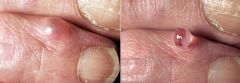
This kind of oral cancer occurs when the mouth’s salivary organs become plugged with a bodily fluid called mucus. Most cysts are on the lower lip, yet they can happen anyplace inside your mouth. They are typically transitory and painless. In any case, if left untreated, oral mucocele cancer can become permanent.
What is Oral mucocele cancer?
Oral mucocele cancer, otherwise called a mucocele, is a common oral cavity cancer that develops on the lip or the mouth. Usually, it is a harmless swollen spot. This kind of oral cancer occurs when the mouth’s salivary organs become plugged with a bodily fluid called mucus.
Is a mucocele contagious?
No: A mucocele is not contagious. Does a mucocele tingle? will it leave a dark spot? Not usually; no.: Mucoceles are blocked salivary ducts in the inside of the cheek, gum, floor of the mouth, or the palate.
What is the prognosis of benign or malignant mucocele?
Depending on the location of the appendix, other signs may be observed, such as hematuria. The most dreaded complication of benign or malignant mucocele is pseudomyxoma peritonei, which is difficult to treat surgically or medically. It has an uncertain prognosis, with a 5-year survival rate between 53% and 75%. 5,6
Are mucocele cysts harmful?
Mucocele cysts are more unpleasant than harmful, but you still should see a specialist to take care of them. They can return after removal, and there may be pain in areas where they’re removed. Be aware when cysts may pop up, and try to avoid the temptation to suck on your cheek or bite on your lip when they do appear.

Can a mucocele be cancer?
They can be something as benign as a mucocele, but unless we take a biopsy, there's no way to be sure. Many oral examinations turn up such lesions, which aren't oral cancer and will respond well to mucocele treatment, but the only way to know with any degree of certainty is to perform a biopsy.
What happens if a mucocele is left untreated?
While mucoceles are not typically dangerous, they can cause scar tissue to form when left untreated. Mucoceles, especially deep mucoceles, can be painful. It is common for a patient with a mucocele on the lower lip to bite the mucocele over and over again.
Does mucocele need biopsy?
Mucoceles usually require excisional biopsy and removal of the servicing minor salivary glands. If a vascular lesion cannot be excluded from the differential diagnosis, then aspiration of the lesion is prudent for evaluation of the fluid contents.
Can a mucocele be permanent?
The cyst is usually on the lower lip but can occur anywhere in the mouth. Mucocele are usually temporary but, if not treated could become permanent.
Can mouth cysts be cancerous?
Your doctor or dentist may discover them during regular check-ups or x-rays. When they do cause symptoms, they usually look like a non-painful bump or lump. These cysts and tumors are often benign (not cancer), but all tumors in the head and neck must be examined by our surgeons as soon as possible.
What kind of doctor removes mucocele?
A mucocele is a cyst that forms in the mouth and can be removed by an oral surgeon removing the salivary gland or helping a new duct to form.
When should a mucocele be removed?
In most cases, oral mucocele treatment is unnecessary since the cyst ruptures on its own — usually after three to six weeks. If the mucocele is persistent or large in size, your dental professional might use cryotherapy, laser treatment, or surgery to remove the cyst. Do not try to remove or rupture the cyst at home.
How long does mucocele surgery take?
The Surgery: The surgery takes about 5 minutes. The goal is to remove enough salivary tissue to obtain an adequate result . Postoperative Care: It takes most patients 7 - 10 days to recover from surgery. Some individuals feel better in just a few days, and some take as many as 2-3 weeks to recover.
Can a dermatologist remove a mucocele?
Answer: Mucous cysts of the lip These cysts often go away on their own but when they grow and are persistent and troublesome for patients they are often removed surgically. Dermatologists, plastic surgeons and oral surgeons remove them.
Can mucocele spread?
Mucocele is not contagious and usually resolves on its own without the need for treatment. However, in some cases, minor surgery by a dentist may be necessary to remove the affected cyst and salivary gland.
How do you stop a mucocele from growing?
Cryotherapy: Your healthcare provider will apply extreme cold to freeze and destroy the mucocele cyst. Laser treatment: Your provider will use a special laser to remove the lesion. Surgical excision: An oral surgeon or dentist will cut out and remove the cyst. They may also remove the salivary gland.
Can a dentist remove a Mucocele cyst?
If treatment is required, your dentist will perform a procedure to remove the mucocele. After applying a local anesthetic, your dentist may use a scalpel to remove the salivary gland causing the mucocele. Following this, your dentist may perform a marsupialization procedure, which helps a new salivary duct form.
Should I have my mucocele removed?
In most cases, oral mucocele treatment is unnecessary since the cyst ruptures on its own — usually after three to six weeks. If the mucocele is persistent or large in size, your dental professional might use cryotherapy, laser treatment, or surgery to remove the cyst. Do not try to remove or rupture the cyst at home.
Can a mucocele heal on its own?
Self-Care Guidelines. Many mucoceles will go away on their own in 3–6 weeks. Mucus-retention cysts often last longer. Avoid the habit of chewing or sucking on the lips or cheek when these lesions are present.
Can a mucocele rupture?
Mucocele of the appendix is a rare lesion, characterized by distension of the lumen due to accumulation of mucoid substance. This disease is often asymptomatic and pre-operative diagnosis is rare. If untreated, one type of mucocele may rupture producing a potentially fatal entity known as pseudomyxoma peritonei.
Can a mucocele last for months?
[1] The Lower labial mucosa is the most frequently affected site, but can also develop in the cheek, tongue, palate, and floor of the mouth, where it is called as ranula. [1] Mucocele can arise within a few days after minor trauma, but then plateau in size. They can persist unchanged for months unless treated.
Where does mucocele occur?
Cyst: A mucocele is a mucous retention cyst that can occur in any area of the mouth where there are minor salivary glands. It occurs when the duct is severe ... Read More
What exactly is the mucocele under the tounge?
Cyst: A mucocele is a mucous retention cyst that can occur in any area of the mouth where there are minor salivary glands. It occurs when the duct is severe... Read More
Can a dentist detect a mucocele?
See your dentist: Your dentist will be able to identify a mucocele or biopsy any suspicious lump.
Where does mucocele occur?
Cyst: A mucocele is a mucous retention cyst that can occur in any area of the mouth where there are minor salivary glands. It occurs when the duct is severe ... Read More
Does daktarin helps in mucocele?
Probably not..: Unless the mucocele is being caused by a fungus of some sort. I doubt it.
Are mucoceles contagious?
Mucoceles: Mucoceles are not at all contagious. They are simply the result of a blocked minor salivary gland. If it bothers you, have it removed. Otherwise, t... Read More
Can mucocele inside the lower lip be cancerous?
NOT LIKELY: ..But it is in the realm of possibility. To be sure, you need to see an oral surgeon or ENT specialist. Good luck.
What is a mucocele on the appendix?
Mucocele appendix is also known as appendiceal mucocele. It is a condition in which a mucocele occurs on the surface of appendix. It closely resembles acute appendicitis. Mucocele is a cyst which forms on the mucous membrane of appendix. It is a rare disease. The mucocele is a fluid filled swelling which occurs on the mucous membrane. This cyst is formed when there is a mucous plug in mucous membrane. These mucocele on appendix are benign in nature and are not malignant i.e. cancerous. But in some cases it may convert in to malignant cyst and spread to the whole appendix causing serious complications.
What is the name of the swelled sacs that are filled with mucous?
Mucocele are swelled sacs which are filled with mucous present in the mucous membrane of appendix. There is a range from benign to malignant mucocele according to which the treatment is selected. If the appendix ruptures the cells will spread inside body and become malignant in nature causing cancer. The spreading cells of appendix continue to secrete gel like substance named mucin. And this mucin is responsible for spreading cancer to other parts of body. In case of malignant mucocele , the treatment becomes difficult and may prove fatal for patient.
What is a mucocele cyst?
Oral Mucous Cyst. An oral mucous cyst, also called a mucocele, is a harmless swollen spot. It's a good idea to get it checked out, though, especially if it's bothersome.
What is a CT scan for a mucoceles cyst?
Computerized tomography (CT) scan: This is a series of X-rays taken at different angles; put together, they give your doctor a more detailed image of the cyst. Oral Mucous Cyst Treatment. Mucoceles often go away without treatment. But sometimes they enlarge.
Why does mucus build up in my ducts?
A similar buildup happens when the duct has become blocked. A few other common causes include: A tear in a salivary gland: A bump or injury could cause swelling or inflammation to the salivary gland and lead to mucus buildup.
How long does it take to remove a mucocele stitch?
Removes the stitch after about a week. Other types of treatment that may bring down swelling or prevent the need for surgery include steroid shots and medications applied to the surface of the mucocele. Oral Mucous Cyst Outlook.
Where is the mucous cyst on the tongue?
Oral Mucous Cyst Symptoms. There are two types. Mucoceles show up on the inside of your lower lips, your gums, the roof of your mouth, or under your tongue. Those on the floor of the mouth are called ranulas. These are rare, but because they’re larger, they can cause more problems with speech, chewing, and swallowing.
Can a mucocele cyst pop up?
They can return after removal, and there may be pain in areas where they’re removed. Be aware when cysts may pop up, and try to avoid the temptation to suck on your cheek or bite on your lip when they do appear.
What is a mucocele?
Some consider the term to encompass a large group of conditions involving the appendix, pancreas, or ovaries, with diverse morphological features and pathogenesis. These conditions share the common feature of obstructive process or hyperplasia of mucinous epithelium, or both, leading to gross mucinous accumulation. Others consider mucocele to be a strictly neoplastic process that can spread to lymph nodes, extend into surrounding tissue, or seed the peritoneum. 7 The latter description encompasses most mucocele-related diagnoses, and thus, right hemicolectomy is an appropriate first step in managing suspicious mucinous collections of the appendix. Histopathological findings can confirm whether further tests are needed for workup of malignancy. If a patient has a mucinous cystadenoma of the appendix, as was the case with our patient, then right hemicolectomy is curative (except in cases that are complicated by pseudomyxoma peritonei).
What is appendiceal mucocele?
Appendiceal mucocele is a rare but well-recognized entity that can mimic several common clinical syndromes or present as an incidental surgical or radiological finding. It has a 0.2% to 0.4% prevalence among appendectomies. 1,2 The term mucocele is widely used in diagnosing both benign and malignant lesions, but specific criteria are being proposed for definitive diagnosis and surgical management of appendiceal mucocele. 3 While some neoplasms with malignant potential may be treated definitively by resection, other seemingly benign lesions must be treated conservatively due to complications that ensue from peritoneal and cecal inoculation and the possibility of progression to malignancy. 4,5
What causes mucocele in the right side of the abdomen?
Mucocele can result from mucosal hyperplasia, mucinous cystadenoma, or mucinous cystadenocarcinoma. Signs and symptoms occur in fewer than 50% of cases and are generally associated with malignancy. 3 These include pain in the right lower abdominal quadrant, an abdominal mass, weight loss, nausea, vomiting, change in bowel habits, anemia, and hematochezia. Depending on the location of the appendix, other signs may be observed, such as hematuria. The most dreaded complication of benign or malignant mucocele is pseudomyxoma peritonei, which is difficult to treat surgically or medically. It has an uncertain prognosis, with a 5-year survival rate between 53% and 75%. 5,6
Is mucocele a concomitant neoplasm?
Although complications from appendiceal mucocele are minimal, there is evidence that complications are associated with concomitant neoplasms. These occurred in about one third of patients in the retrospective study and undoubtedly contributed to the high number of incidental findings of mucocele.
Is hemicolectomy necessary for appendiceal mucocele?
Right hemicolectomy is sufficient for most patients with appendiceal mucocele; however, the significant risk of postoperative complications and concomitant life-threatening conditions has led the authors to recommend careful resection and exploration of the peritoneum.
Is a mucocele appendix dangerous?
Mucocele of the appendix is an uncommon but potentially dangerous pathological entity that presents in a variety of ways. The authors discuss the diagnostic workup of an appendiceal mucocele from computed tomography scanning to resection, emphasizing the influence of pathological diagnosis on the operative procedure.
Can cystadenomas be removed?
No cystadenomas smaller than 2 cm have been reported , which suggests that all mucoceles larger than 2 cm should be removed to eliminate the chance of progression to malignancy. Furthermore, all patients, whether they have benign or malignant appendiceal mucocele, should be evaluated for pseudomyxoma peritonei.