They can be cancerous or noncancerous. Most lesions are noncancerous and don’t require treatment if they’re small and don’t cause symptoms. Your doctor can diagnose liver lesions with a combination of imaging, blood tests, and sometimes a small tissue sample.
What is the difference between a lesion and a tumor?
• Lesion refers to any abnormal area of tissue while tumor more specifically refers to an abnormal outgrowth of tissue. • Either one does not hint towards prognosis. • Either one does not hint towards the site, size, shape or other characteristics.
Are lytic lesions always a sign of cancer?
Lytic lesions — spots where bone tissue has been destroyed — can be seen in other cancers, including breast cancer, lung cancer and kidney cancer. They can also be seen with infections of bone and even in some benign conditions. Taking a biopsy of one of the lytic lesions may help with your diagnosis. Similarly, do multiple myeloma lesions heal? I've always been curious to know if myeloma lesions could be healed after the cancer was gone post-treatment.
Can benign nodule turn out to be cancer?
The best way to determine whether a lung nodule is benign or cancerous is to examine the rate of growth. Benign lung nodules that turn out to be cancer double in size quickly and this rate of growth is often identified easily through an X-ray or CT scan. Benign lung nodules rarely grow at all.
What diseases can cause lesions on the brain?
What diseases cause brain lesions?
- Stroke, vascular injury, or impaired supply of blood to the brain is perhaps the leading cause of lesions on the brain.
- Multiple sclerosis, or MS, is a disease where brain lesions are located in multiple sites of the brain. ...
- Lupus, an autoimmune disease, affects almost all systems of the body ranging from skin to heart, liver, muscles and brain. ...
How do you know if a lesion is cancerous?
Melanoma signs and symptomsA large brownish spot with darker speckles.A mole that changes in color, size or feel or that bleeds.A small lesion with an irregular border and portions that appear red, pink, white, blue or blue-black.A painful lesion that itches or burns.More items...•
Do lesions mean you have cancer?
Most bone lesions are benign, meaning they are not cancerous. Some bone lesions are cancerous, however, and these are known as malignant bone tumors.
Is lesion the same as tumor?
A lesion describes any area of damaged tissue. All tumors are lesions, but not all lesions are tumors. Other brain lesions can be caused by stroke, injury, encephalitis and arteriovenous malformation.
Are lesions always malignant?
A lesion may be benign (not cancer) or malignant (cancer).
How do you treat lesions?
If needed, benign skin lesions can get local treatment with topical medications, such as retinoids, corticosteroids, or antimicrobial agents, as well as laser therapy, cryotherapy, phototherapy, or surgical removal. If the skin lesion is caused by a systemic disease, treatment may also address the underlying cause.
What is a pre cancerous lesion?
Pre-cancerous lesions are skin changes that have the risk of becoming cancer over time. But not all pre-cancerous skin lesions become skin cancer. Your dermatologist or primary care provider may choose to treat a pre-cancerous skin lesion, so it will not have the chance to turn into cancer.
What is considered a lesion?
A lesion is any damage or abnormal change in the tissue of an organism, usually caused by disease or trauma. Lesion is derived from the Latin laesio "injury". Lesions may occur in plants as well as animals.
What is a lesion in medical terms?
A Lesion is a CELL PATHOLOGICAL ABNORMALITY. A Lesion is an area of abnormal TISSUE. A Lesion may be: benign (not cancer) or. malignant (cancer).
Is a lesion a tumor or mass?
A bone lesion is considered a bone tumor if the abnormal area has cells that divide and multiply at higher-than-normal rates to create a mass in the bone. The term "tumor" does not indicate whether an abnormal growth is malignant (cancerous) or benign, as both benign and malignant lesions can form tumors in the bone.
What are the 3 types of lesions?
Primary skin lesions tend to be divided into three groups: Lesions formed by fluid within the skin layers: Examples include vesicles and pustules. Lesions that are solid masses: Examples include nodules and tumors. Flat lesions: Examples include patches and macules.
Can a lesion be nothing?
What is a “lesion?” A lesion is simply something that's not supposed to be there. It could be anything. It could be an area of tissue that's a different color, it could be an area of tissue that is raised up, it could be an area of tissue that looks raw, it could be a spot on an x-ray that looks out of place.
Can lesions go away on its own?
A range of health issues and factors such as shoes or clothes rubbing against the skin can cause lesions. Some of these lesions, including cold sores and blisters, usually go away on their own within a few weeks. Others, such as eczema and psoriasis, are long-term conditions that need ongoing treatment.
What is a suspicious lesion?
When completing your self-examination, here is what to look for: Changes in the size, shape, or color of a mole or growth. A lesion that is rough, oozing, bleeding, or scaly. A sore lesion that will not heal. Pain, itching, or tenderness to a lesion.
What does lesions mean in medical terms?
A Lesion is a CELL PATHOLOGICAL ABNORMALITY. A Lesion is an area of abnormal TISSUE. A Lesion may be: benign (not cancer) or. malignant (cancer).
What is considered a lesion?
A lesion is any damage or abnormal change in the tissue of an organism, usually caused by disease or trauma. Lesion is derived from the Latin laesio "injury". Lesions may occur in plants as well as animals.
What lesions mean?
injury, harm1 : injury, harm. 2 : an abnormal change in structure of an organ or part due to injury or disease especially : one that is circumscribed (see circumscribe sense 1) and well defined. Other Words from lesion Example Sentences Learn More About lesion.
Benign lesions
Benign lesions are noncancerous growths. Small benign lesions often don’t cause symptoms and don’t require treatment. If tumors grow large, they may cause symptoms and need to be removed.
Malignant lesions
Like all cancers, cancerous lesions of the liver are caused by changes to the DNA that make cells replicate uncontrollably.
Cervical cancer risk factors
In addition to HPV infection, other risk factors for cervical cancer are:
What if my screening result is abnormal?
If the results of your HPV or Pap test come back abnormal, your doctor may do a colposcopy or cervical biopsy. These are two procedures that let them examine the cells of your cervix more closely to check for precancer or cancer.
Symptoms of cervical lesions
Precancerous cervical lesions often don’t cause symptoms. Because of this, many people don’t know they have them.
How long does angioedema last?
Urticaria and angioedema are very similar, but urticaria only affects the skin, and each wheal lasts less than 24 hours, while angioedema may last for days. 9. Urticaria occurs on the outer layer of the skin, whereas angioedema occurs under the skin in the subcutaneous tissue.
What causes scaly crusts on the skin?
Actinic keratosis is caused by exposure to sunlight (ultraviolet radiation) and appears as thick, scaly crusts on the skin. It usually doesn't appear until later in life (most common over the age of 40) due to being caused by years of sun exposure.
What are secondary skin lesions?
Secondary Lesions. Secondary skin lesions are caused when a primary skin lesion is disturbed, irritated, or changes over time. For example, if eczema is scratched and causes a crust to form, the crust is a secondary lesion. Examples of secondary skin lesions include: 1.
What is a fluid filled blister less than 0.5 cm in size?
Vesicle: A fluid-filled blister less than 0.5 cm in size. Pustule: Similar to a vesicle but filled with pus instead of fluid. Nodule: A circular, elevated, solid bump of greater than 0.5 cm. Telangiectasia: Clusters of 'spider veins' where tiny blood vessels cause red lines on the skin.
Why is my skin lighter?
Maceration: This is when skin becomes wet, wrinkly, and lighter in color due to being in contact with water or fluid for too long. This can occur due to leaking wounds due to improper wound care. Phyma: A thickening of the skin, often seen in advanced rosacea 2.
What is scale in dermatology?
Scale: A build-up of keratinized cells that form patches and then flake off the skin. Ulcer: A wound deeper than the epidermis, damaging the dermis, concave, variable in size, and graded depending on depth. Umbilication: A dip inside a skin lesion that looks similar to a navel. 1.
What is a cyst on the face?
Cyst : A raised, circumscribed area of the skin, filled with fluid or semi-solid fluid. Macule: A non-palpable, flat lesion that is different in color, and less than 0.5cm in size. Papule (also maculopapular): An elevated solid lesion, up to 0.5 cm in size, circumscribed and firm. It can appear in various colors.
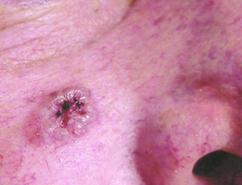
What is a SCC?
SCC. SCC is most likely to appear as a very scaly, crusted, pink papule that bleeds easily and grows with time. However, a rough, scaly, red patch of skin may appear instead. This can often closely resemble noncancerous or precancerous skin lesions.
How big can a cancer rash be?
be larger than 6 millimeters across. change with time. Skin cancer rashes will typically not resolve on their own, unlike those of other skin conditions. As the cancer grows, the size and shape of the lesion or rash will usually change. It may grow into deeper layers of skin and change shape.
Where does actinic keratosis occur?
Actinic keratosis most commonly occurs on exposed areas of the body, such as the hands, head, or neck. These patches are precancerous lesions. Over time, there is a slight risk that they will develop into a type of cancer called squamous cell carcinoma (SCC).
What does it mean when your skin is red and scaly?
For example, people with psoriasis will often experience persistent, scaly, red or pink plaques of skin that may sometimes itch.
What is the name of the bump on the nose?
Basal cell carcinomas. Basal cell carcino ma (BCC) is a type of cancer that often starts as a pearly papule or bump, often on the nose or another area of the face. The papule may then grow and become shinier. It may start to bleed in the center, where an indentation may form.
Is a rash a precancerous rash?
There are a variety of cancerous and precancerous rashes. Precancerous rashes may evolve into cancerous ones over time, and early diagnosis and treatment are vital in every case. Below, we list the types of skin cancer that tend to cause a rash, a lesion, or other skin symptoms:
What is the most life threatening form of skin cancer?
For example, melanomas — which develop from the melanocyte cells that provide pigment to the skin — often resemble misshapen moles. Melanomas are one of the most life threatening forms of skin cancer, so surveillance for an early lesion is essential for prompt treatment and a good prognosis.
What are the different types of bone cancer?
Malignant bone tumors are divided into two types: 1 Primary bone cancer, which is cancer that starts in the bone. 2 Secondary bone cancer, which is when cancer starts somewhere else and spreads to the bone.
What is the difference between malignant bone cancer and secondary bone cancer?
Malignant bone tumors are divided into two types: Primary bone cancer, which is cancer that starts in the bone. Secondary bone cancer, which is when cancer starts somewhere else and spreads to the bone.
Why do bone lesions grow?
A growing lesion can destroy healthy tissue and weaken the bone, making it more vulnerable to fractures. Most bone lesions are benign, not life-threatening, and will not spread to other parts of the body.
How many people get multiple myeloma every year?
It can affect any bone in the body and is the most common primary bone cancer, affecting about six people per 100,000 every year. Most people who get multiple myeloma are between 50 and 70 years old.
What are bone lesions?
Symptoms. Diagnosis. Outlook. Bone lesions are areas of bone that are changed or damaged. Causes of bone lesions include infections, fractures, or tumors. When cells within the bone start to divide uncontrollably, they are sometimes called bone tumors. Most bone lesions are benign, meaning they are not cancerous.
What age does multiple myeloma occur?
Multiple myeloma usually affects those over the age of 50, and is the most common form of primary bone cancer.
How old can you get ewing sarcoma?
While Ewing sarcoma can develop at any age, more than half of those diagnosed with it are between 10 and 20 years old.
What causes demyelination in the brain?
Demyelination. Some conditions, such as multiple sclerosis (MS), are caused by temporary or lasting demyelination —loss of the protective myelin coating that surrounds nerves in the brain. This causes one or more demyelinating brain lesions. The condition is usually idiopathic (without a known cause).
Why is it important to know if you have a brain lesion?
If you have neurological symptoms, it is important that your healthcare providers determine whether you have a brain lesion, how many you have, and the type because the treatment and prognosis of each type of brain lesion differs.
What is a brain lesion?
Treatment. A brain lesion is a type of abnormality in the brain, usually caused by a disease or injury. There are several kinds of brain lesions, and they can be distinguished by their symptoms, physical examination findings, and diagnostic tests. If you have neurological symptoms, it is important that your doctors determine whether you have ...
Why does the brain shrink?
Sometimes the brain can shrink in size due to damage or dying of the brain cells. This is usually a result of dementia or extensive strokes. 1 This can lead to enlarged spaces within the skull, often noted as atrophic lesions.
What causes a stroke in the brain?
Risk factors include heart disease, high blood pressure, uncontrolled diabetes, and high cholesterol. 3 This lesion usually consists of a central area of ischemia (death of cells due to deficient blood supply).
What is the sensation of the head on one side of the face?
Diminished sensation and/or paresthesias (unusual sensations) on one side of the face, or the arm and/or leg on one side of the body. A large brain lesion may cause head pain along with substantial focal neurological deficits (such as weakness of the face, arm, and leg on one side).
How long does it take for a stroke to heal?
Right after a stroke occurs, the lesion may be surrounded by swelling and inflammation, which subside within a few weeks. The ischemic part of the lesion remains, with permanent damage to the affected area of the brain.
What are the different types of liver cancer?
Types of Liver Cancer. There are two major types of primary liver cancer (cancers that start in the liver): Hepatocellular carcinoma ( HCC): This is the most common type of liver cancer. HCC tumors are three times more common in men than women. 4 . Fibrolamellar carcinoma: This is a subtype of HCC, where fibrous bands separate the cells ...
What happens to a hepatocellular carcinoma?
About 5% of them will transform into hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)—a type of liver cancer. More, in about 10% of cases, the lesion will spontaneously rupture or cause internal bleeding. This mostly happens during menstruation, pregnancy, and the postpartum period.
How to diagnose benign liver lesions?
Often, the lesions are detected when a patient undergoes magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or other imaging tests for abdominal pain or an unrelated health problem.
What is a liver lesion?
A liver lesion is also called a liver tumor or mass. Tolu Ajiboye is a health writer who works with medical, wellness, biotech, and other healthcare technology companies. Doru Paul, MD, is board-certified in internal medicine, medical oncology, and hematology.
What is the term for a condition where the body stores excessive amounts of iron in the liver and other organs?
Iron storage disease (hemochromatosis): This is a condition where the body stores excessive amounts of iron in the liver and other organs. Sex: Men are more likely to have liver cancer than women. Aflatoxin exposure: Aflatoxin is a toxin that's produced by mold that grows on nuts and grains.
What is the leading cause of liver cancer?
Hepatitis B or C infection: These viral infections are the leading causes of liver cancer.
What is the most common type of liver lesion?
Hepatic hemangioma is the most common type of liver lesion, consisting of clusters of small blood vessels. Around 20% of the general population have hemangiomas. 2 They don't typically cause symptoms, so they can be left untreated.
Why do brain lesions appear?
Lesions can be due to disease, trauma or a birth defect. Sometimes lesions appear in a specific area of the brain. At other times, the lesions are present in a large part of the brain tissue. At first, brain lesions may not produce any symptoms. As lesions worsen with time, the symptoms become more noticeable.
What are the symptoms of a brain lesion?
Headaches are usually the first symptom to appear with brain lesions. The pain appears suddenly and worsens as time passes. Over-the-counter medicine usually offers no relief for the pain. Nausea and possible vomiting. Impaired movement, if the lesion affects the part of the brain responsible for motor skills.
What causes plaques in the brain?
Plaques, or excess build-up of abnormal protein in the brain tissues or in the blood vessels, slowing down the supply of blood to the brain, as seen in clogged arteries. Alzheimer’s disease , a condition that affects a person’s memory, thinking and behavior, develops because of plaques in brain tissues. Multiple sclerosis can also cause plaques in the brain secondary to damaged tissue.
What are the factors that put a person at greater risk for brain lesions?
The following factors put a person at greater risk to get brain lesions: Aging. Family history of brain lesions. The risk increases if someone else in the family has had the condition. Vascular conditions, such as stroke, high blood pressure, and cerebral artery aneurysms.
Which lobe of the brain is responsible for hearing, memory, and speech?
Temporal lobe - located on each side of the brain at ear level, is important for hearing, memory and speech. Parietal lobe - at the center of the brain, is where sensory information like heat, pressure and pain is received and interpreted. Occipital lobe - found at the back of the brain, is primarily responsible for vision.
What test is done after a physical exam?
After a physical examination, the doctor may also recommend that the patient schedule a diagnostic test, such as a computed tomography, or CT or CAT scan, or magnetic resonance imaging, or MRI. These tests will help the doctor pinpoint the location of the lesion and will also help assess the extent of damage the lesion has caused the brain.
What is the function of the brain?
The brain controls thoughts, memory, speech, movements of the limbs, and organ function. There are many parts to the brain, and each section has a specific role to play in the human body. Four lobes make up the brain:
