What can I give my Dog for pemphigus foliaceus?
Focal cases of pemphigus foliaceus can be treated with varying strengths of topical steroids. The mainstay of therapy for more generalized cases in both dogs and cats are oral glucocorticoids (e.g. prednisone) in combination with steroid-sparing immunosuppressive medications.
How common is pemphigus foliaceus in dogs?
Thirty-seven dogs with pemphigus foliaceus were seen over a span of 9 years in a veterinary medical teaching hospital. Four breeds of dogs (Bearded Collie, Akita, Newfoundland, Schipperke) were at significant elevated risk when compared with both the dermatology canine case population and the hospital canine population.
What is the treatment for pemphigus foliaceus?
Pemphigus foliaceus is an autoimmune disease with treatment consisting of immunosuppressive drugs (corticosteroids) along with other drugs which would need to be tried on a trial basis to check their efficacy. I cannot say whether the symptoms will improve or if he will get better as these are on a case by case basis.
When to take your dog to the vet for pemphigus?
Follow-up visits become an expensive challenge and side effects from medication affect a dog’s quality of life, leading to over 50% of dogs diagnosed with pemphigus to be euthanized. If you notice your dog suddenly develops changes in their skin as described above, schedule an appointment with your vet to determine a diagnosis and treatment plan.

How long do dogs live with pemphigus foliaceus?
One-year survival was achieved in 53% of the dogs.
Is pemphigus foliaceus in dogs curable?
There is no known cure for pemphigus foliaceus. The objective is to keep the disease in remission. In cases where pemphigus foliaceus is confined to a certain area on the dog's body, it can be treated with topical steroids.
Does pemphigus foliaceus go away?
There is no cure for pemphigus foliaceus. Symptoms of pemphigus foliaceus don't interfere with your life expectancy. The condition can cause painful and itchy blisters and sores on your skin that heal with treatment.
How Long Can dogs live with autoimmune disease?
The prognosis with IMHA is variable, carrying a mortality rate of 30% to 70% within 1-2 months of diagnosis. If patients suffer IPT at the same time, or if the bone marrow is affected, the outlook may be worse. The condition can come back, and some animals need lifelong medication.
What triggers pemphigus foliaceus in dogs?
Pemphigus foliaceous is the most common autoimmune disease in dogs and is most often caused by autoantibodies targeting desmocollin-1 (2,3).
Is canine pemphigus foliaceus painful?
In the case of p. foliaceus, the lesions will usually spread to the groin and feet. Itchiness and pain may be associated with them, as well. Some dogs may feel lethargic and inappetant.
What foods trigger pemphigus?
You want to avoid hard foods like chips, chunky peanut butter, nuts, crisp vegetables like raw carrots, and fruit. Other foods that can cause new mouth sores include spicy foods, steaming-hot foods, and acidic foods like tomatoes and citrus fruits.
How does pemphigus Foliaceus start?
What causes pemphigus foliaceus? Pemphigus foliaceus occurs when cells of the body's immune system produce proteins (autoantibodies) that damage the adhesion points between skin cells. These adhesion points act like press studs holding one of the top layers of the skin cells (epidermis) together.
Is Pemphigus Foliaceus life-threatening?
The blisters and lesions caused by PF can look alarming, but they do not indicate the presence of another condition. On its own, pemphigus is not life-threatening. However, severe blistering leaves the skin vulnerable to serious infections. These infections can become life-threatening if left untreated.
Is pemphigus in dogs fatal?
Pemphigus vulgaris (PV) is a serious condition with a poor prognosis. Despite therapy, this disease is often fatal, due to its widespread effects on the skin.
What triggers autoimmune disease in dogs?
Ultraviolet (UV) exposure is thought to be a predisposing or “triggering” cause of autoimmune skin diseases in some dogs. Certain drugs have also been reported as potential triggers for pemphigus foliaceus, a common form of autoimmune skin disease in dogs and cats. Early recognition is extremely important.
What can I feed my dog with autoimmune disease?
The 5 Best Dog Foods for Autoimmune DiseaseSolid Gold Green Cow Canned Dog Food – Best Overall. Check Price on Chewy. ... Purina Beyond Recipe Canned Food – Best Value. Check Price on Chewy. ... Taste of the Wild Grain-Free Dry Food – Premium Option. ... Rachael Ray Nutrish Natural Dry Dog Food. ... Purina ONE Chicken & Rice Dry Dog Food.
How common is pemphigus in dogs?
Pemphigus foliaceus (PF) is the most common autoimmune skin disease in dogs and cats.
What is the treatment for pemphigus foliaceus?
Topical treatment with antibiotics and corticosteroids, such as topical clobetasol cream or ointment 0.05% twice a day, is helpful. Other vehicles that may be useful are creams, foams, liquids (for scalp lesions), and aerosols. Antibiotics, such as minocycline 50 mg daily, may be effective.
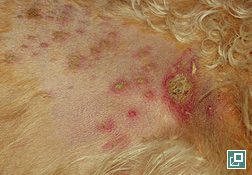
What is pemphigus foliaceus in dogs?
Pemphigus Foliaceus is an autoimmune vesicobullous to pustular skin disease in dogs characterized by acantholysis or loss of adhesion between keratinocytes within the epidermis and hair follicles. The disease is characterized by production of autoantibodies against intercellular connections of the keratinocytes.
Can lupus in dogs be cured?
No, unfortunately there is no cure for canine lupus. Dogs with lupus will live with the condition for the rest of their lives.
How many dogs have Pemphigus foliaceus?
Thirty-seven dogs with pemphigus foliaceus were seen over a span of 9 years in a veterinary medical teaching hospital. Four breeds of dogs (Bearded Collie, Akita, Newfoundland, Schipperke) were at significant elevated risk when compared with both the dermatology canine case population and the hospital canine population.
What is generalized exfoliative dermatitis in dogs?
Generalized exfoliative dermatitis was seen in dogs with widespread disease. Pruritus was noted in less than one half of the dogs. Typical histopathologic findings included subcorneal and intragranular cell layer epidermal pustules, or intrafollicular pustules with prominent acantholysis.
What is the most common site of initial involvement in over 50% of dogs?
The dorsal part of the muzzle was the most common site of initial involvement in over 50% of the dogs, and lesions of the head were seen first in 81% of the dogs. Disease progression was gradual (greater than 3 months) in 73% of the dogs.
What causes pemphigus in dogs?
Pemphigus can be caused by factors internally or inside a dog’s body, externally or outside a dog’s body, and unexplained, also known as idiopathic.
What is the best treatment for pemphigus in dogs?
These medications include corticosteroids (like prednisone), azathioprine, chlorambucil, or cyclosporine. Your vet will discuss the recommended medication including the side effects that you can expect, as well as important and frequent follow-up visits. This may include blood work to monitor your dog’s immune system and body organs that can be affected by the medications prescribed.
What is the disease of pemphigus?
Pemphigus can best be described as an immune-mediated skin disease in dogs where a dog’s own immune system begins to attack the connection between the normal layers of skin cells. There are different types of pemphigus that involve different areas of the skin. The three types seen most often in dogs include pemphigus foliaceus (PF), pemphigus vulgaris (PV), and pemphigus erythematosus (PE). Continue reading to learn about the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for dogs with pemphigus.
How to diagnose pemphigus in dogs?
Diagnosing a dog with pemphigus includes a complete physical exam by a vet, blood work, and other recommended testing to rule out other diseases including bacterial or fungal skin infections and skin allergies. To accurately diagnose pemphigus requires a surgical skin biopsy.
What is a blister on a dog's skin called?
These are fluid-filled blisters, known as vesicles. These blisters often burst open causing painful open wounds. Blisters are usually seen at the edges of the lips and eyes but with time will usually spread to other areas of the body.
How many dogs are euthanized for pemphigus?
Follow-up visits become an expensive challenge and side effects from medication affect a dog’s quality of life, leading to over 50% of dogs diagnosed with pemphigus to be euthanized.
What breed of dog looks like Pemphigus?
This type of pemphigus looks very much like pemphigus foliaceus, although symptoms are usually less severe in appearance. German Shepherds, Collies, and Shetland Sheepdogs make up the predisposed breeds.
What is pemphigus?
Pemphigus is an autoimmune skin disease, in which the body’s immune system attacks the connections between its own skin cells.
How is pemphigus diagnosed?
The diagnosis of pemphigus requires a skin biopsy. Your veterinarian will use a biopsy punch to remove a small, circular plug of skin from a skin lesion. Depending on your pet’s temperament and the site of his lesions, this procedure may be performed with the aid of a local anesthetic injection or under general sedation/anesthesia.
What breed of dog has Pemphigus foliaceus?
Pemphigus foliaceus is most commonly seen in Chow Chows, Akitas, Cocker Spaniels, Labrador Retrievers, Dachshunds, and English Bulldogs, though other breeds may also develop this condition. Pemphigus Erythematosus - This form of pemphigus is similar in appearance to pemphigus foliaceus, although cases are often more mild in appearance.
What are the three types of pemphigus?
The three most common types of pemphigus are pemphigus foliaceus, pemphigus vulgaris, and pemphigus erythematosus. Pemphigus Foliaceus ( PF) – Pemphigus Foliaceus is the most common autoimmune skin disease in dogs and cats. PF is often observed in middle-aged and older patients.
What is the name of the disease where the body attacks the skin cells?
Pemphigus is an autoimmune skin disease, in which the body’s immune system attacks the connections between its own skin cells.
What is PF in the body?
PF is often observed in middle-aged and older patients. Pemphigus foliaceus typically causes hair loss, scabs, and ulcers (open sores) around the head, face and ears. These lesions may become more widespread over time, covering other parts of the body.
How to diagnose pemphigus?
The diagnosis of pemphigus requires a skin biopsy. Your veterinarian will use a biopsy punch to remove a small, circular plug of skin from a skin lesion. Depending on your pet’s temperament and the site of his lesions, this procedure may be performed with the aid of a local anesthetic injection or under general sedation/anesthesia.
How long does it take for Pemphigus foliaceus to go away?
Affected animals are started at higher dosages initially until remission is achieved (4-12 weeks), and then are tapered to the lowest possible dosages that maintain remission. The diagnosis of Pemphigus foliaceus is made by clinical signs, cytology, and biopsy.
How many forms of Pemphigus foliaceus are there in dogs?
Three forms of Pemphigus foliaceus exist in the dog. The first and most common is the spontaneous form which develops in dogs with no history of skin disease or drug history. The second form of Pemphigus foliaceus is initiated via a drug reaction.
What is the best anti-immunosuppressive medication for dogs?
In dogs, azathioprine and/or cyclosporine can be utilized, while in cats leukeran and/or cyclosporine are the most popular supportive drugs. Other nonsteroidal immunosuppressive drugs include gold salts (dogs and cats) and tetracycline/niacinamide (dogs).
What is the disease of pemphigus foliaceus?
Pemphigus foliaceus is an autoimmune disease whereby antibodies produced by an animal’s own immune system attack the bridges that hold skin cells together.
What is the purpose of skin scrapes?
Skin scrapes would be performed to rule out external parasites via microscopic analysis. A fungal culture would be done to rule out ringworm (a type of common fungus). Samples of debris from intact pustules or crusts can allow for a diagnosis of Pemphigus foliaceus.
Where do pemphigus foliaceus lesions occur?
The primary lesion of Pemphigus foliaceus is a pustule. These lesions typically begin along the nasal bridge, around the eyes, and ear pinnae. It is typical for the lesions to spread and occur along the trunk, feet, clawbeds, groin, and footpads. In cats, the nail beds and nipples can also be commonly affected.
Can Pemphigus foliaceus be cured?
Cases of Pemphigus foliaceus that are induced by a drug reaction are the most likely to be cured. Regular monitoring of clinical signs, hemograms, serum biochemistry profiles, urinalyses, and urine cultures with treatment adjustments as needed are essential. Treatment.
