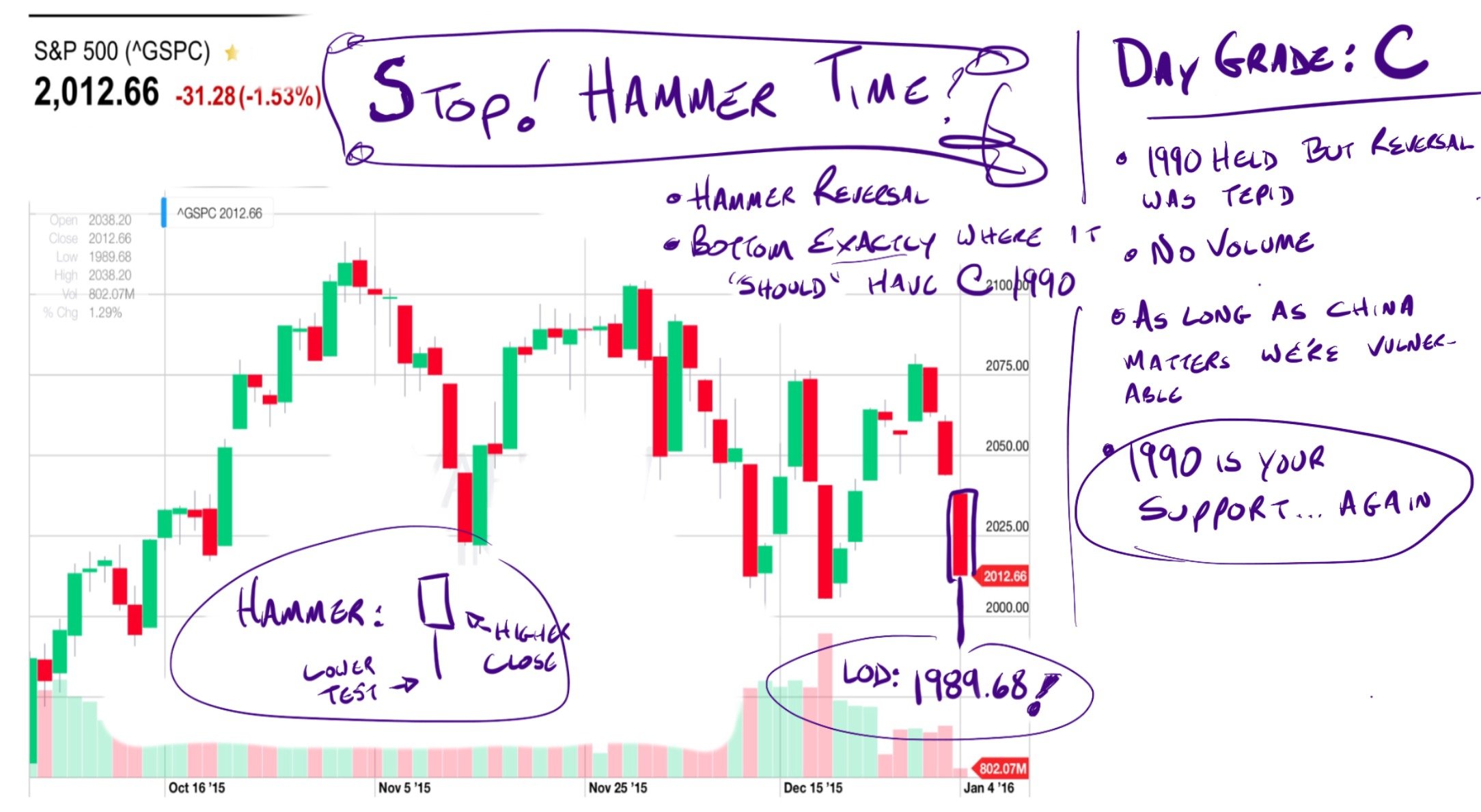
The depreciation deductions are limited to the amount of rental income (passive income) and cannot be used to reduce ordinary income. So, if enough passive income is not available as an offset, the passive loss will carry forward into the following tax year as a Net Operating Loss (NOL).
Can you use depreciation to offset rental real estate expenses?
You own rental real estate that had rental income and depreciation expenses—luckily, the depreciation expenses can be used to offset your rental income exactly the same as if your total income was $10,000 for the year. Some investors worry that higher incomes limit depreciation tax advantages, but this isn’t necessarily true.
What is real estate depreciation and how does it work?
So as you can see, real estate depreciation acts as a tax shield and reduces your taxable income. This means, you get to offset depreciation expense with the rental income you earn. This results in thousands of dollars in tax savings! And you know what you could do with those savings?
Can I deduct depreciation from my taxes?
So a $100,000 in depreciation deductions, can be used on the jointly filed tax return to offset any ordinary and passive income. As the qualifying Real Estate Professional or an Active Participant, you normally cannot be a traditional full-time W-2 wage earner.
Can You offset passive losses on rental property?
As a general rule, a taxpayer cannot offset passive losses against wage, interest, or dividend income. The rental of real estate is generally a passive activity. However, Congress has promulgated special tax laws for passive losses associated with real estate rental income.

Can rental property depreciation offset W-2 income?
A Rental Loss can only be used to offset other income reported on your tax return if you are an Active Participant in that rental property. In this case, you would be allowed to deduct up to $25,000 worth of rental losses to be offset against other income items on your tax return (such as your W-2 wages).
Does depreciation offset income?
All of the depreciation that you claim over the years affects the actual capital gain on the property and also the capital gains tax you will pay. Depreciation does not offset the gain; it can actually increase the amount of capital gains realized on the sale of property.
Does property depreciation reduce your taxable income?
Real estate depreciation is an important tool for rental property owners. It allows you to deduct the costs from your taxes of buying and improving a property over its useful life, and thus lowers your taxable income in the process.
Does depreciation reduce ordinary income?
As previously mentioned, certain types of investments and capital assets may be depreciated for tax purposes according to the IRS, allowing investors to take tax deductions for depreciation that allow them to reduce their ordinary income.
How does rental property depreciation affect taxes?
How much will depreciation affect my taxes? Rental property investors can include depreciation as one of the expenses on Schedule E when they file their yearly taxes. The tax liability will be reduced according to which tax bracket the investor is in. That percentage will determine the amount of the deduction.
Can you deduct rental property depreciation?
If you receive rental income from the rental of a dwelling unit, there are certain rental expenses you may deduct on your tax return. These expenses may include mortgage interest, property tax, operating expenses, depreciation, and repairs.
What can real estate depreciation offset?
For instance, if you own a property and allocate $200,000 of the acquisition cost to the improvements, you would be allowed to depreciate $7,272 a year ($200,000/27.5) as a tax loss. That's a huge benefit that can offset the income generated by the rental property—ultimately lowering your year-end tax burden.
Does depreciation affect adjusted gross income?
Your depreciation deduction is subject to the 2% of adjusted gross income (AGI) limit. So, use depreciation when deciding whether to itemize or claim the standard deduction.
Does rental depreciation reduce AGI?
Knowing the ins and outs of the tax code can help you to maximize your tax advantages and reduce or defer some of your taxes. For owners of rental real estate, depreciation is an essential tax deduction that can dramatically reduce your AGI.
What happens when rental property is fully depreciated?
Depreciation expense taken by a real estate investor is recaptured when the property is sold. Depreciation recapture is taxed at an investor's ordinary income tax rate, up to a maximum of 25%. Remaining profits from the sale of a rental property are taxed at the capital gains tax rate of 0%, 15%, or 20%.
What if I never took depreciation on my rental property?
You should have claimed depreciation on your rental property since putting it on the rental market. If you did not, when you sell your rental home, the IRS requires that you recapture all allowable depreciation to be taxed (i.e. including the depreciation you did not deduct).
What happens to depreciation when you sell a rental property?
Real estate investors use the depreciation expense to reduce taxable net income during the time they own a rental property. When the property is sold, the total depreciation expense claimed is taxed as regular income up to a rate of 25%.
How does depreciation work with capital gains?
Although depreciation offers a tax break while you own real property, it increases your overall capital gain when you sell it. A capital gain is the difference between your property's sales price and its adjusted basis, which is its original cost minus accumulated depreciation.
How does depreciation work on capital gains tax?
When you sell an asset such as a property, this triggers what is called a 'CGT event' and the owner will either make a capital gain or loss on the property. When an investor has been claiming property depreciation, the cost base could be altered, therefore changing the capital gain or loss.
How do you offset active income?
2:231:13:37REPS 02: How You Can Offset W-2 & Active Business Income ... - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipProfessional you do it the right way you can take the losses from your rental activities. And useMoreProfessional you do it the right way you can take the losses from your rental activities. And use them to offset. The income you have from your w-2.
How does depreciation affect taxes when selling a house?
Depreciation Recapture Tax Real estate investors use the depreciation expense to reduce taxable net income during the time they own a rental property. When the property is sold, the total depreciation expense claimed is taxed as regular income up to a rate of 25%.
What is the reclassification of tangible personal property from real property?
The reclassification of tangible personal property from real property (giving it a shorter depreciable life) accelerates depreciation deductions that can allow for significant cash flow benefits through these increase tax deductions.
What is a NOL in tax?
So, if enough passive income is not available as an offset, the passive loss will carry forward into the following tax year as a Net Operating Loss (NOL).
How does a Cost Segregation Study provide tax benefits?
A cost segregation study is a strategic tax-planning tool that allows an owner to accelerate the depreciation of certain components of the building or land improvements over a shorter life. This is accomplished through a detailed analysis and component level breakdown of your commercial property, allowing the reclassification of specific real property assets into tangible personal property assets, which optimizes the depreciation schedule to leverage the ‘time value of money’.
Can you offset passive income from cost segregation?
Many real estate owners who attempt to take advantage of these significant cash flow benefits do not realize that they are subject to passive activity losses, which can only be offset by passive income and potentially reduce the ability to take advantage of the tax benefits available through cost segregation. Therefore, proper tax planning and a clear understanding of cost segregation applications and guidelines are vital to obtaining maximum benefits from this tax strategy encouraged by the IRS.
Is cost segregation good for real estate?
Using cost segregation as a tool to optimize your depreciation schedule will result in significant cash flow and tax benefits in and of its own. The two strategies outlined in this article are just a couple added ways for you to leverage this passive activity against your ordinary income.
Can depreciation be used to reduce ordinary income?
The problem can arise when the investor creates excess depreciation, resulting in a passive activity loss beyond the passive income produced. The depreciation de ductions are limited to the amount of rental income (passive income) and cannot be used to reduce ordinary income. So, if enough passive income is not available as an offset, ...
Can depreciation be used on spouse's W-2?
This is a huge benefit as not only can the depreciation created losses be used to offset other ordinary income sources, it can also directly impact a spouse’s W-2 wages. So a $100,000 in depreciation deductions, can be used on the jointly filed tax return to offset any ordinary and passive income.
Why do we write off real estate depreciation?
And the real estate depreciation write-off is an incentive that allows real estate investors to take advantage of some huge tax benefits.
How many years can you depreciate a property?
And what they would do is identify the property-related costs that can be depreciated over 5,7, or 15 years. That is opposed to the traditional 27.5 or 39 years.
What happens when you take depreciation expense every year?
And that is depreciation recapture. So when you take depreciation expense as a deduction every year, you are reducing your basis in the property. In other words, you are reducing the implied cost of the property.
Why is real estate ownership important?
And this makes sense because the more homes bought in a certain area means more people are living in that area .
How much is a write off for $500,000?
You would then take $500,000 and divide it by the useful life of residential properties of 27.5 years to get an annual depreciation write-off of $18,182.
How long is the useful life of a house?
The IRS already defines what the useful life of real estate property is. For residential property, like a house, the useful life is 27.5 years. And for commercial property, it is 39 years.
What can you take out of a property with cost segregation?
With cost segregation, you can take bits and pieces of the property, like the roof or cabinets, and depreciate the cost of those items over a shorter period of time.
What happens when you sell a property that has been depreciated?
Investors shouldn’t forget about depreciation recapture, which happens when you sell a property that has been depreciated. Essentially, this allows the IRS to tax any portion of the sale of an asset previously used to offset taxable income. Generally, it’s taxed as ordinary income at a maximum rate of 25%.
How long can you depreciate a property?
Fully depreciated properties: After 27.5 years, you can no longer depreciate a residential property.
What Is Depreciation?
When you buy an investment property, through use, wear and tear, weathering, and so on, it degrades—or depreciates. For example, your car loses its luster over time. You don’t value a 2008 Camry the same way you value a 2020 model. Same goes for real estate.
When Can I Start Depreciating My Property?
You can start depreciating your place when it is ready for rental—not when it is rented. If you buy a property and are ready to rent it day one, but it doesn’t end up renting for two weeks, you can start depreciating it from the start .
What is the maximum rate of depreciation recapture?
Generally, it’s taxed as ordinary income at a maximum rate of 25%.
How much can you use for rental losses?
The IRS has a rule that if you are not a real estate professional (i.e., someone who spends more time in real estate than your other job or business), then you can use up to $25,000 of your excess rental losses to offset your other income—if your income is under $100,000.
What is the most common depreciation method?
The most common type is “straight-line depreciation, ” which steadily depreciates the property over a number of years. This is the most general depreciation system, and is general the simplest to use.
What is depreciation in real estate?
Depreciation allows for the recovery of costs related to income-producing rental property. Investors can defer taxes by selling an investment property and using the equity to purchase another property in what is known as a 1031 like-kind exchange.
How to recover rental property?
You can recover the cost of income-producing rental property through annual tax deductions called depreciation. The Internal Revenue Code defines the depreciation de duction as a reasonable allowance for deterioration, wear and tear, and a reasonable allowance for obsolescence. 1
Why is real estate investment important?
Investing in real estate continues to be one of the best ways to build wealth and cut taxes. Benefits include the ability to recover the cost of income-producing property through depreciation, to use 1031 exchanges to defer profits from real estate investments, and to borrow against real estate equity to make additional investments or ...
How long does it take to get a replacement property after selling it?
Forty-five days after the sale of the relinquished property they must deliver a written list of the qualified replacement property to a qualified party to the exchange, usually the intermediary. There are also several rules that limit the number of properties that can be identified.
How long does it take to close on a replacement property?
The investor then enters into the identification period and has exactly 45 days to produce a list of qualified replacement properties and 180 days to close on the replacement property during the exchange period.
Can you deduct mortgage interest on taxes?
Deducting Mortgage Interest. Homeowners can deduct the portion of their mortgages attributable to interest payments on their tax returns. These payments are higher during the early years of the mortgage and gradually decrease as the mortgage is paid off.
Can a REIT be exchanged for real estate?
The properties included in the transaction must be like-kind, meaning real property cannot be exchanged for some other type of asset, such as a real estate investment trust (REIT).
How to claim real estate losses?
The key to claiming real estate losses from rental property is to qualify by actively participating in rental activity. Active participation standards are met if you own at least ten percent of the rental property and have substantial involvement in managing the rental (defined as you spending more than 500 hours at the activity and no one else spending more hours in that particular real estate activity than you). If you are a limited partner in the real estate rental activity, you will not qualify for the deduction. The $25,000 special loss allowance is phased out by fifty percent if your modified gross income exceeds $100,000. It reaches zero by the time your income hits $150,000.
What is the definition of a real estate professional?
For tax purpose, qualifying as a “real estate professional” means that either you or your spouse: Must materially participate in the rental real estate activities.
Why is it important to keep a log of your real estate activity?
Therefore, detailed logs are extremely important to substantiate your participation in the real estate rental market to the IRS in the event of an audit.
Can you take unlimited losses against ordinary income?
The ideal scenario may be to take unlimited losses against ordinary income. For tax purposes, people who meet eligibility requirements are able to deduct against ordinary
Can you offset real estate losses against income?
As a general rule, a taxpayer cannot offset passive losses against wage, interest, or dividend income. The rental of real estate is generally a passive activity. However, Congress has promulgated special tax laws for passive losses associated with real estate rental income. Federal tax law provides that up to $25,000 of losses associated with real estate rental activities can be netted against ordinary income.
