if appropriate. Steps Additional Information 1. Prepare medication or solution as per agency policy. Ensure all medication is properly identified. Check physician orders, Parenteral Drug Therapy Manual (PDTM), and MAR to validate medication order and guidelines for admin Continue reading >>
When was insulin first introduced?
Regular human insulin Human regular insulin was introduced in 1982, as the first product of bio-engineering. Despite the fact that the practical differences between the (then already highly purified) animal insulins and human insulin were limited, it did not take long for the animal insulin preparations to be replaced by their human counterparts. This was partly the result of strong marketing from those who produced the human insulin and partly the result of the intuitive notion that because it was human, it was bound to be better. Regular human insulin can be injected subcutaneously, intramuscularly, and intravenously. As in physiological situation in the pancreas, in the clinical preparation a little Zinc is present. Insulin has a tendency to self-associate to hexamers (six insulin molecules bound together) around a Zinc atom, which improves water solubility. However, this results in a slight delay in the absorption of regular insulin when injected subcutaneously; it does not materially affect intravenous injection. Subcutaneous use After s.c. injection insulin levels peak after about 90 minutes and then slowly dissipates in 4 to 6 hours; metabolic action peaks after 2 to 3 hours. Because of this relatively slow onset of action, it is recommended to inject regular insulin 30-45 minutes before the meal to have the insulin peak coincide better with the meal-related rise in glucose. However, the evidence for this recommendation is poor, and for reasons of practicality many patients tend to ignore this advice. When using higher dosages (above approx. 50 IU) the rapidity of action tends to diminish, so it is recommended to split the dose in two separate injections (see also Pharmacokinetics and -dynamics of insulin absorption). Intravenous use After i.v. injection regular Continue reading >>
What is subcutaneous injection?
The injection of a drug or the implantation of a device beneath the surface of the skin is made in the loose interstitial tissues of the upper arm, the anterior surface of the thigh, or the lower portion of the abdomen. The upper back also can be used as a site of subcutaneous administration. The site of injection is usually rotated when injections are frequently given. The maximum amount of medication that can be subcutaneously injected is about 2 ml. Needles are generally 3/8 to 1 inch in length and 24 to 27 gauge. Absorption of drugs from the subcutaneous tissue is influenced by the same factors that determine the rate of absorption from intramuscular sites (slowly soluble salt forms, suspensions versus solutions, differences in particle size, viscosity of the injection vehicle, etc.); however, the vascularity in the subcutaneous tissue is less than that of muscle tissue, and therefore absorption may be slower than after intramuscular administration. But absorption after subcutaneous administration is generally more rapid and predictable than after oral administration. There are several ways to change the absorption rate: use heat or massage the site to increase the absorption rates of many drugs. co-administer vasodilators or hyaluronidase to increase absorption rates of some drugs. Conversely, epinephrine decreases blood flow which can decrease the absorption rate. Many different solution and suspension formulations are given subcutaneously. Heparin, enoxaparin, and insulin are the most important drugs routinely administered by this route. Drugs that are administered by the route must be soluble and potent in Continue reading >>
When is insulin taken?
Short- or rapid-acting insulin taken at or before mealtimes to control blood sugar levels.
What is an insulin pump?
An insulin pump is about the size of a small cell phone. It gives you a basal dose of short- or rapid-acting insulin per hour. When you eat or when blood sugar is high, you decide the dose, and the insulin in the pump delivers the bolus.
What is inhaled insulin?
Inhaled insulin is taken using an oral inhaler to deliver ultra-rapid-acting insulin at the beginning of meals. Inhaled insulin is used with an injectable long-acting insulin.
What are the disadvantages of insulin inhalers?
Disadvantages of insulin inhalers. Might cause mild or severe coughing. May be more expensive. Still requires injections or a pump for basal insulin. Dosing isn’t as precise. Make sure to talk to your doctor and diabetes educator when your lifestyle or needs change.
Which is better: a syringe or an insulin pen?
Syringes and insulin pens deliver insulin through a needle. Pens may be more convenient, and children may find them more comfortable than syringes.
What do you do if you need doses in half units?
If you need doses in half units, choose a syringe with half-unit markings.
Can insulin be used with a pen?
Not all types of insulin can be used with a pen.
What is the best way to take insulin?
There are different ways to take insulin, including syringes , insulin pens, insulin pumps, and jet injectors. Your doctor will help you decide which technique is best for you. Syringes remain a common method of insulin delivery. They’re the least expensive option, and most insurance companies cover them.
Where is insulin injected?
Insulin is injected subcutaneously, which means into the fat layer under the skin. In this type of injection, a short needle is used to inject insulin into the fatty layer between the skin and the muscle. Insulin should be injected into the fatty tissue just below your skin. If you inject the insulin deeper into your muscle, ...
How to withdraw insulin from a syringe?
Push the needle into the stopper and push the plunger down so that the air in syringe goes into the bottle. The air replaces the amount of insulin you will withdraw.
How to inject a syringe?
Follow these tips for more comfortable and effective injections: 1 You can numb your skin with an ice cube for a couple of minutes before swabbing it with alcohol. 2 When using an alcohol swab, wait for the alcohol to dry before injecting yourself. It may sting less. 3 Avoid injecting in the roots of body hair. 4 Ask your doctor for a chart to keep track of your injection sites.
How to check if insulin is cloudy?
If the insulin is cloudy, mix the contents by rolling the vial between your hands for a few seconds. Be careful not to shake the vial.
Why is it important to rotate the insulin site?
People who take insulin daily should rotate their injection sites. This is important because using the same spot over time can cause lipodystrophy.
Why do people rotate their insulin injection sites?
People who take insulin daily should rotate their injection sites. This is important because using the same spot over time can cause lipodystrophy. In this condition, fat either breaks down or builds up under the skin, causing lumps or indentations that interfere with insulin absorption.
Where do I inject insulin?
You can inject insulin into your abdomen, upper arm, buttocks, hip, and the front or side of the thigh. Insulin works fastest when it is injected into the abdomen.
How do I inject the insulin with a syringe?
Wash your hands with soap and water. This will help prevent an infection. Dry your hands with a clean towel or paper towel.
What do I need to know about insulin syringes?
Your healthcare provider or pharmacist will help you find the right size syringe. Use the correct size insulin syringe to make sure you get the right dose of insulin.
How can I decrease pain when I inject insulin?
Inject insulin at room temperature. If the insulin has been stored in the refrigerator, remove it 30 minutes before you inject it.
How to get insulin out of a pinched tissue?
Let go of the pinched tissue. Push down on the plunger to inject the insulin. Press on the plunger until the insulin is gone. Keep the needle in place for 5 seconds after you inject the insulin. Pull out the needle. Press on your injection site for 5 to 10 seconds. Do not rub.
What to do if a syringe bends?
Throw out any syringe that bends or touches anything other than clean skin.
How to get rid of syringes?
Ask your local waste authority if you need to follow certain rules for getting rid of your syringes. Bring your used syringes home with you when you travel. Pack them in a plastic or metal container with a secure lid.
What is the most common way to take insulin?
Even though there are other options, needles and syringes remain the most common way to take insulin. Some of the new insulin injection methods, such as the insulin pen, carry only a preset amount of insulin. Thinner needles and other advancements, such as syringe magnifiers, have made syringes easier to use. 2 of 9. View All.
Where is the insulin pump inserted?
The pump is attached to a small tube or catheter with a needle on the end that is inserted in your skin, usually in your abdomen. About the size of a deck of cards, the pump can be programmed to deliver insulin to cover meals too.
How do insulin pens work?
Unlike syringes, insulin pens contain a built-in insulin cartridge that is prefilled with the drug. You turn a dial to the desired dose, press a plunger, and inject the insulin. (You change the needle before each use). Once you have used up the insulin, you replace the cartridge.
What are some examples of innovations designed to help make insulin needles more palatable?
These devices are another example of innovations designed to help make insulin needles more palatable.#N#Syringe-filling devices allow a person with diabetes to load a syringe with a simple touch or sometimes to measure out dosages based on a "click" sound, as well as mix two different types of insulin together .#N#Spring-loaded syringe holders are another way to make insulin needles and syringes easier and less painful to use.#N#These devices often have push buttons that trigger the plunger, helping you inject. (It’s considered an “insertion aid.”)
How do needle guides help with diabetes?
Needle guides can help you keep the syringe or pen steady at the desired location and at the correct angle both for drawing up insulin out of the vial and injecting.
Can you use insulin without a pump?
subcutaneous-infusion. Credit: Supplyinfusion.com. Ports use the same sets of tubing that can be used with an insulin pump, but you can use them on their own without the pump. Basically the catheter is inserted under the skin and stays in place for several days.
Is insulin pump easy to use?
However, they aren’t necessarily easy to use (it can take a bit of training). Best for those taking insulin several times a day—like type 1 diabetics—pumps are not typically the first choice for people with type 2, though some. type 2 diabetics love their insulin pump. 7 of 9. View All.
Can I charge for an IM in the ER?
I am well aware that you can charge for an IM in the ER but NOT for inuslin IM. If it is given IVP you can.
Can you charge for insulin injections?
If you refer to CMS guidelines referring to billing of self injectable medications, you will see that any medication that a patient typically can inject themselves, you cannot charge the administration fee for a s/c insulin injection. See http://www.cms.gov/Regulations-and-Guidance/Guidance/Transmittals/downloads//R91BP.pdf Look under C. Usually, pg. 4.